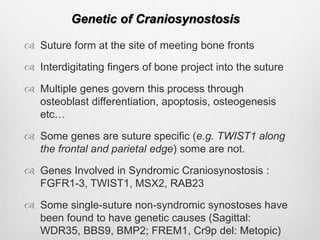
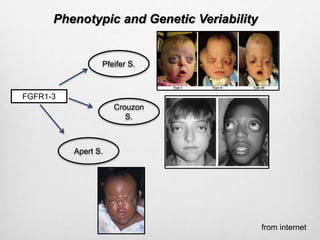
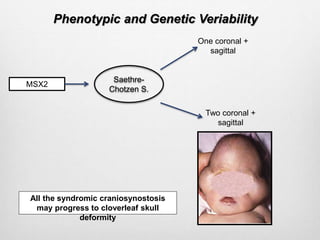
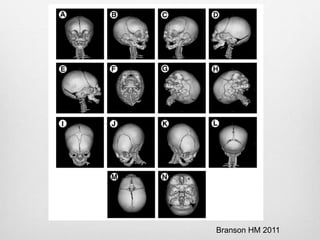
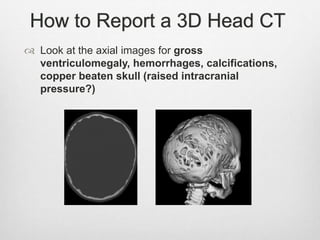
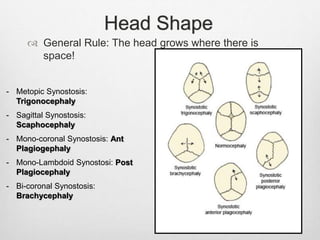
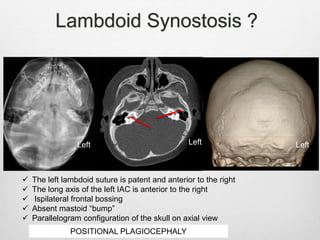
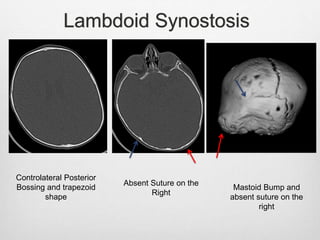
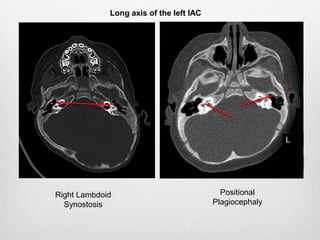
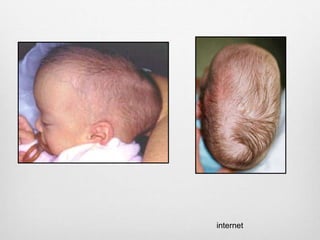
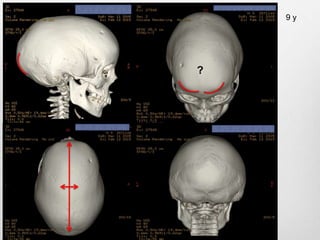
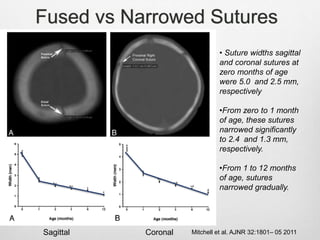
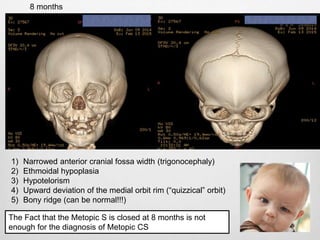
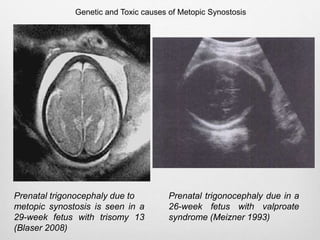
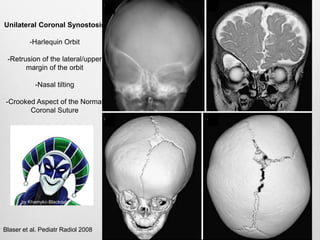
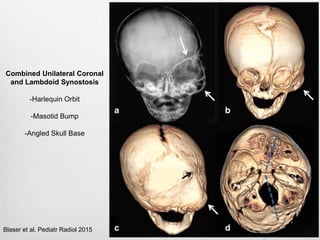
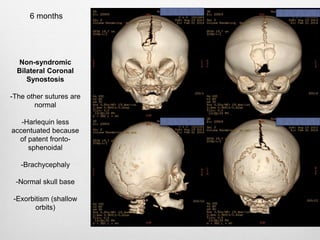
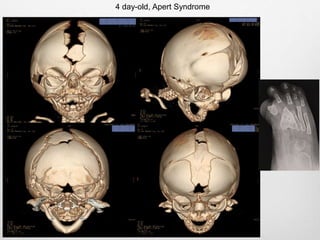
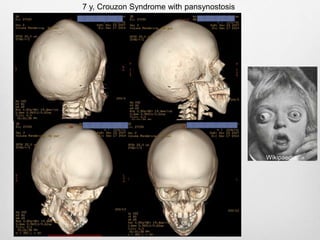
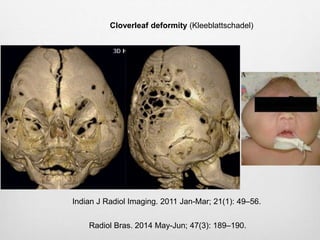
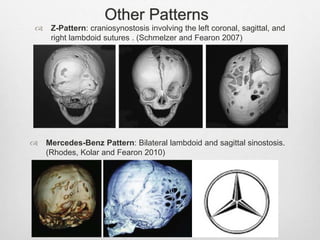
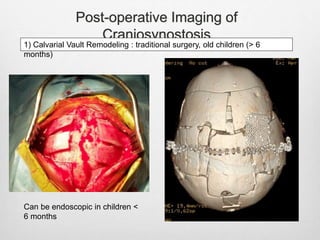
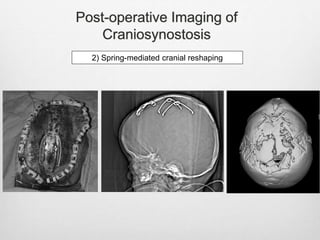
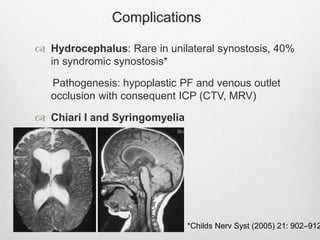
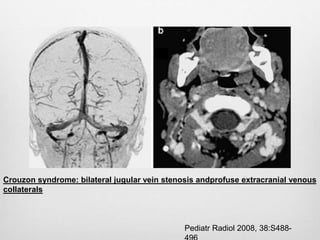
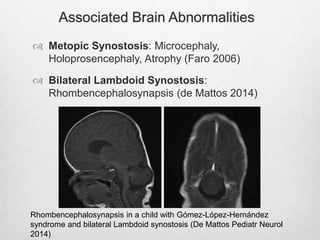
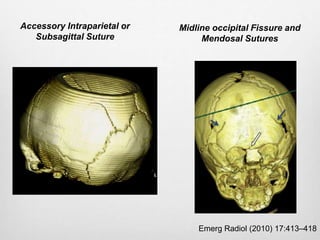
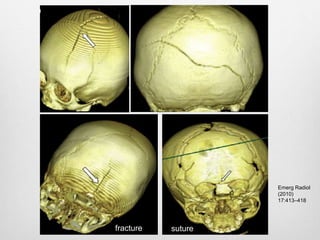
This document details the radiological approach to craniosynostosis, outlining normal cranial development, genetic factors, imaging techniques, and associated complications. Key imaging methods such as low-dose 3D CT are emphasized for diagnosing and planning treatment, while also noting genetic implications and imaging patterns of various craniosynostosis types. The document concludes by stressing the importance of understanding anatomy and embryology for accurate diagnosis and evaluation.