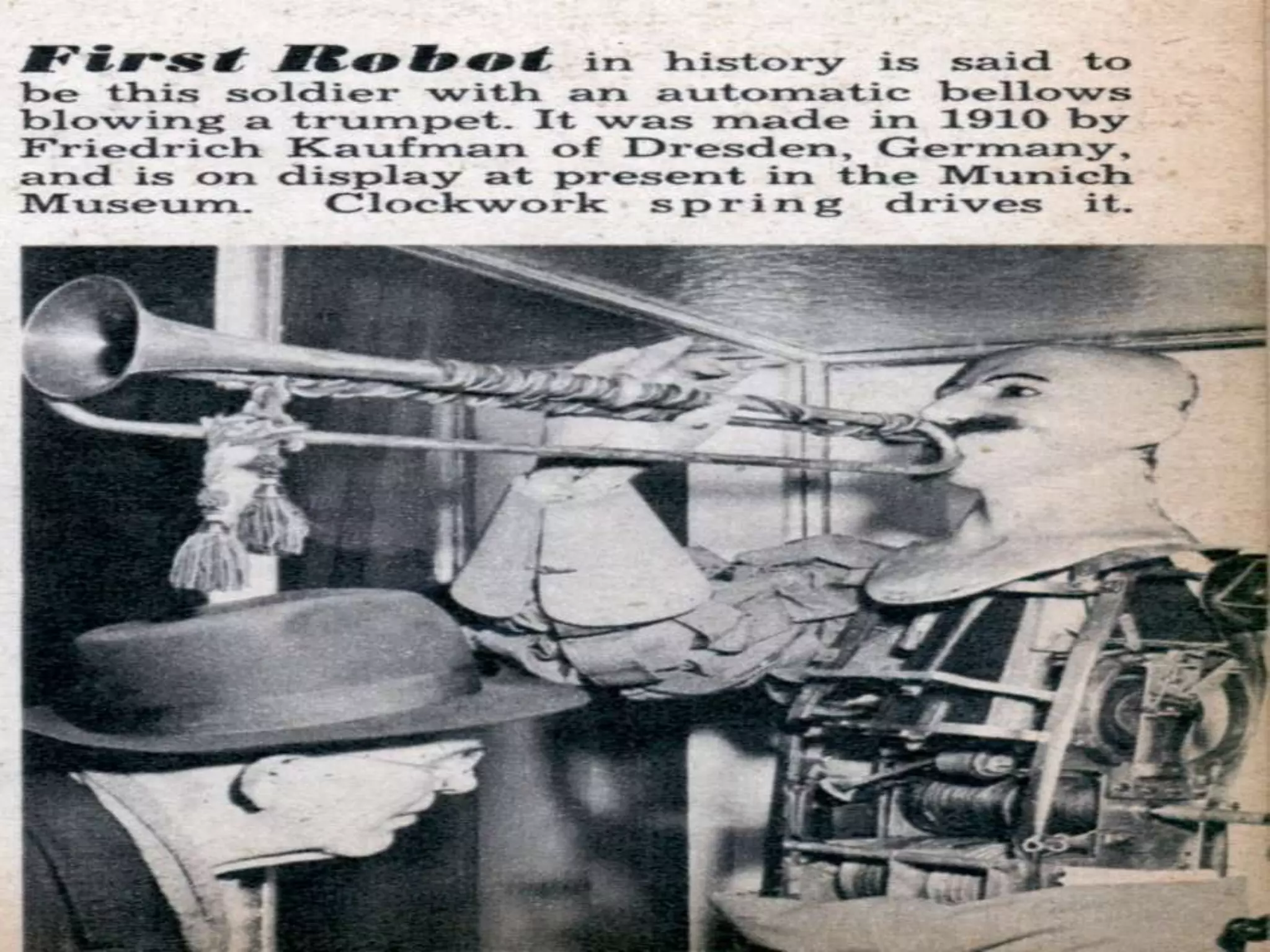
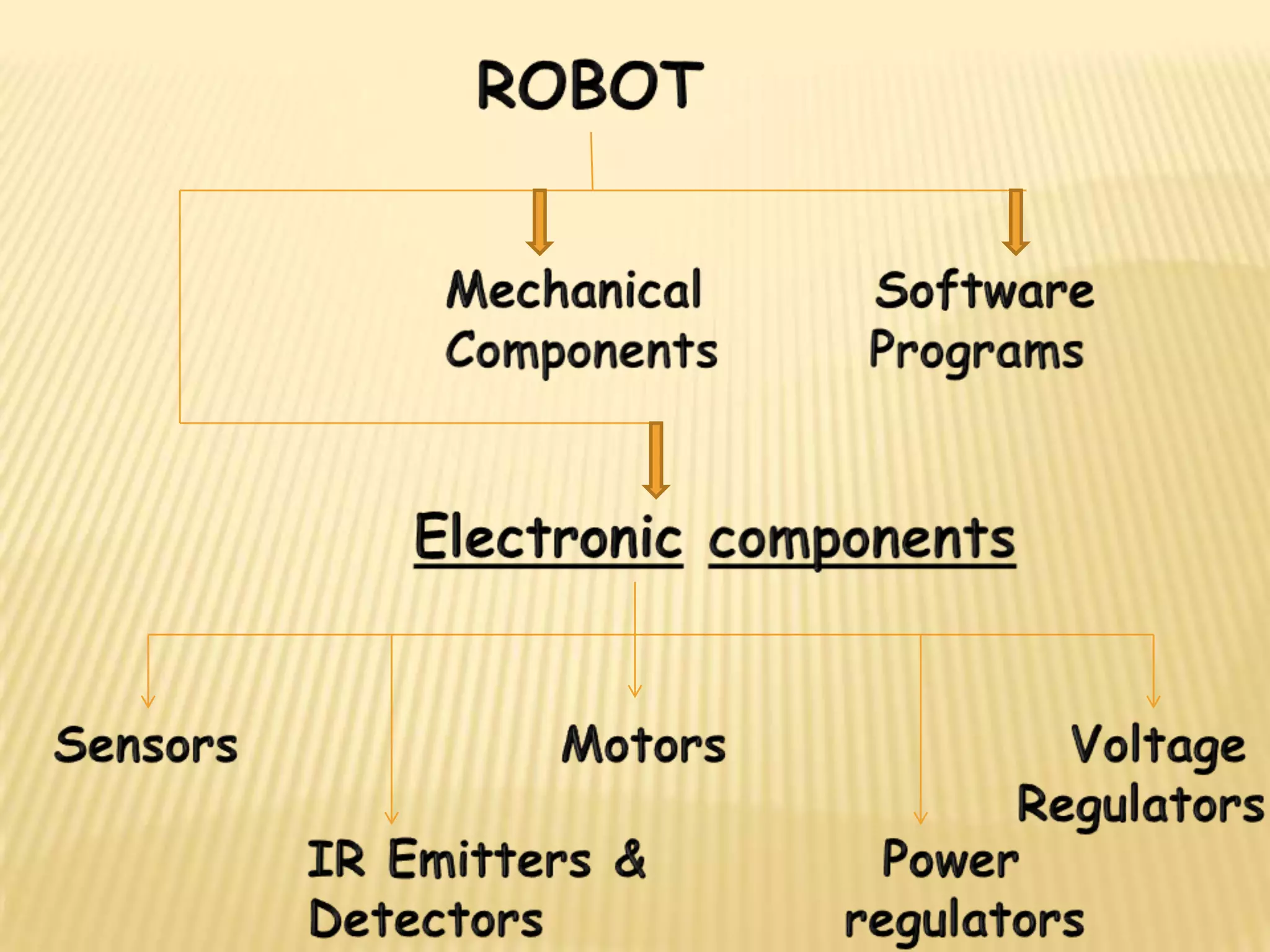
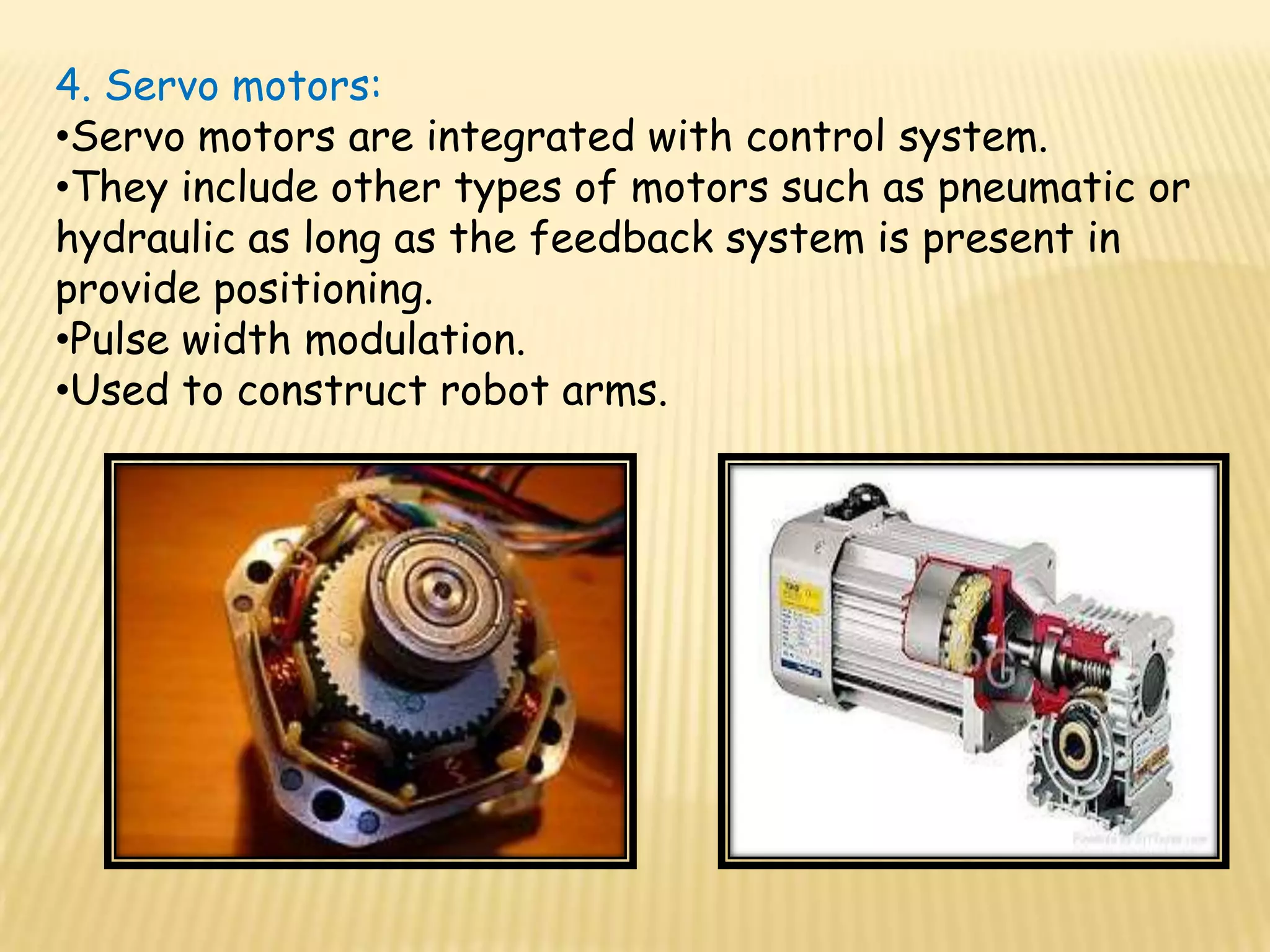
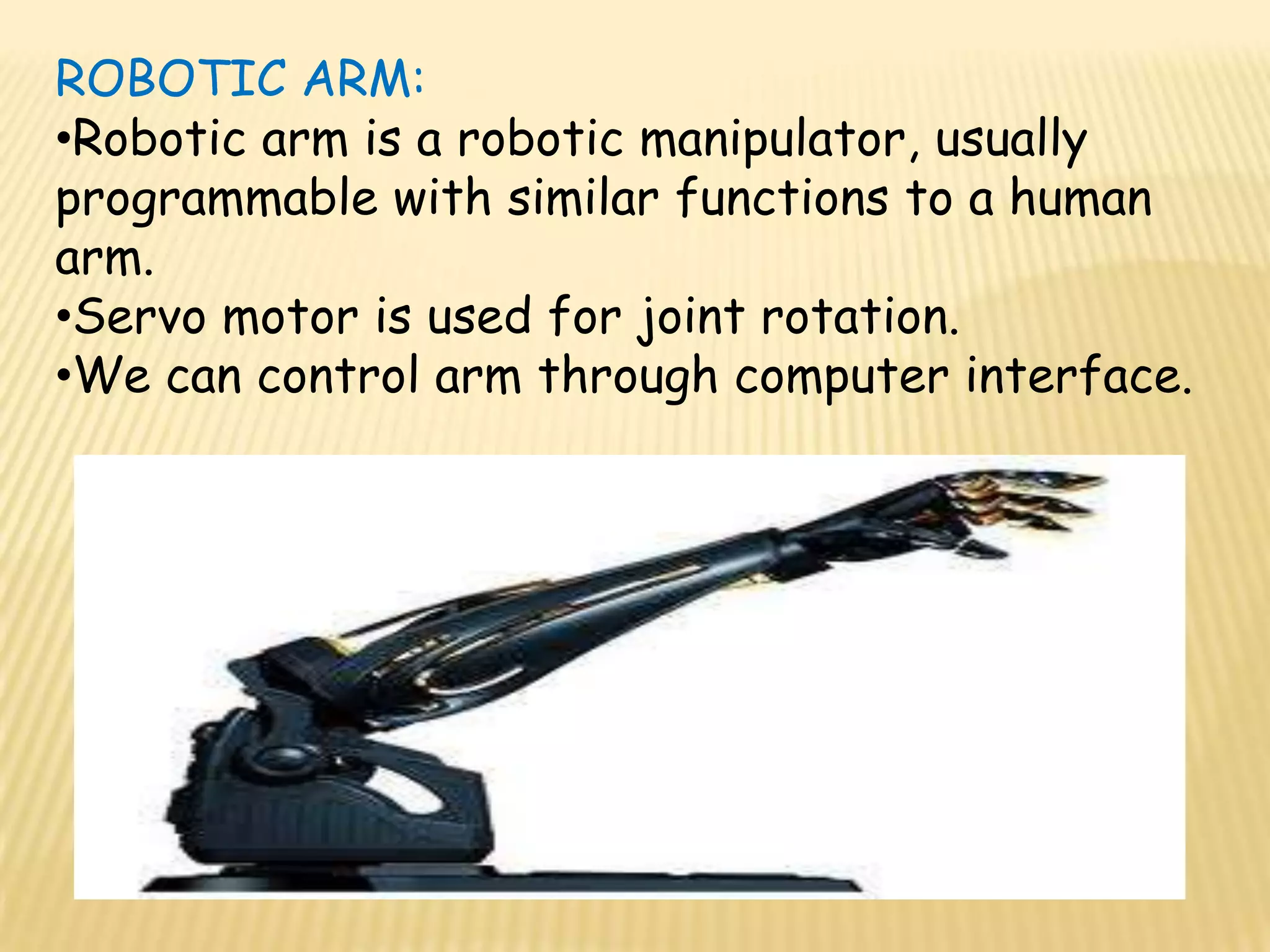
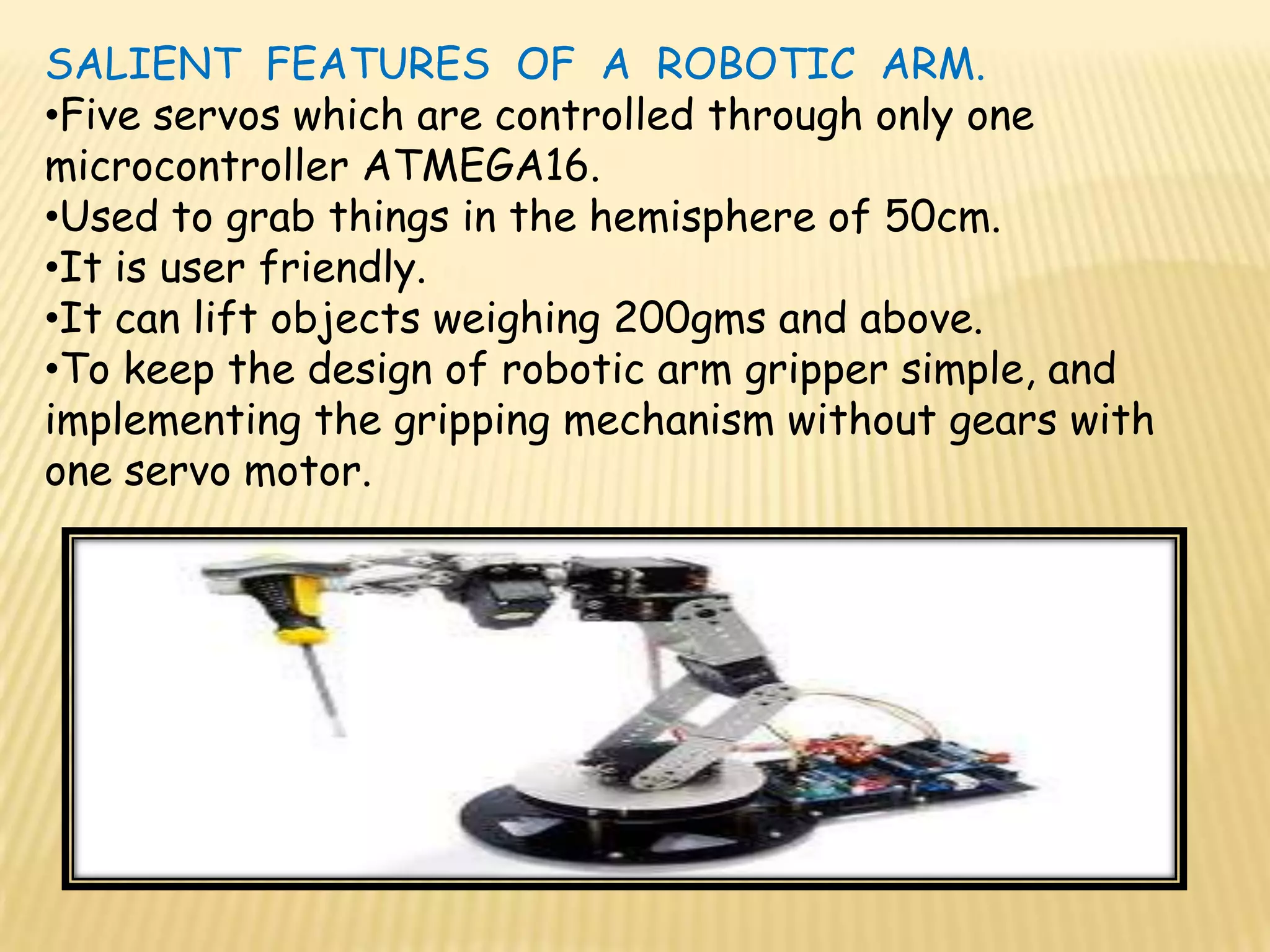
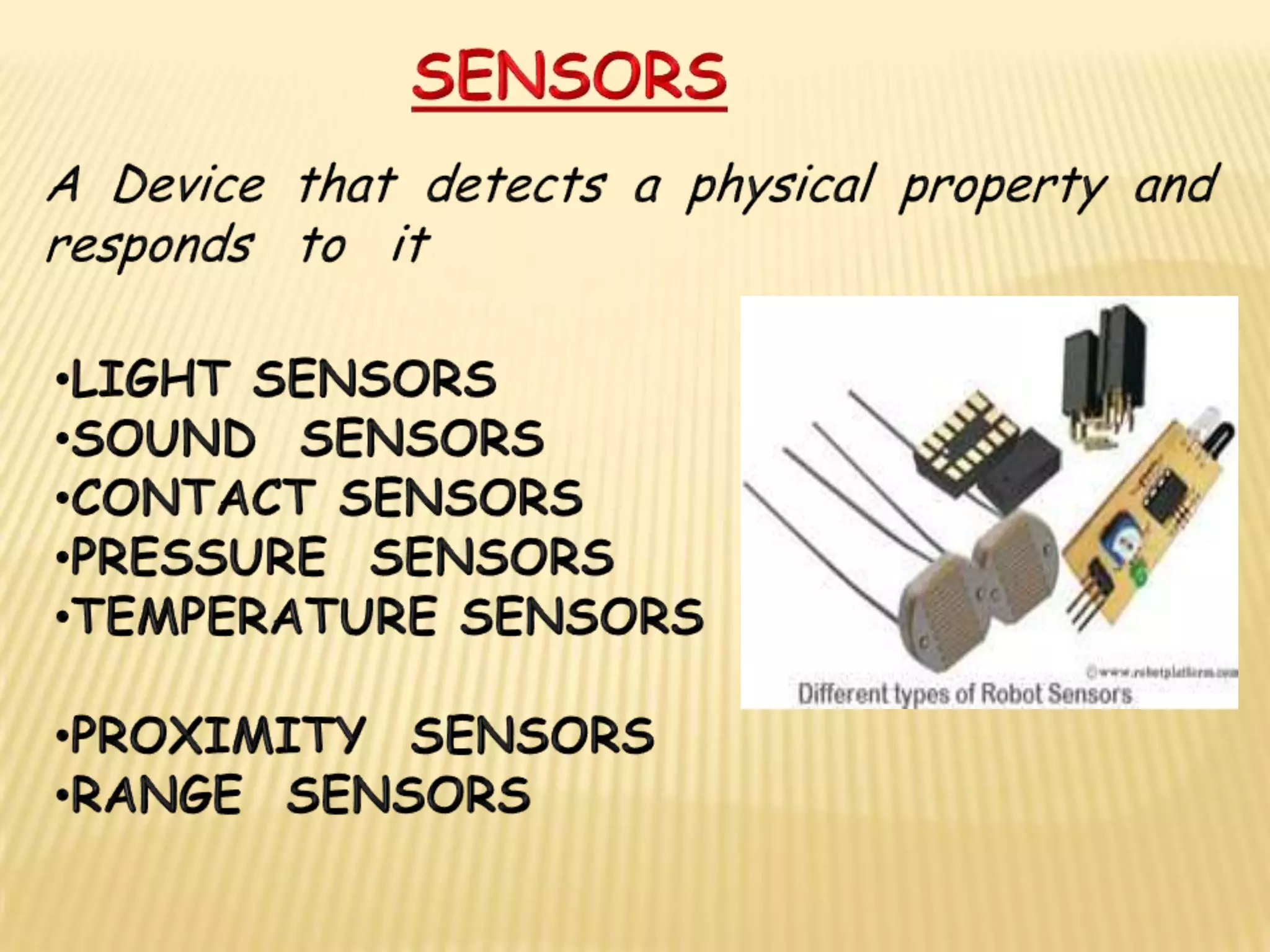
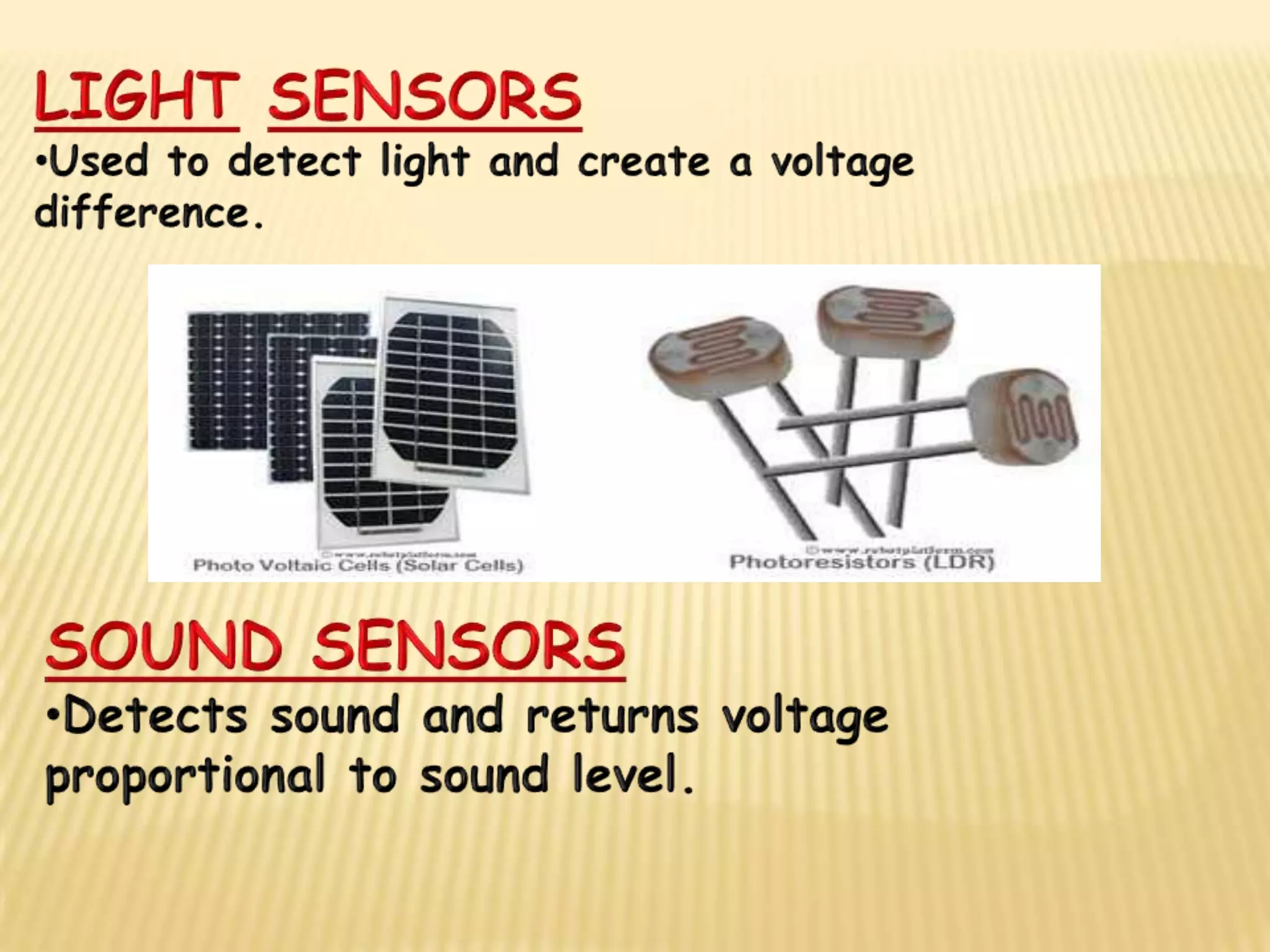
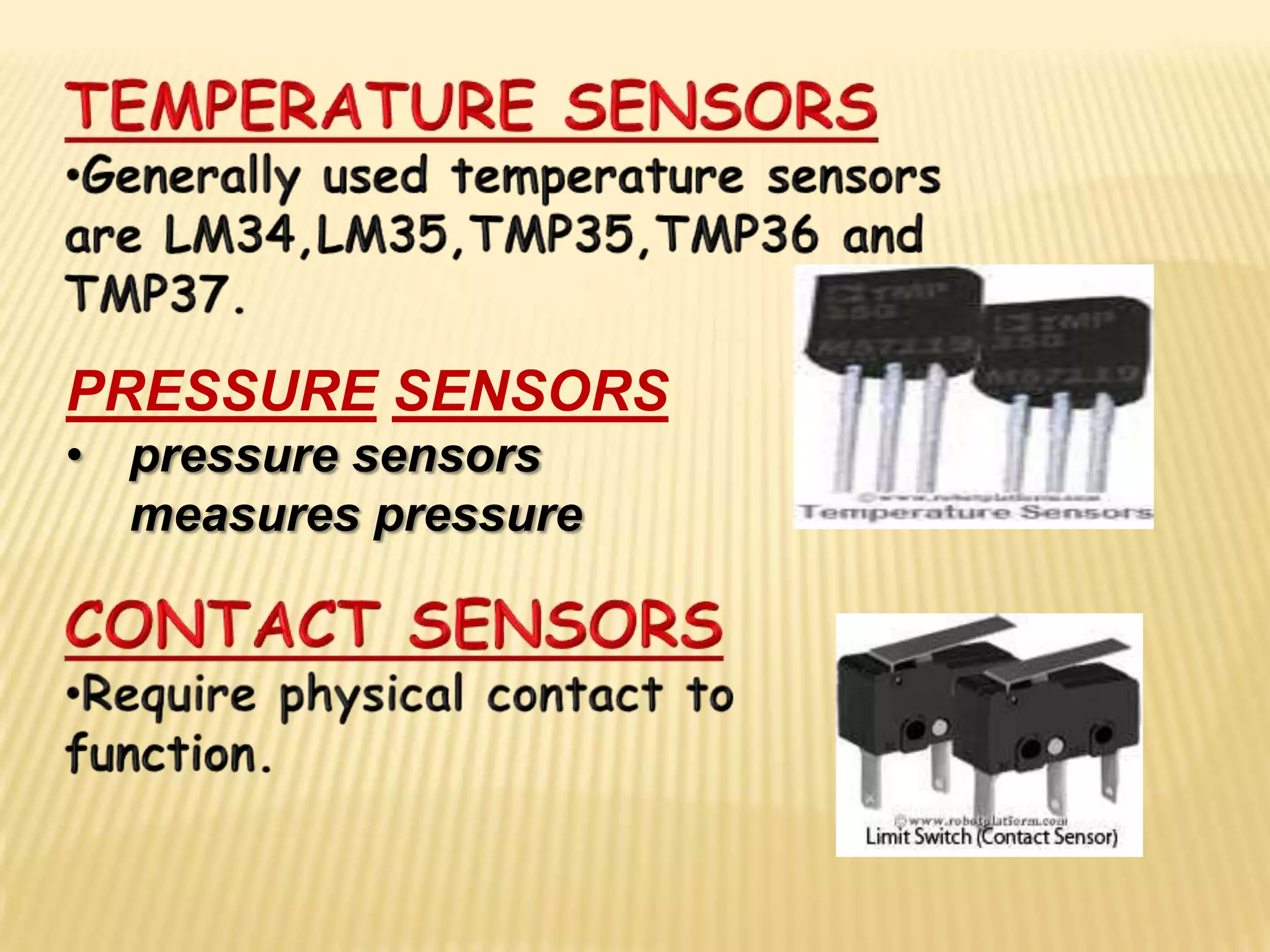
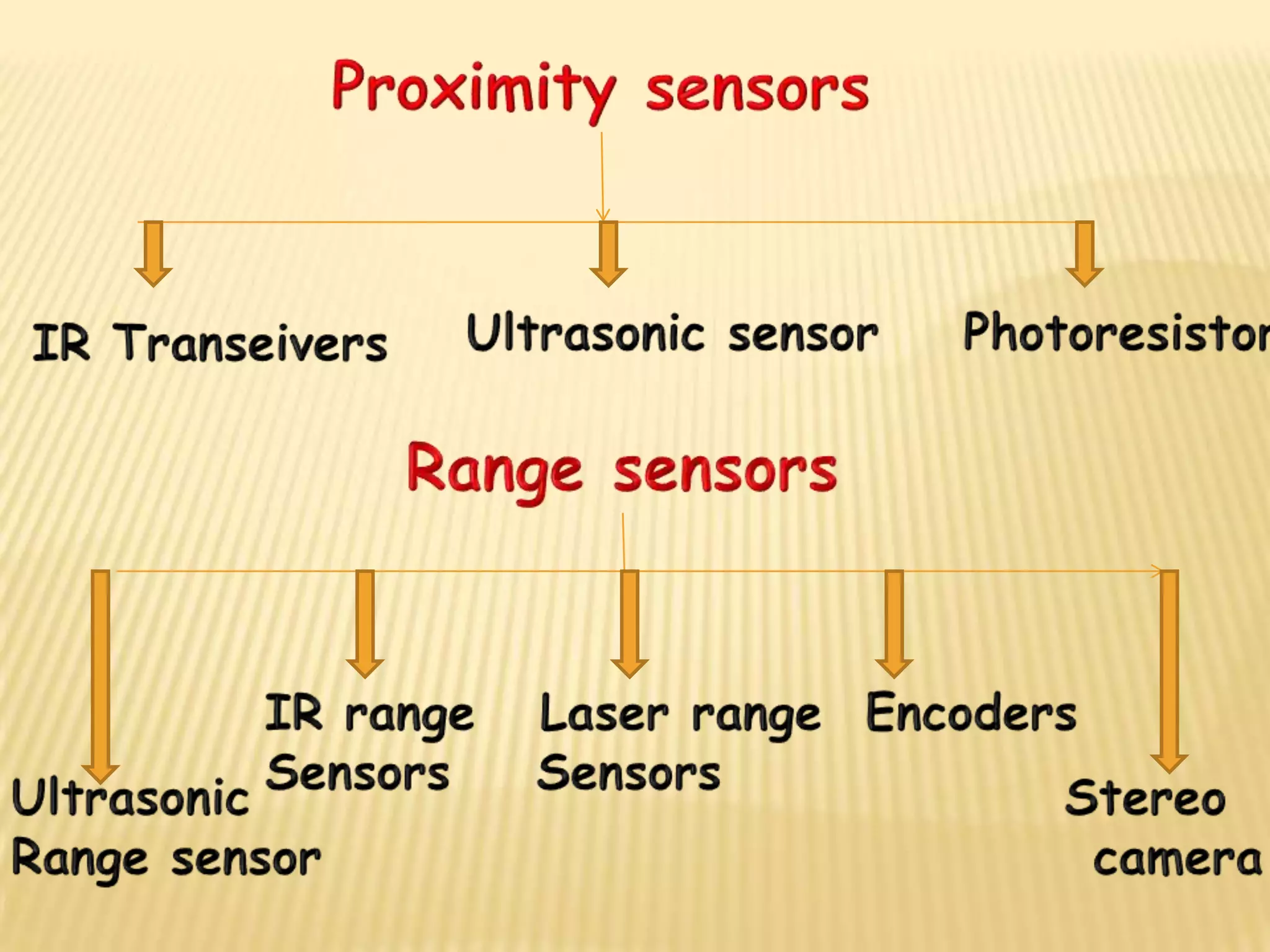
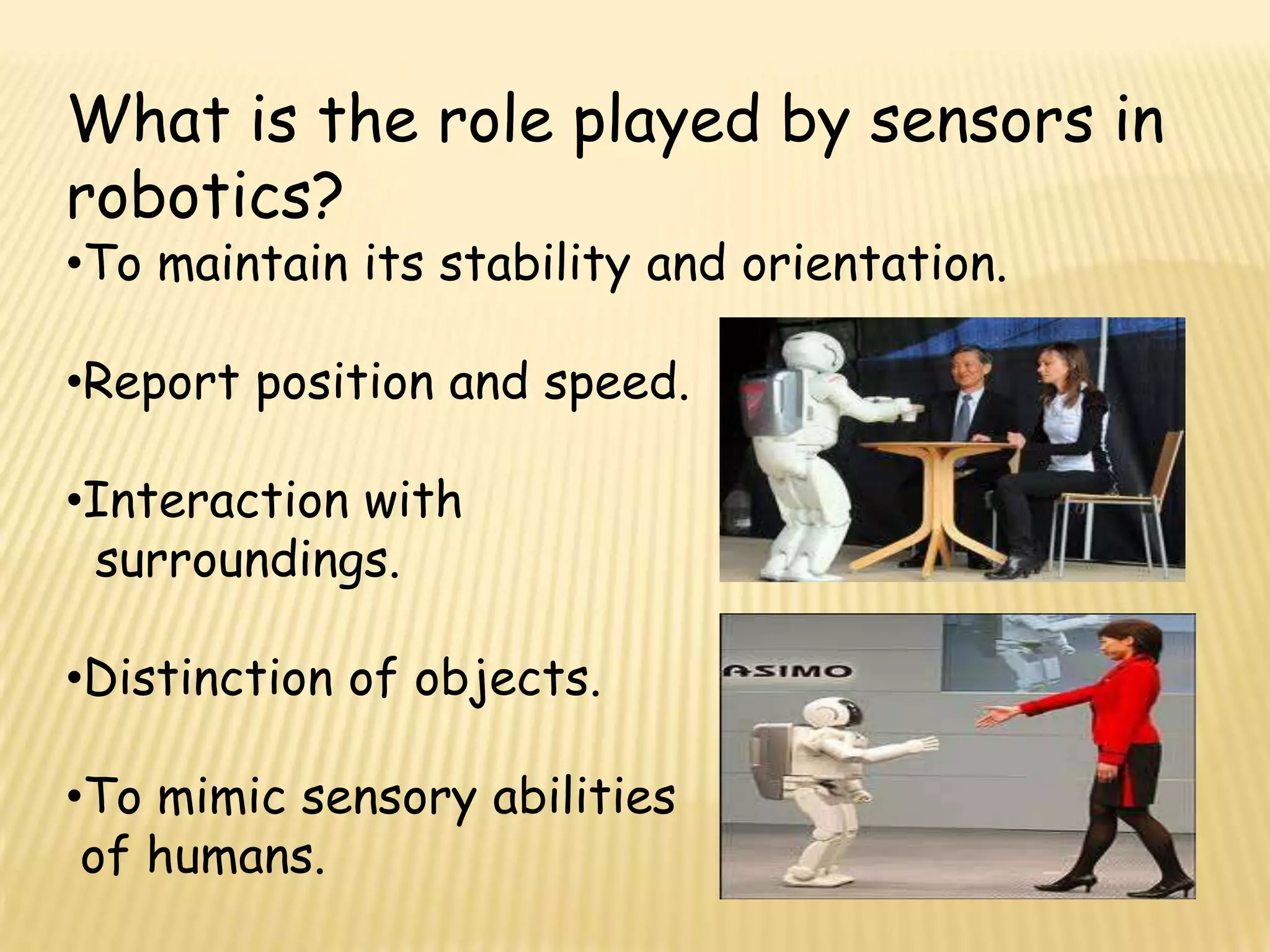
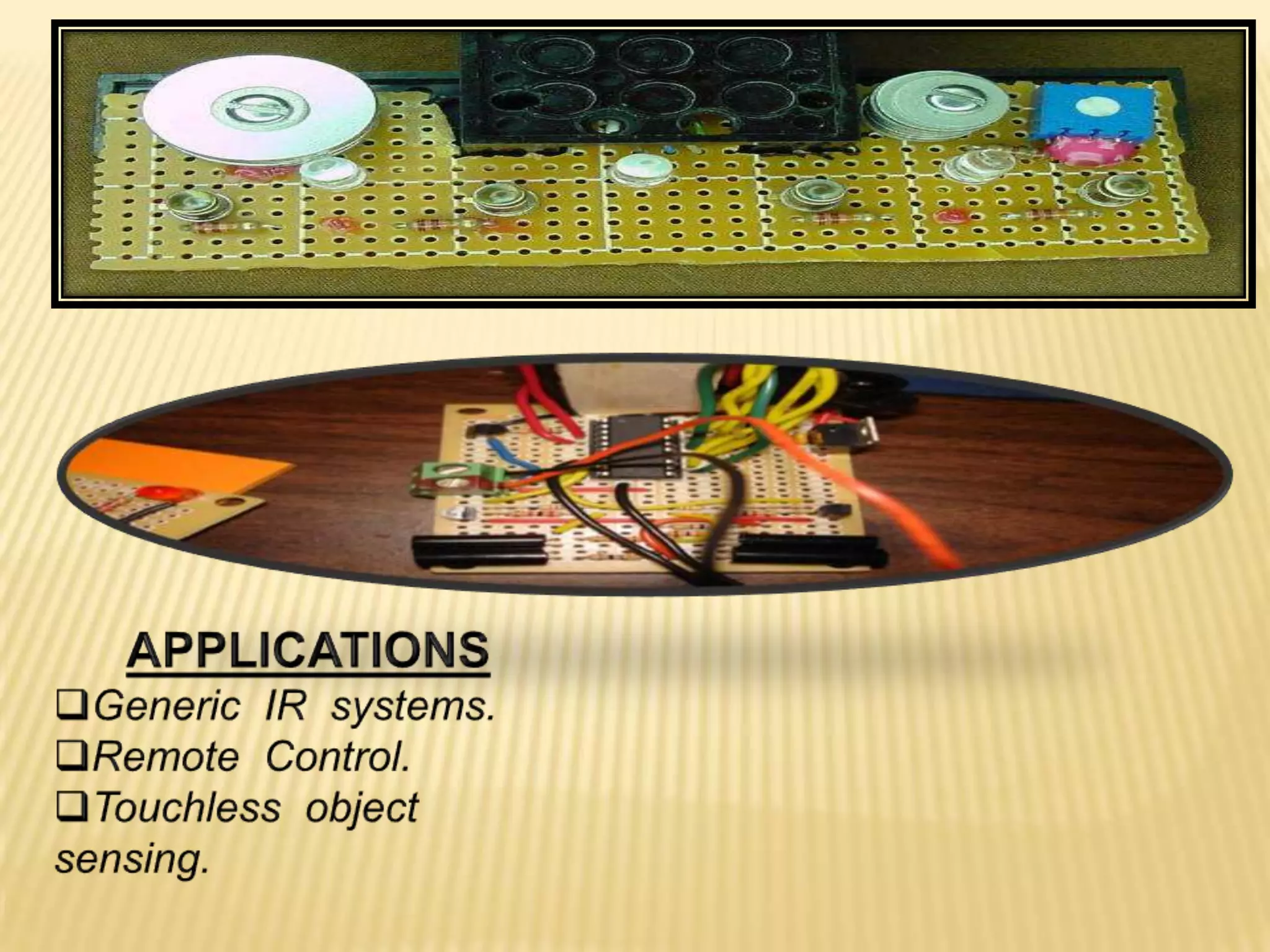
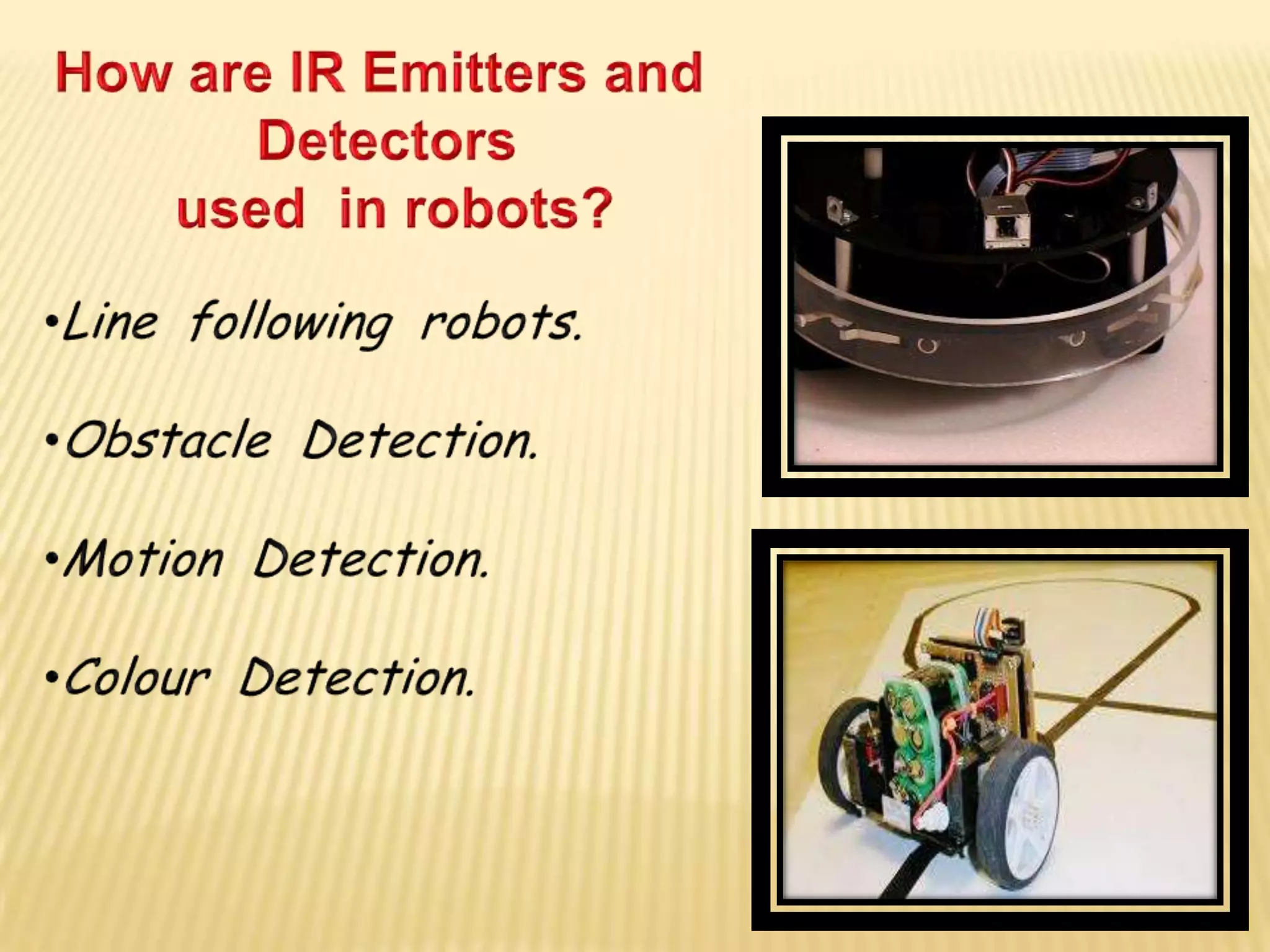
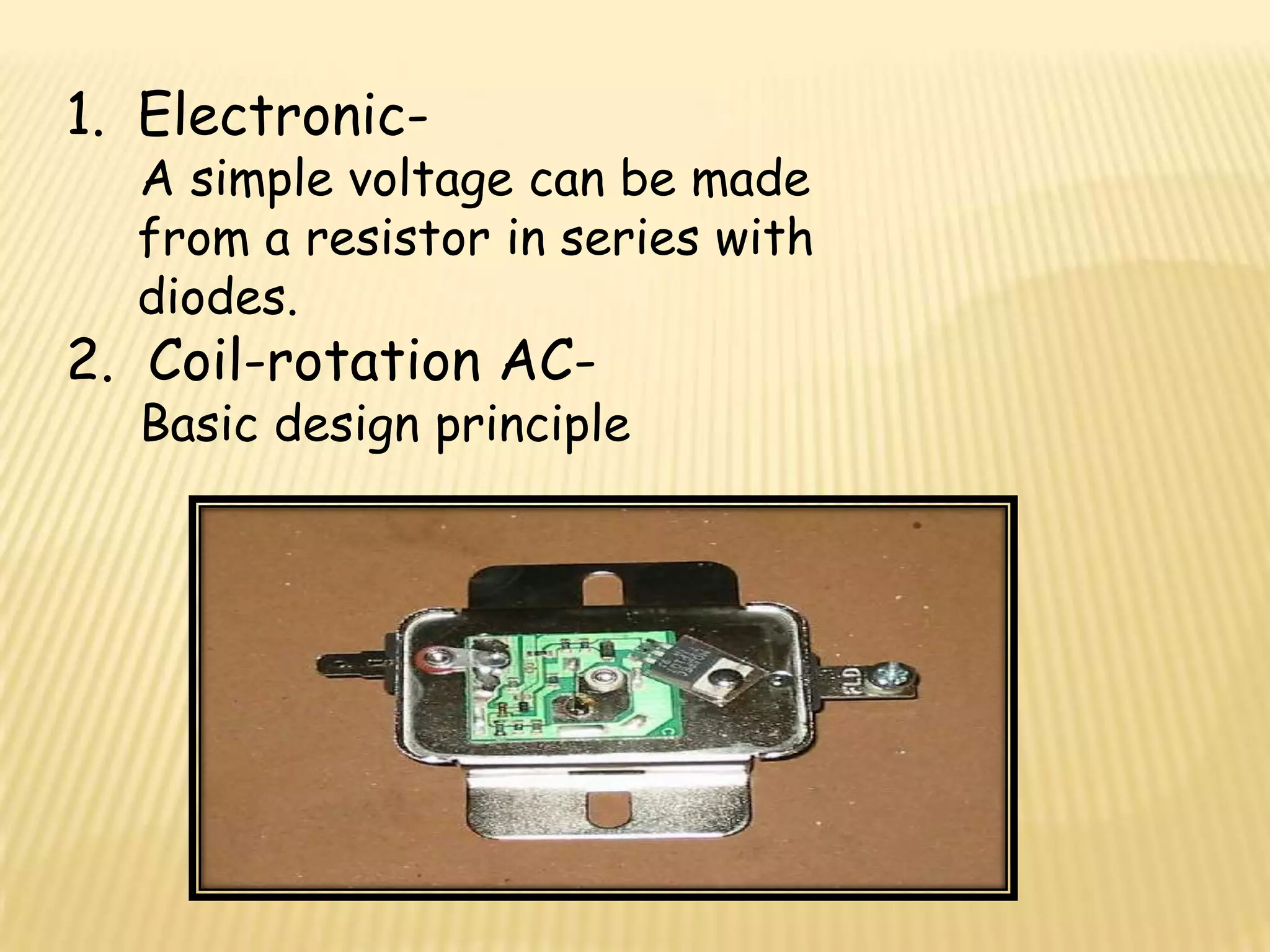
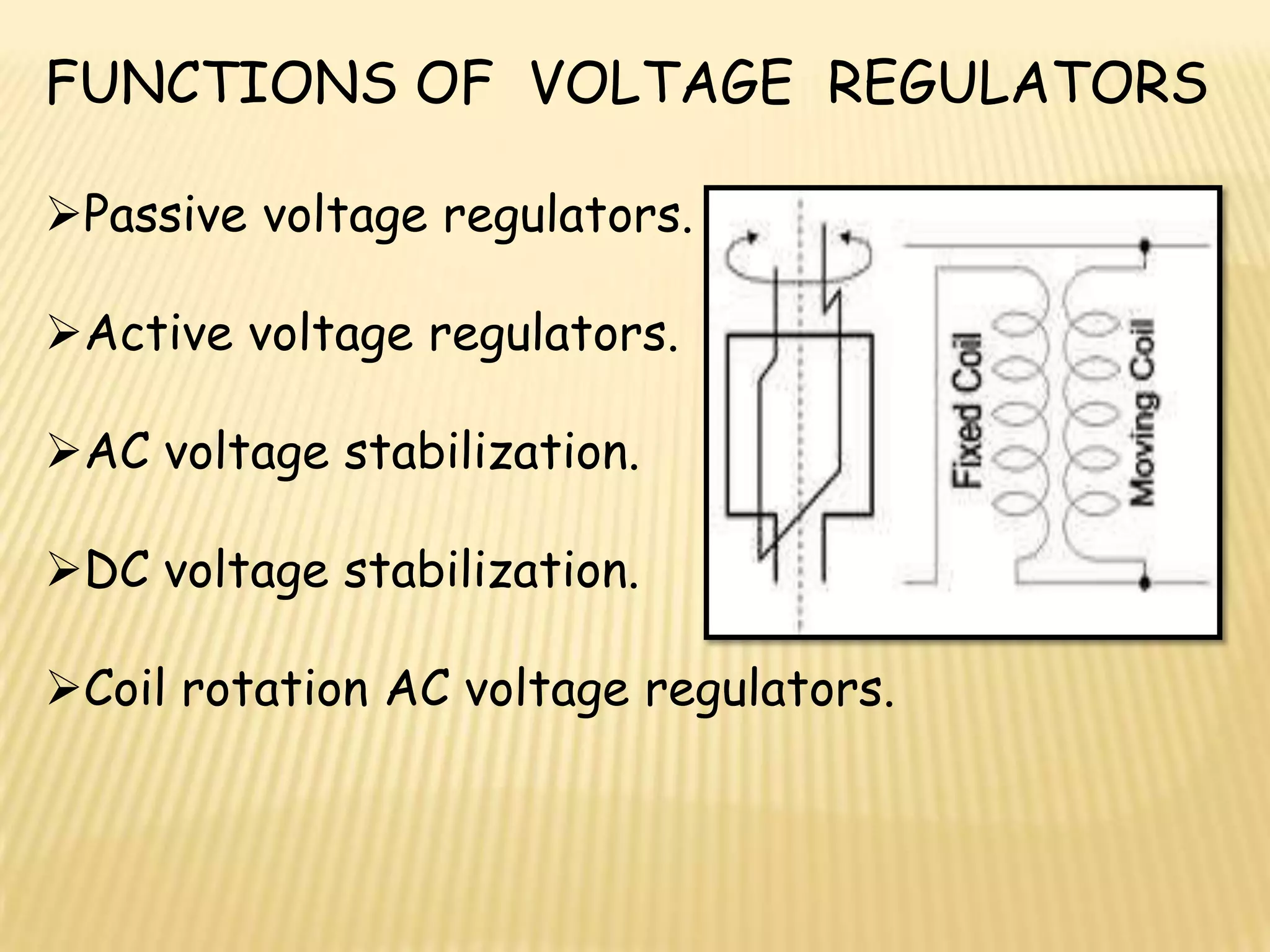
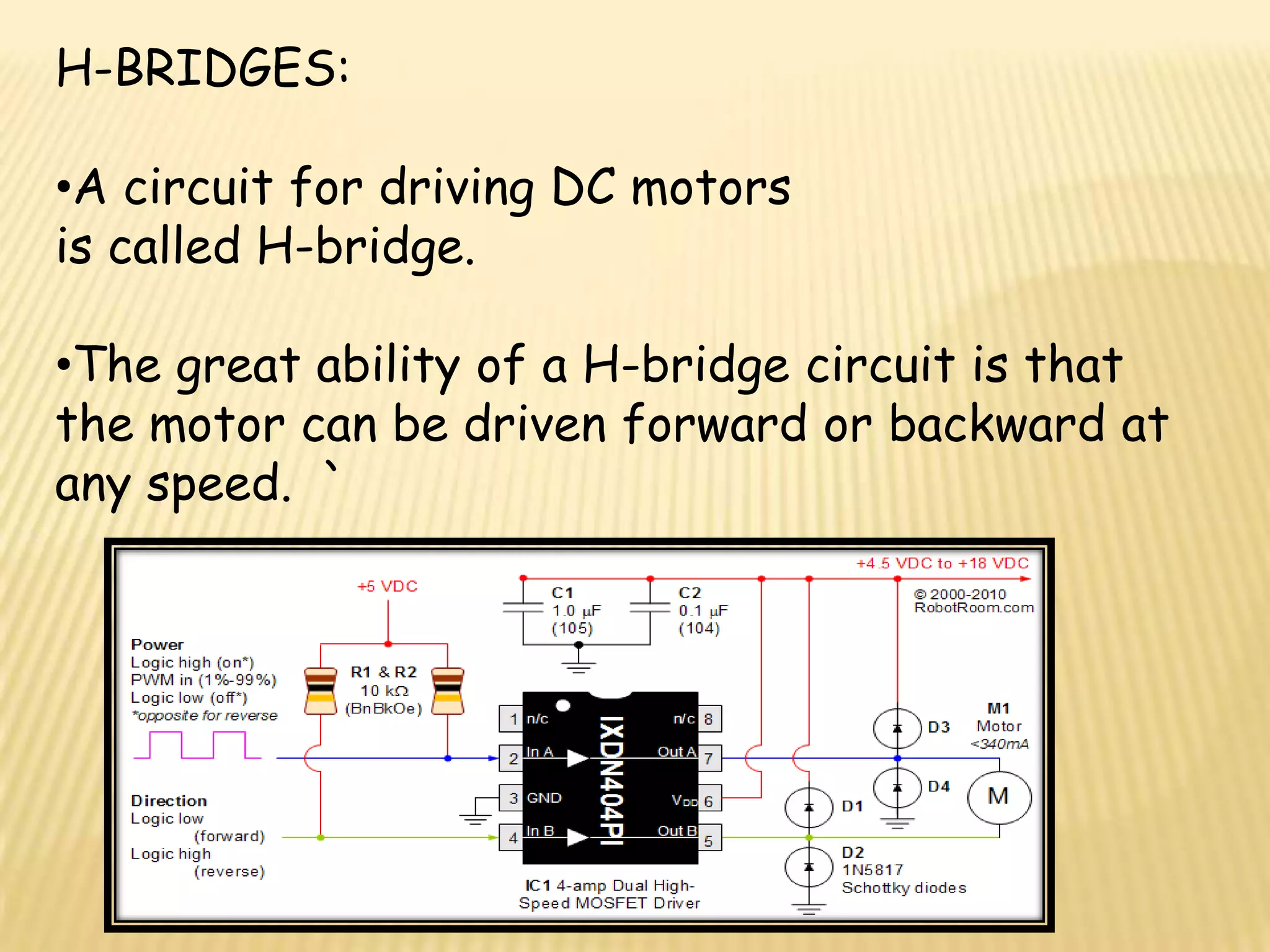
This document discusses various components used in robotics including electric motors, sensors, voltage regulators, and H-bridges. It describes how electric motors convert electrical energy to mechanical energy and lists common types like brushed DC motors, brushless DC motors, stepper motors, and servo motors. Sensors are outlined as playing a key role in robotics by allowing robots to maintain stability, report position/speed, interact with surroundings, distinguish objects, and mimic human senses. Voltage regulators are defined as devices that maintain a constant voltage level and various types are identified. H-bridges are described as circuits for controlling DC motor direction. Potential future applications of robotics discussed include expanded use in industrial, military, medical, and space