This document discusses water and electrolyte balance in the human body. It covers several key points:
1) Water is the most abundant component of the body, accounting for 60-70% of total body weight in adults. Humans can survive one month without food but only about a week without water.
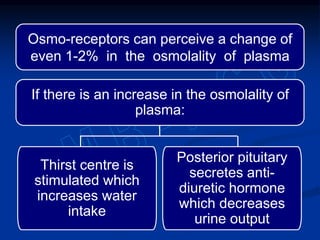
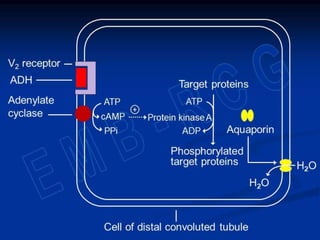
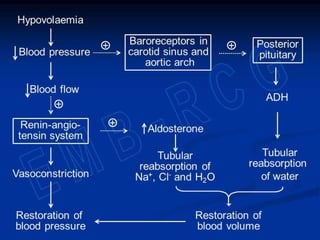
2) Water content varies between tissues and changes with age. It is regulated to maintain homeostasis through thirst, antidiuretic hormone secretion, and kidney function.
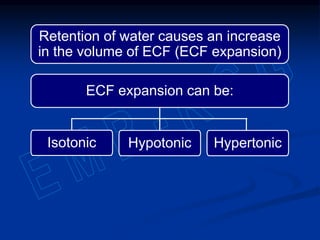
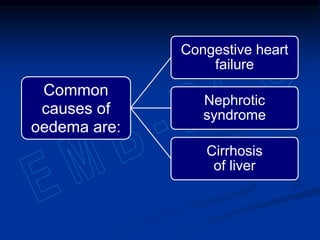
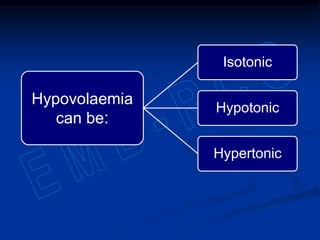
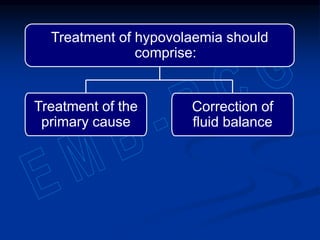
3) Sodium, potassium, and chloride are the major electrolytes and their plasma levels are tightly controlled. Imbalances can cause dehydration or water retention.
4) Diuretics are sometimes used to treat water