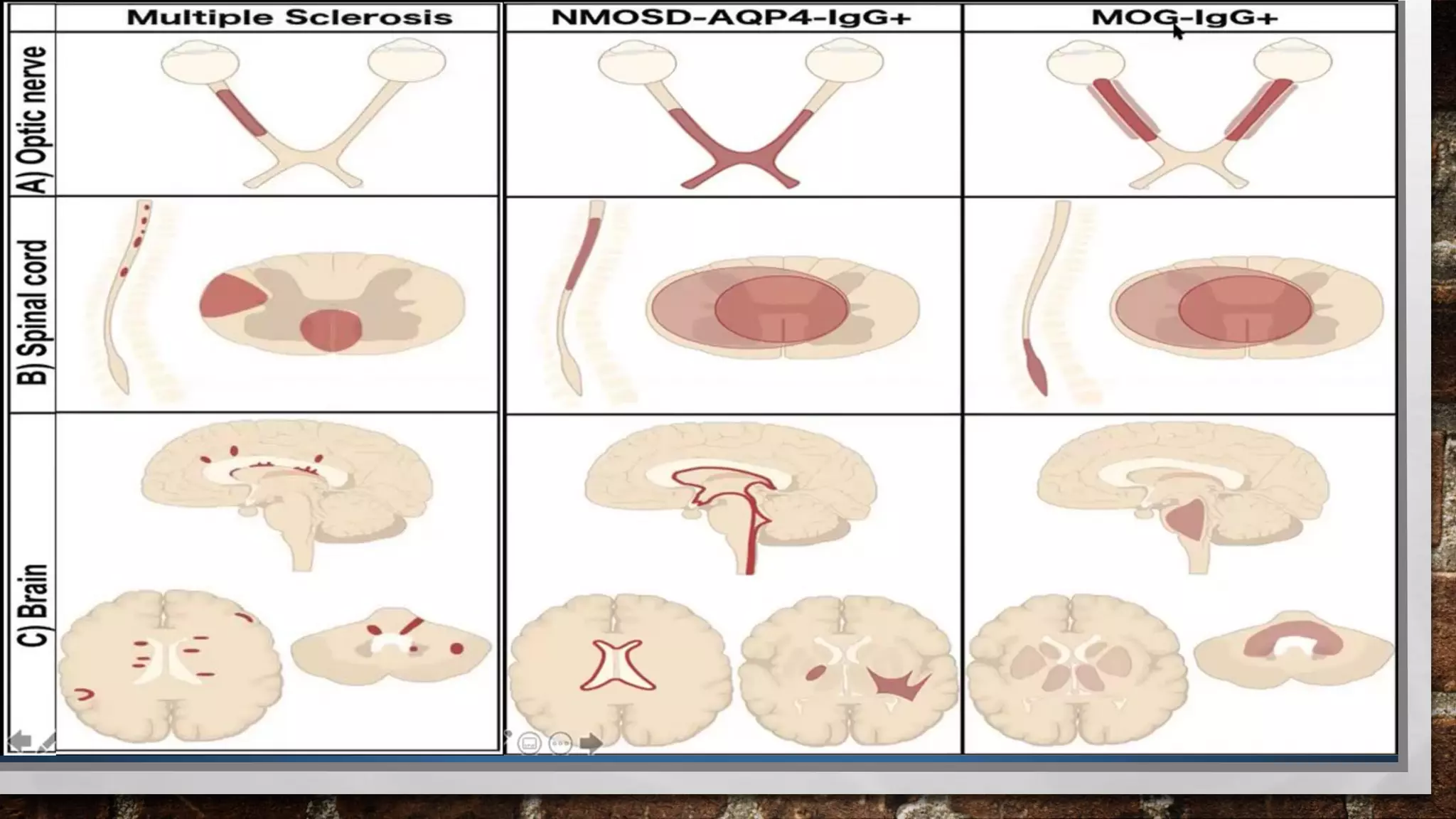
Oligodendrocytes produce myelin sheaths around axons that insulate and speed up nerve conduction. Demyelinating disorders involve damage to existing myelin sheaths, while dysmyelinating disorders impair myelin formation. Common demyelinating conditions include multiple sclerosis, acute disseminated encephalomyelitis, and neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder. Diagnostic tools include neurological exam, MRI, and lumbar puncture. Differential diagnosis requires considering alternative causes such as infection, autoimmune disease, or metabolic derangement.