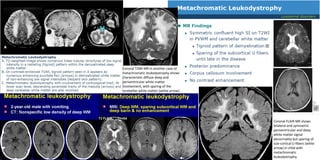
This document provides information on various leukodystrophies and leukodystrophy mimics. It compares their white matter and gray matter involvement patterns on MRI as well as other key imaging and clinical features. Common leukodystrophies discussed include Canavan disease, Alexander disease, vanishing white matter disease, X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy, and metachromatic leukodystrophy. Leukodystrophy mimics such as mitochondrial, inflammatory, and ischemic/hypoxic conditions are also mentioned. Images demonstrate characteristic MRI patterns for some examples.