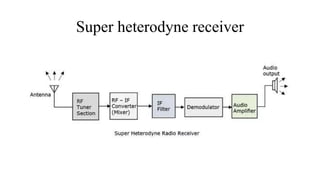
The document discusses the components and operation of a super heterodyne receiver. It consists of 5 main stages: 1) an RF tuner section that selects the desired frequency, 2) a mixer that combines the received RF signal with a local oscillator signal to produce an intermediate frequency (IF) signal, 3) an IF filter that eliminates unwanted frequencies and noise, 4) a demodulator that retrieves the original audio signal, and 5) an audio amplifier that strengthens the audio signal for output. The super heterodyne receiver overcomes drawbacks of ordinary receivers by translating all signals to a fixed IF for improved selectivity and sensitivity.