The document discusses three important electrolytes: sodium, potassium, and chloride.
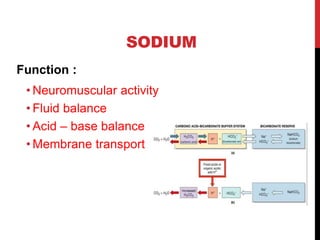
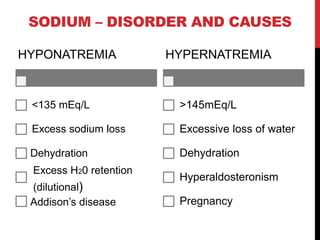
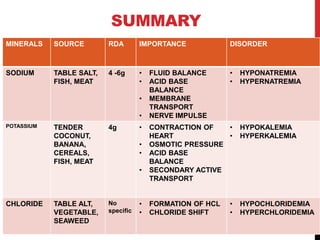
Sodium is obtained mainly from table salt, fish, and meat. Its daily requirement is 4-6g and it is important for fluid balance, nerve impulse conduction, and acid-base balance. Disorders include hyponatremia and hypernatremia.
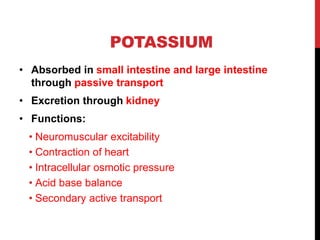
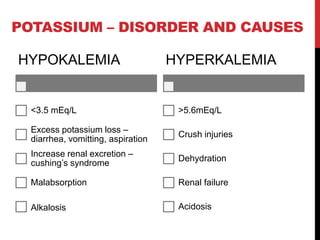
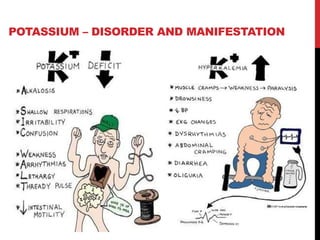
Potassium is obtained from foods like bananas, cereals, and fish. Its daily requirement is 4g and it is crucial for heart contraction, intracellular pressure, and acid-base balance. Disorders are hypokalemia and hyperkalemia.
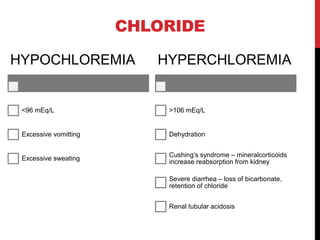
Chloride does not have a set daily requirement as its main source is sodium. It is important for