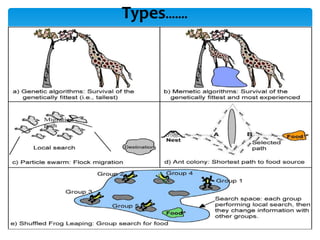
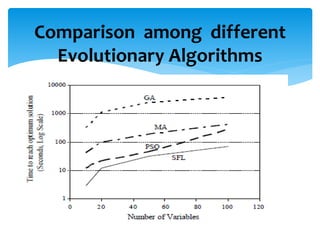
The shuffled frog leaping algorithm is an evolutionary algorithm inspired by the behavior of frogs searching for food. It works by first randomly generating a population of solutions and dividing them into groups. Each group conducts a local search, and the best solutions are shared among groups in shuffling processes. This continues until a convergence threshold is reached. The algorithm has applications in optimization problems like power grid design, construction scheduling, and water network planning by evaluating many potential solutions efficiently.