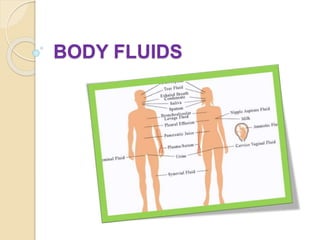
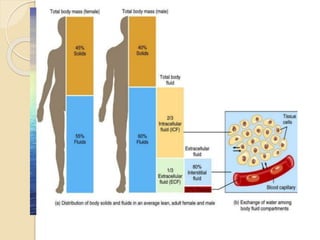
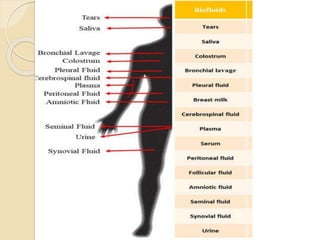
Body fluids make up over two-thirds of the human body, with water being the primary component. Body fluids are distributed between two compartments - extracellular fluid (ECF) and intracellular fluid (ICF). The concentration of body fluids is expressed in terms of osmolality, osmolarity, and tonicity. Isotonic fluids have the same concentration as body fluids, while hypertonic fluids are more concentrated and hypotonic fluids are less concentrated. The body maintains water balance through various mechanisms to prevent dehydration or water intoxication.