This document provides an overview of white matter diseases. It discusses:
1. Primary demyelinating diseases like multiple sclerosis and neuromyelitis optica which are characterized by loss of myelin.
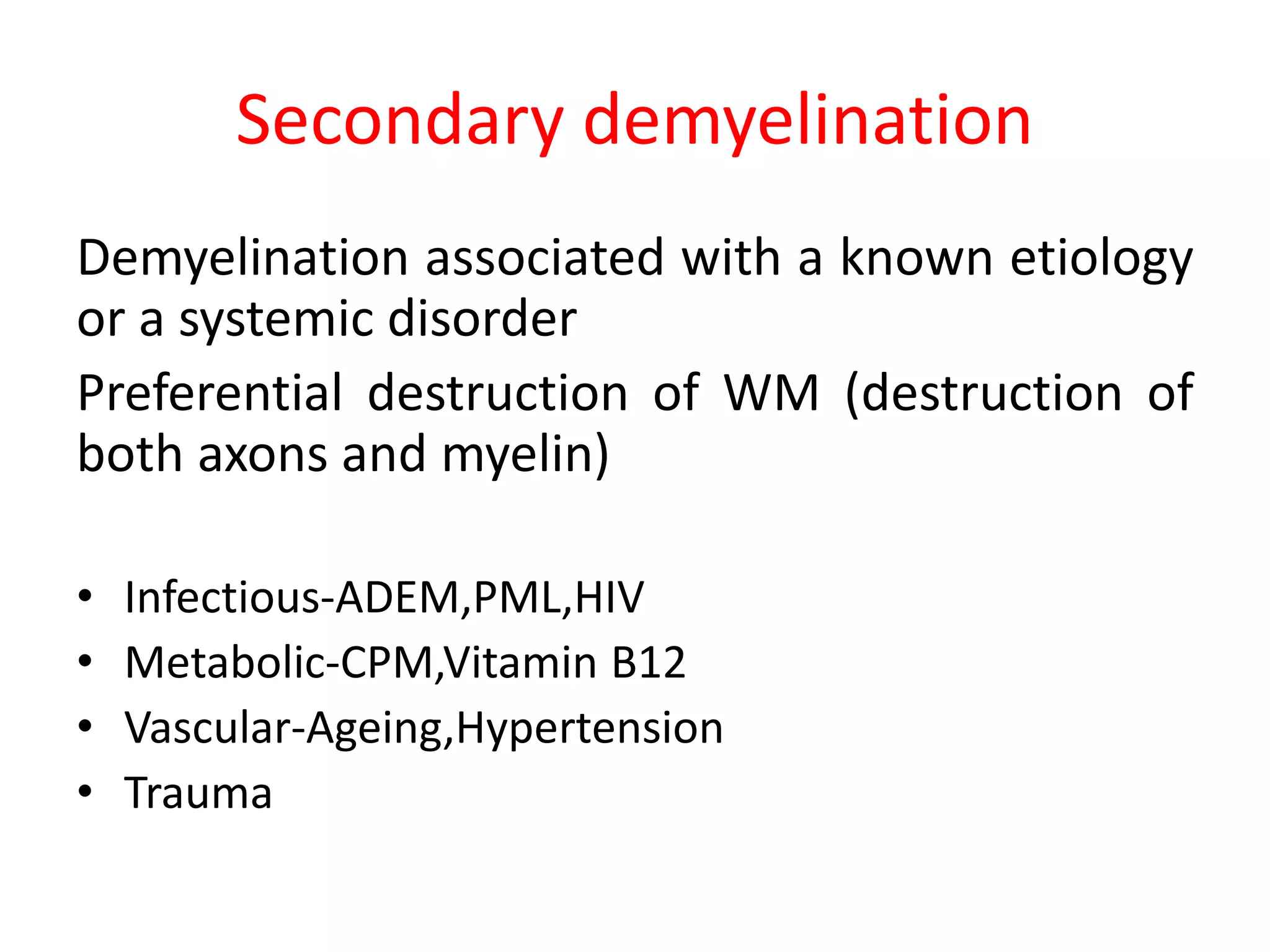
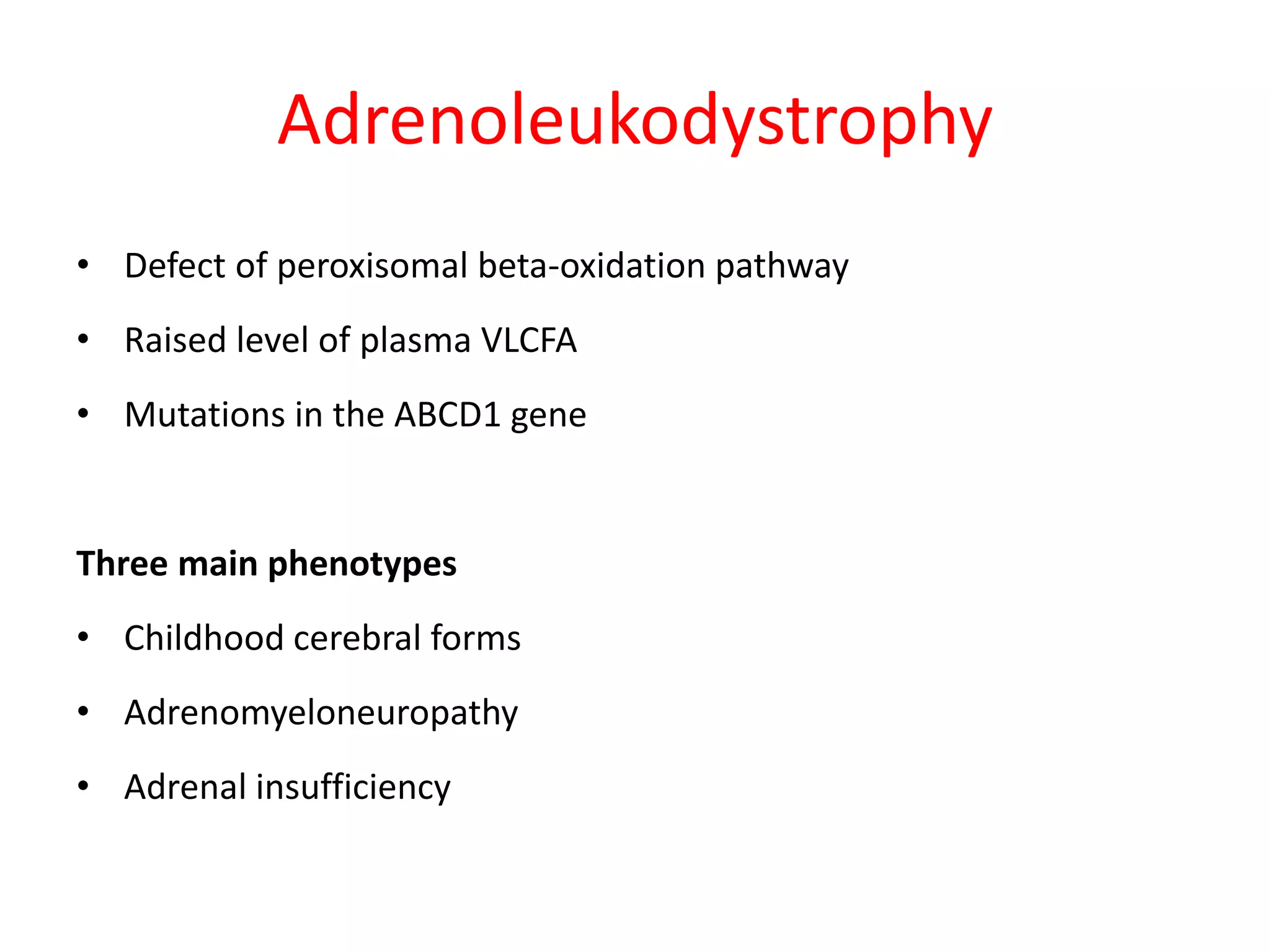
2. Secondary demyelination caused by known etiologies like infections, metabolic disorders, or vascular issues which result in destruction of both axons and myelin.
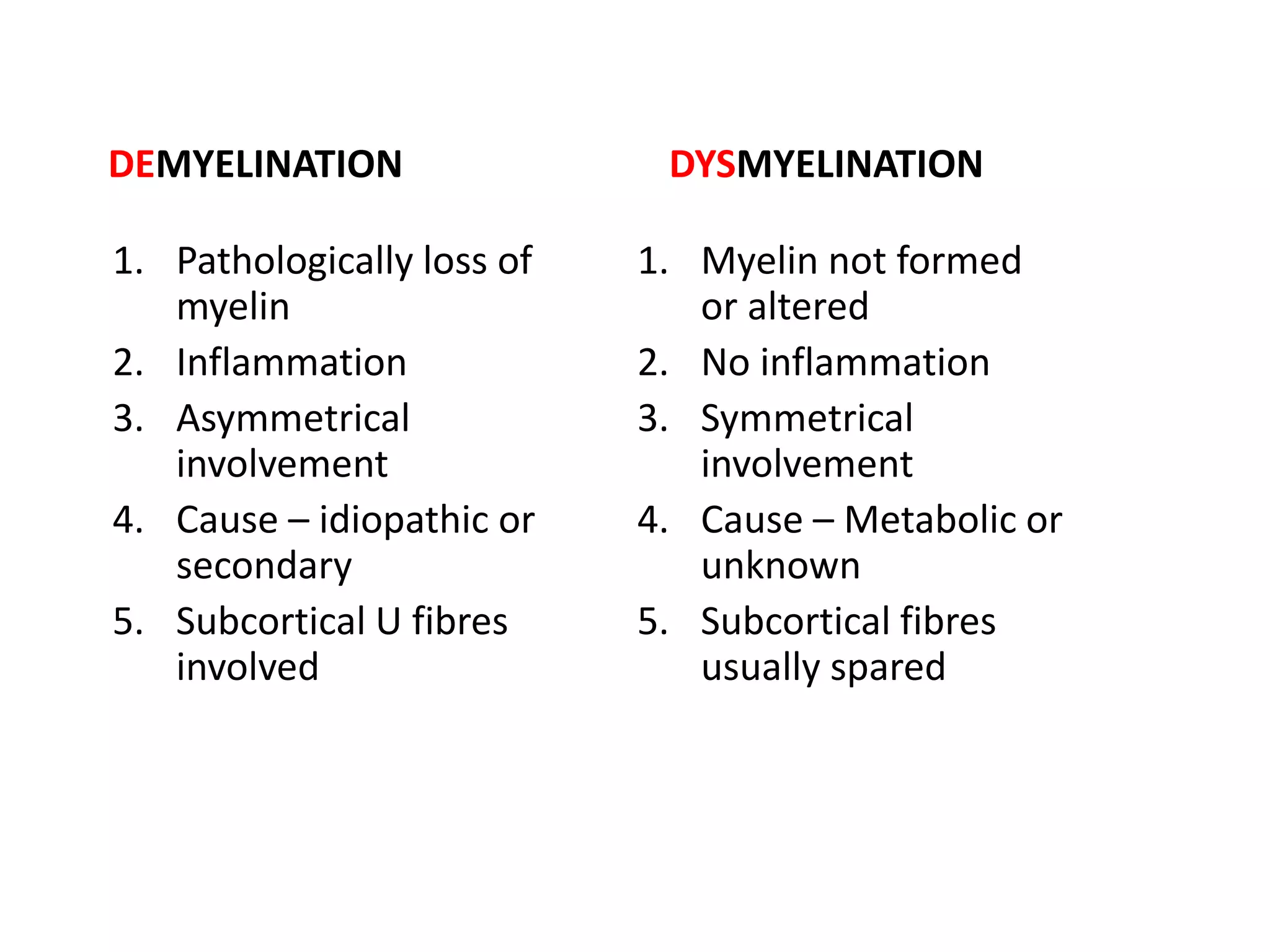
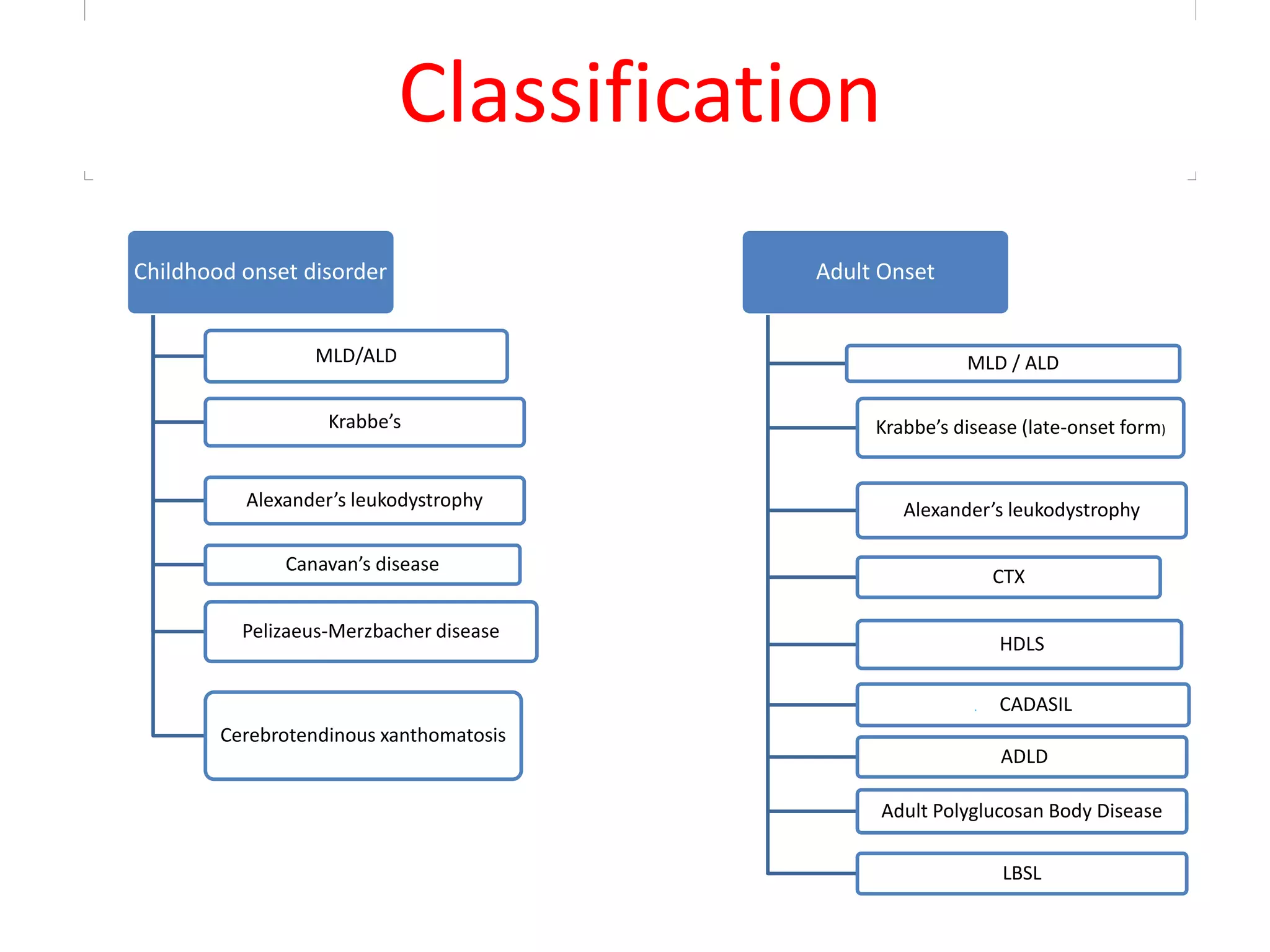
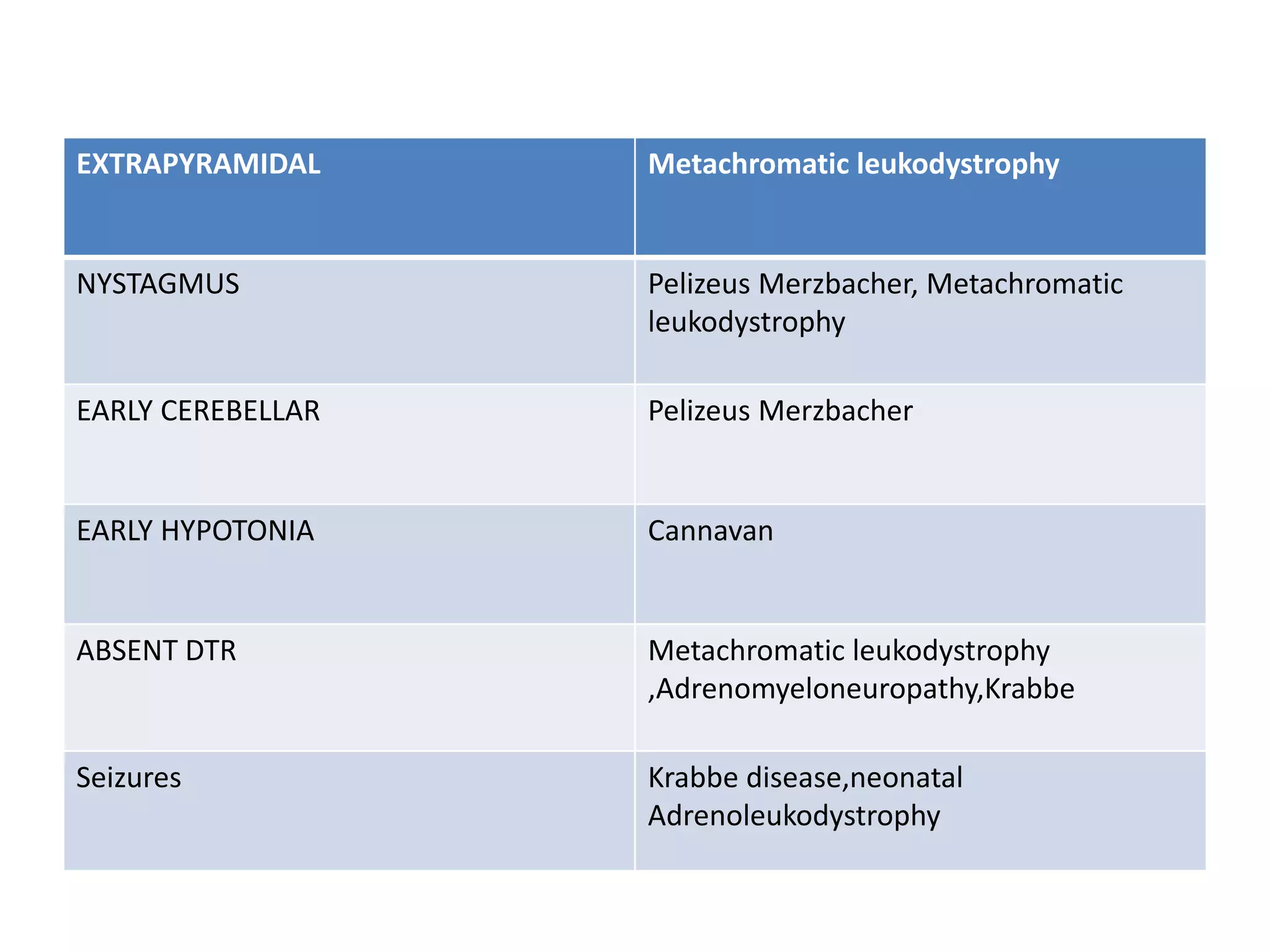
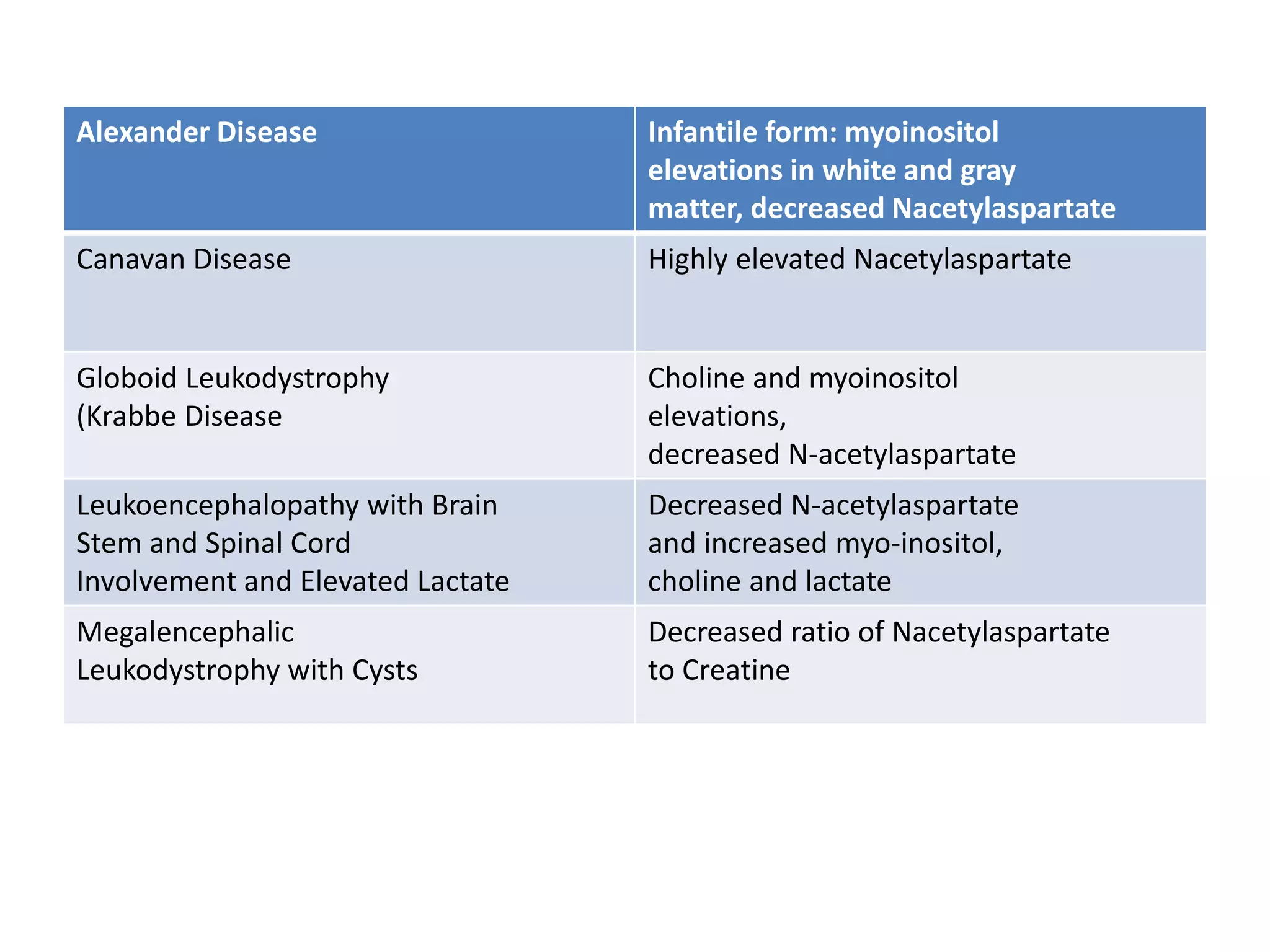
3. Dysmyelinating/hypomyelinating leukodystrophies which involve defective or incomplete myelin formation, including some common causes like metachromatic leukodystrophy.
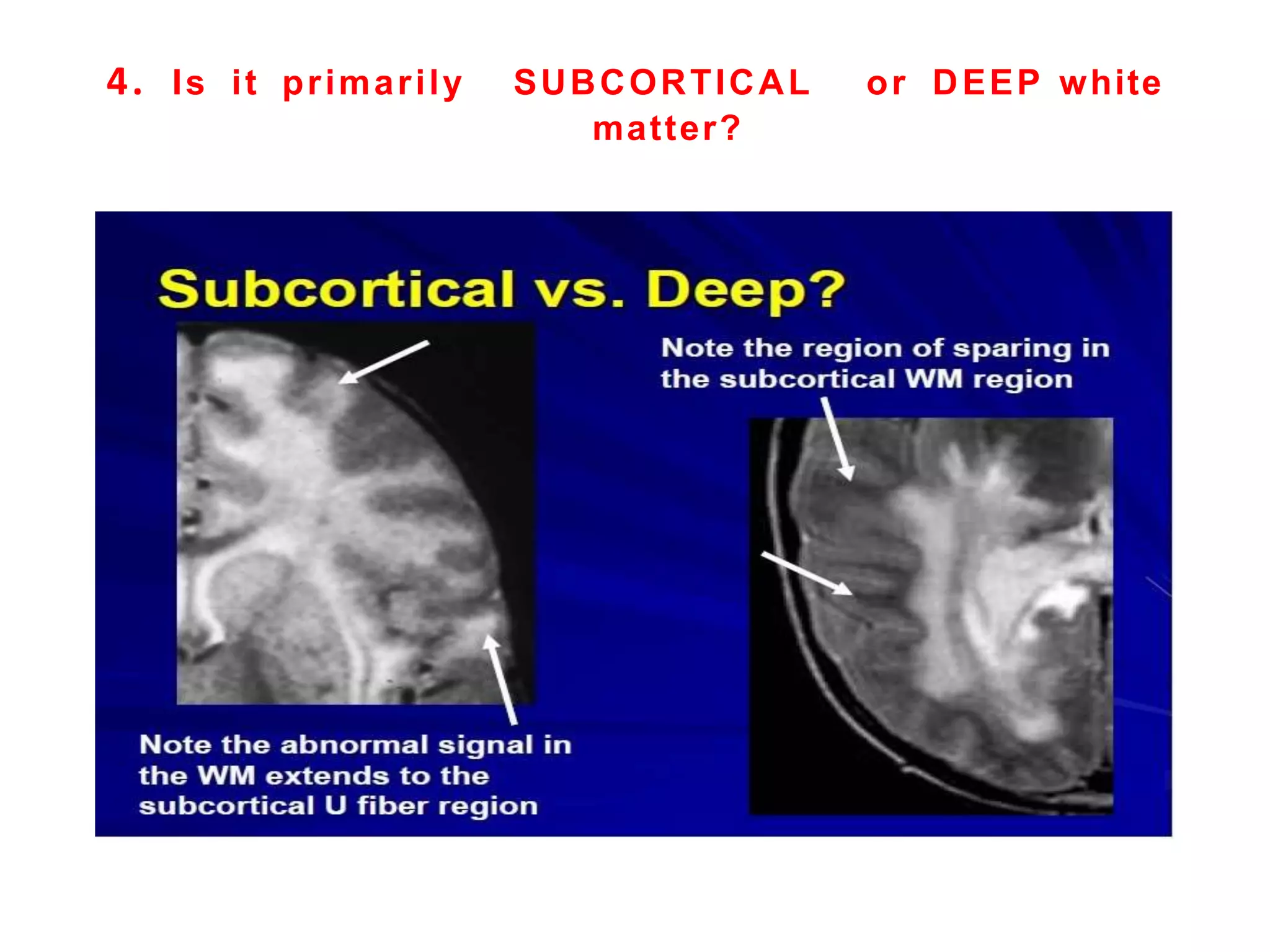
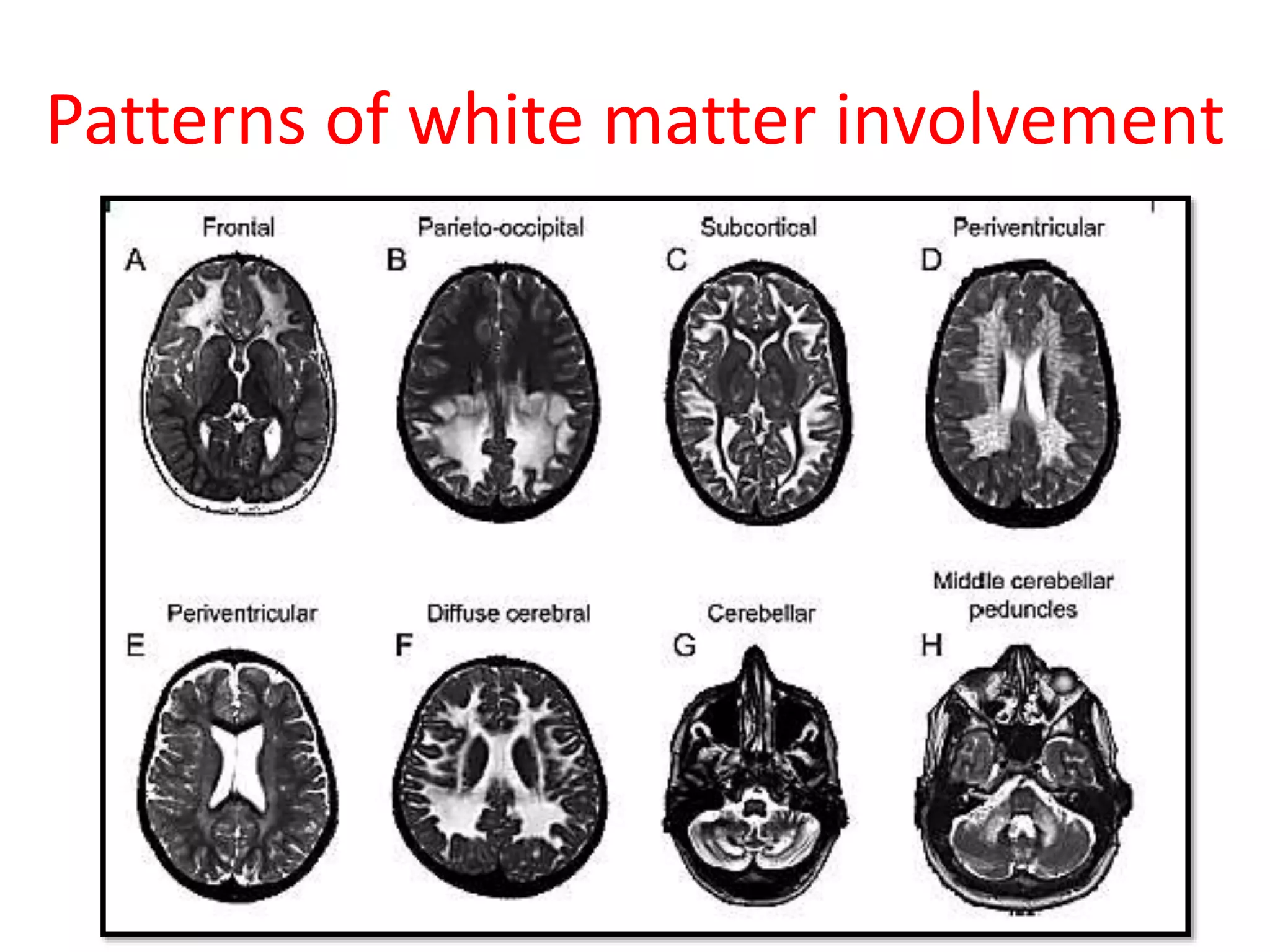
4. The clinical approach involves considering features like onset, progression, family history, involvement of other organs, and patterns