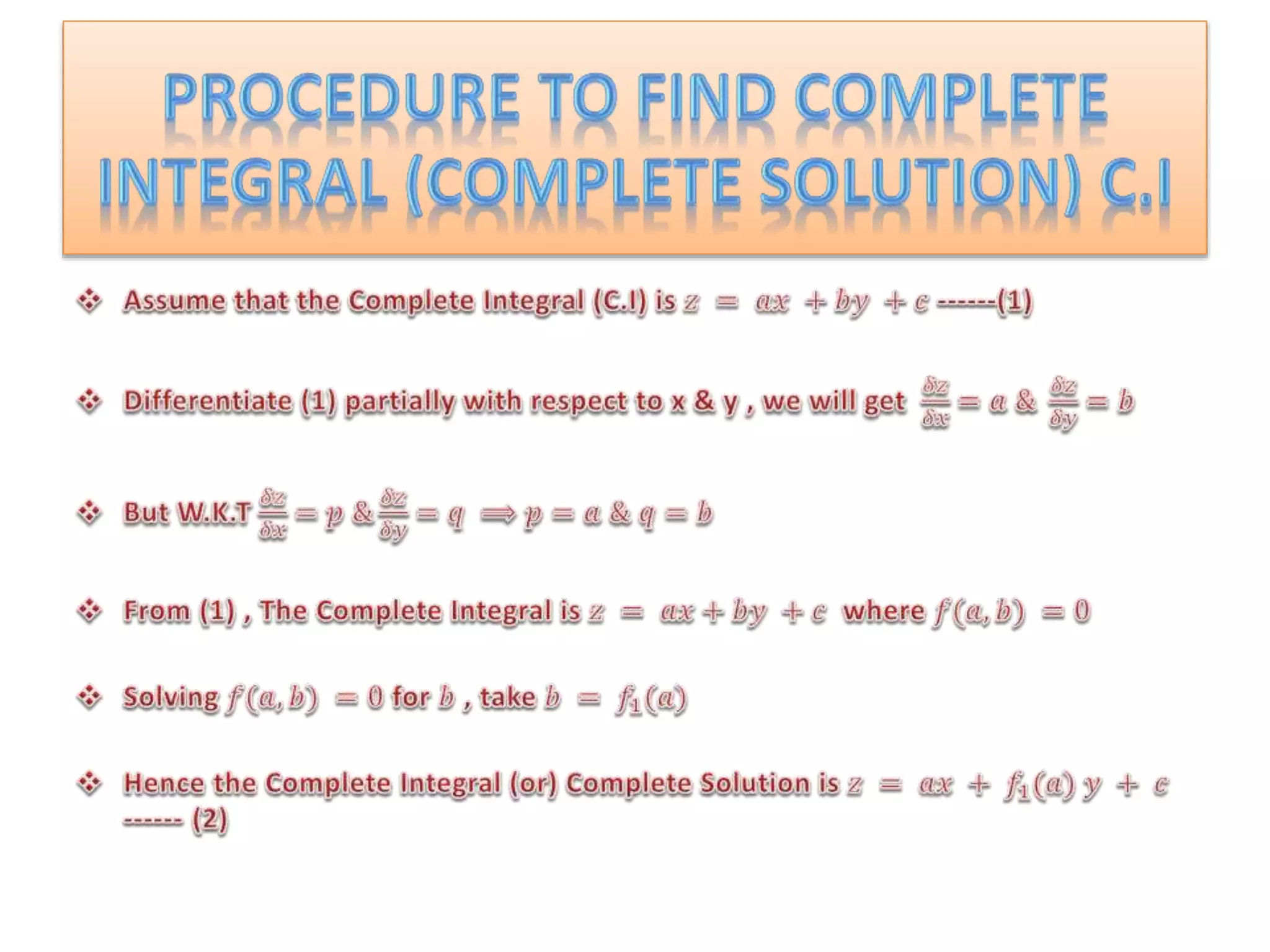
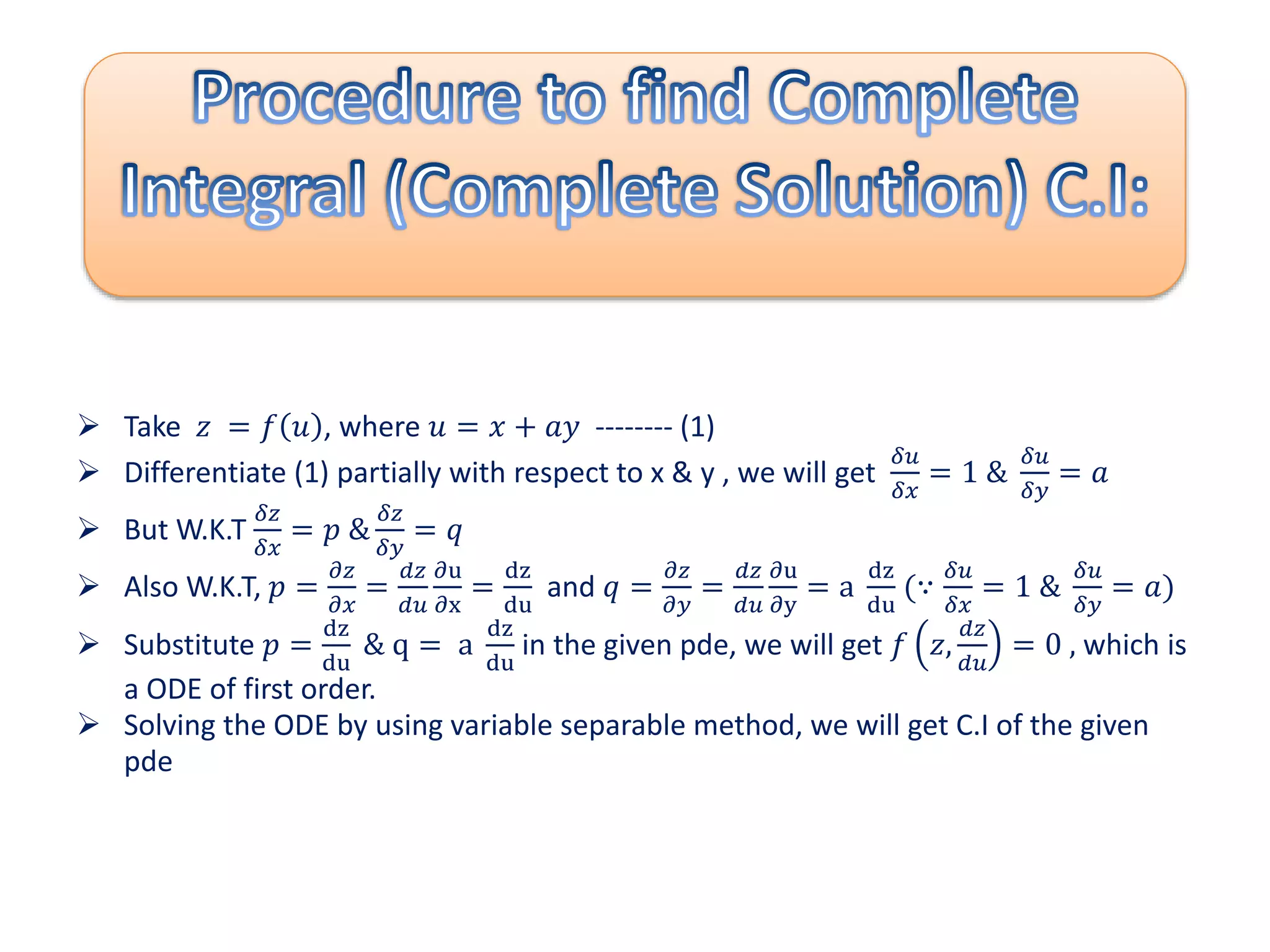
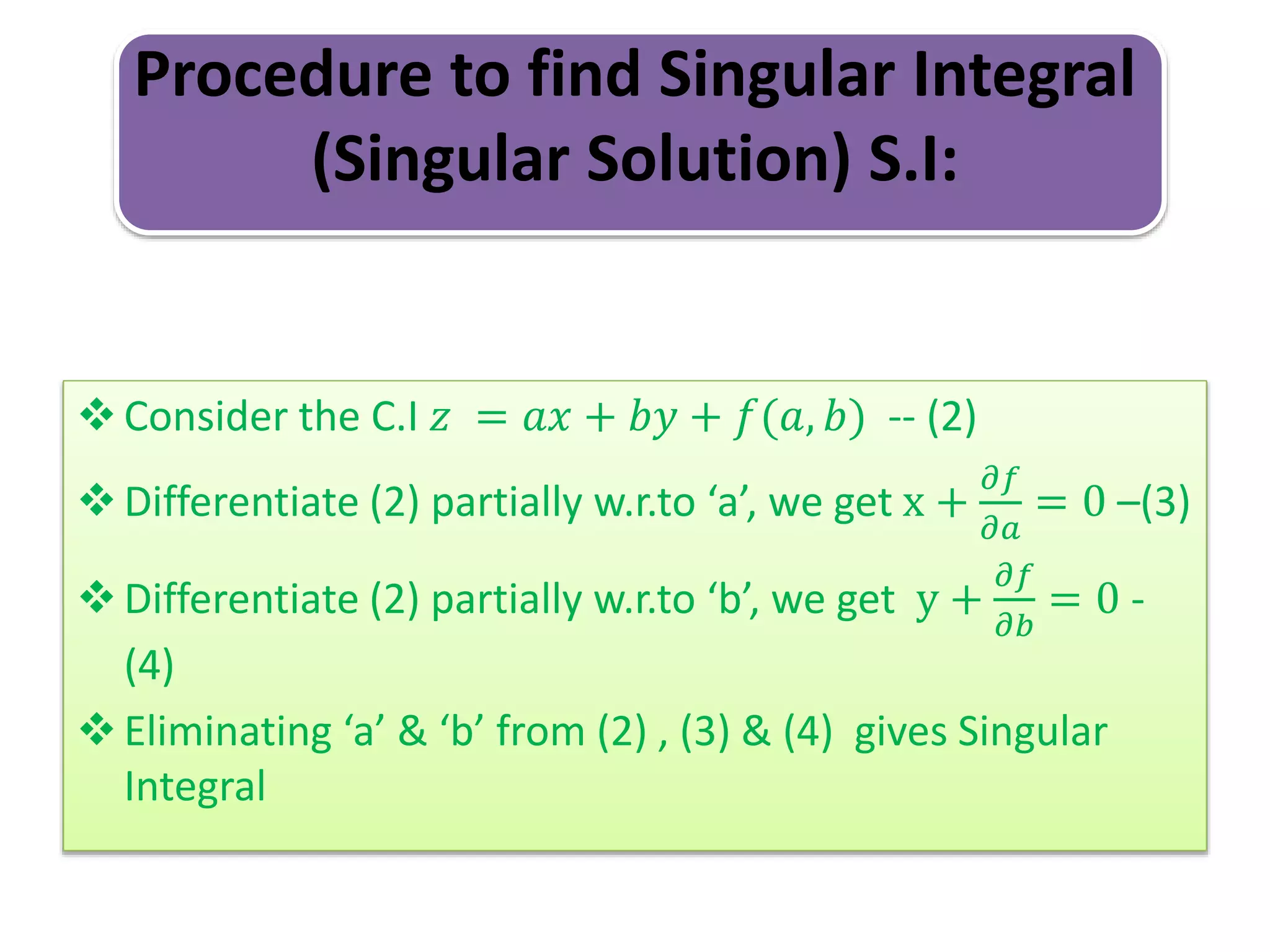
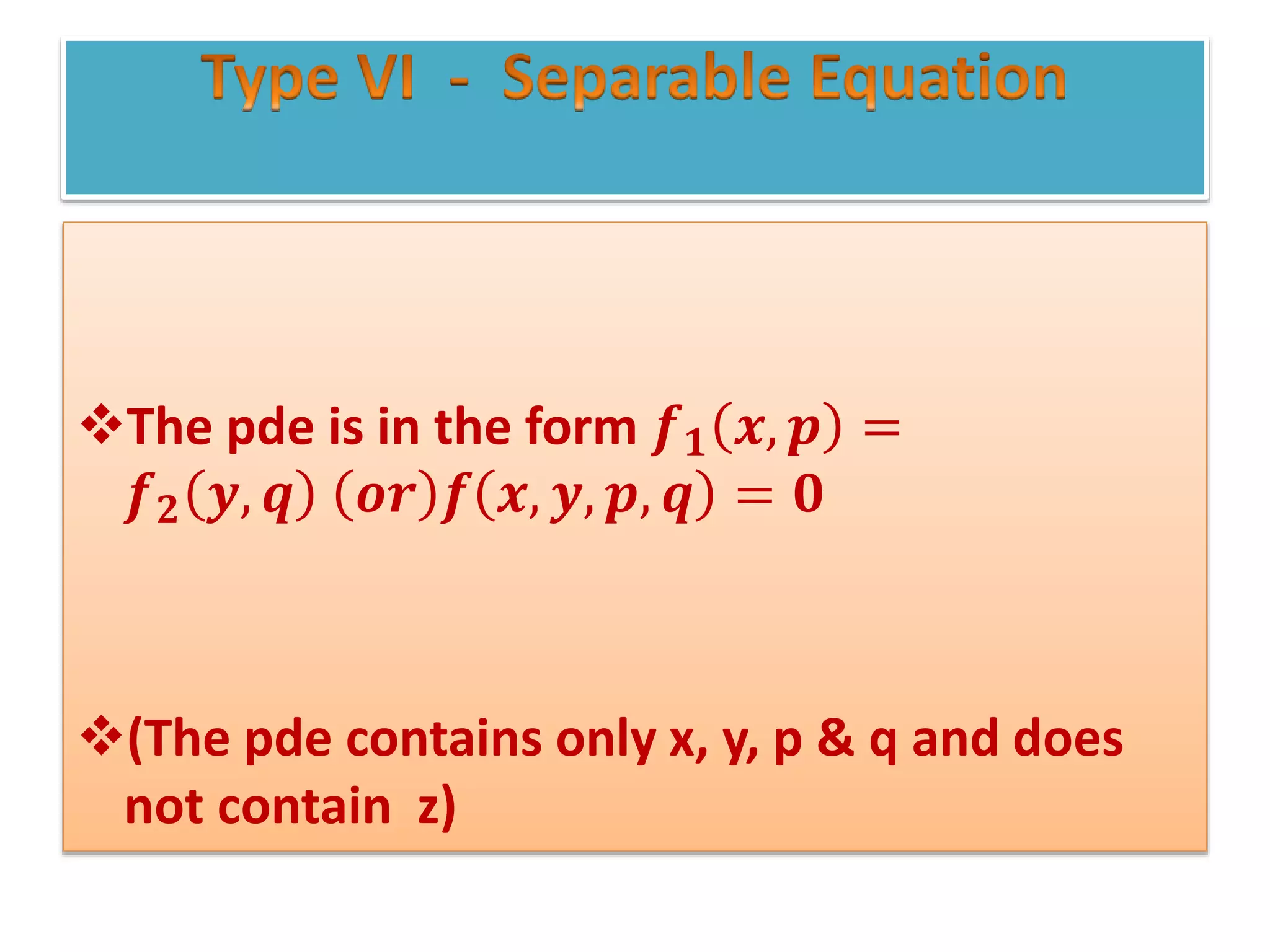
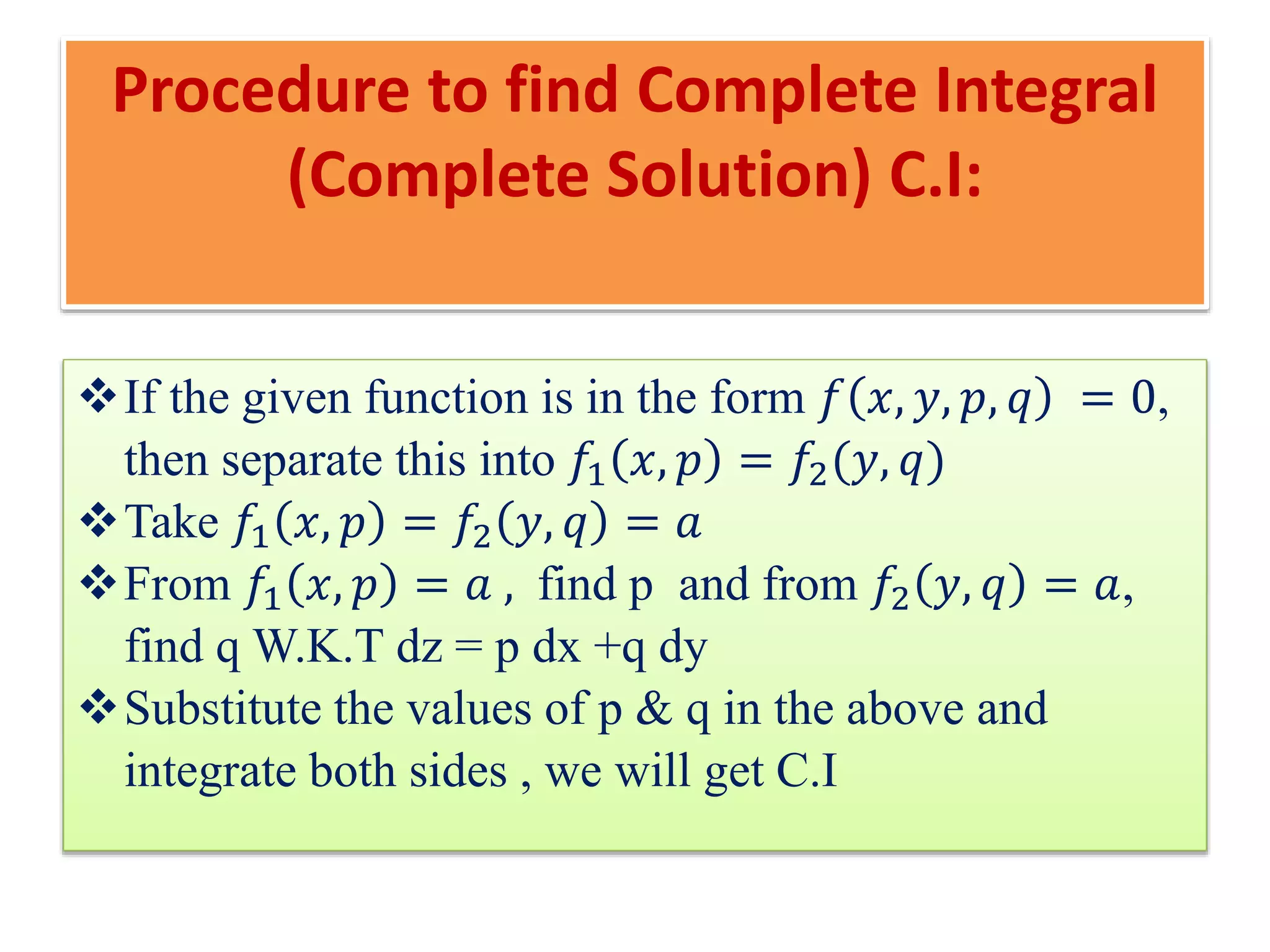
The document discusses concepts related to solutions of partial differential equations (PDEs), differentiating between complete, particular, singular, and general solutions. It outlines procedures for finding complete integrals, singular integrals, and general integrals based on the forms of the equations involved. Various cases and methods for reducing equations and solving them are also presented.