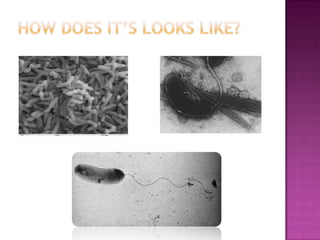
Vibrio cholerae is a gram-negative, curved rod-shaped bacteria that is the cause of the disease cholera. It is found in fresh and brackish water throughout the world. There are three pathogenic strains that cause disease in humans. Cholera is transmitted through ingesting contaminated food or water and causes acute, watery diarrhea that can lead to severe dehydration and death if untreated. Diagnosis involves culturing the bacteria from stool samples and identifying its unique biochemical characteristics.