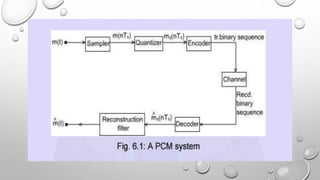
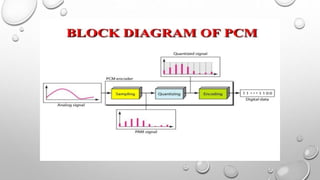
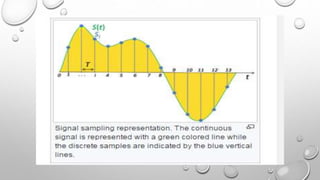
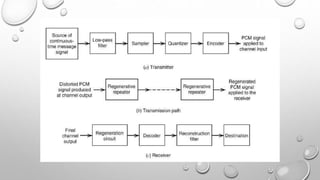
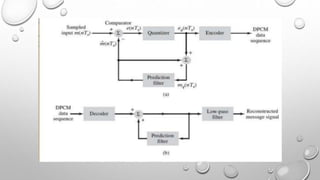
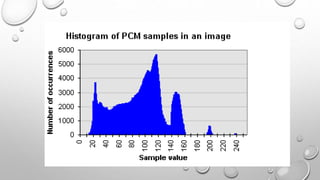
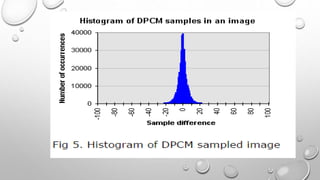
Differential Pulse Code Modulation (DPCM) is a technique for converting analog signals to digital by sampling the analog signal and quantizing the difference between the current and predicted values. DPCM reduces bandwidth and quantization error compared to traditional Pulse Code Modulation (PCM) by exploiting the correlation between successive samples, making it efficient for applications like audio compression. The document discusses DPCM's advantages, coding methods, and practical uses, including its relationship with Adaptive Differential Pulse Code Modulation (ADPCM).










![MATLAB CODE
• PREDICTOR = [0 1]; % Y(K)=X(K-1)
• PARTITION = [-1:.1:.9];
• CODEBOOK = [-1:.1:1];
• T = [0:PI/50:2*PI];
• X = SAWTOOTH(3*T); % ORIGINAL SIGNAL
• % QUANTIZE X USING DPCM.
• ENCODEDX = DPCMENCO(X,CODEBOOK,PARTITION,PREDICTOR);
• % TRY TO RECOVER X FROM THE MODULATED SIGNAL.
• DECODEDX = DPCMDECO(ENCODEDX,CODEBOOK,PREDICTOR);
• PLOT(T,X,T,DECODEDX,'--')
• DISTOR = SUM((X-DECODEDX).^2)/LENGTH(X) % MEAN SQUARE ERROR](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hello-170325144226/85/DPCM-18-320.jpg)




