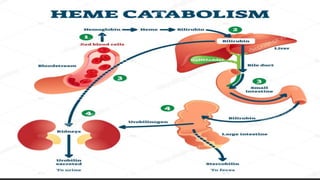
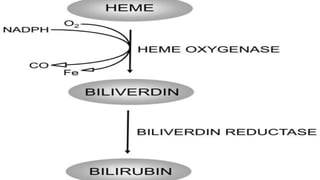
The document outlines the heme degradation pathway and the metabolism of bilirubin following the breakdown of red blood cells, primarily occurring in the liver, spleen, and bone marrow. It details how bilirubin is produced, conjugated, and excreted, as well as the conditions leading to different types of jaundice, including hemolytic, hepatic, and obstructive jaundice. It also discusses the causes and metabolic abnormalities associated with elevated bilirubin levels and their effects on the body.