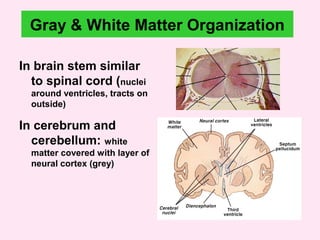
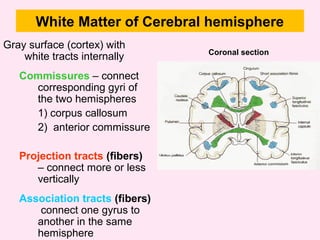
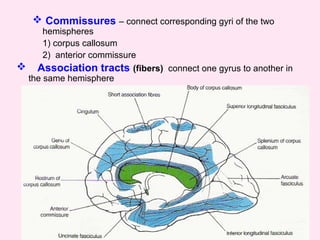
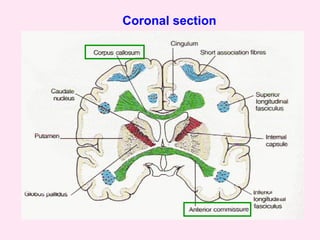
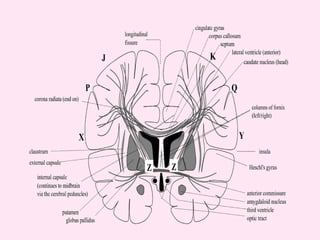
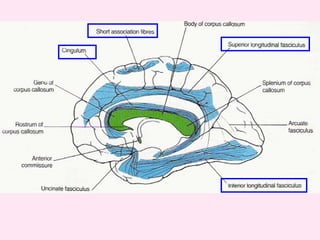
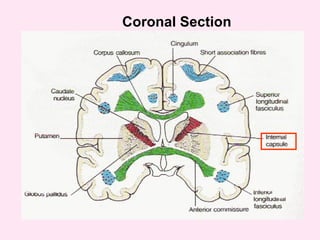
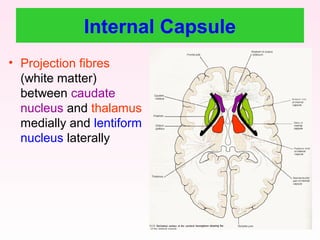
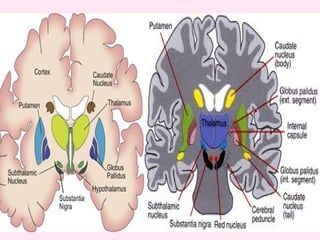
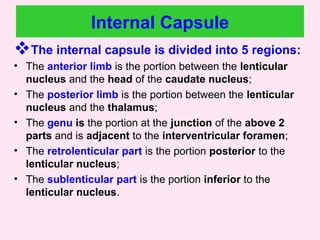
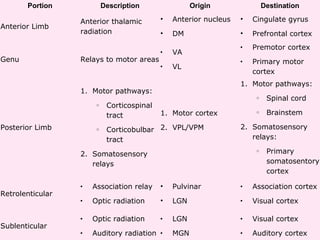
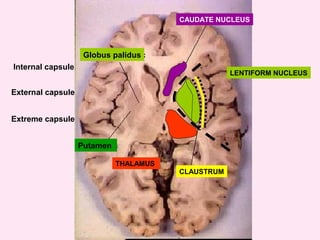
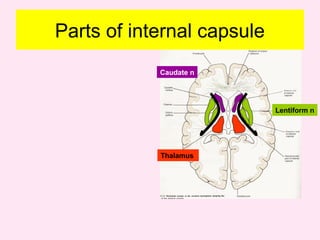
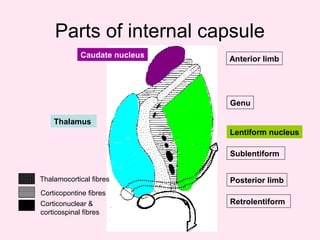
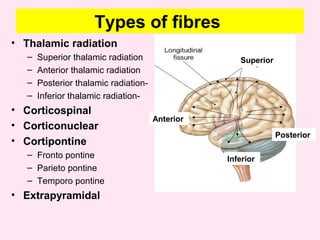
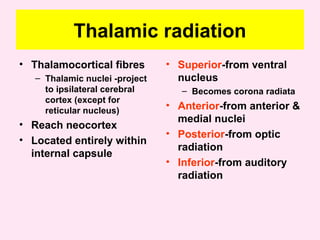
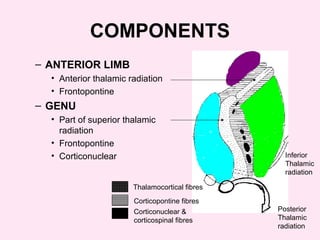
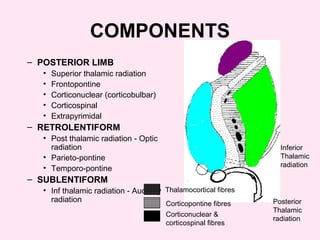
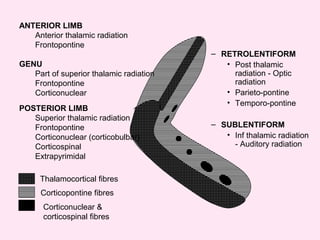
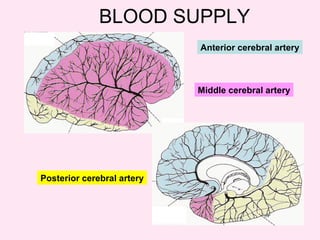
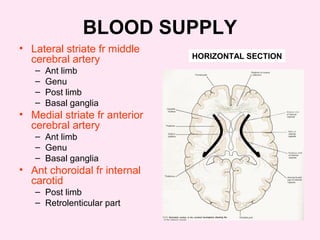
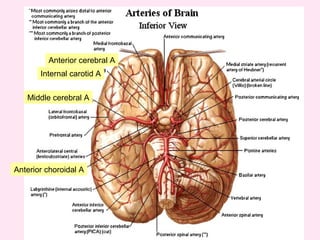
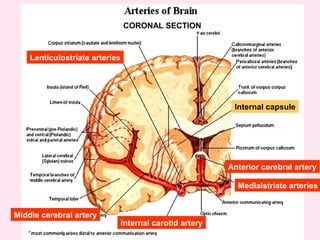
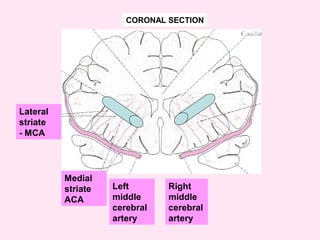
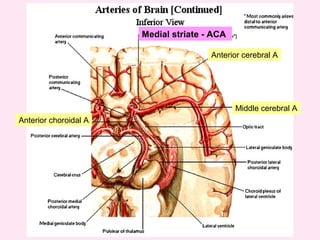
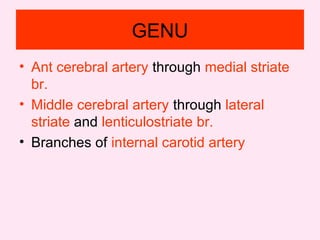
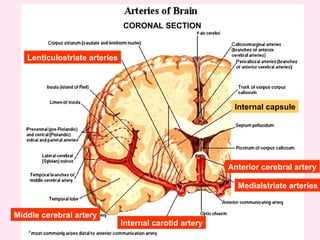
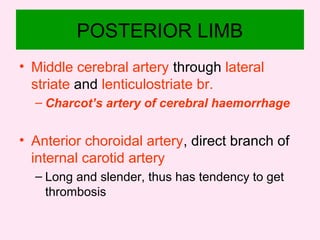
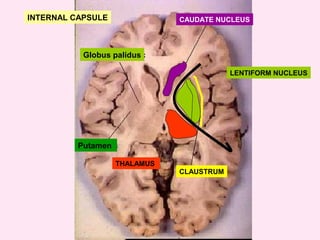
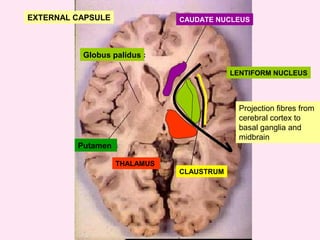
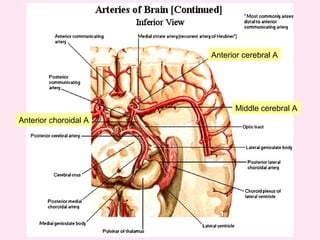
The internal capsule is a central white matter structure that contains important projection fibers connecting the cerebral cortex with deep gray matter structures. It is divided into the anterior limb, genu, posterior limb, retrolenticular and sublenticular parts. The internal capsule receives its blood supply from the middle cerebral artery, anterior cerebral artery, and anterior choroidal artery. Strokes or lesions involving the internal capsule can cause motor or sensory deficits depending on the fibers affected.