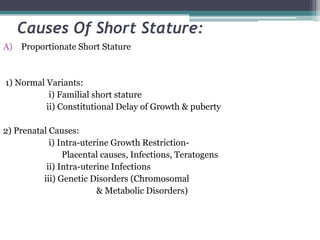
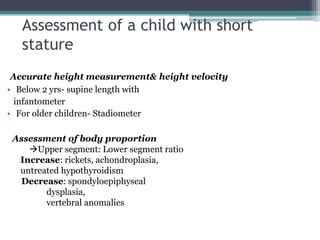
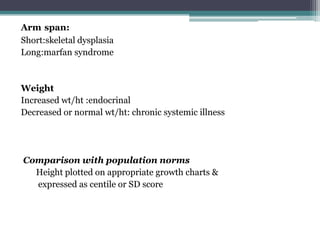
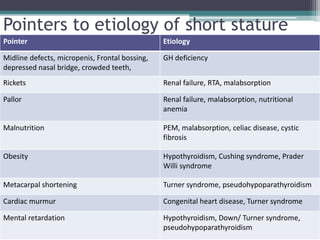
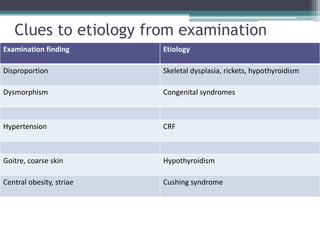
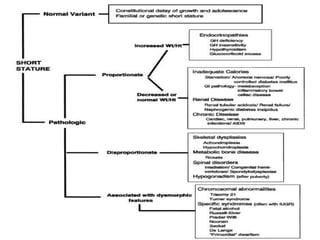
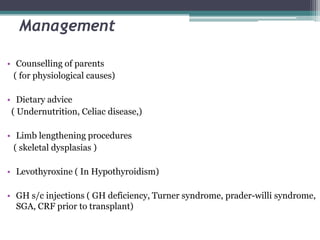
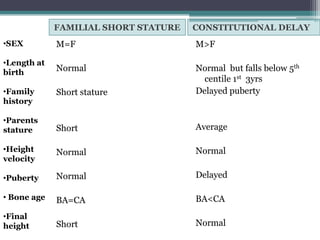
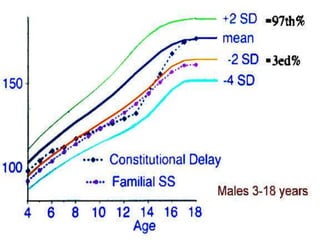
Short stature is defined as height below the 3rd percentile or more than 2 standard deviations below the median height for age and sex. Approximately 3% of children are short, with half having normal variants like familial or constitutional short stature. Investigations include blood tests, bone age, growth hormone stimulation tests, and karyotyping. Management depends on the underlying cause and may include dietary changes, medication like levothyroxine or growth hormone, or surgical procedures. Common causes of proportionate short stature include familial short stature, constitutional delay of growth, and certain genetic or medical conditions.