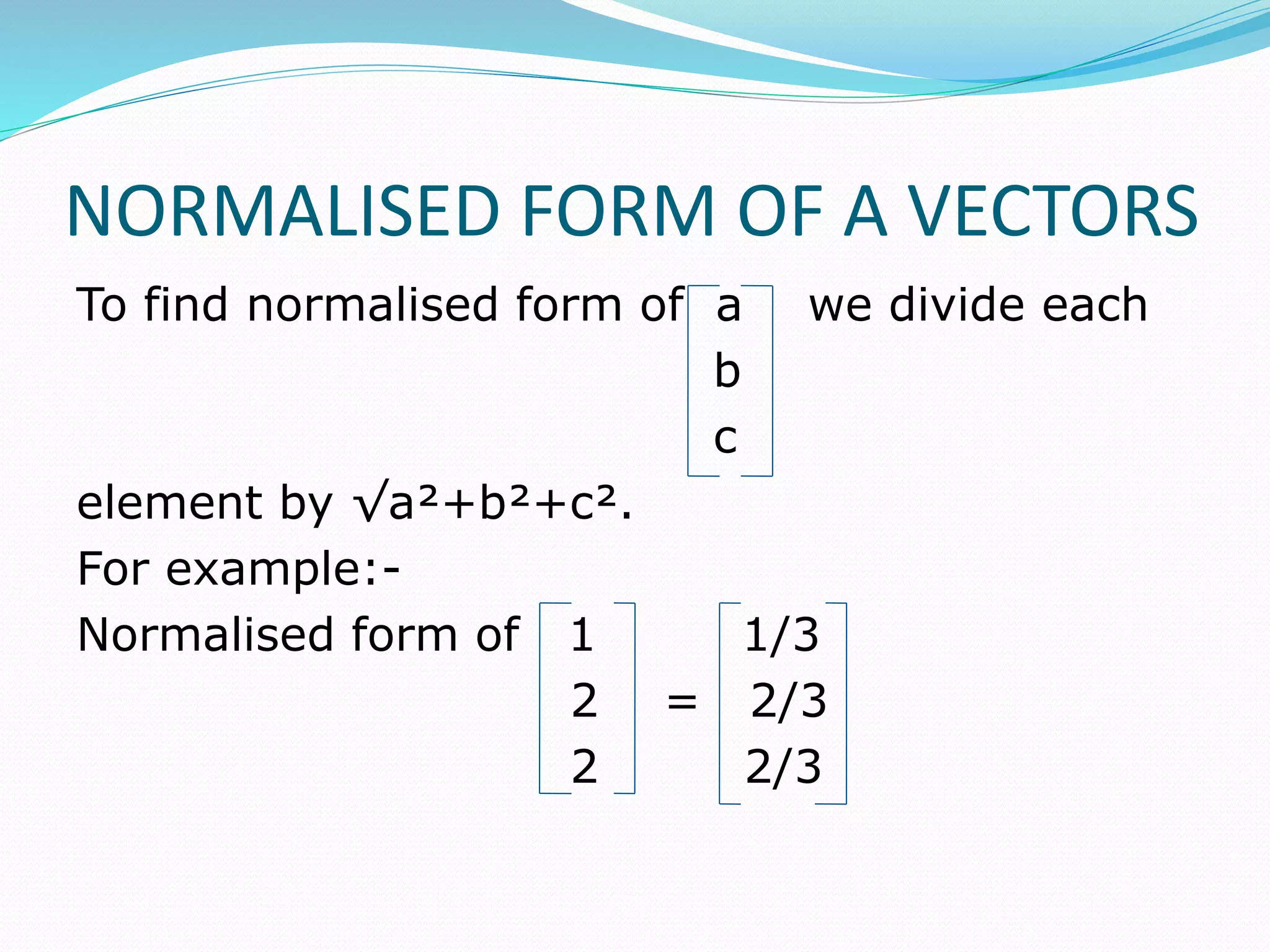
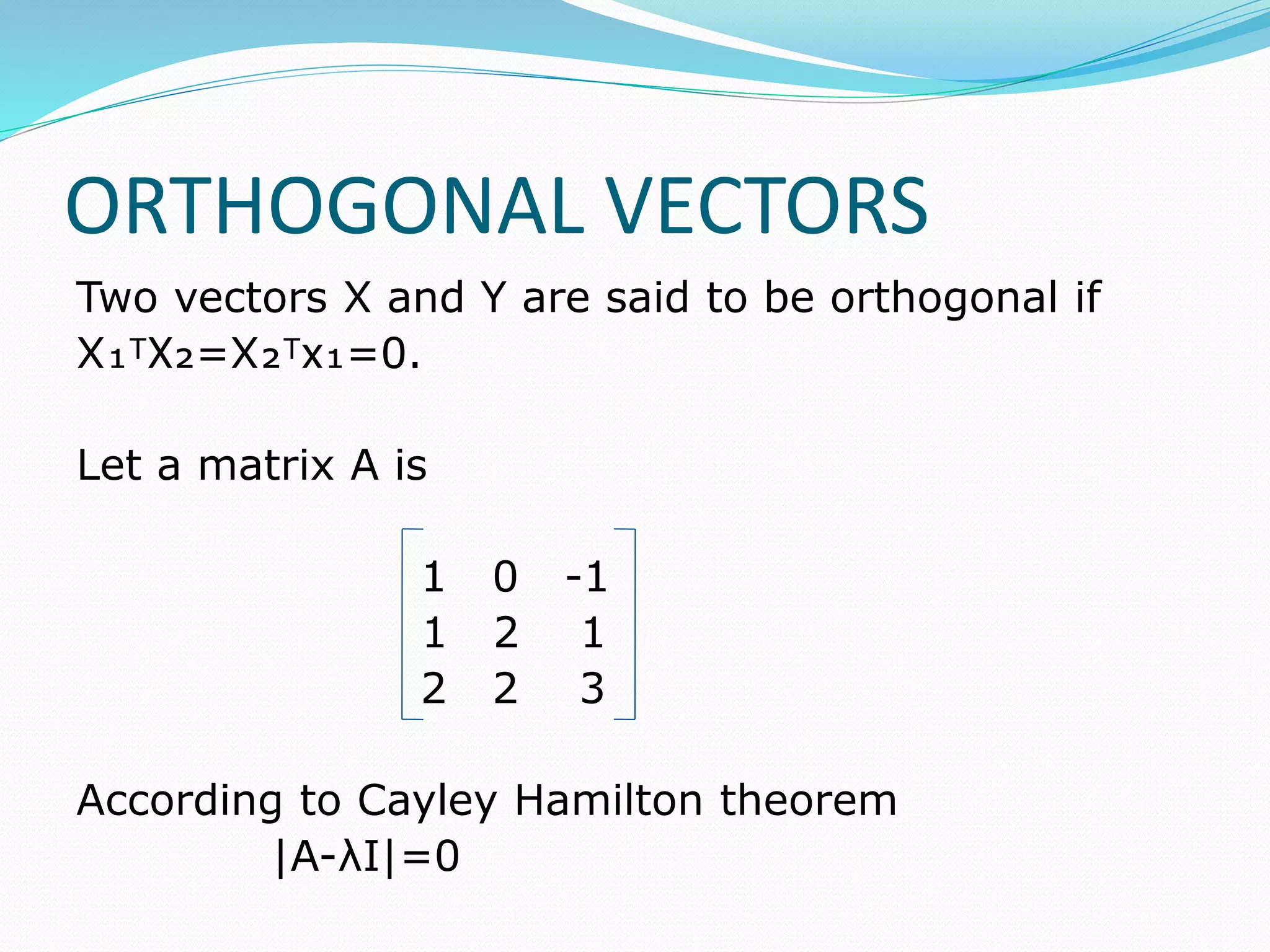
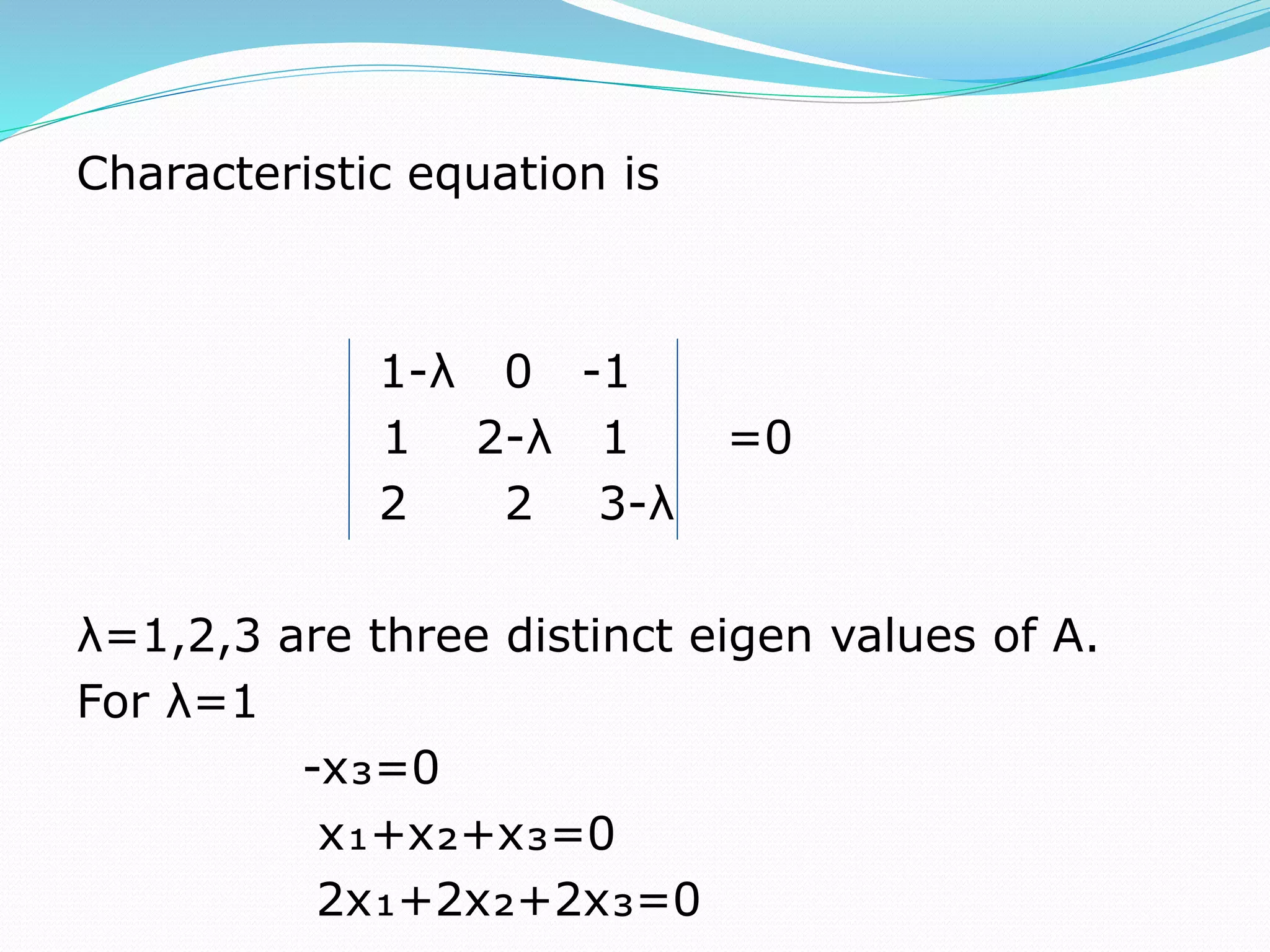
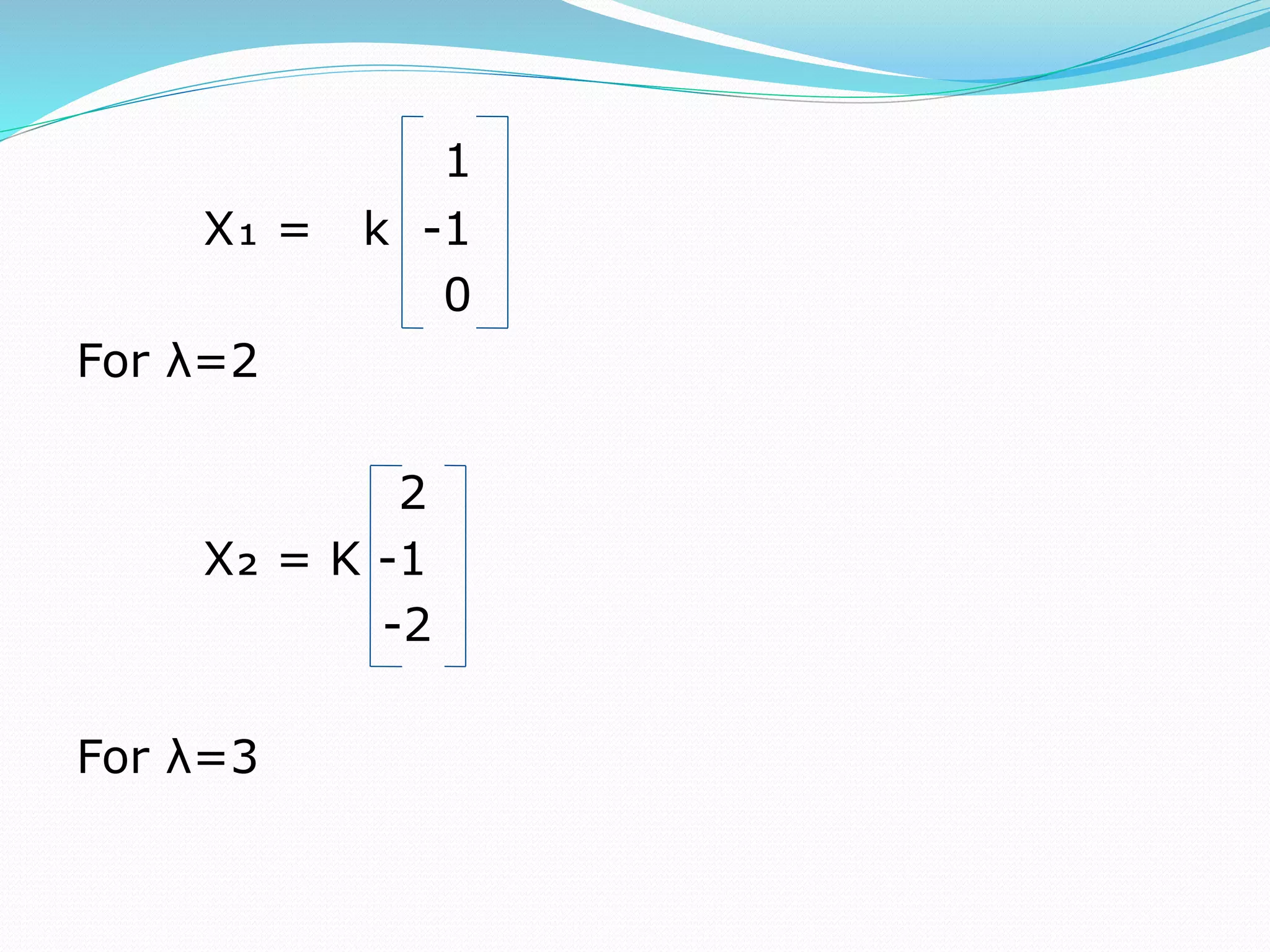
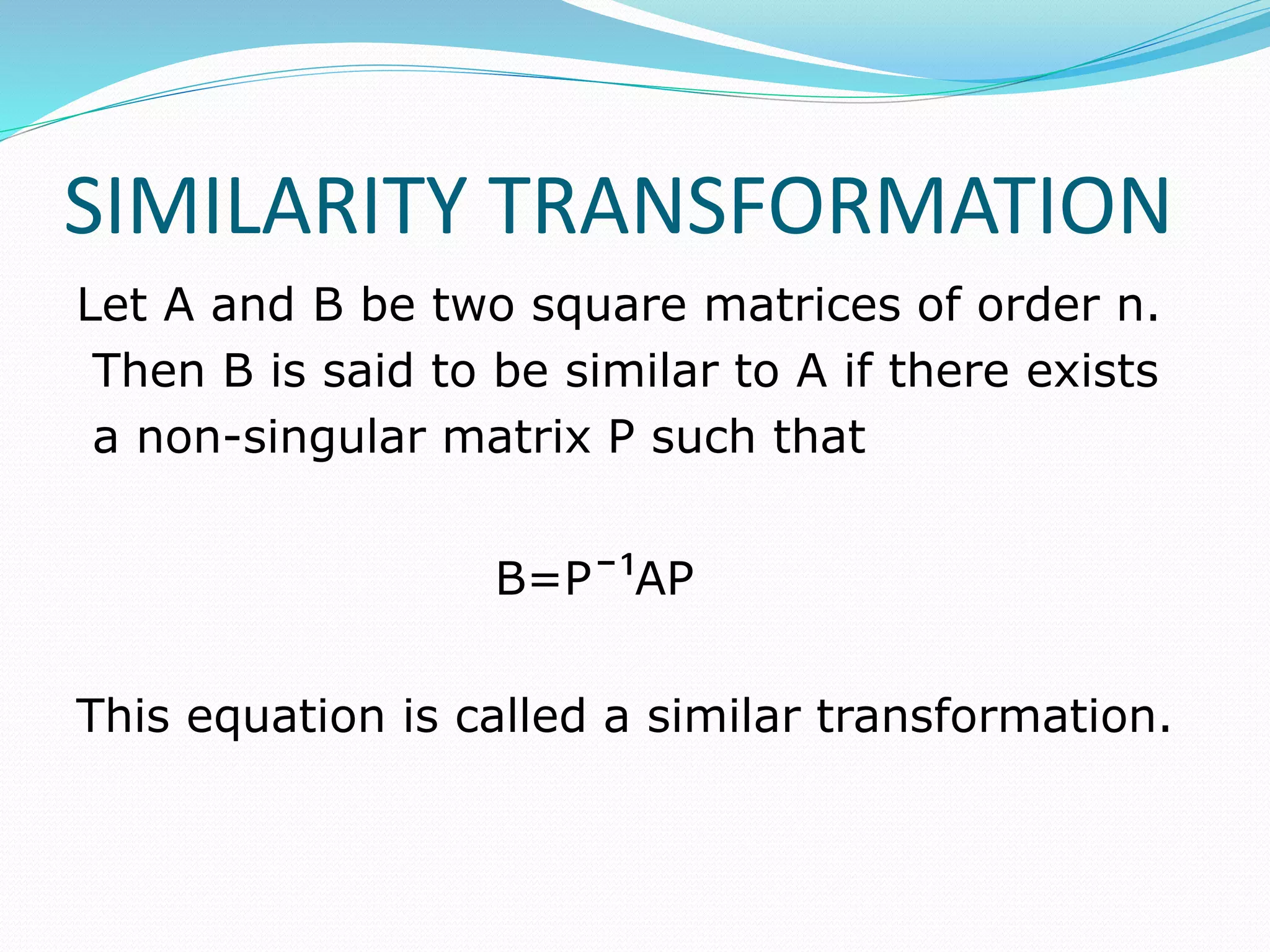
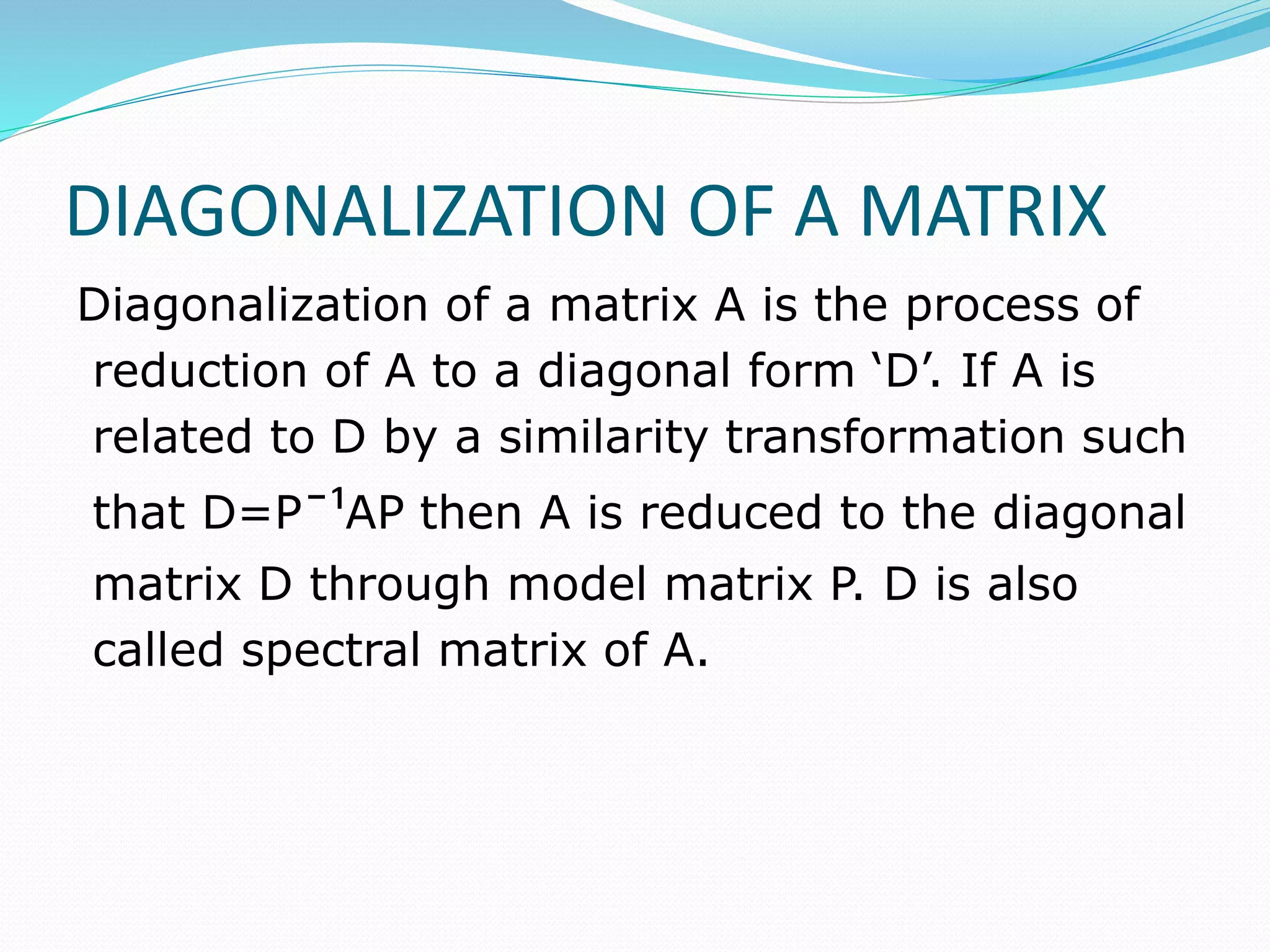
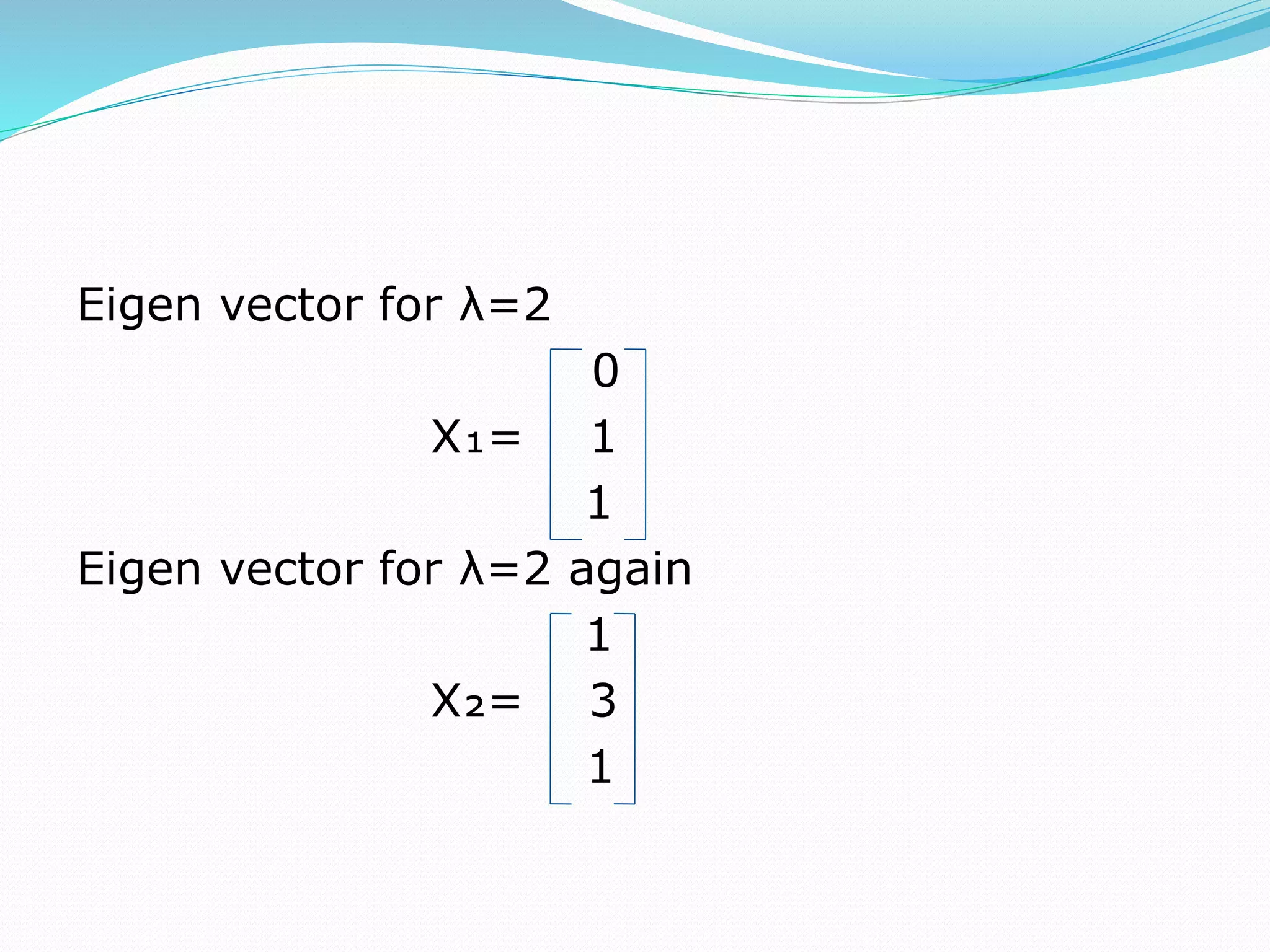
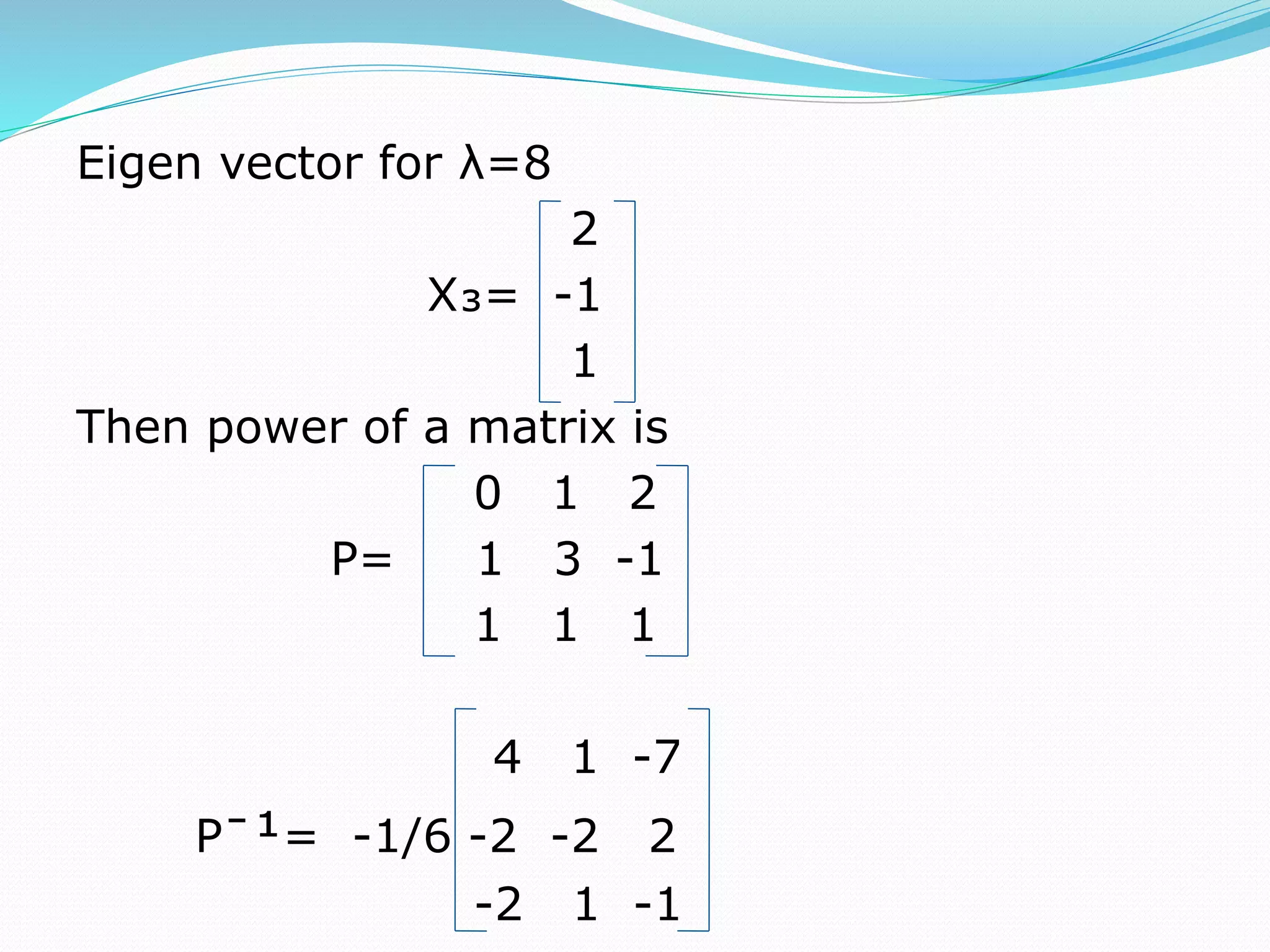
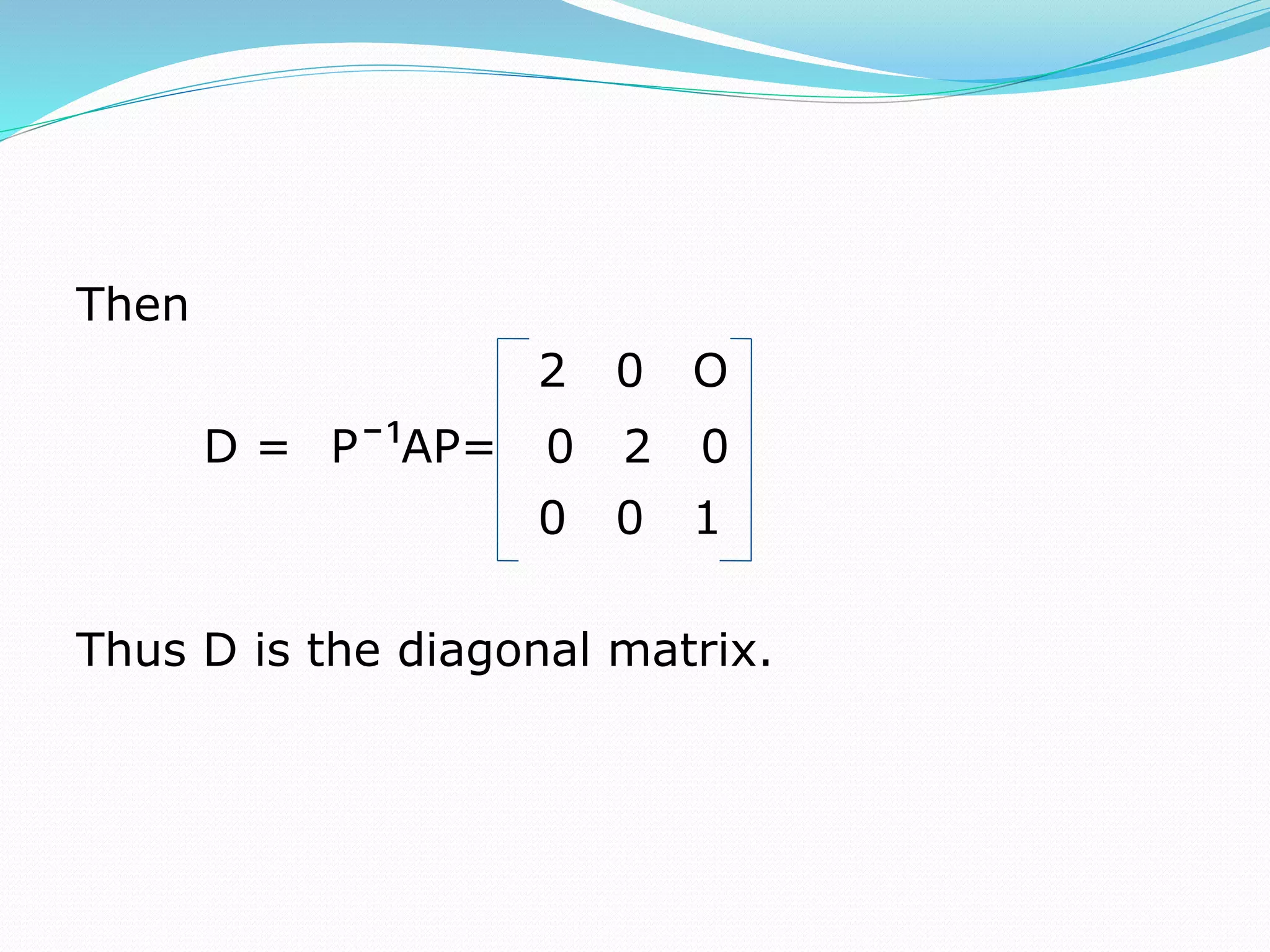
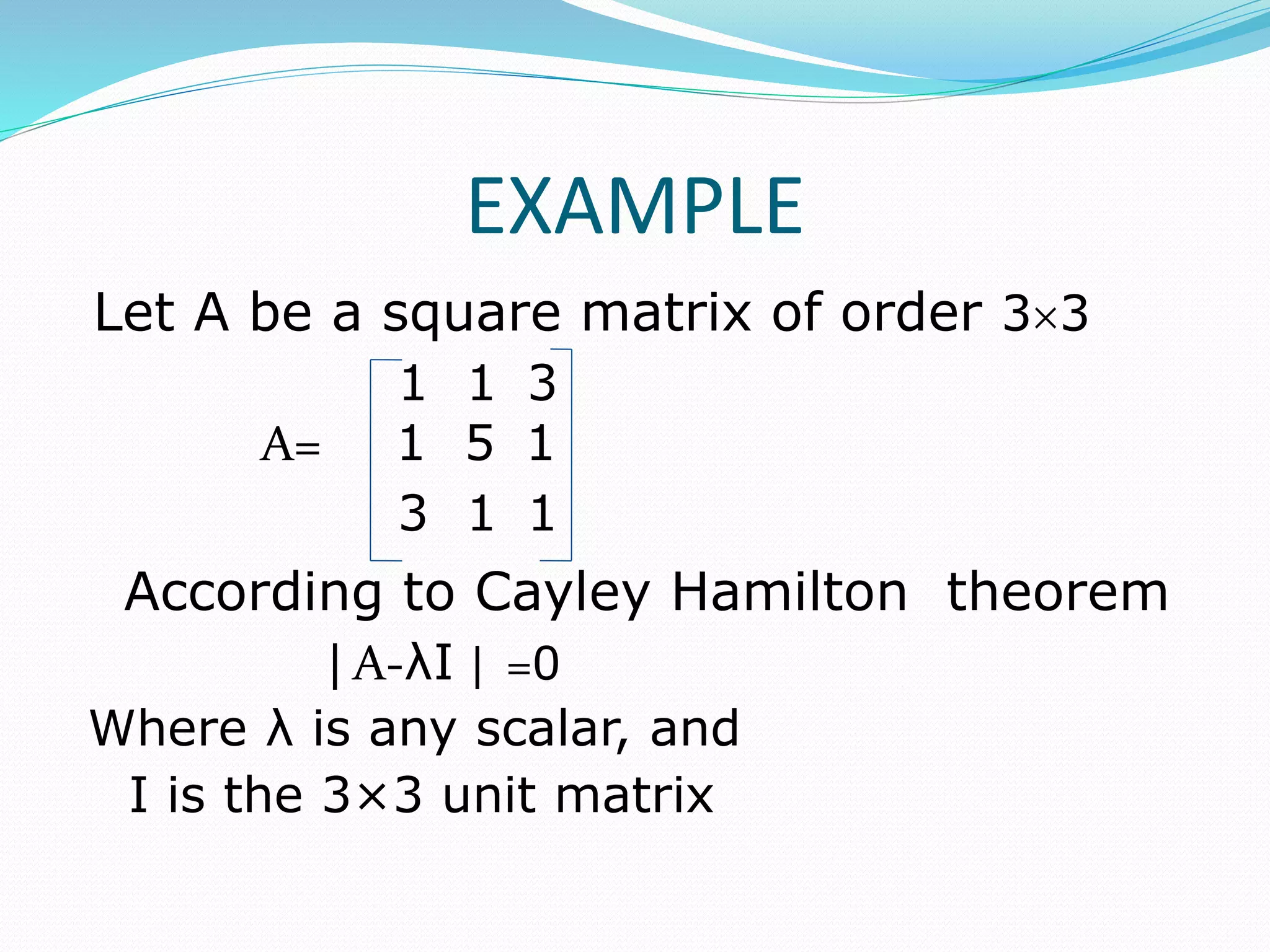
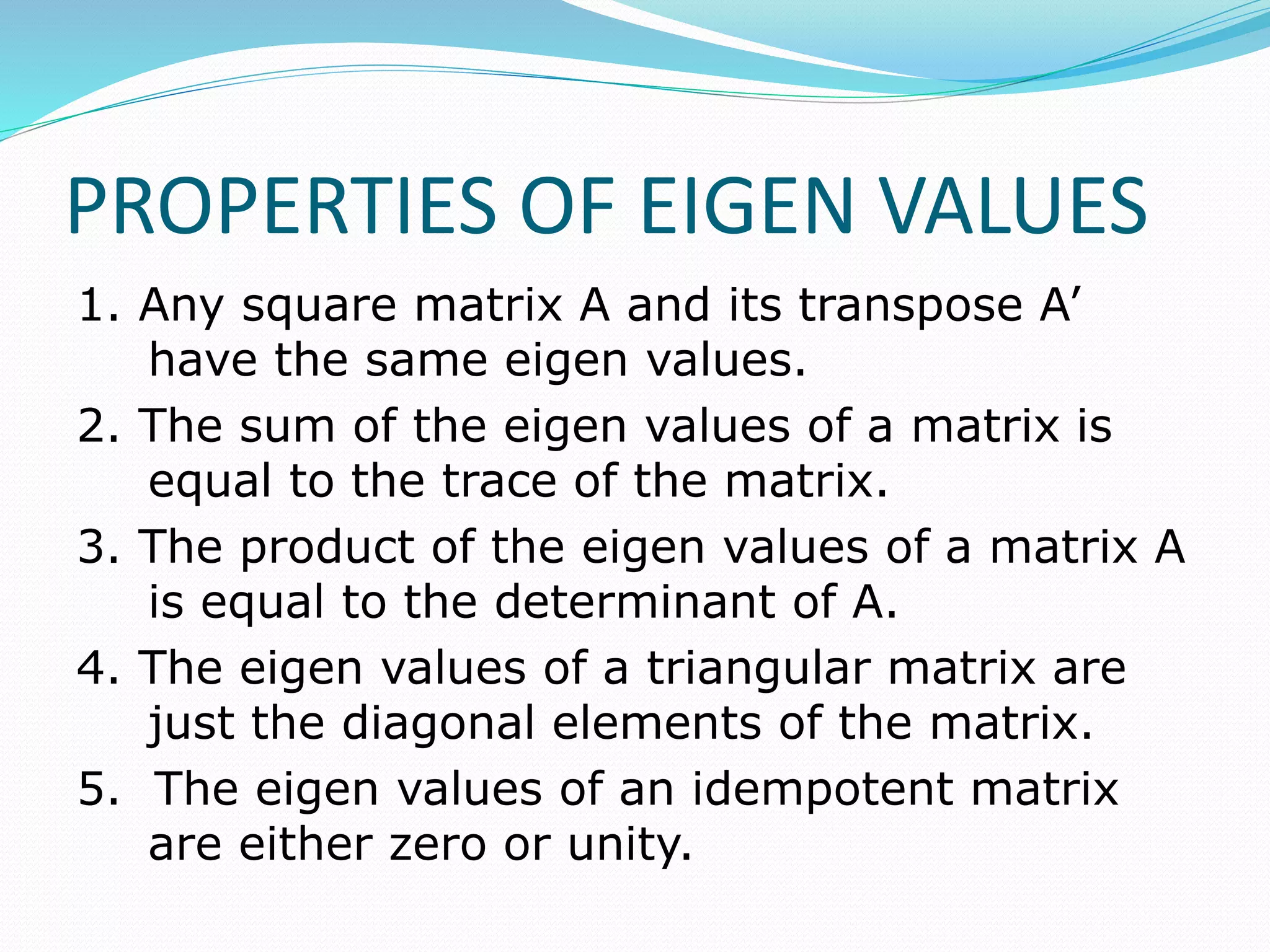
This document discusses eigen values, eigen vectors, and diagonalization of matrices. It defines eigen values as the roots of the characteristic equation of a matrix. Eigen vectors are non-zero vectors that satisfy AX=λX, where λ is the eigen value. Diagonalization is the process of transforming a matrix A into a diagonal matrix D using a similarity transformation with an invertible matrix P, such that D=P-1AP. The document provides examples to illustrate these concepts and lists various properties of eigen values and eigen vectors.





![EIGEN VECTOR
An eigen vector of a square matrix A is a non
zero vector X such that for some number λ,
we have,
AX=λX
AX-λIX=0
[A-λI]X=0
Where 0 represents the zero vector.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/diagonalizationofmatrix-191128120818/75/Diagonalization-of-matrix-8-2048.jpg)