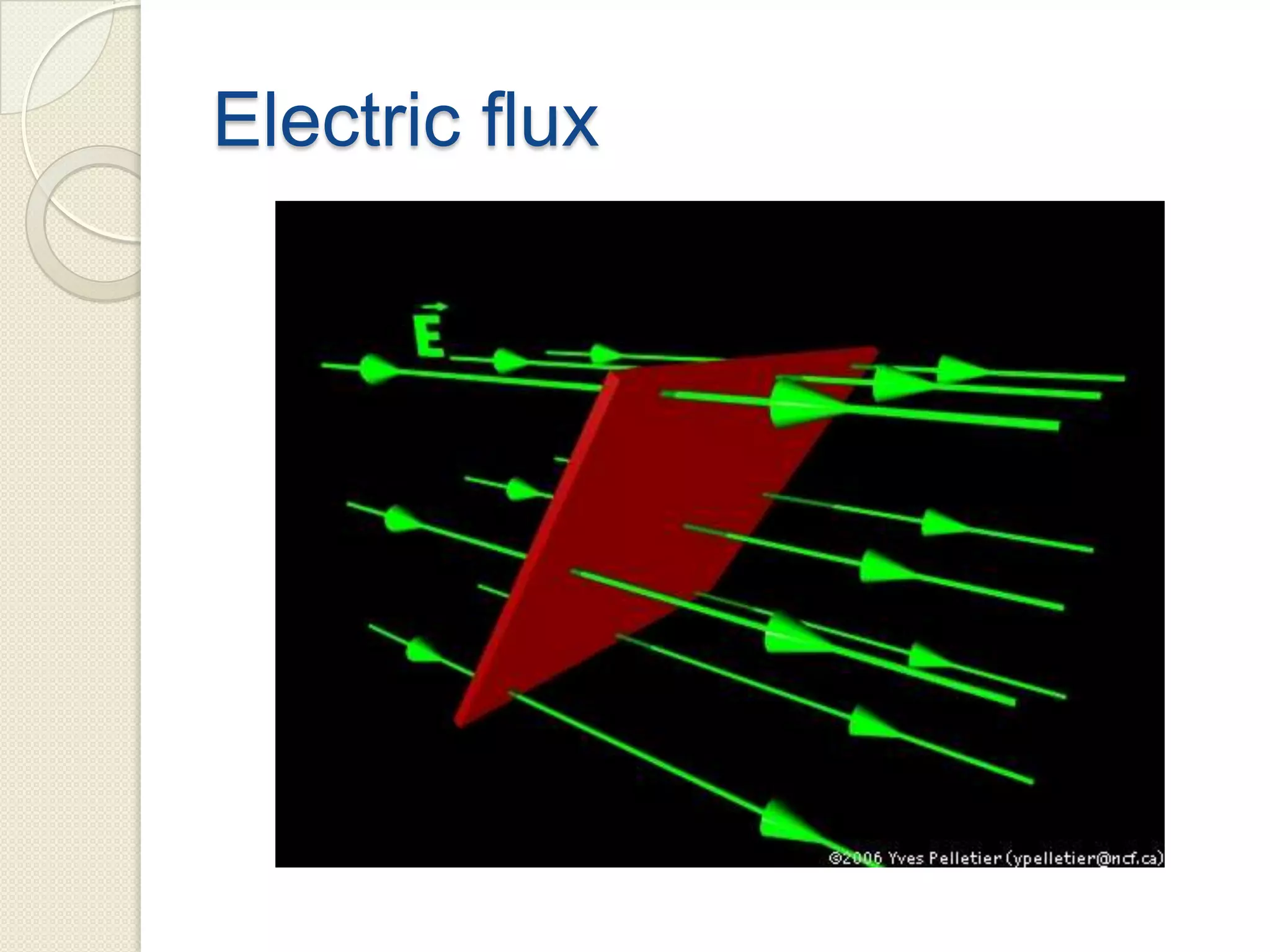
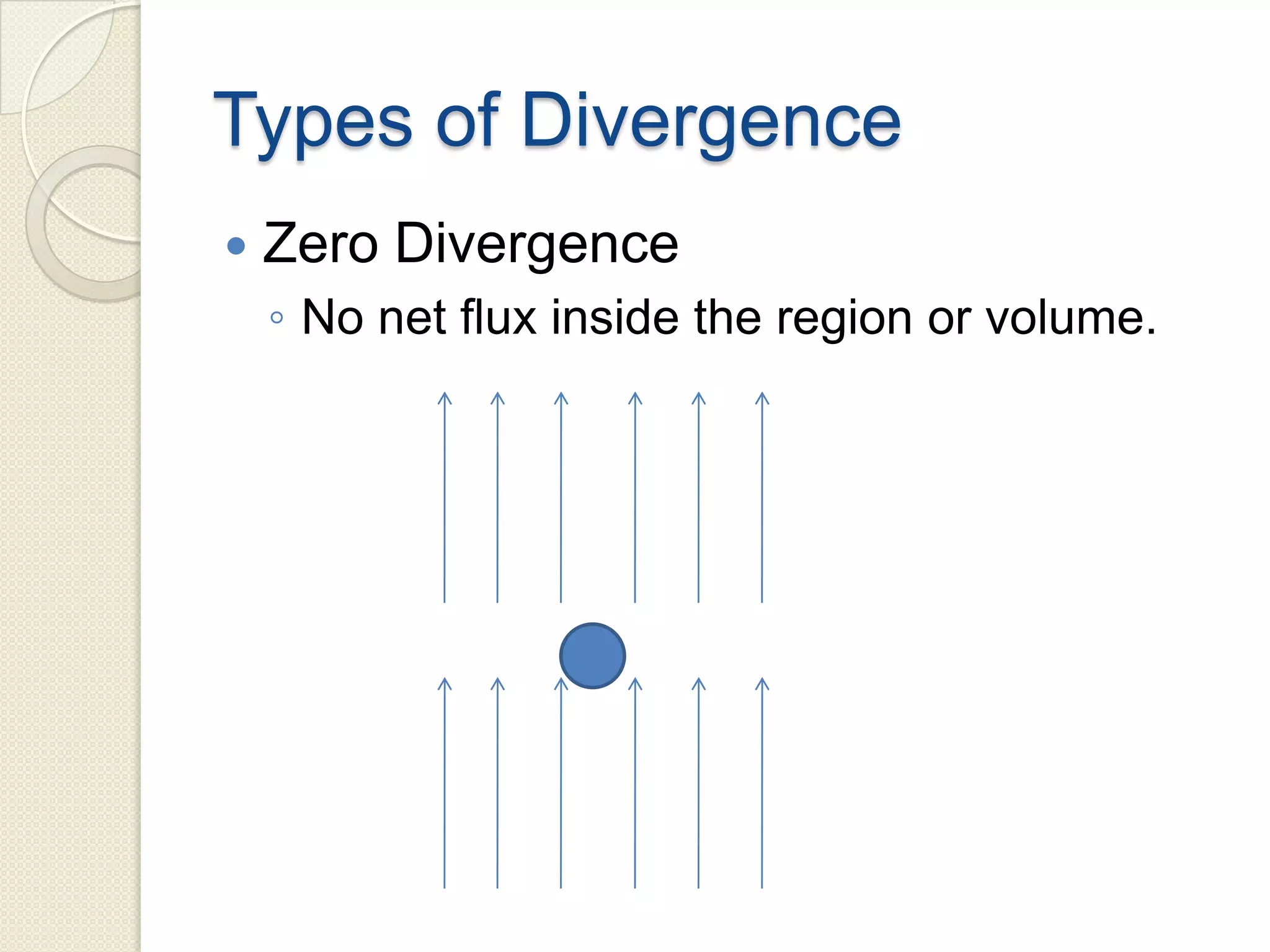
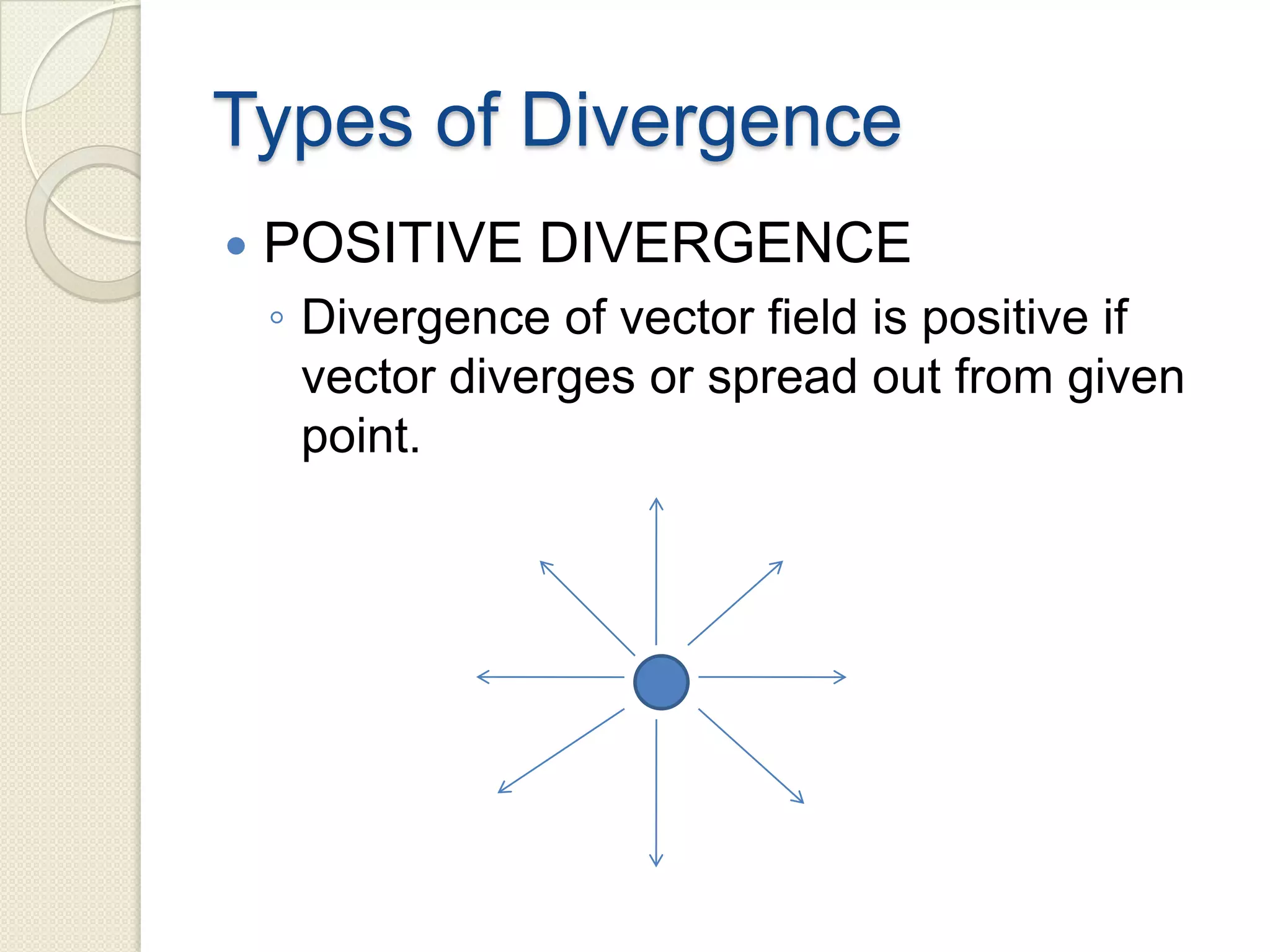
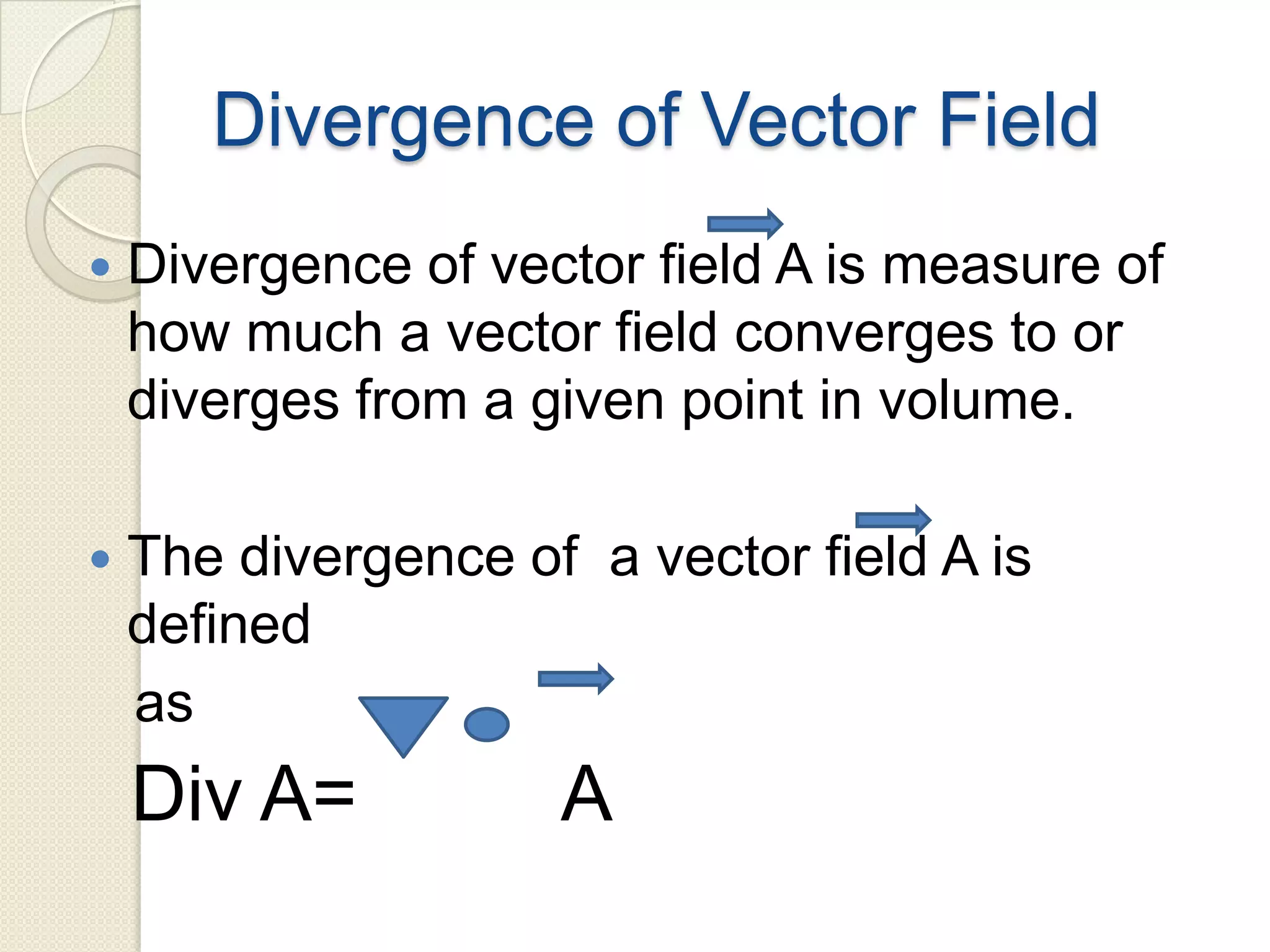
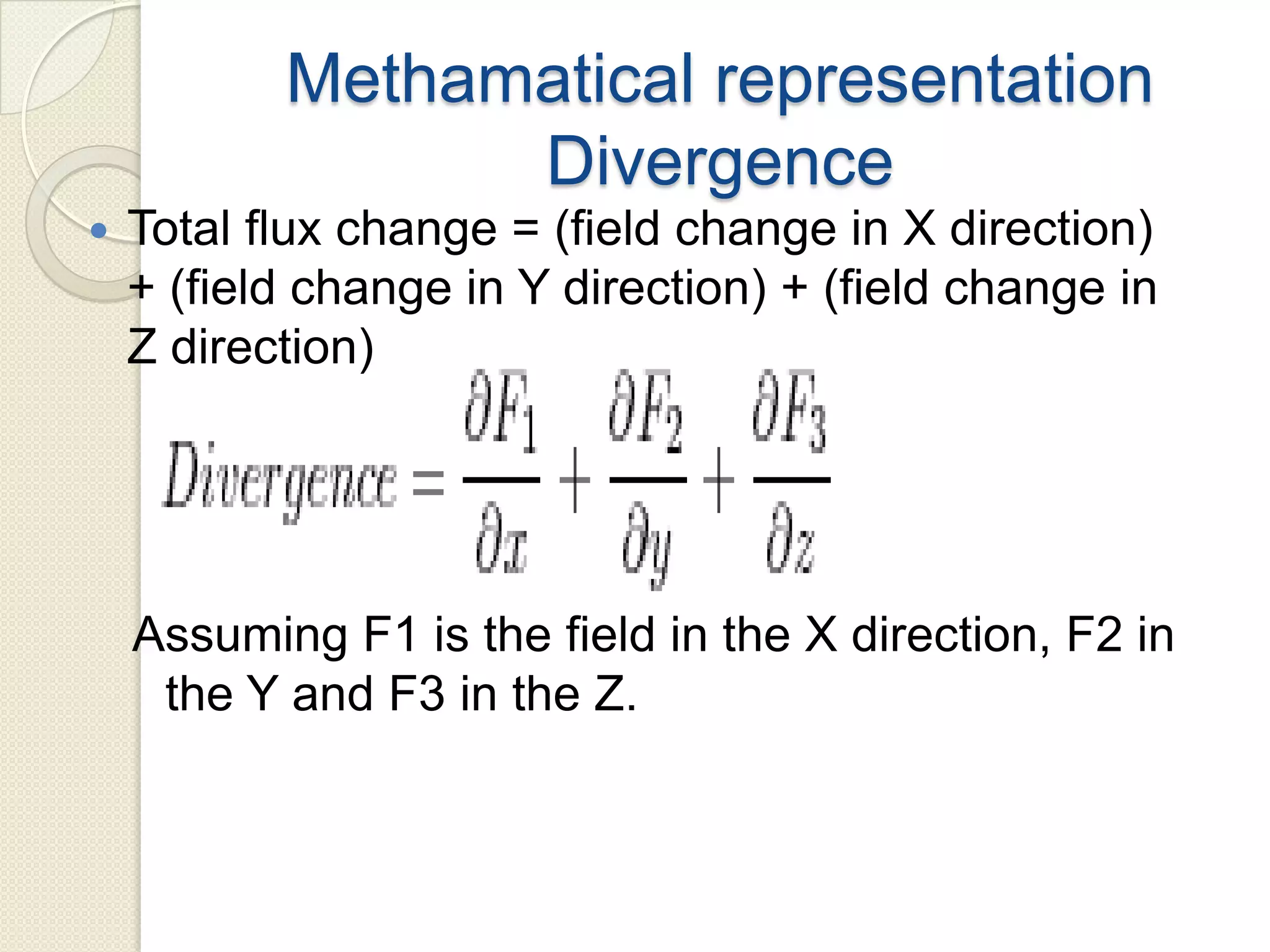
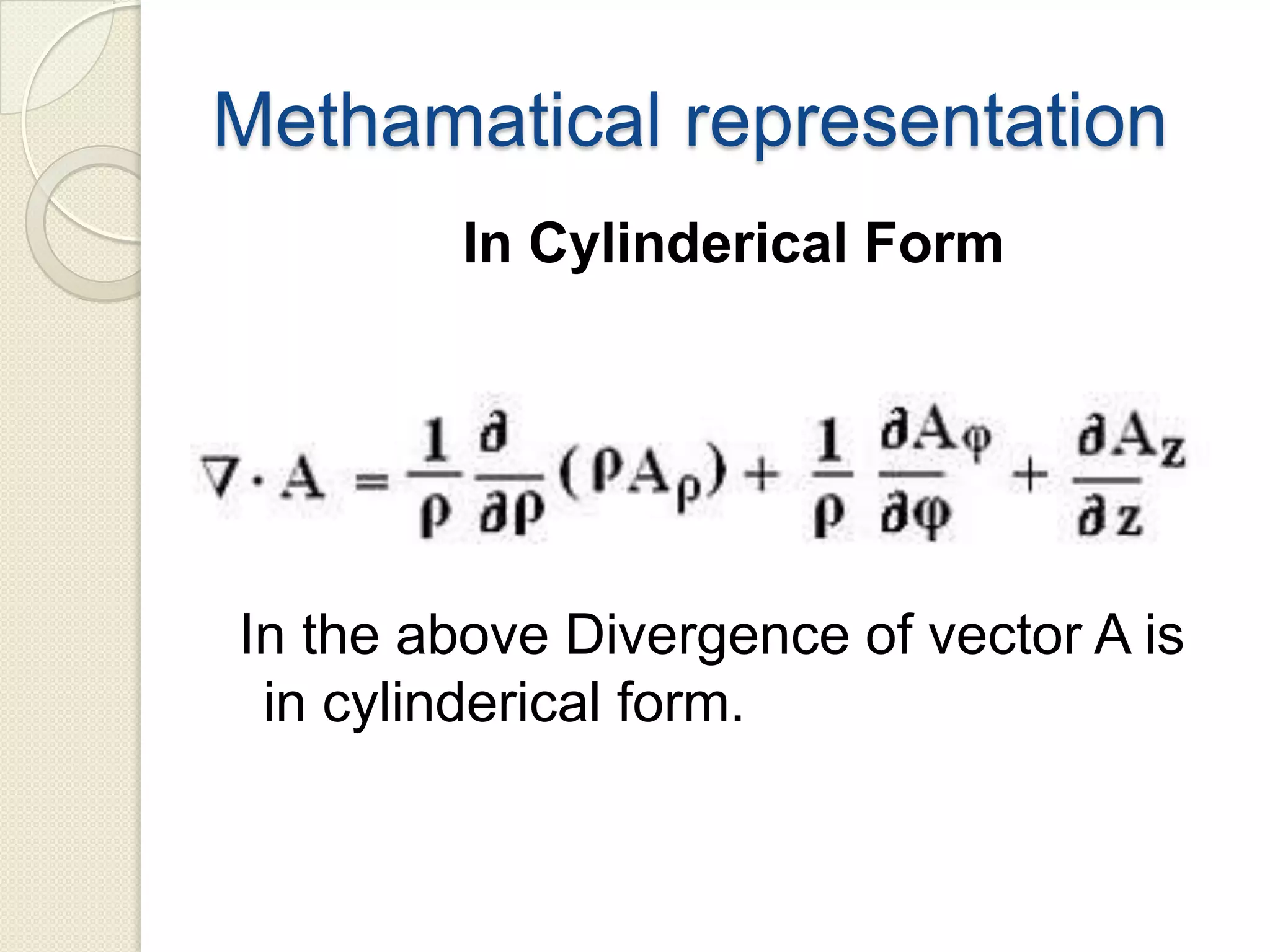
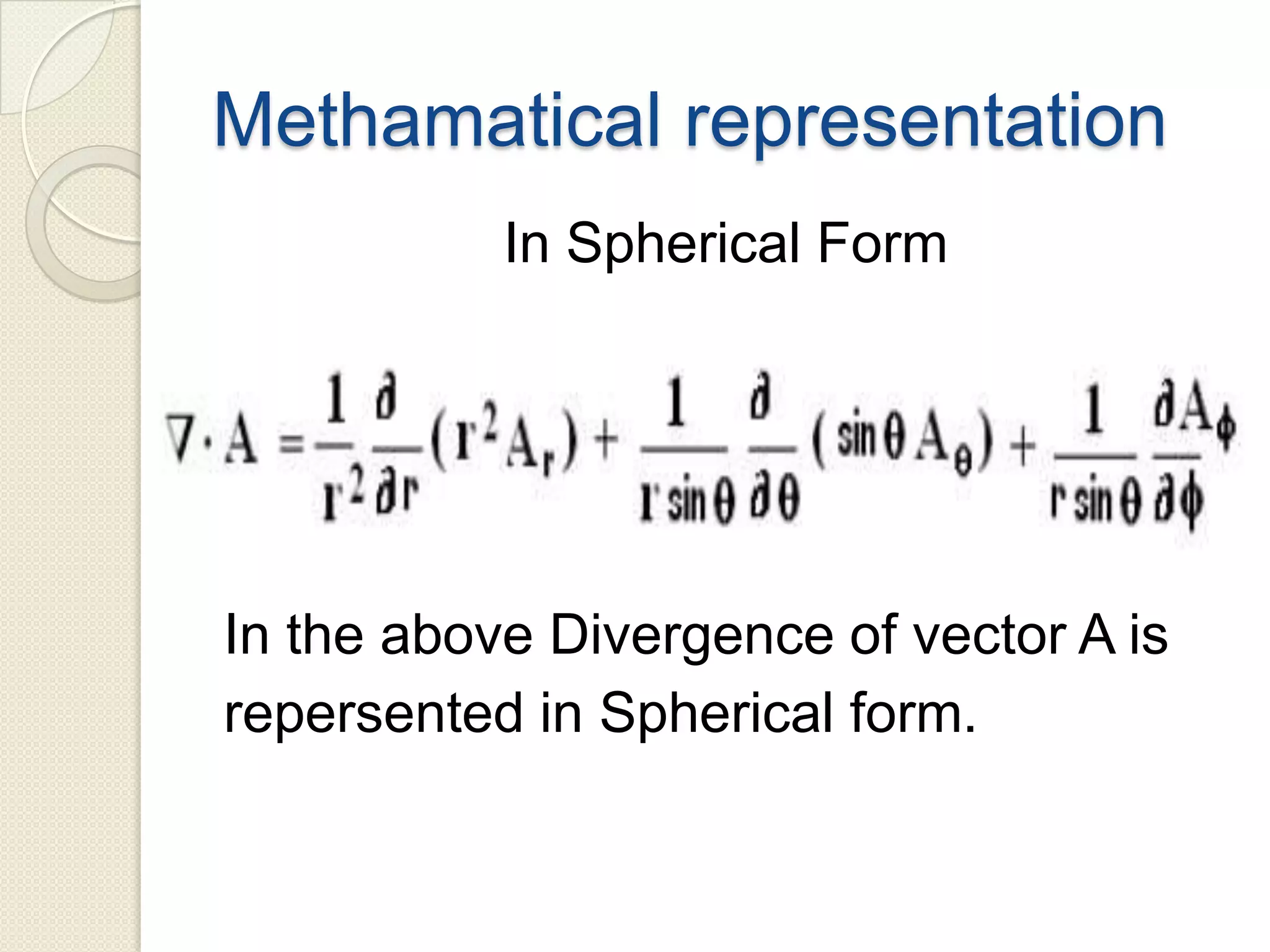
Divergence is a mathematical operation on a vector field that calculates the density of the vector field's source at a given point. It measures the flux of a vector field out of an infinitesimally small volume element at that point. Divergence equals flux per unit volume, so a positive divergence means flux is spreading out from the point and a negative divergence means flux is converging at the point. Divergence can be represented in Cartesian, cylindrical, or spherical coordinate systems using partial derivatives and the del operator.