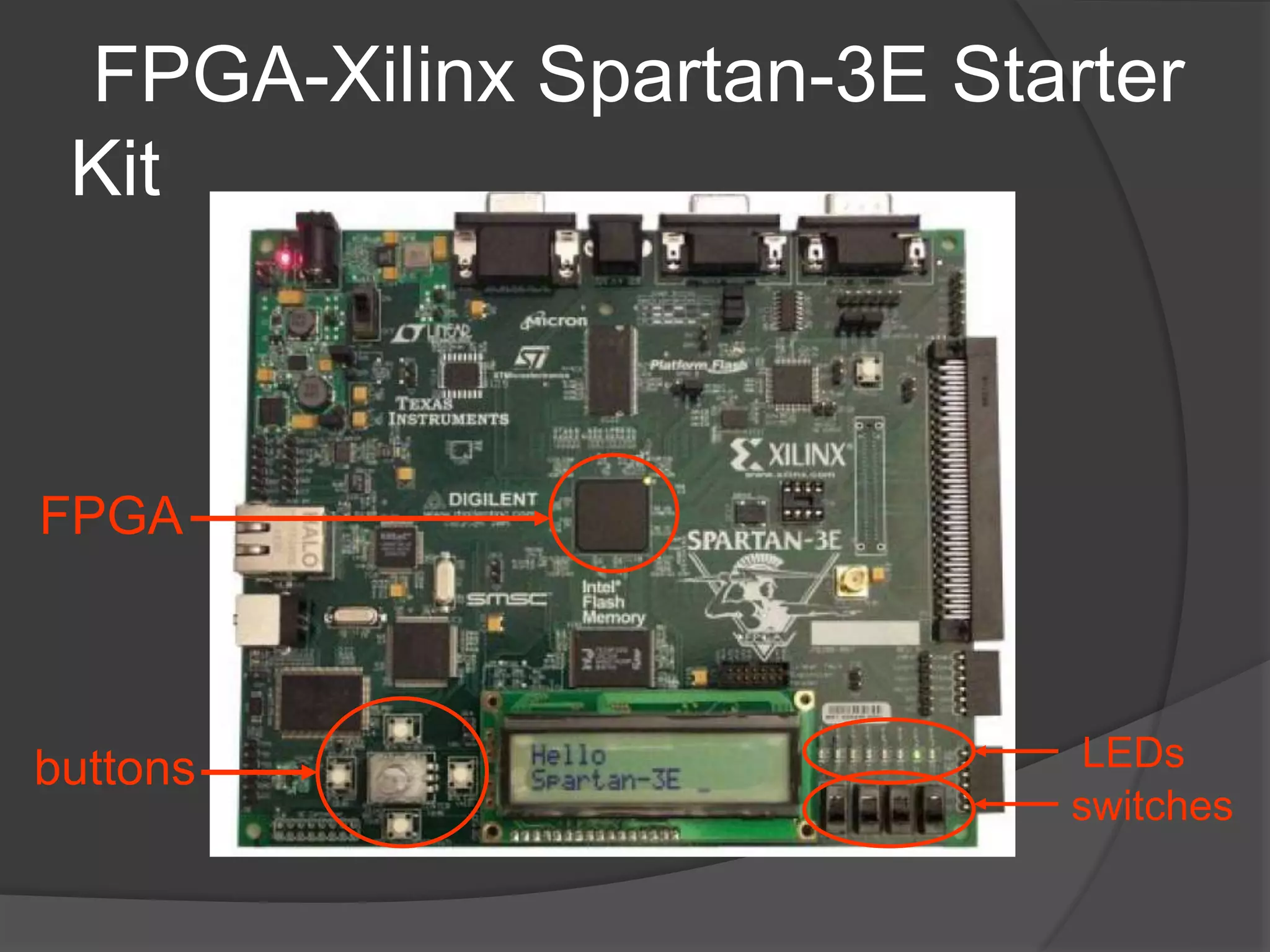
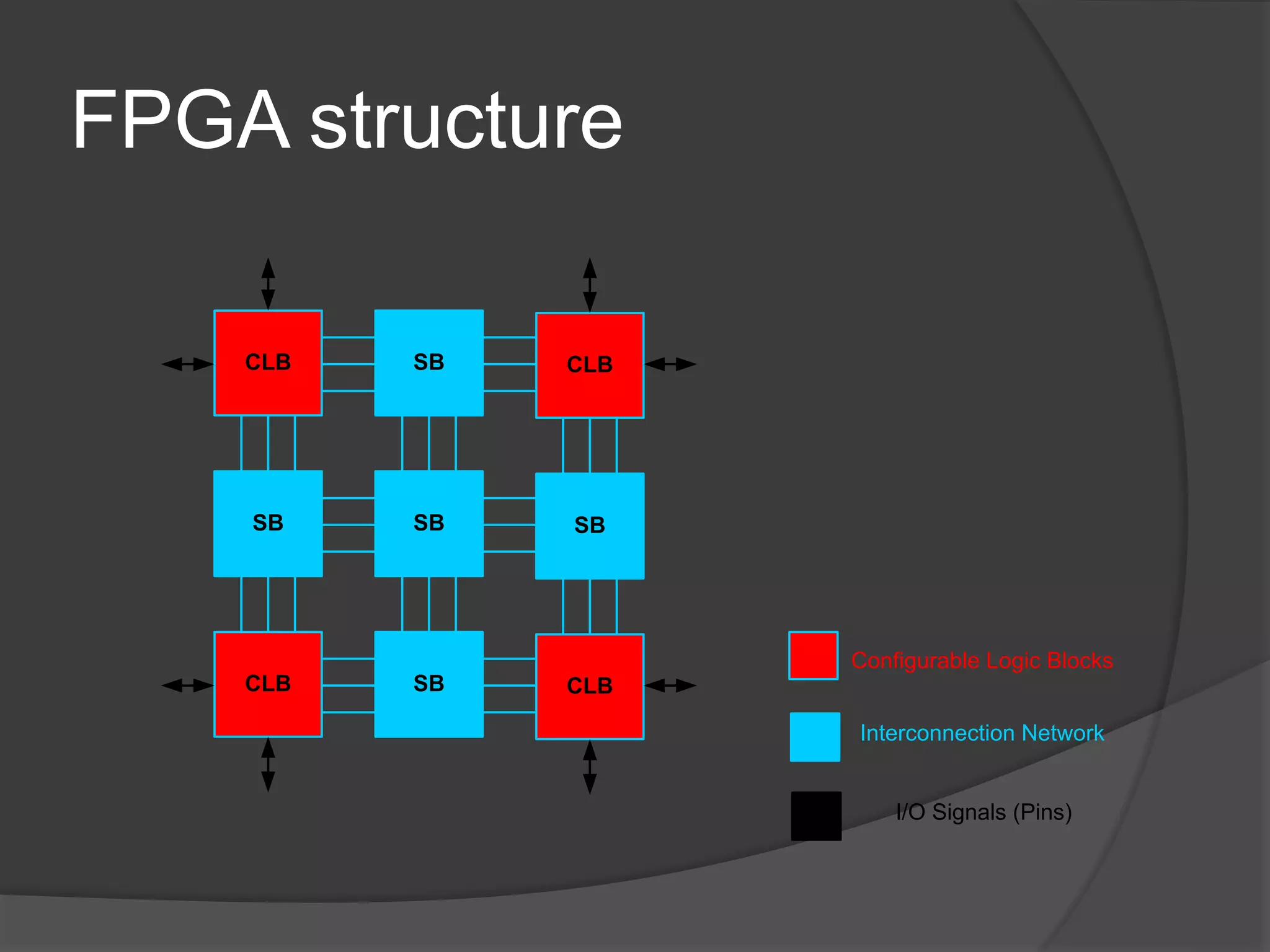
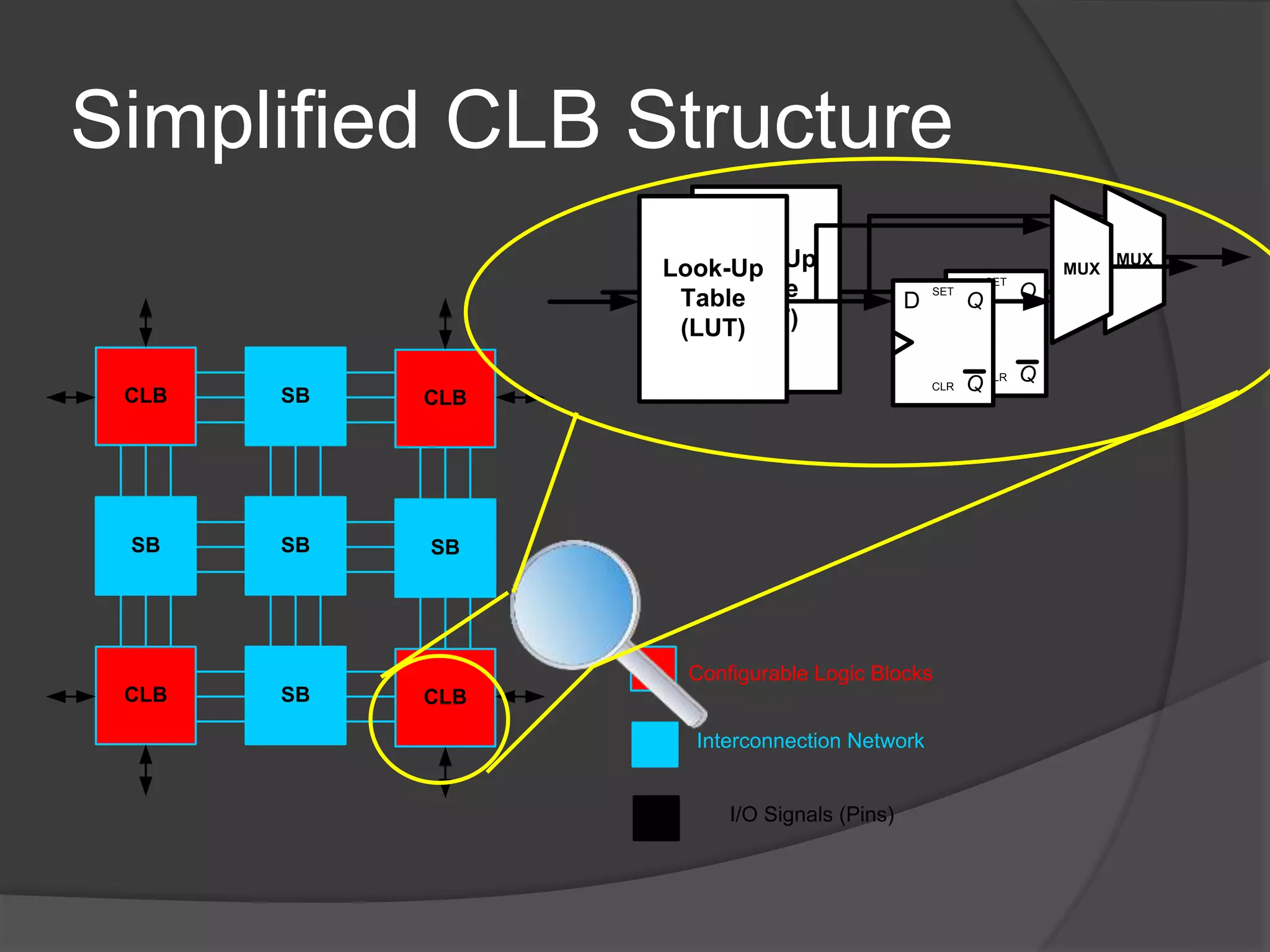
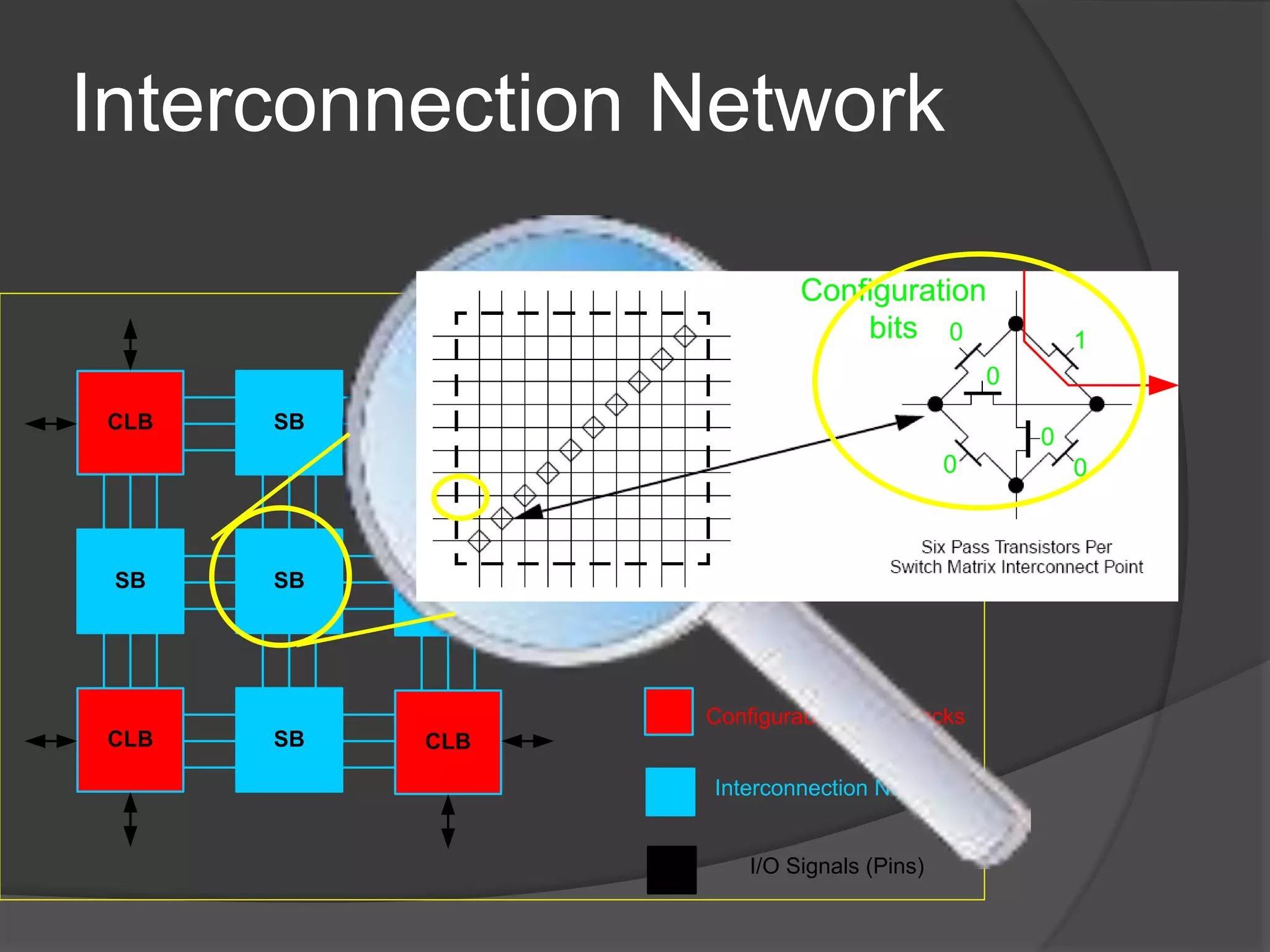
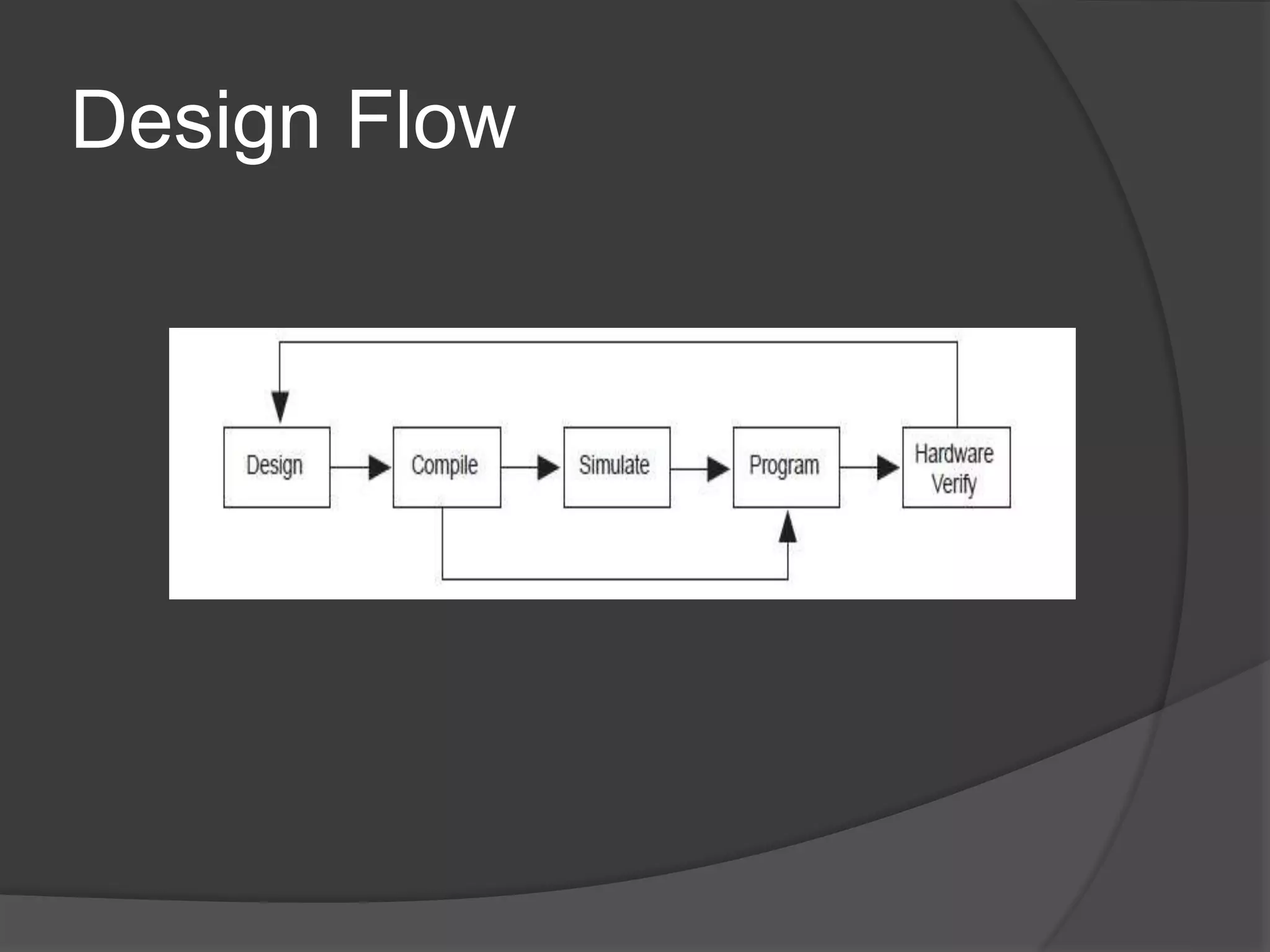
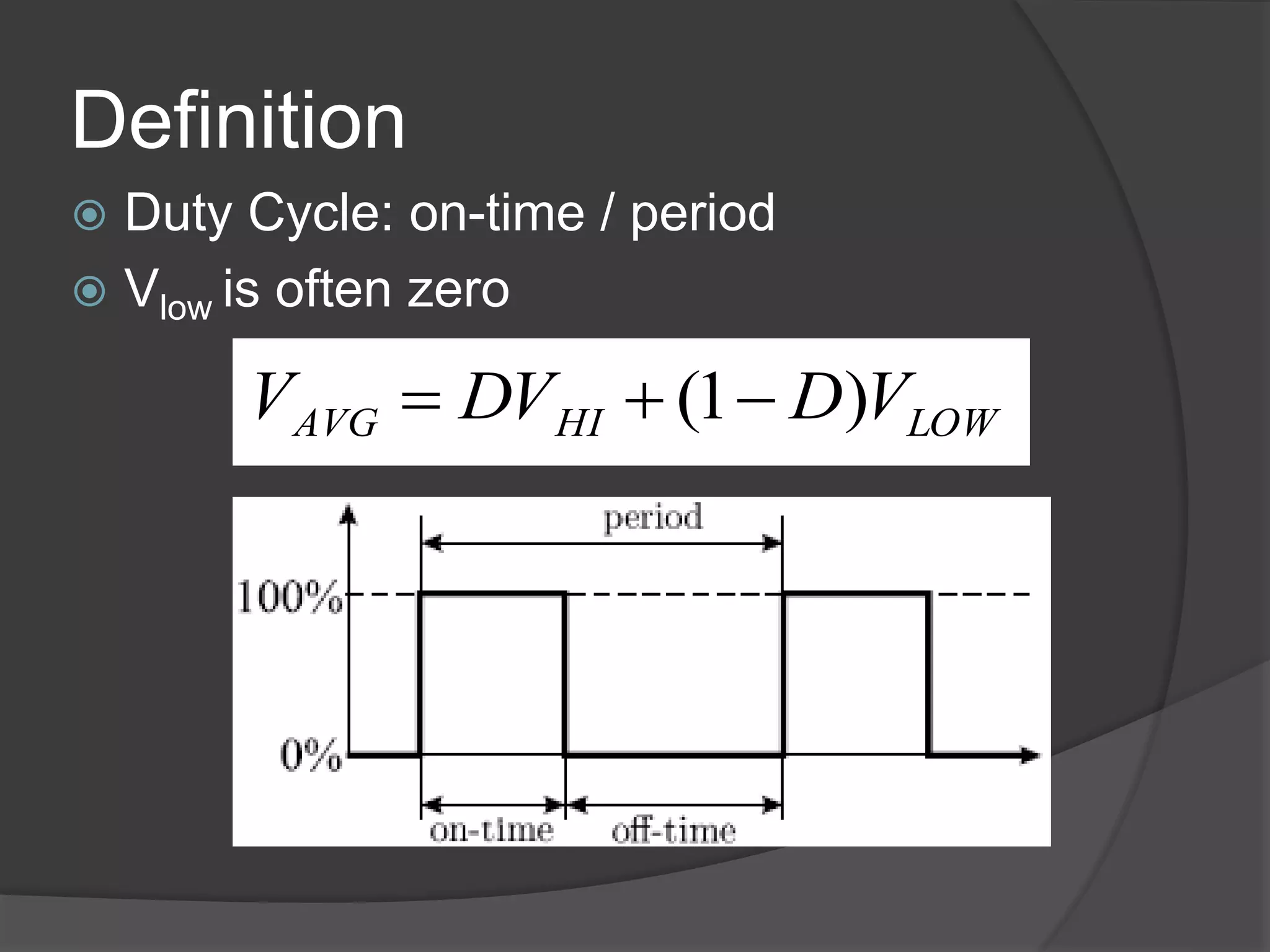
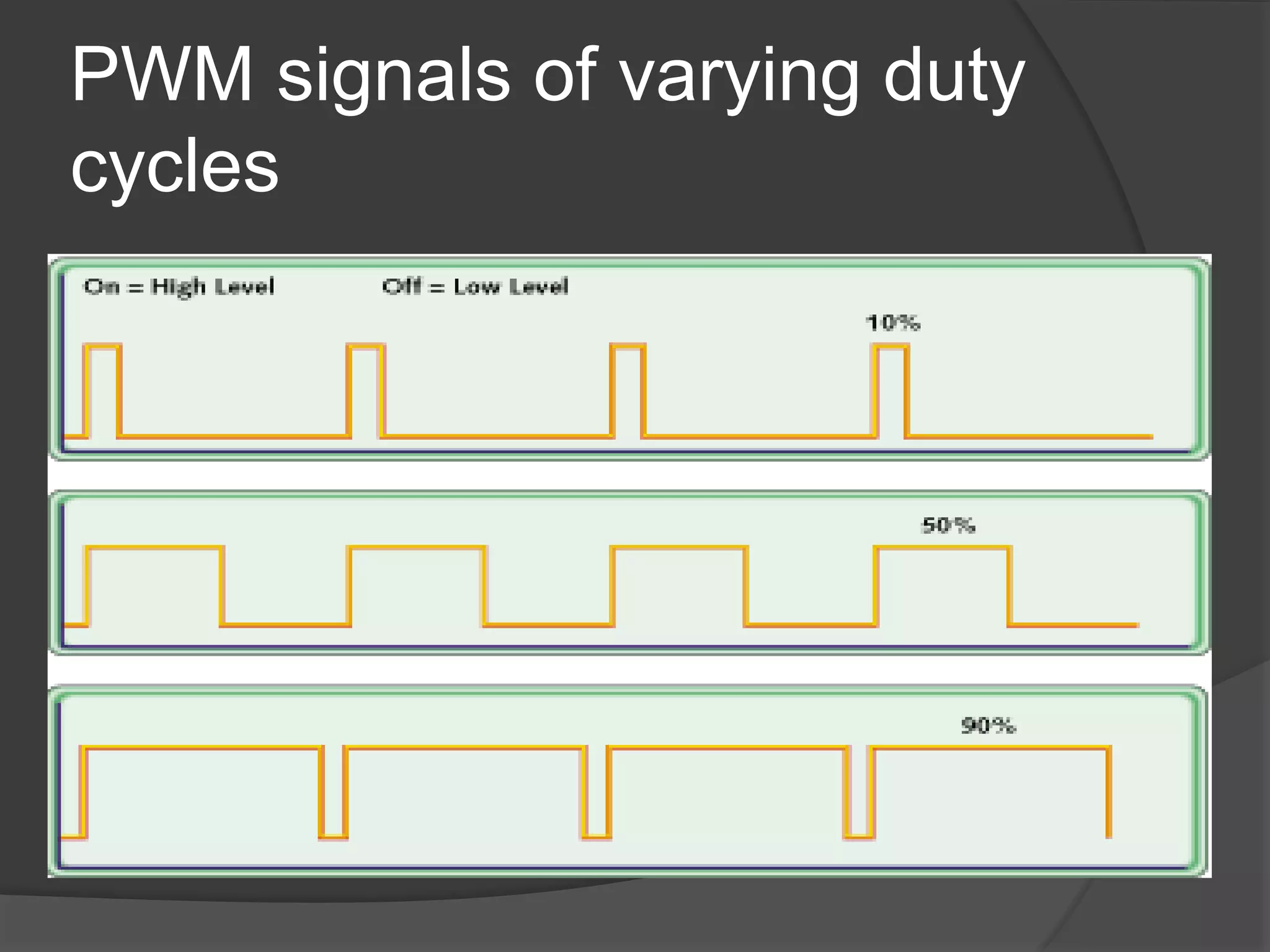
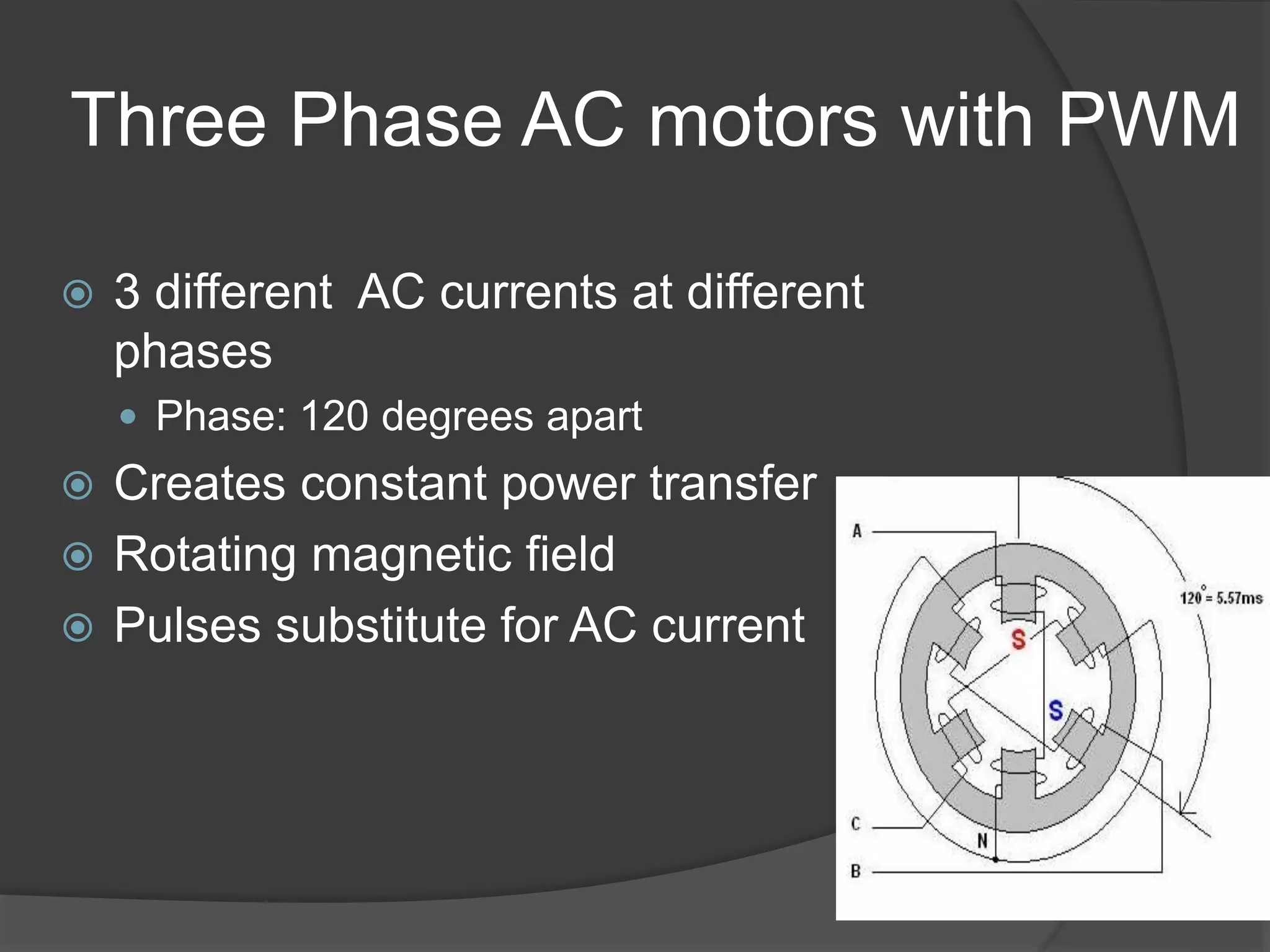
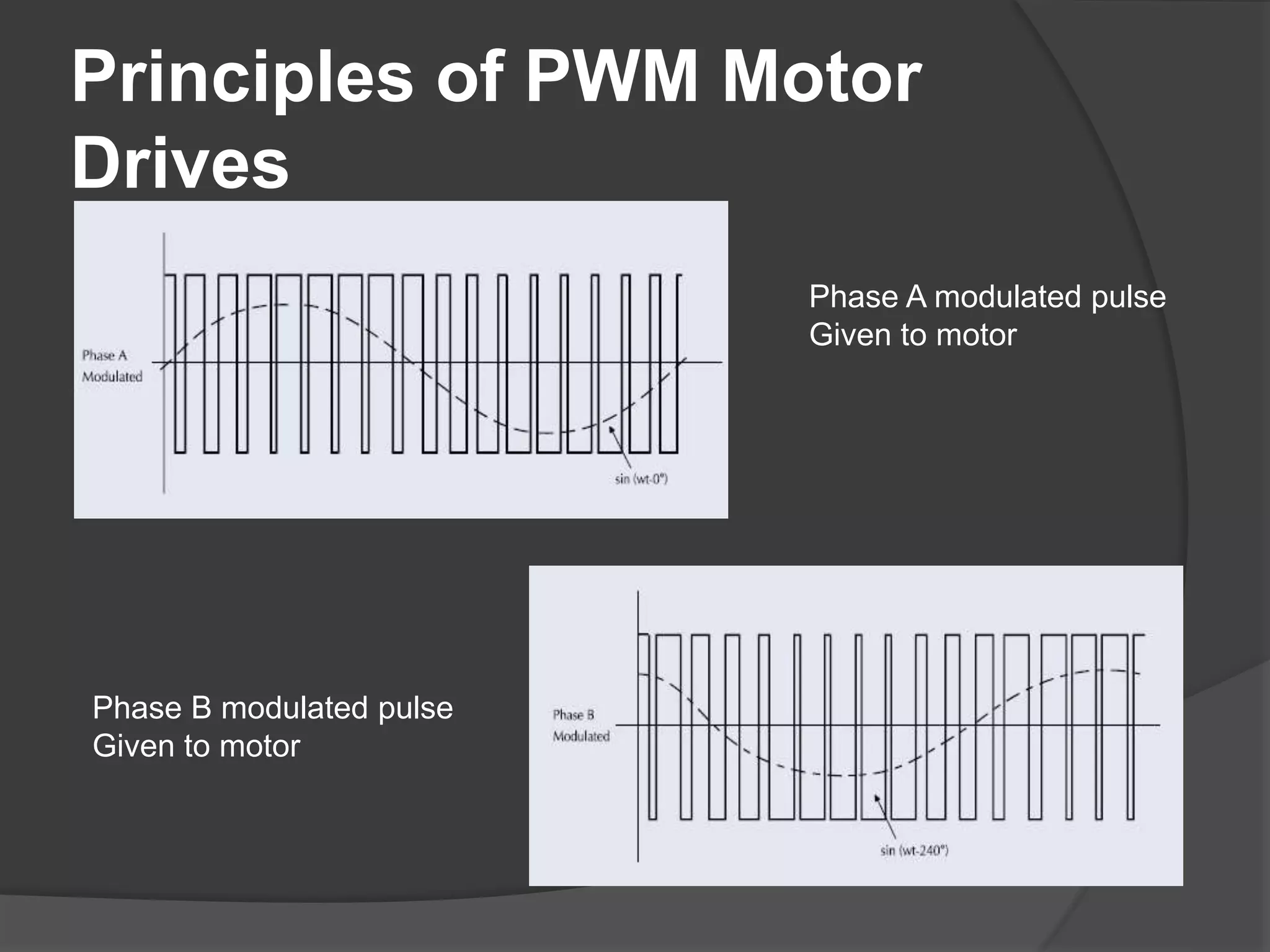
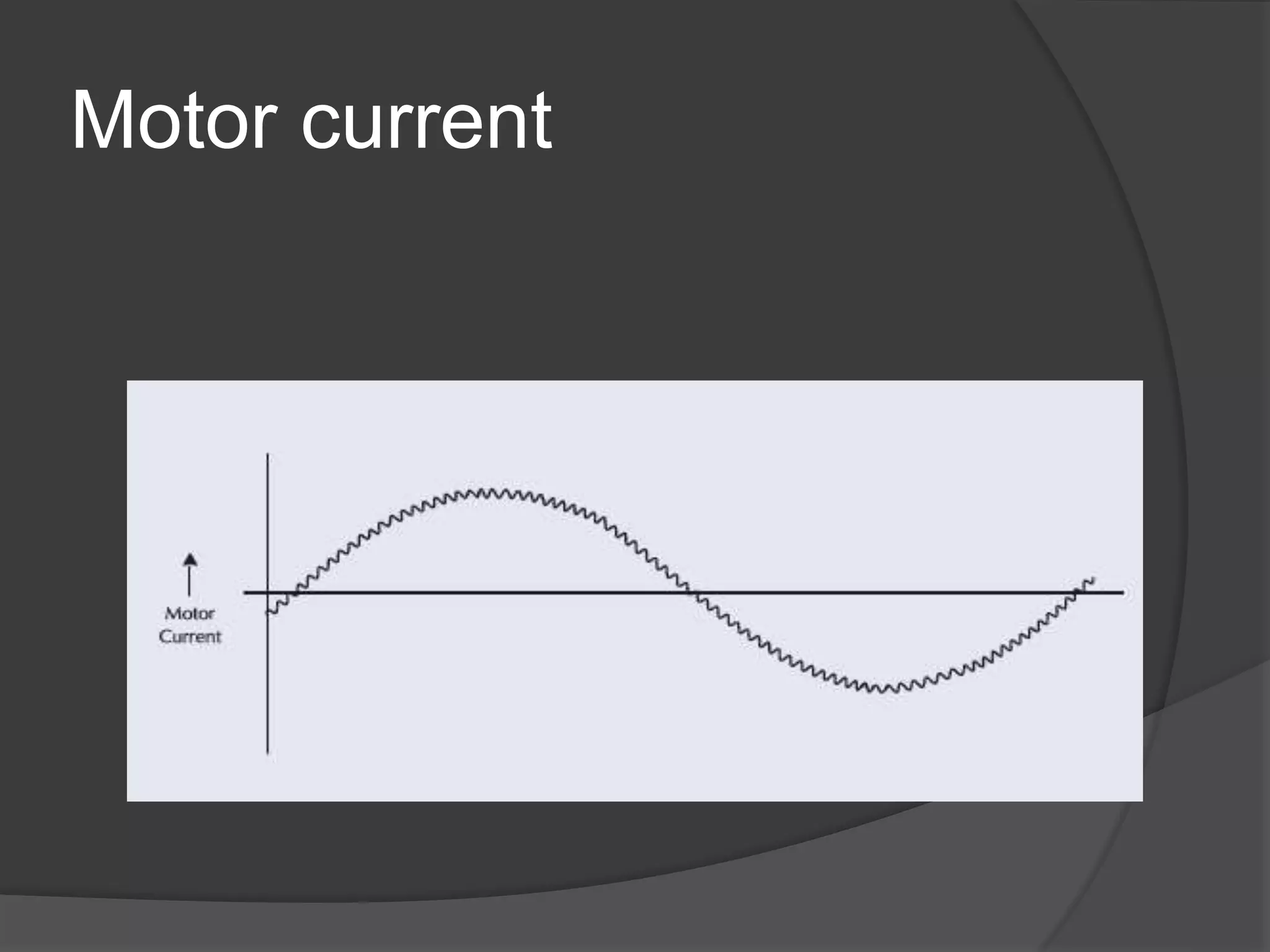
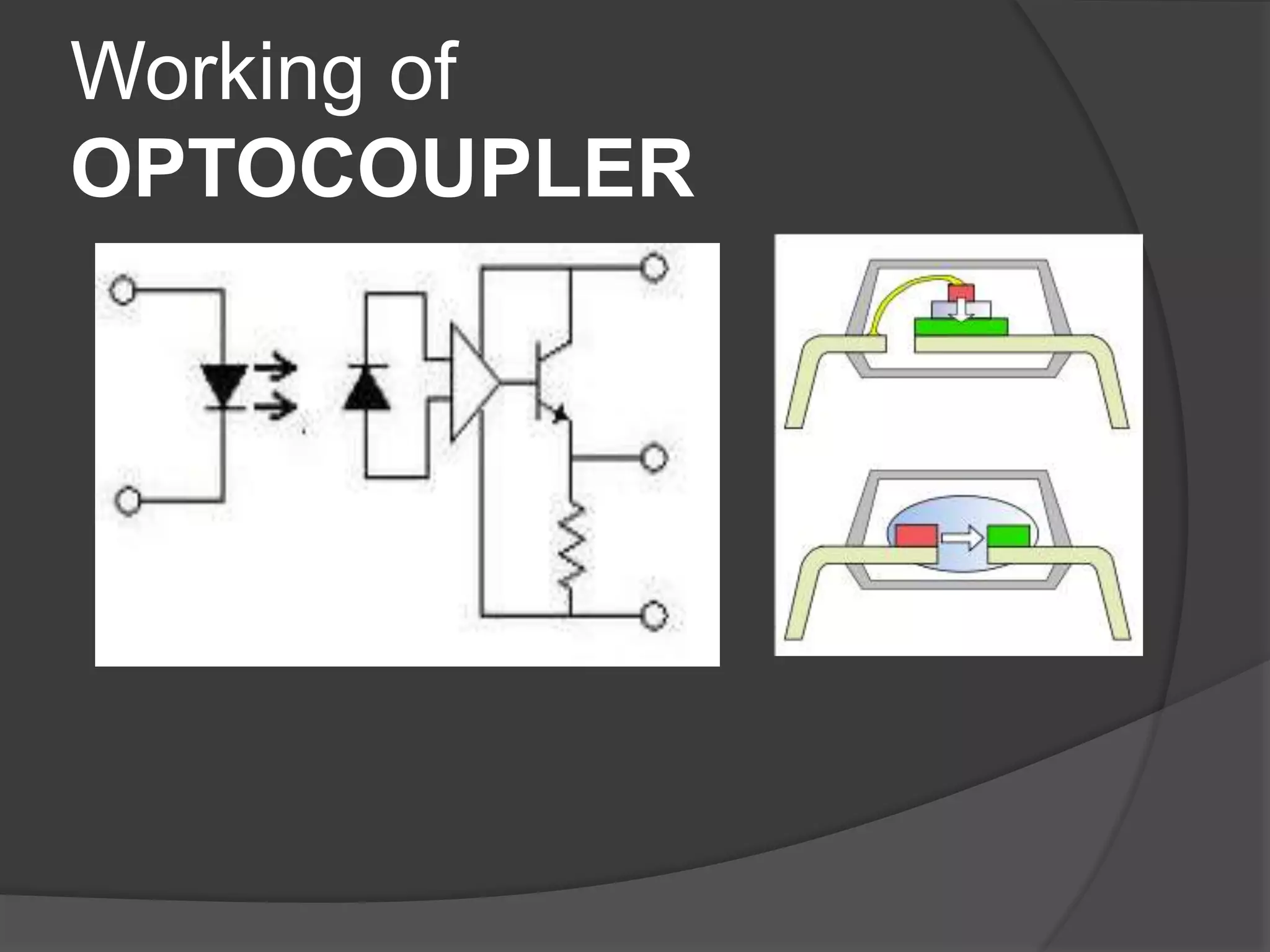
The seminar discusses the use of FPGA technology in motor control, highlighting its advantages such as low cost, high performance, and reduced latency. It covers the principles of FPGA operation, pulse width modulation (PWM) for motor drives, and the role of optocouplers in transferring signals while preventing high voltages from affecting sensitive components. The conclusion emphasizes the capability of PWM drives to effectively control three-phase motors by manipulating waveform amplitude and frequency.