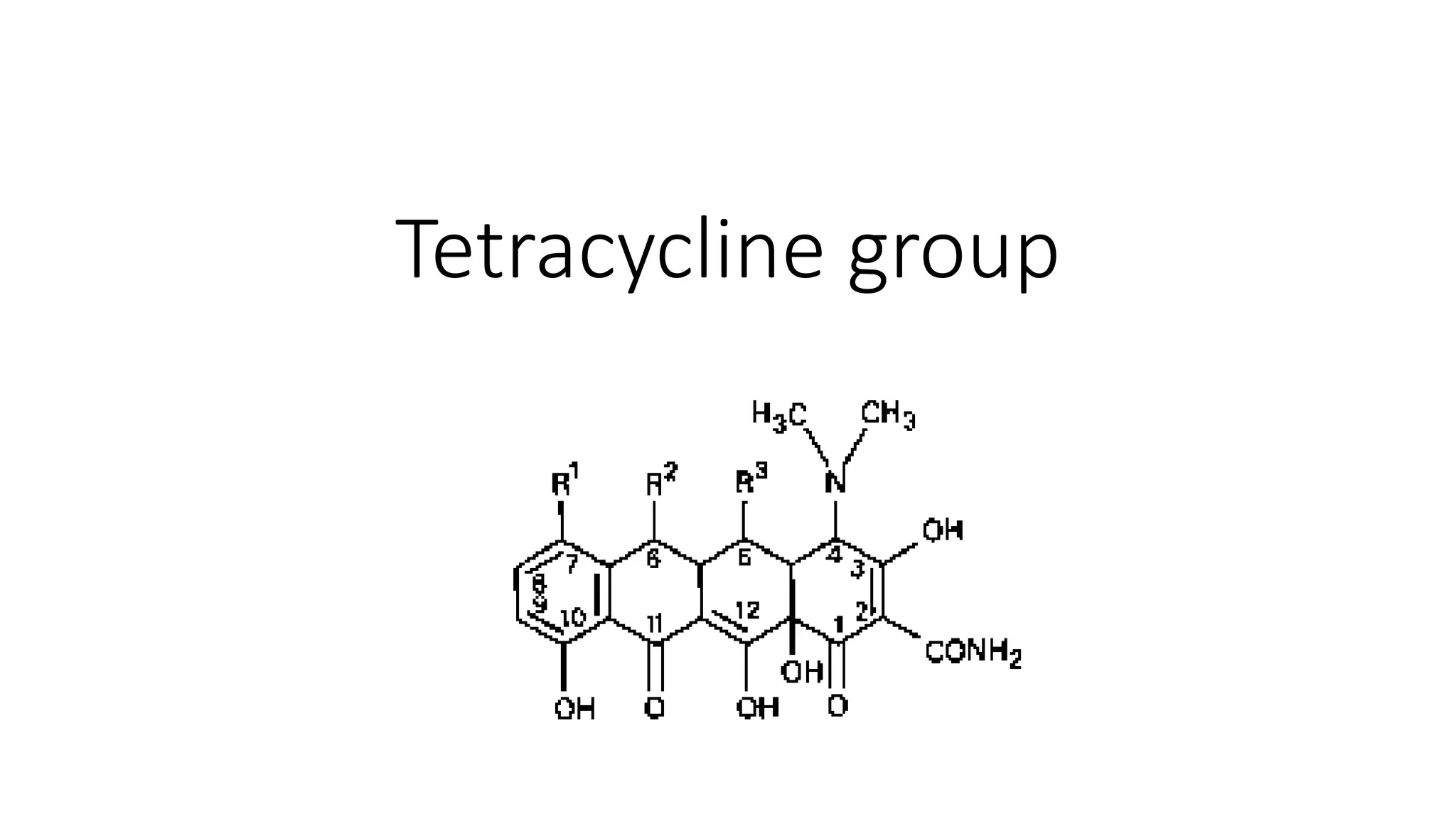
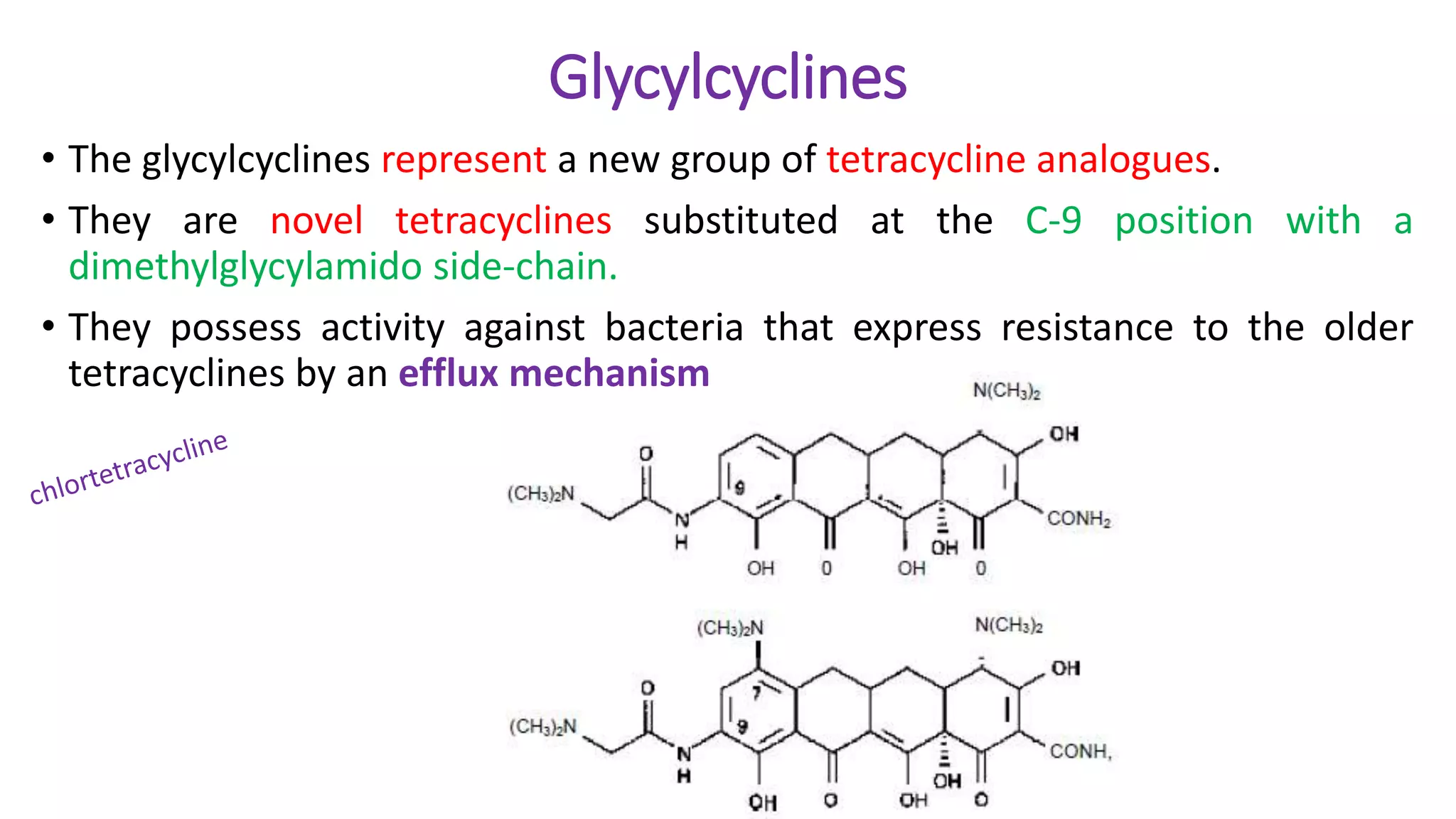
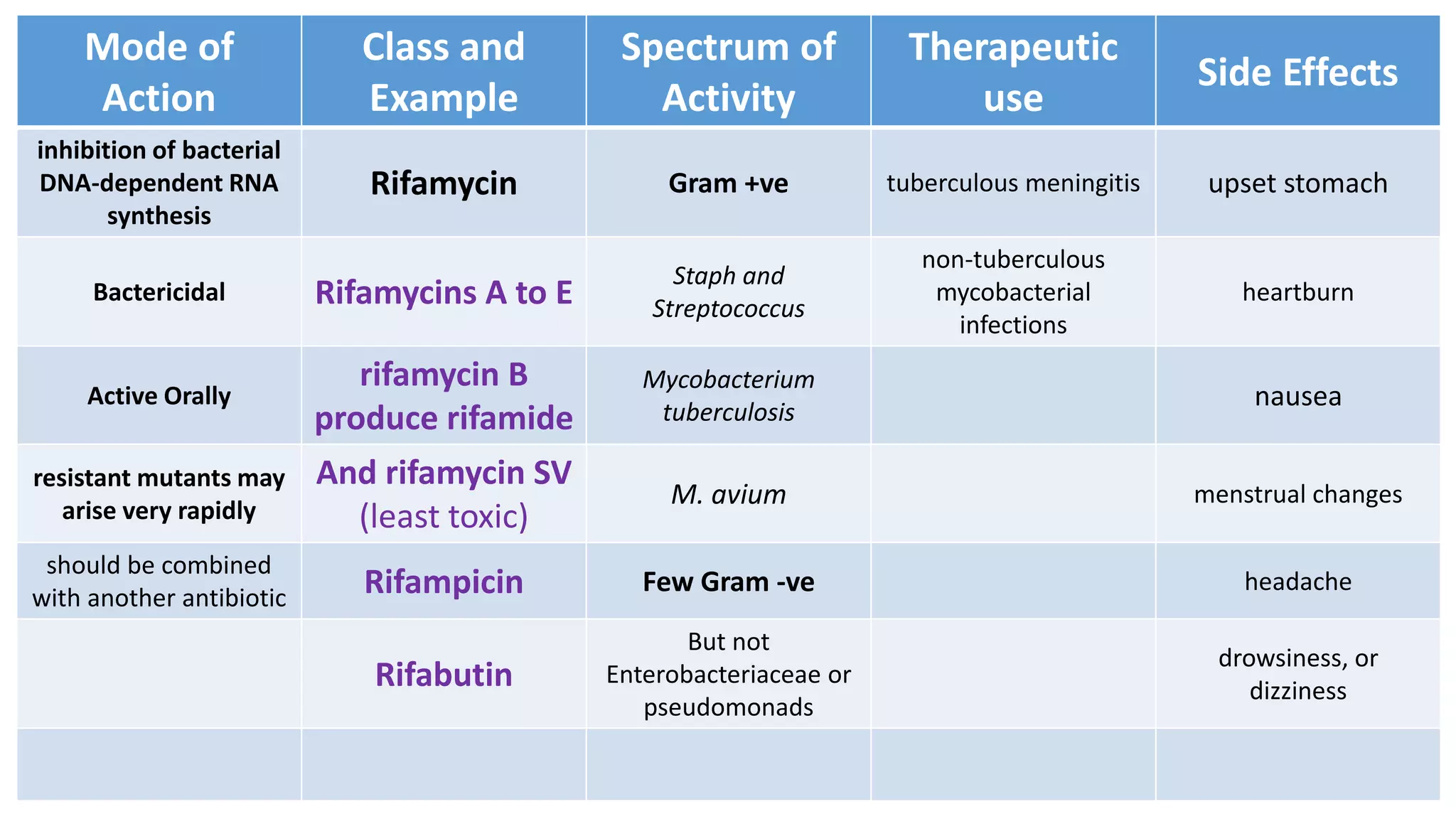
Tetracycline group antibiotics are obtained from Streptomyces bacteria. They inhibit bacterial protein synthesis by binding to the 30S ribosomal subunit. Examples include tetracycline, minocycline, and doxycycline. They are used to treat infections caused by gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria but resistance has developed. Side effects include nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity.
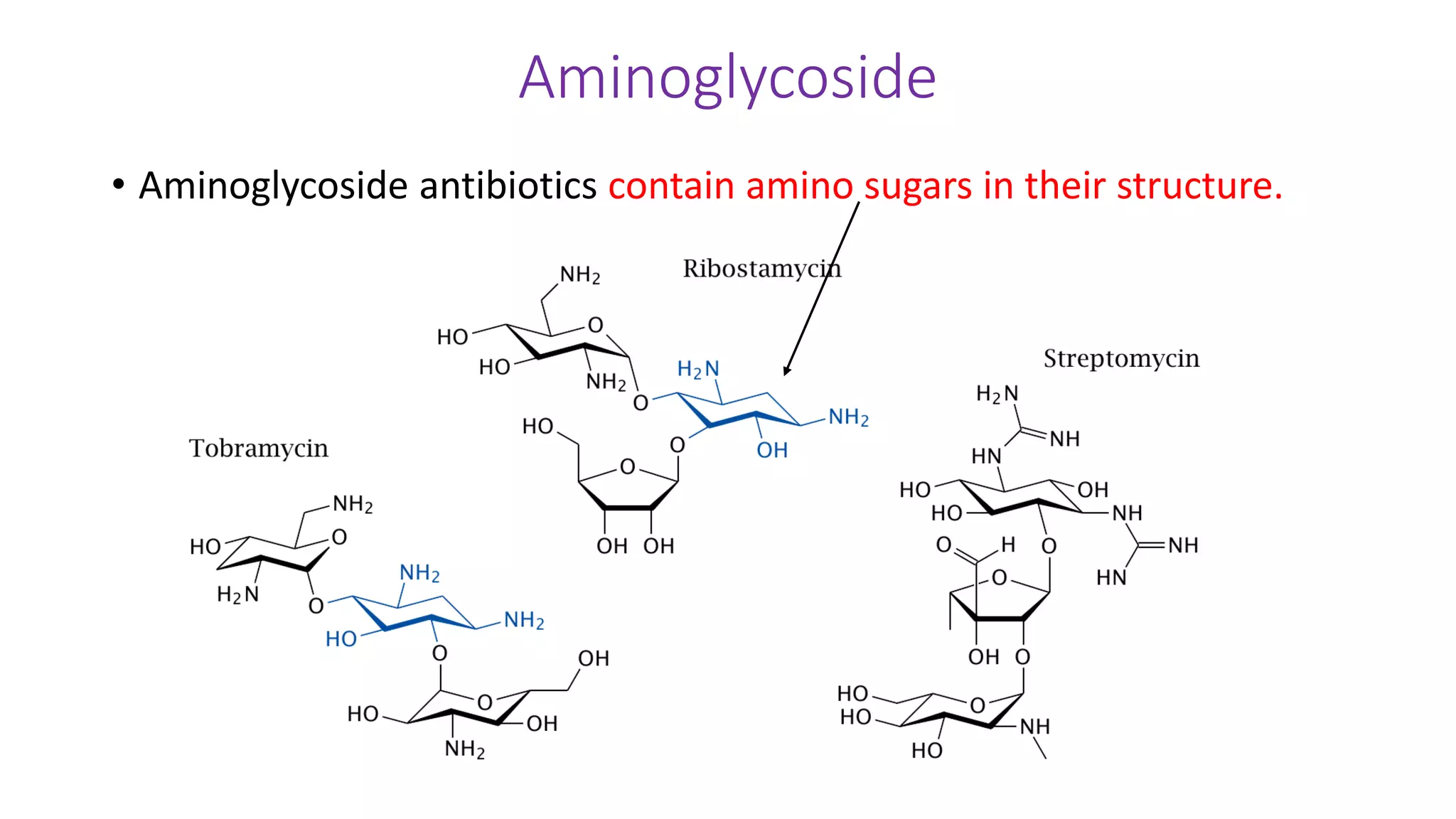
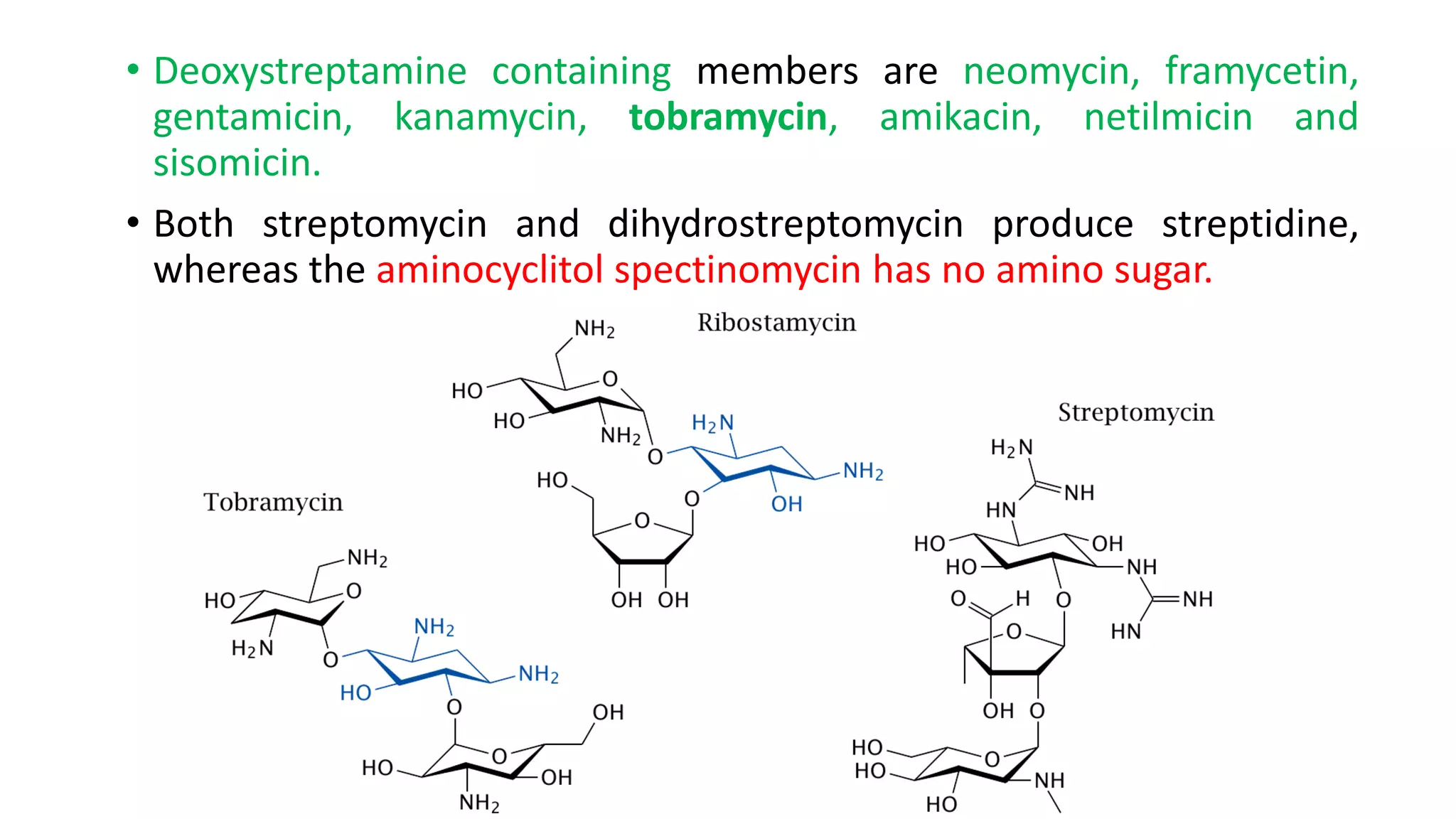
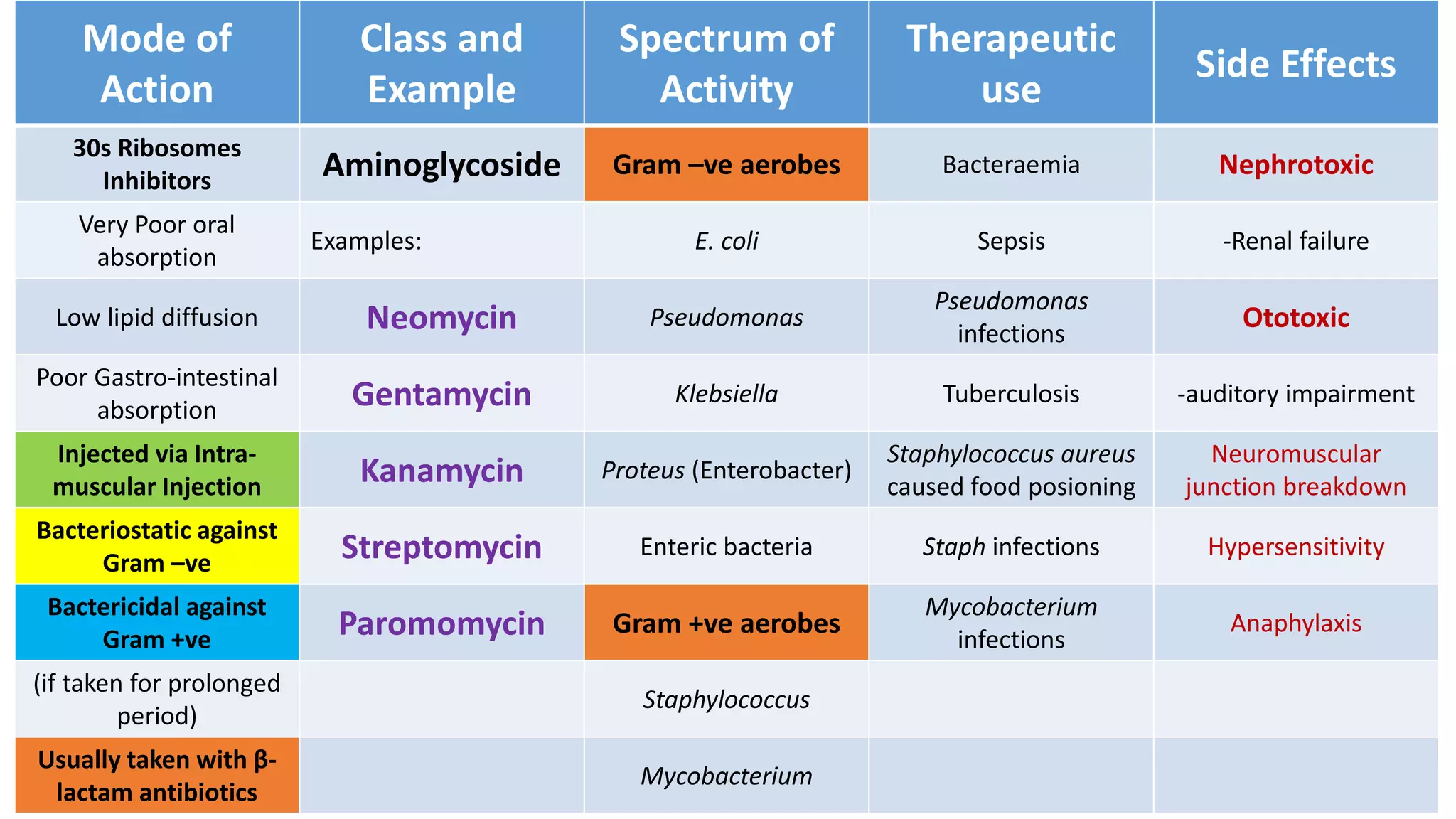
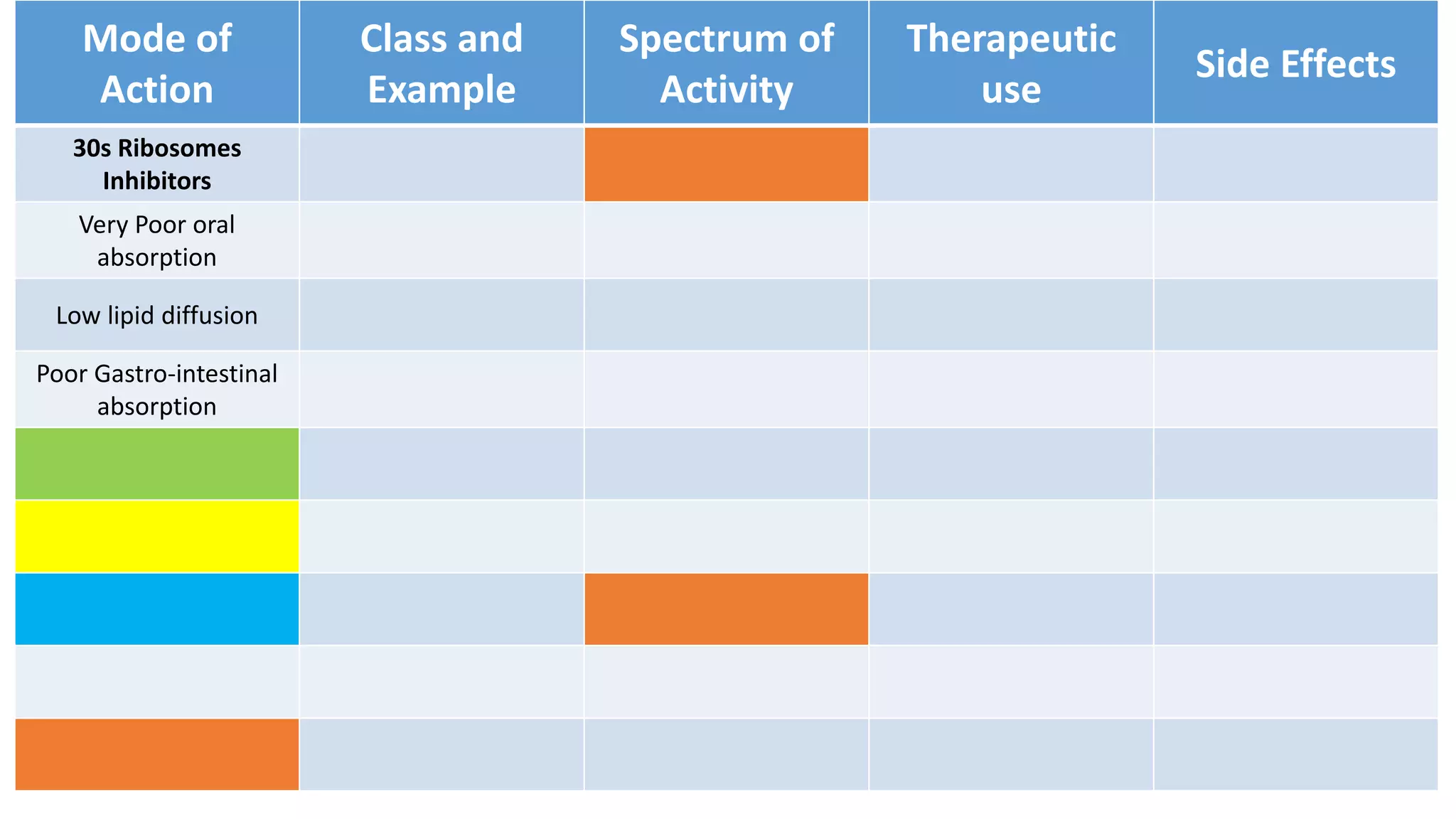
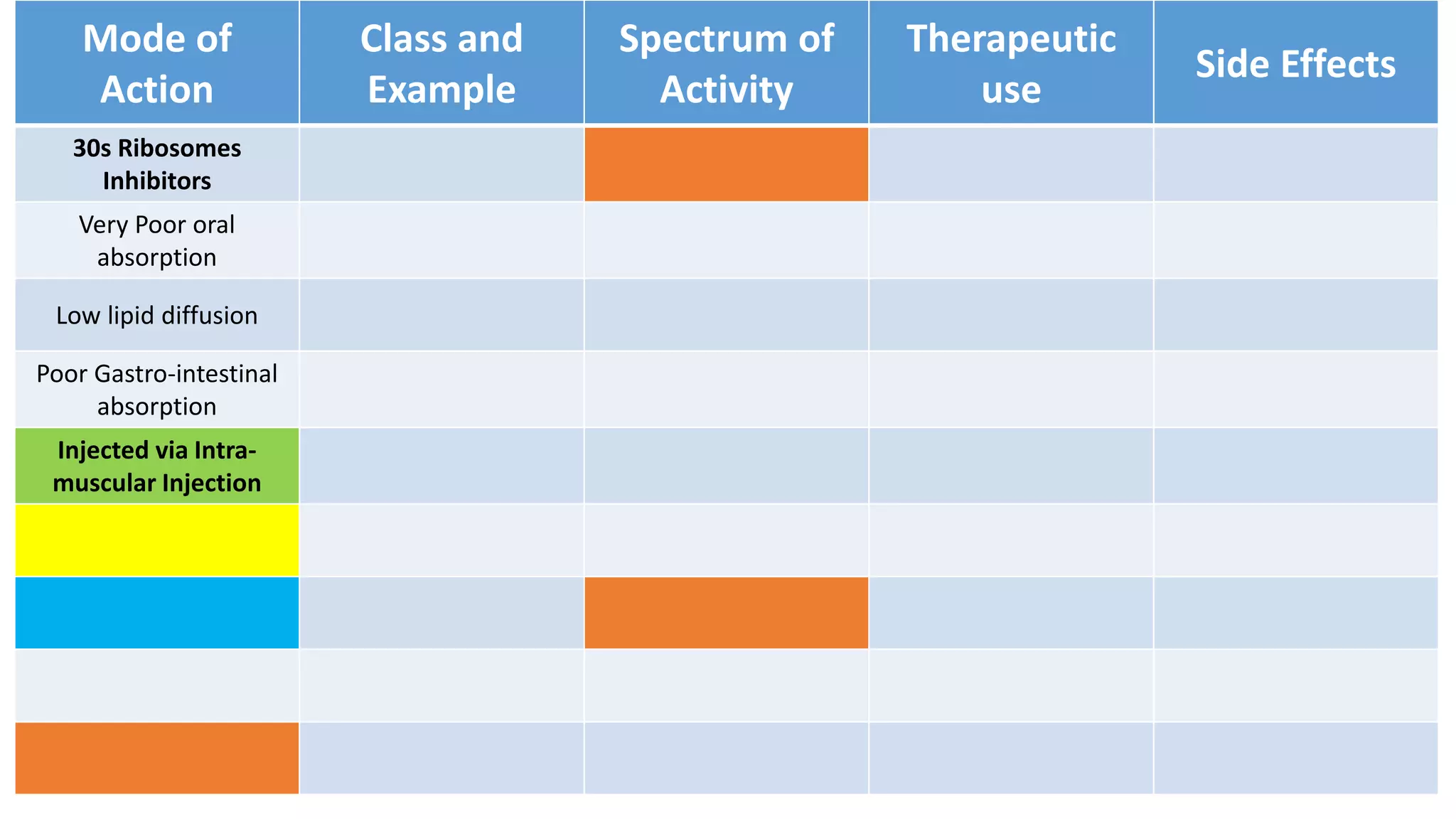
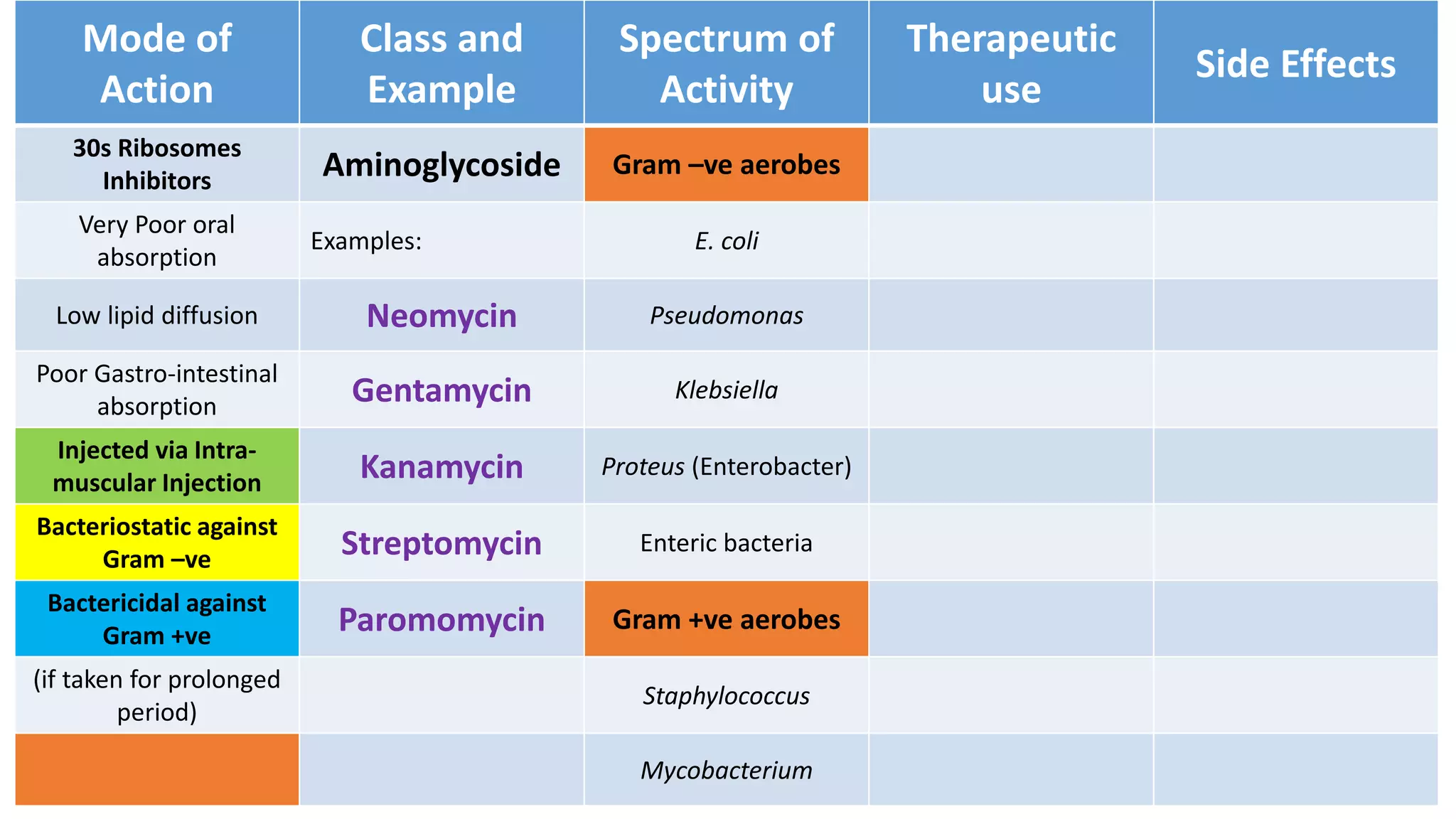
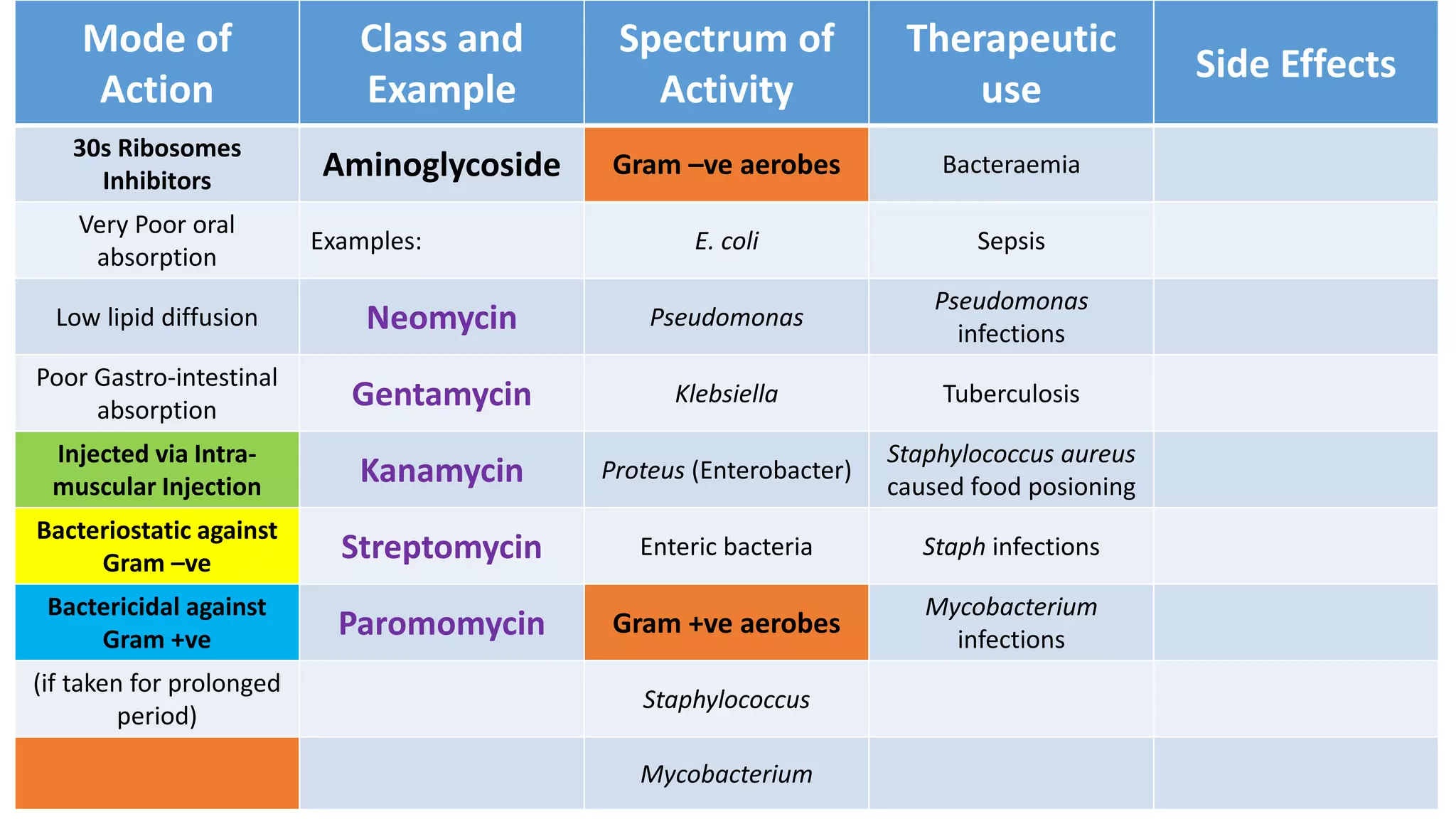
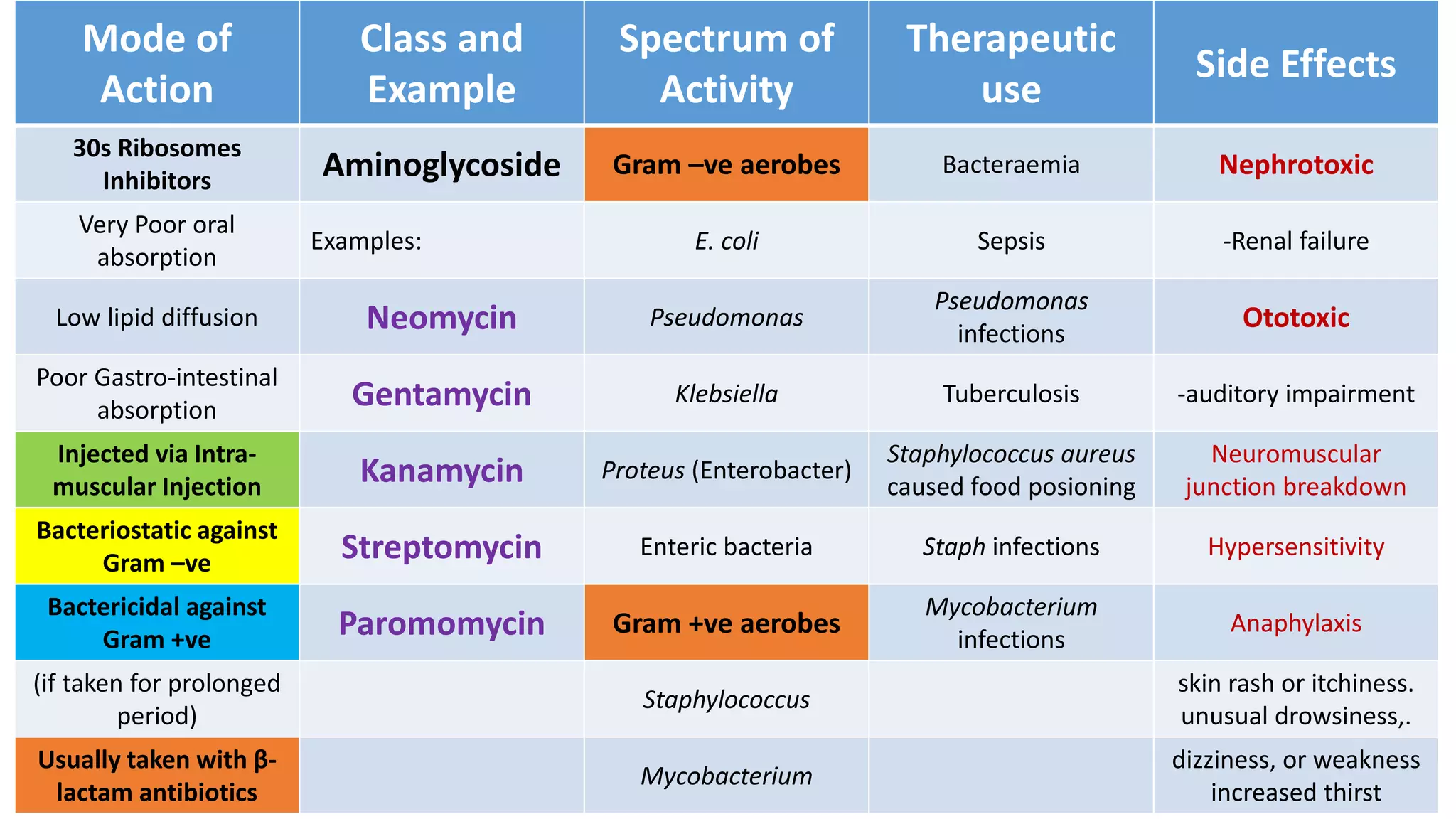
Aminoglycosides like streptomycin and gentamicin are poorly absorbed orally and injected intramuscularly. They inhibit bacterial protein synthesis by binding to the 30S ribosomal subunit. Used for serious gram-negative infections but are nephrotoxic and ototoxic. Resistance develops slowly when combined with other antibiotics