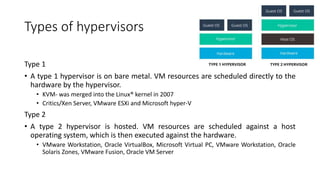
A virtual machine (VM) uses software to run programs and deploy apps instead of using physical computer hardware. Multiple VMs can run on a single physical host machine. Each VM runs its own operating system separately from other VMs. VMs provide benefits like cost savings, agility, scalability, and security by isolating applications. However, VMs can also result in slower performance compared to physical machines. A hypervisor manages interactions between the physical hardware and VMs, enabling virtualization. There are two main types of hypervisors - type 1 runs directly on the hardware while type 2 runs within a host operating system.