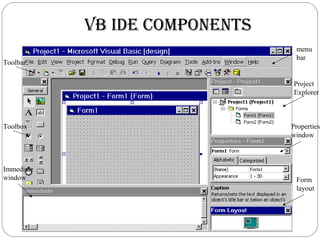
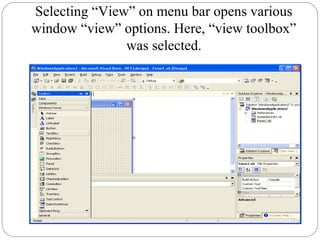
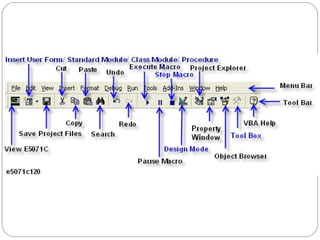
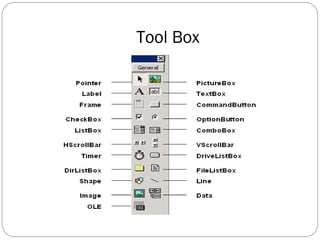
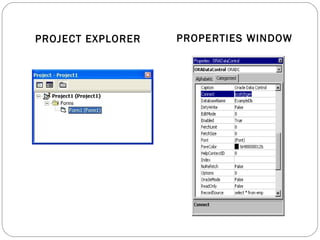
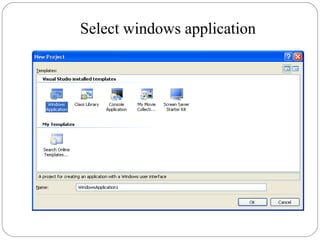
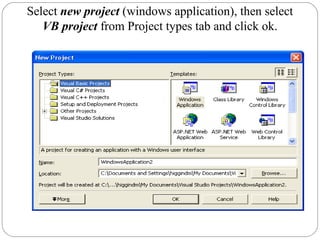
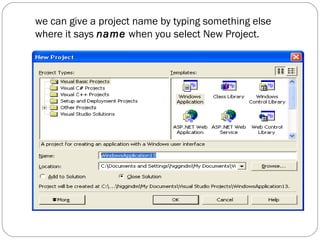
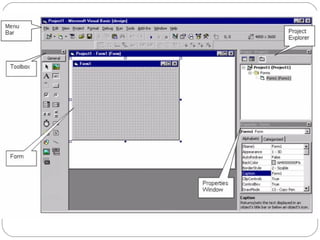
Visual Basic is an ideal programming language for developing Windows applications using a graphical user interface. It was developed from the BASIC programming language. The Visual Basic integrated development environment includes components like a menu bar, toolbars, project explorer, properties window, toolbox, form designer, and object browser to help developers build applications. Developers can drag and drop controls from the toolbox onto forms to create the application interface.



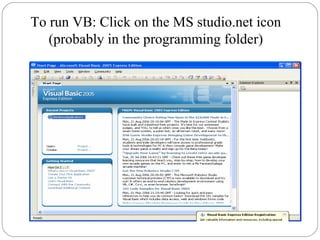
![IDE [INTEGRATED DEVELOPMENT
ENVIRONMENT]
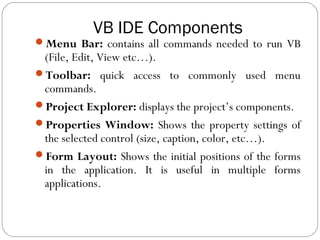
Menu Bar
Toolbars
Project Explorer
Toolbox
Properties Window
Form Designer
Form Layout window
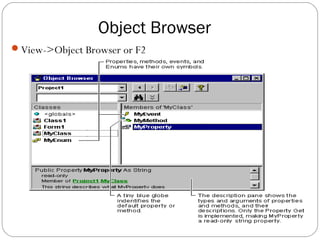
Object Browser](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vbunitt1-150416061140-conversion-gate02/85/Vb-unit-t-1-1-12-320.jpg)