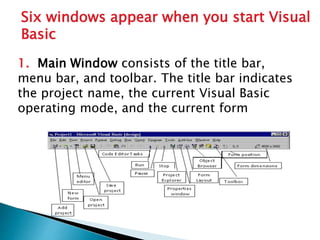
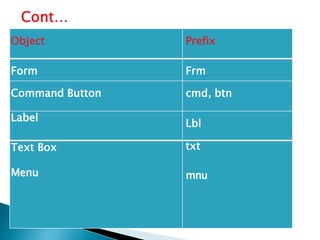
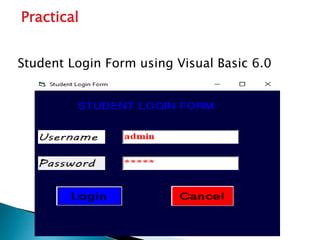
This document summarizes the key features and development process in Visual Basic 6.0. It discusses the evolution of Visual Basic from earlier versions. When building an application in VB6, developers draw the user interface, set control properties, and attach code to controls. The interface contains elements like the main window, form window, toolbox, and project window. Code is then added to controls to define application logic and behavior. An example login form is provided to illustrate this process.