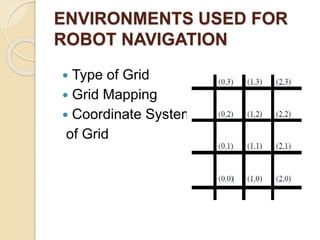
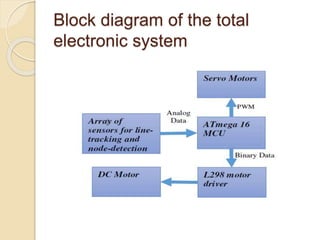
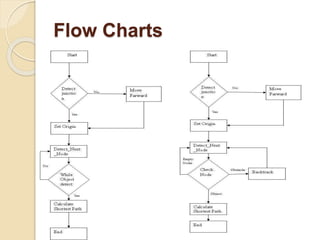
The document discusses the development of a grid-solving robot using IR sensors for line navigation and an Atmega16 microcontroller for path planning through Dijkstra's algorithm. It outlines hardware components, the system architecture, and future improvements involving FPGA technology and A* search algorithm. The project aims to enhance autonomous navigation systems for industrial applications.






![REFERENCES
Lalit Gehlod, Vaibhav Jain, Mala Dutta, Devesh
Kumar Lal. A Grid Based Robot Navigation by
Using Priority Algorithm. IJARCCE Magazine,
Vol. 2, Issue 8, August 2013.
Ahmedullah Aziz, Md. Shafayat Hossain ,
Mohammad Wahidur Rahman. Programming
And Construction Of Ahemaddula-A Fast Grid-
Solving Robot. IJITCA ,Vol.3, No.1, January
2013.
Toshendra K. Sharma, Robotics with AVR, RSI
publication, second edition 2011.
Atmel. (2010, Oct. 20). “ATMEGA 16
datasheet.” [On-line]. Pp. 1-356.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gridsolvingrobot-150415052053-conversion-gate01/85/Grid-solving-robot-17-320.jpg)
