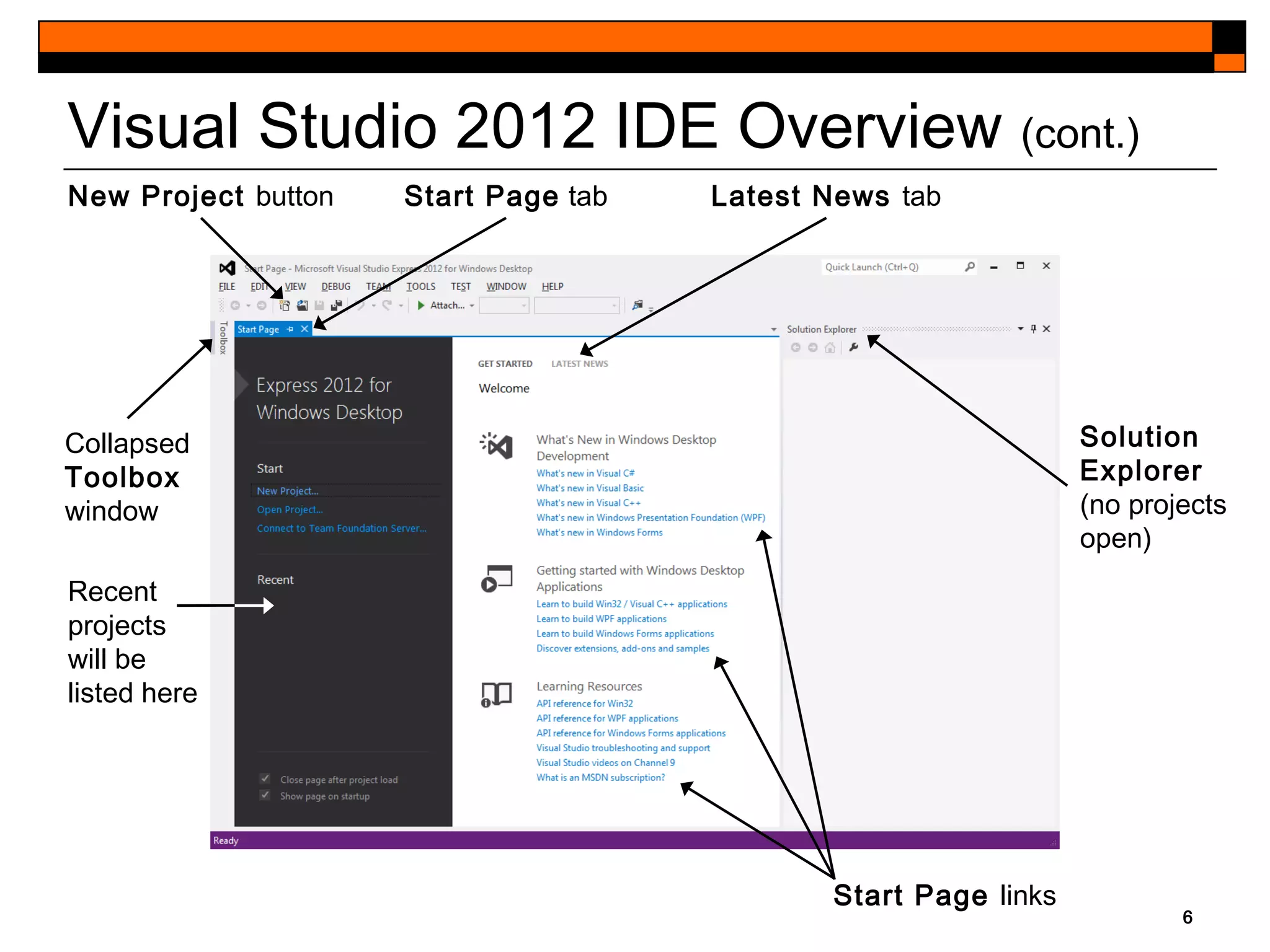
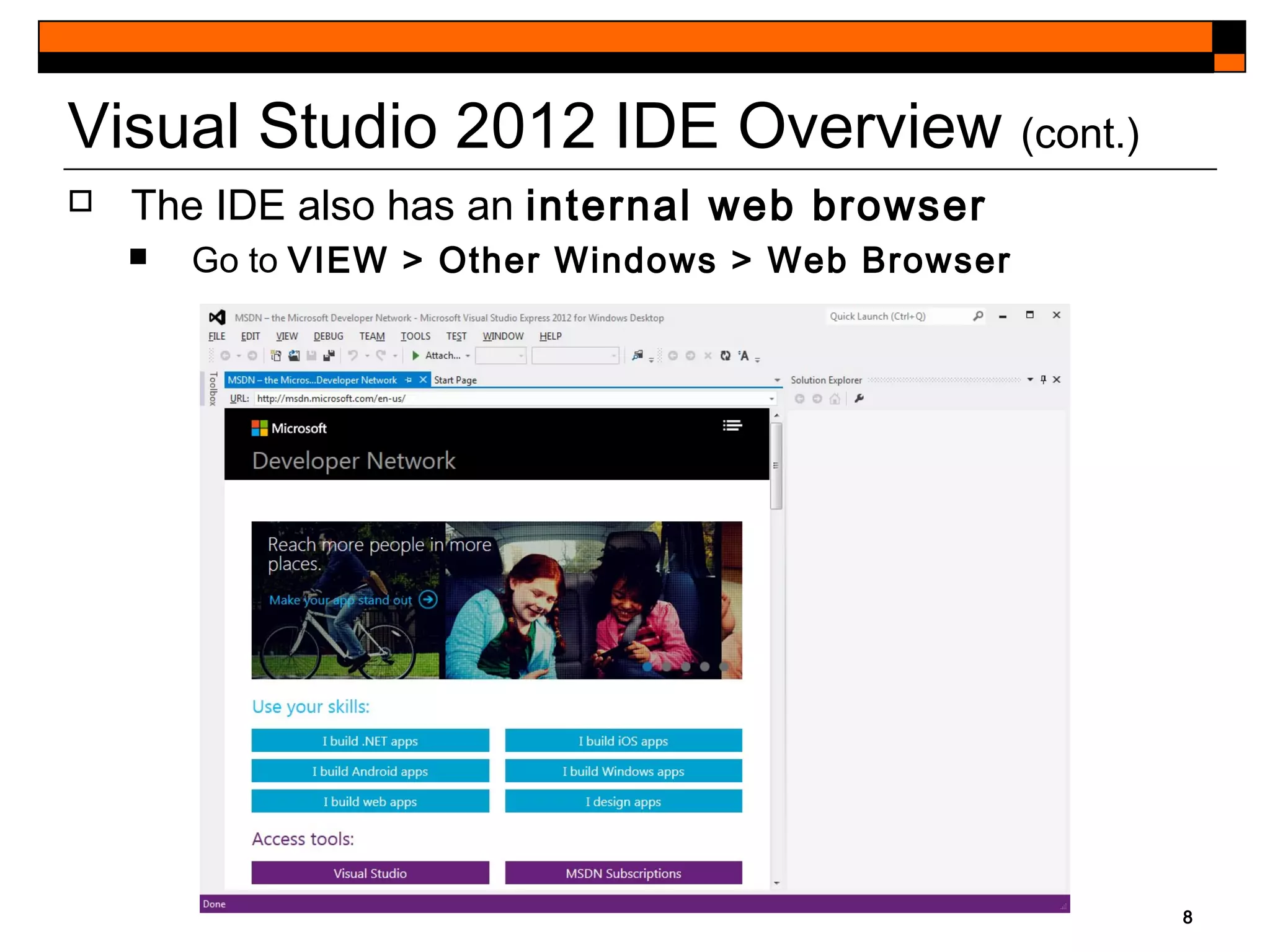
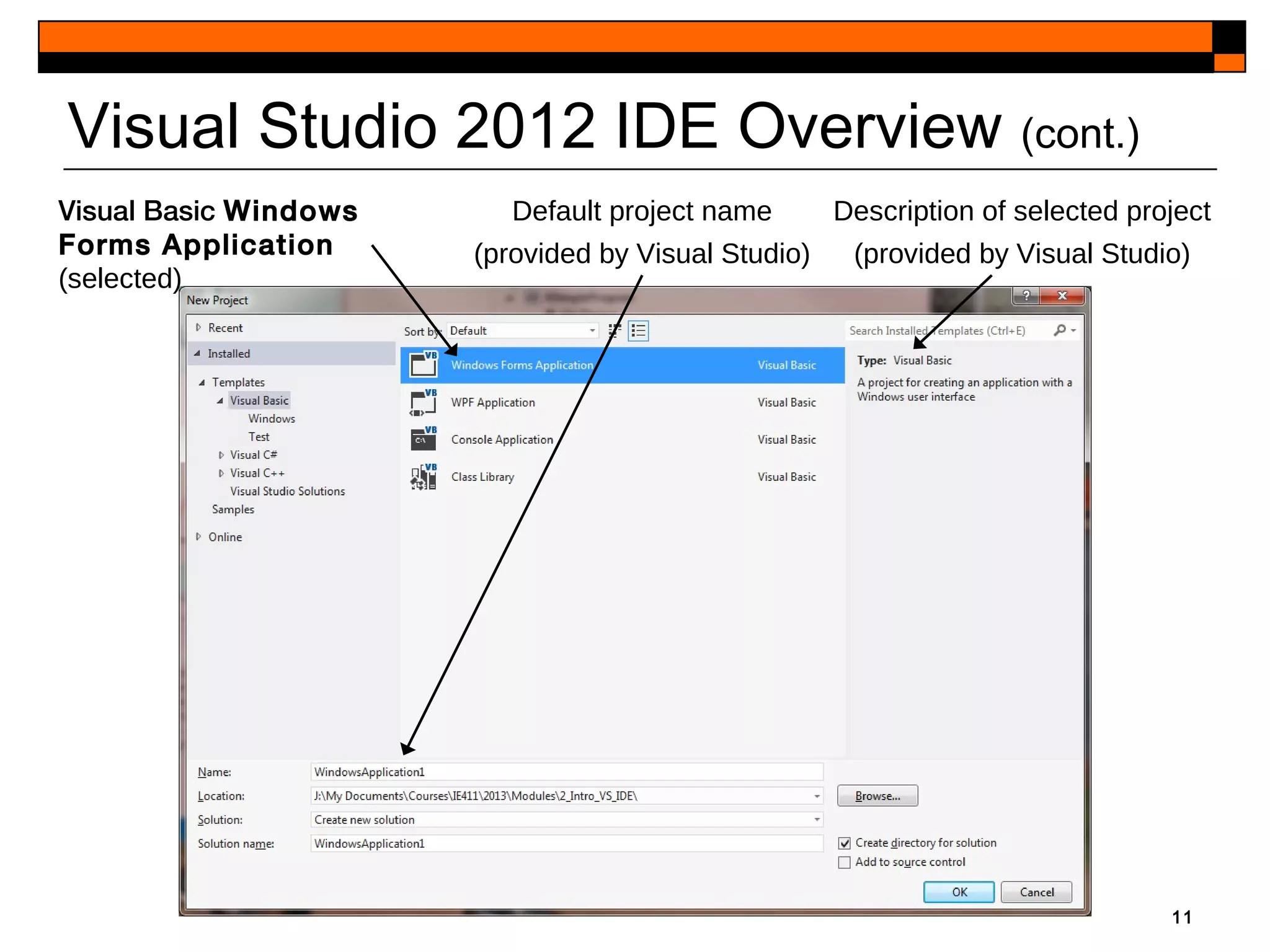
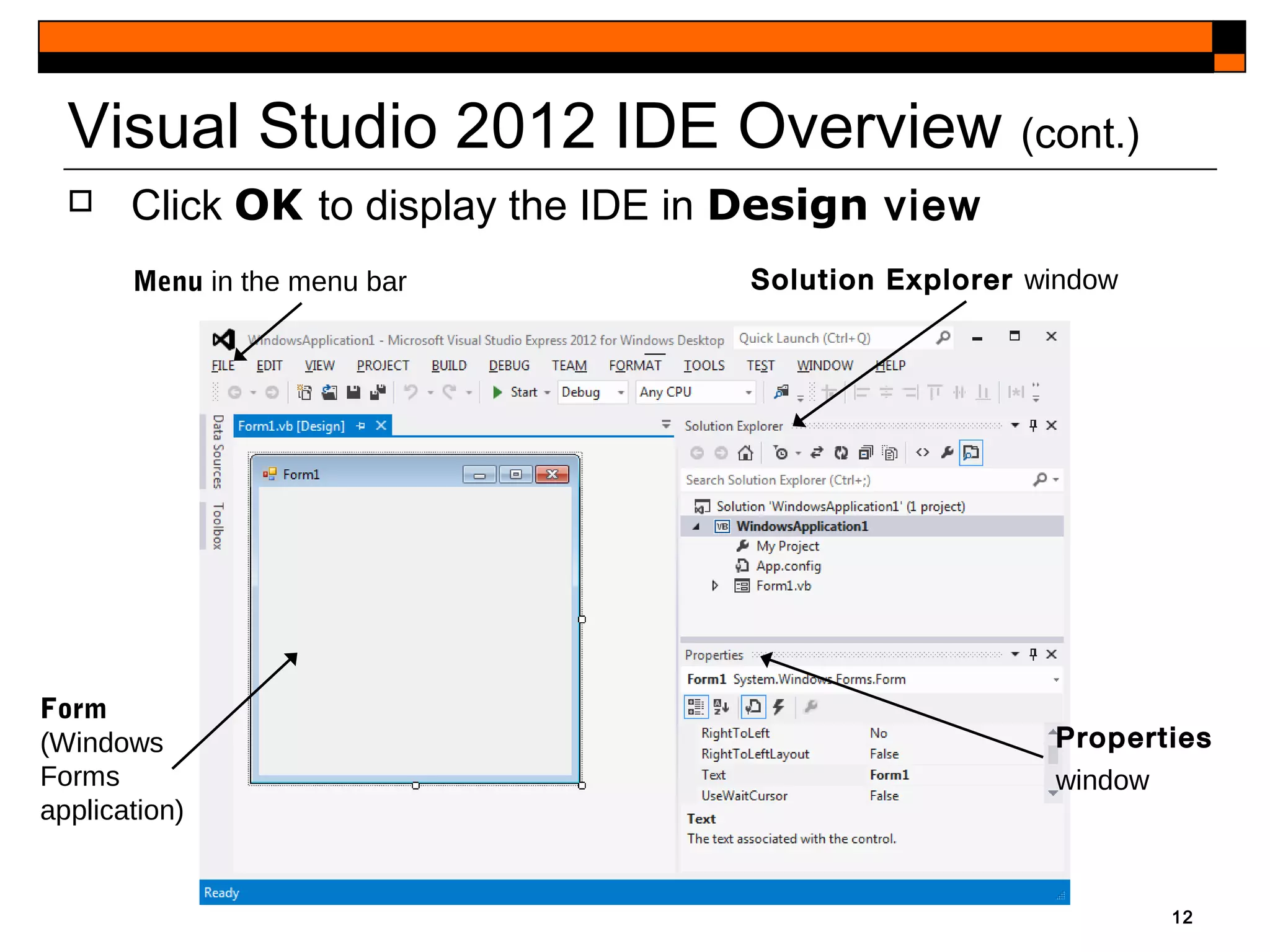
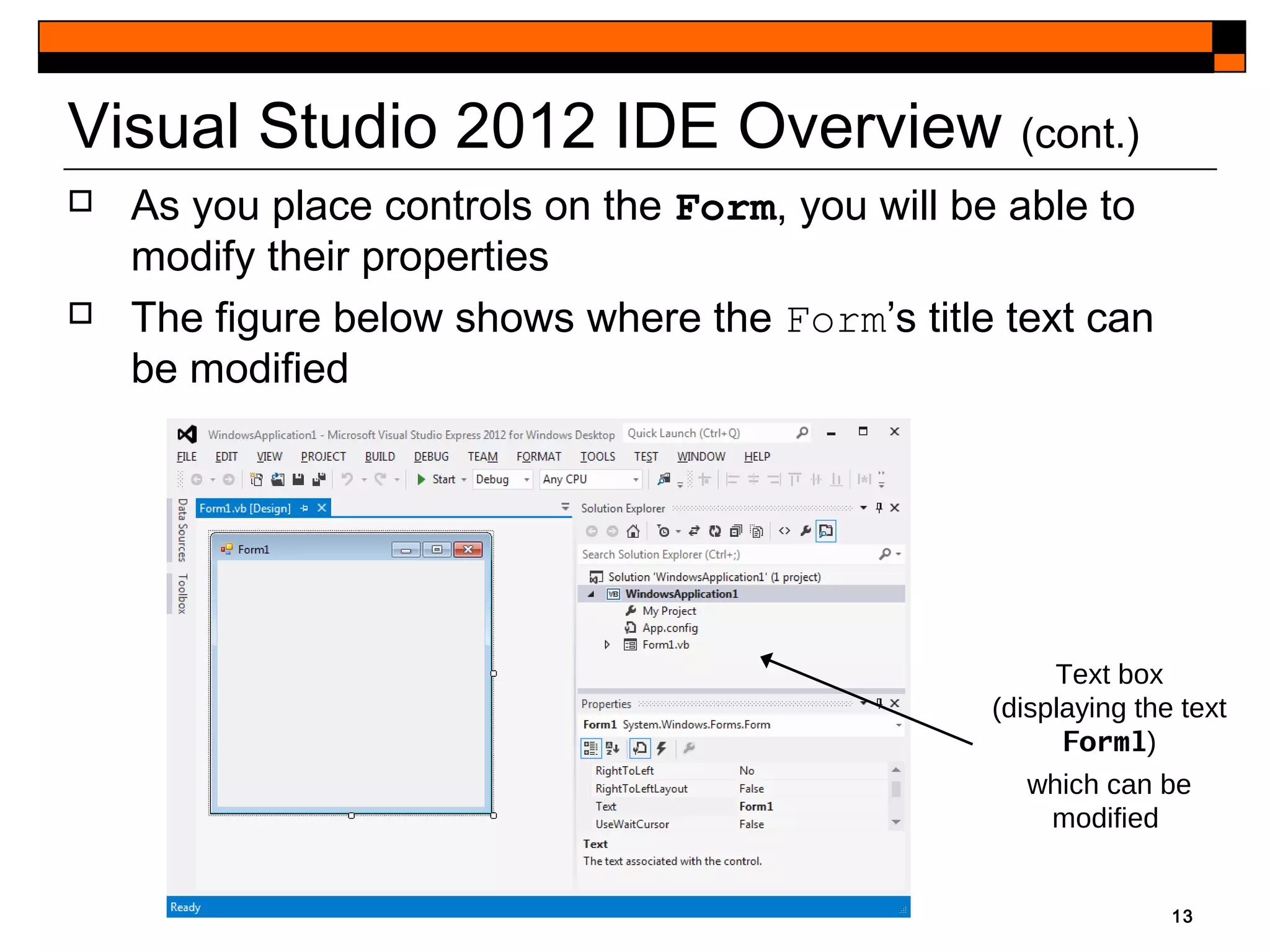
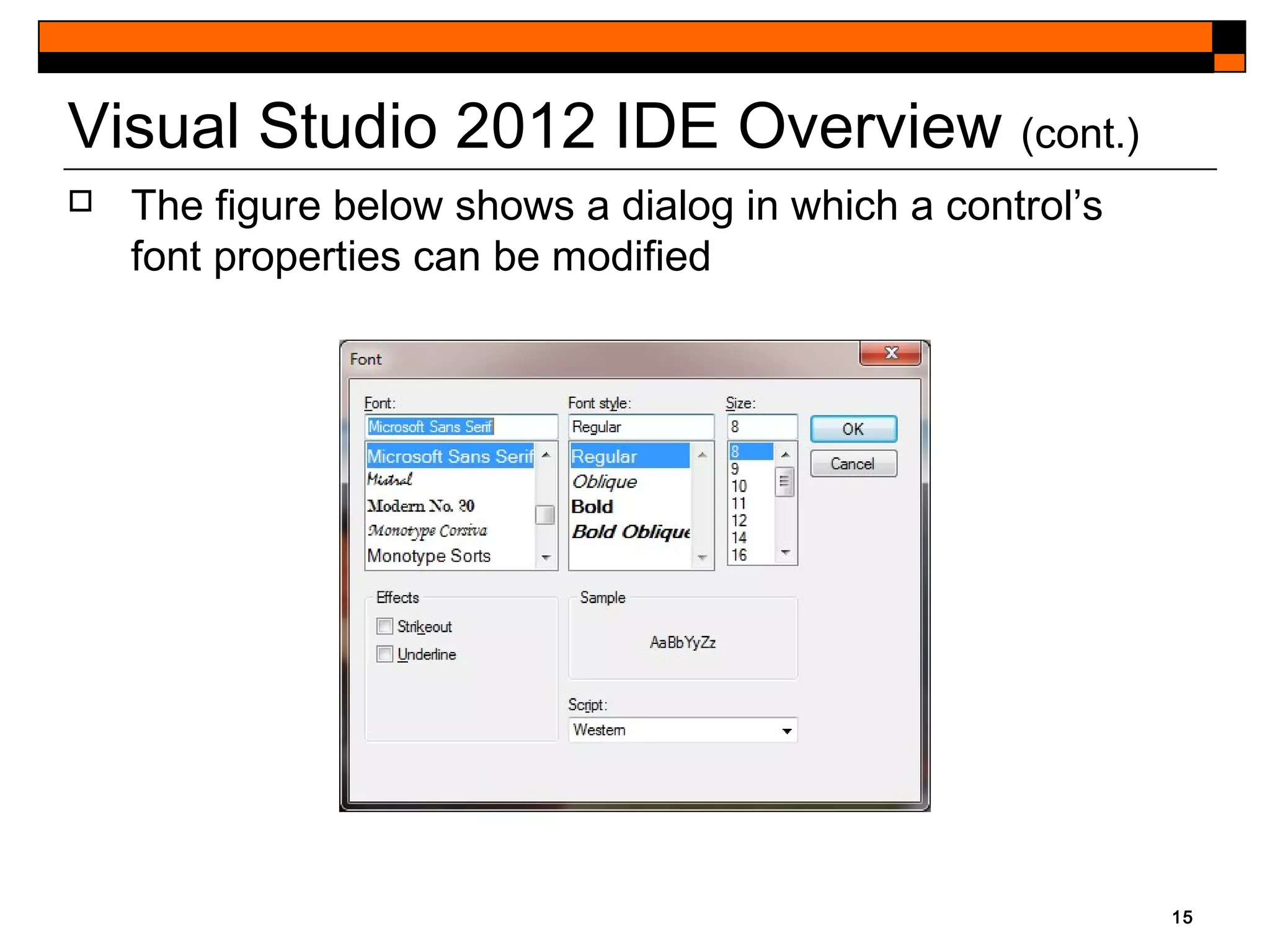
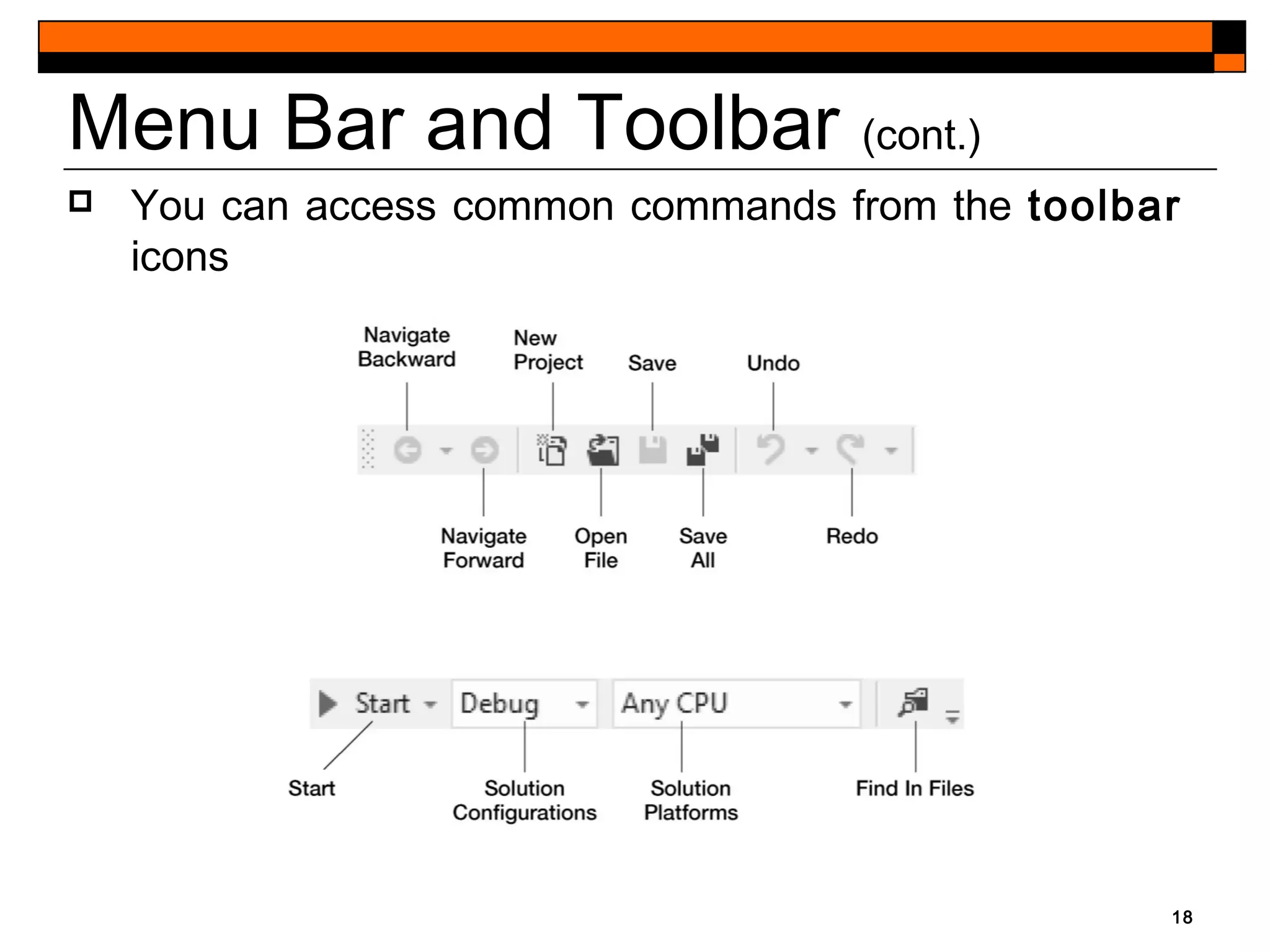
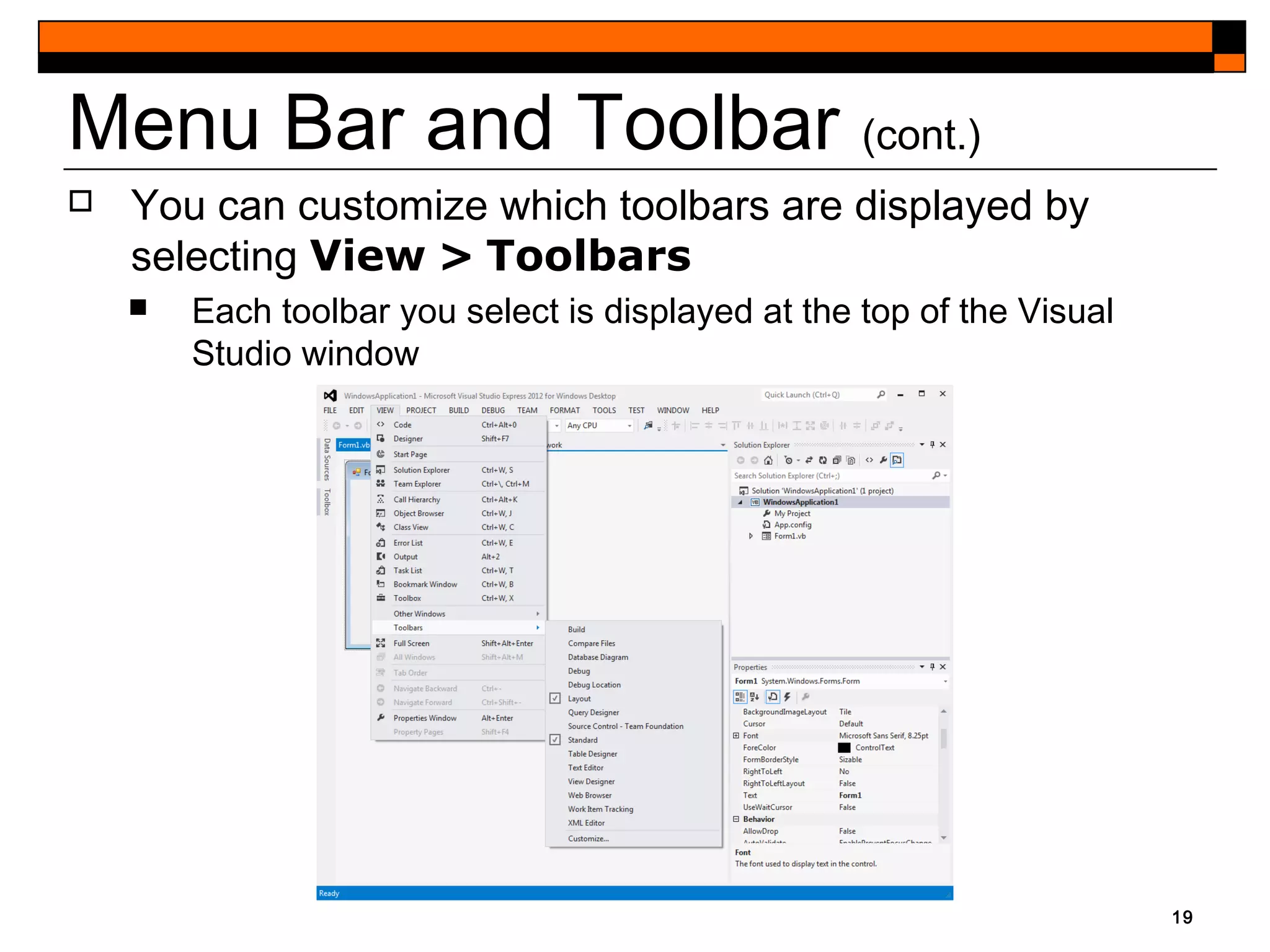
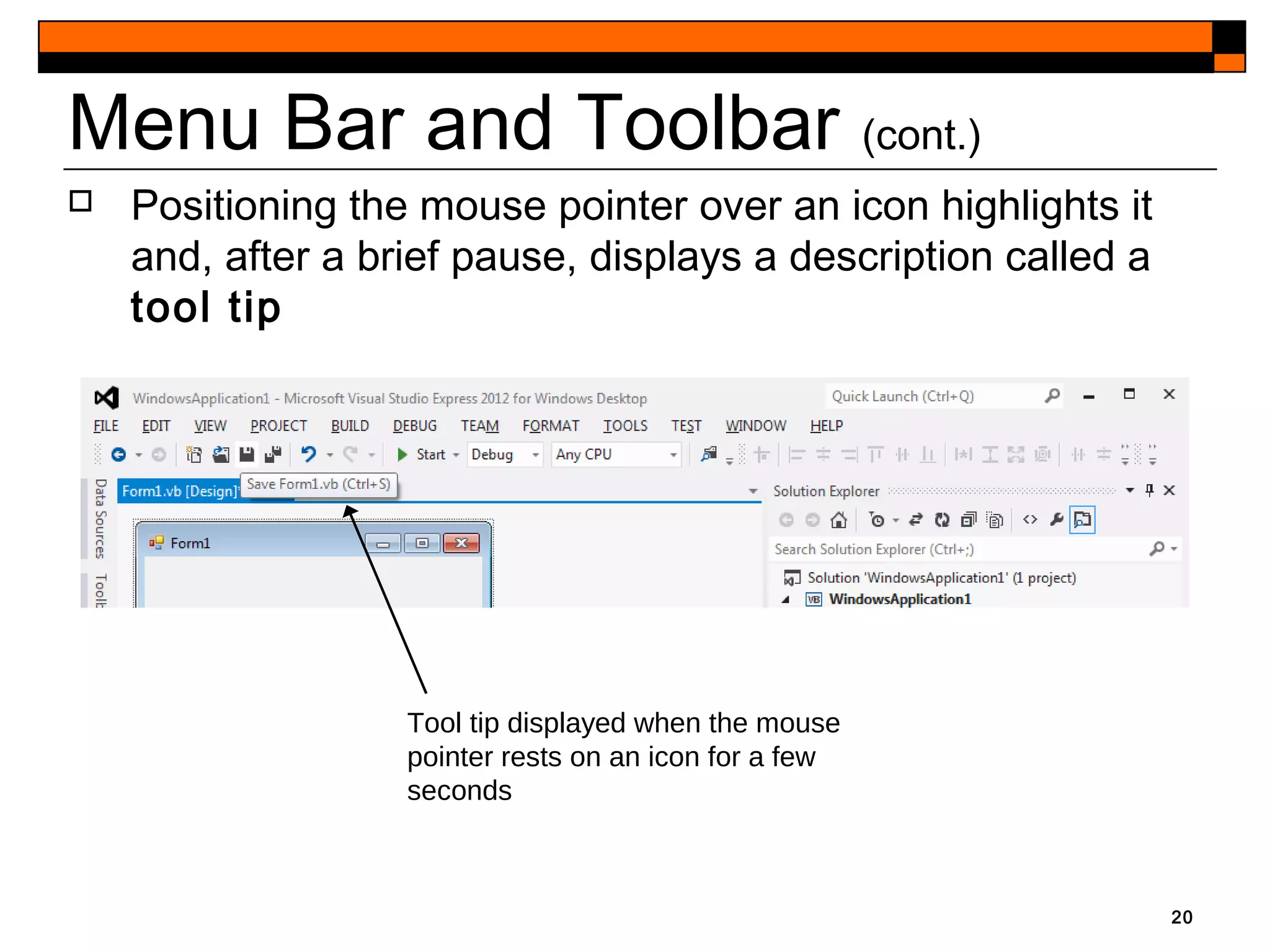
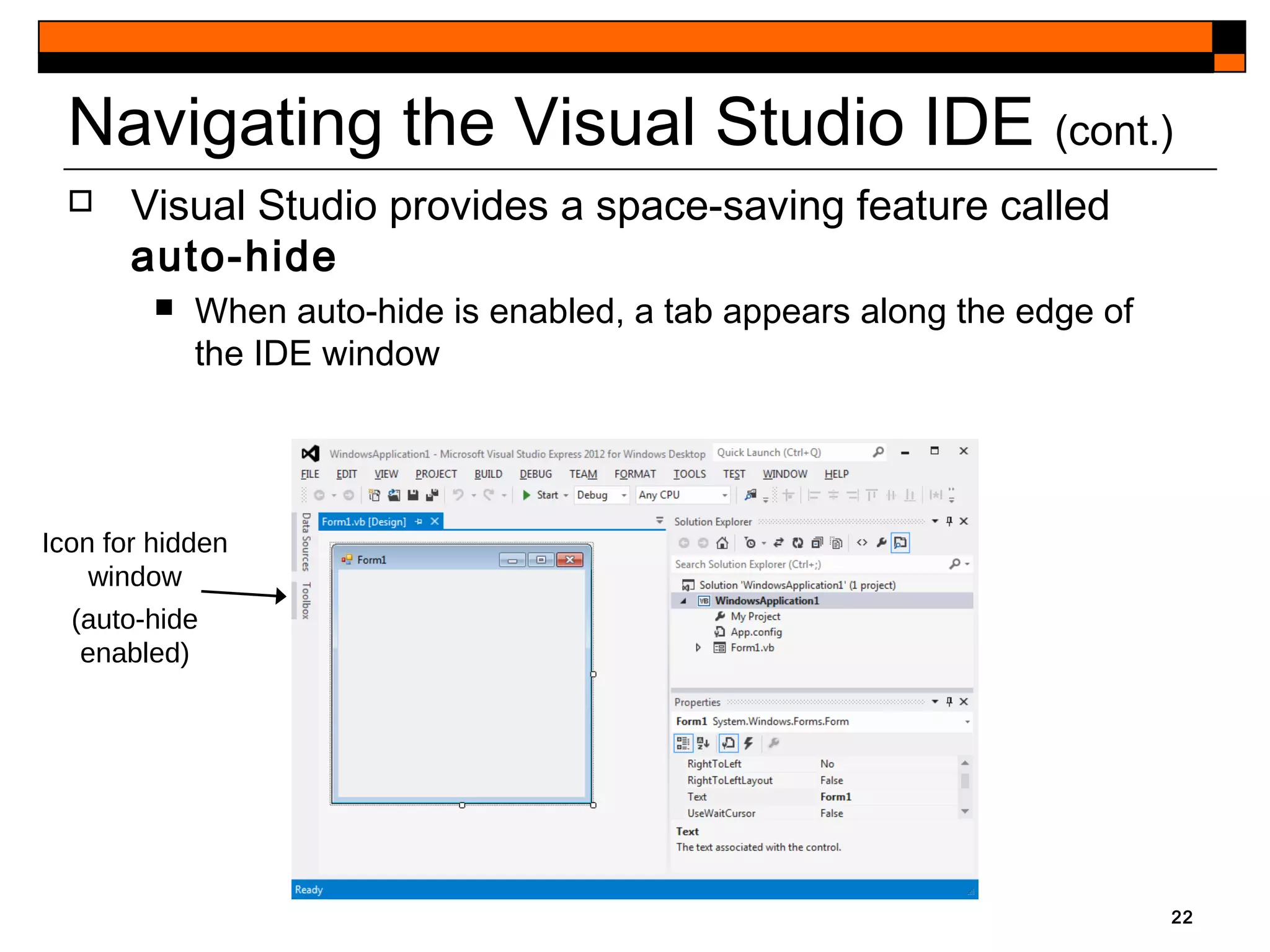
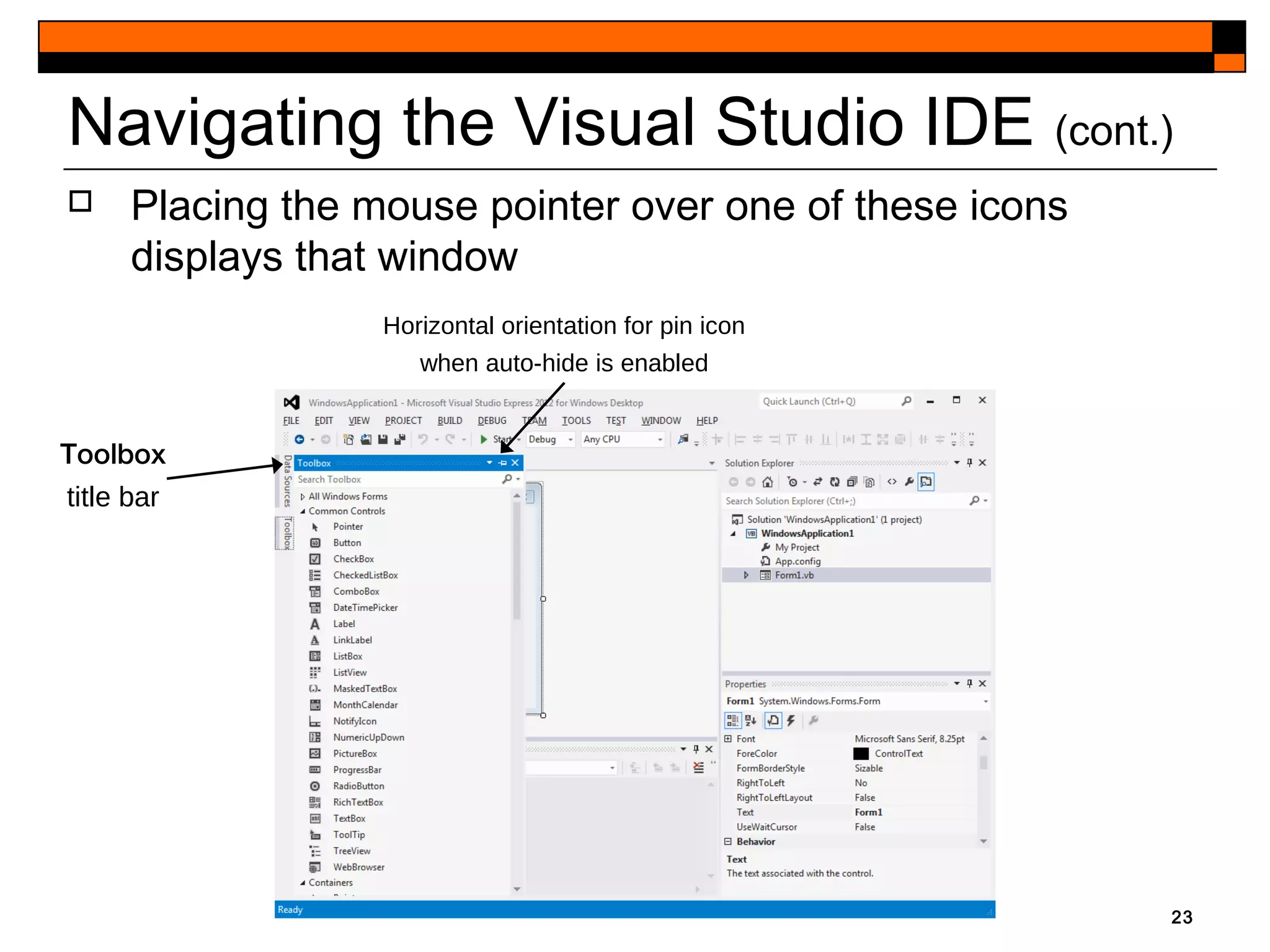
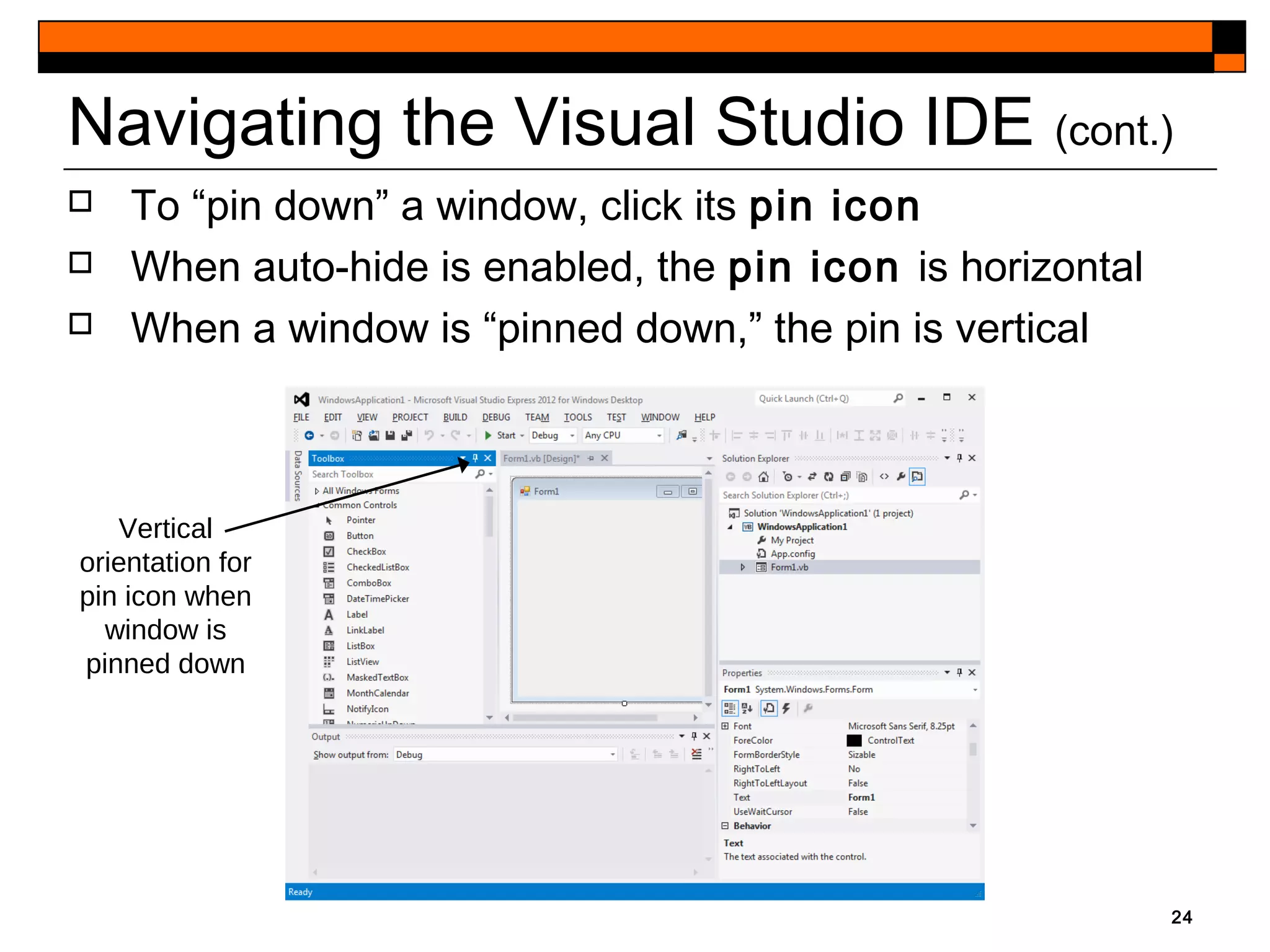
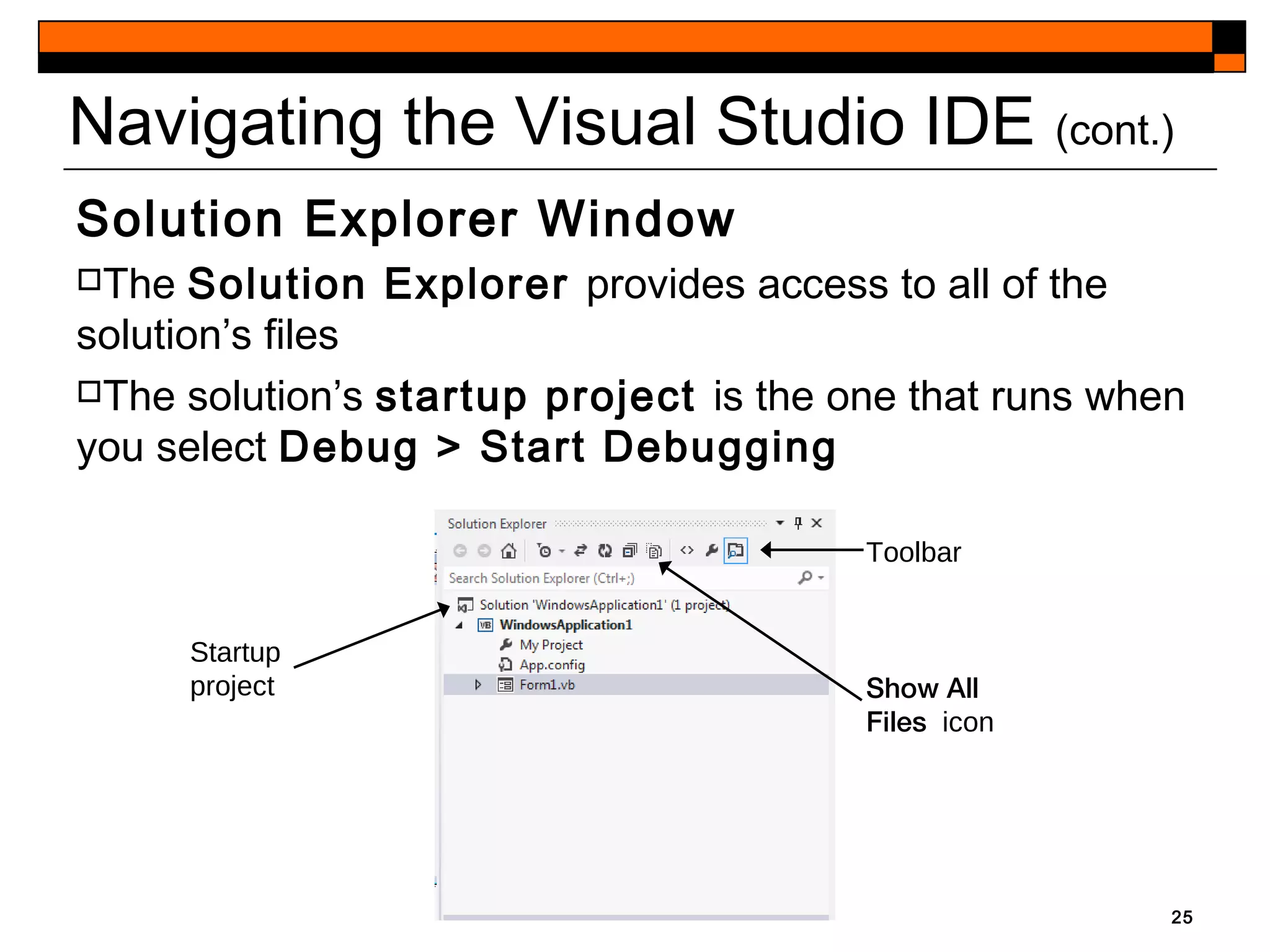
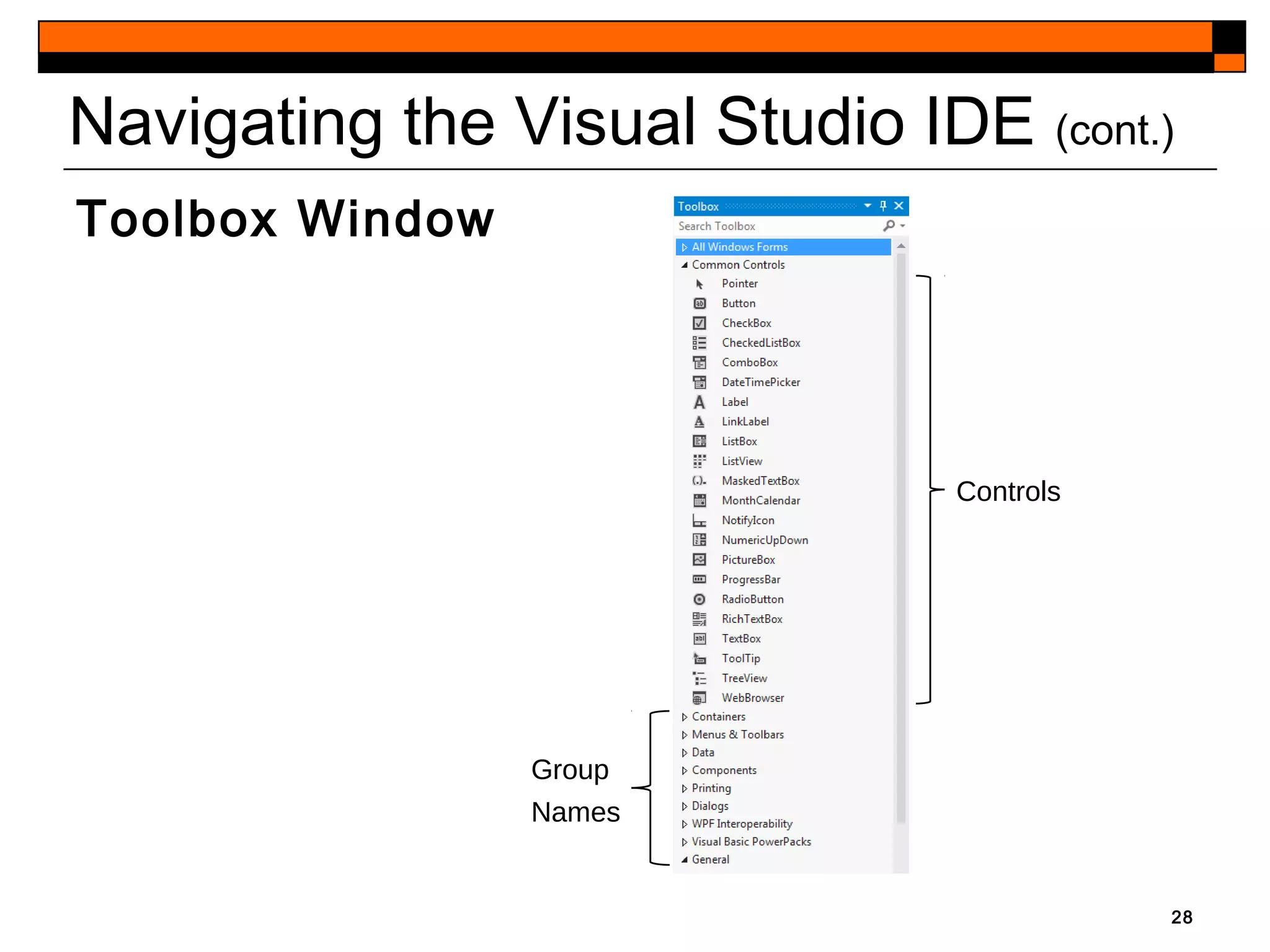
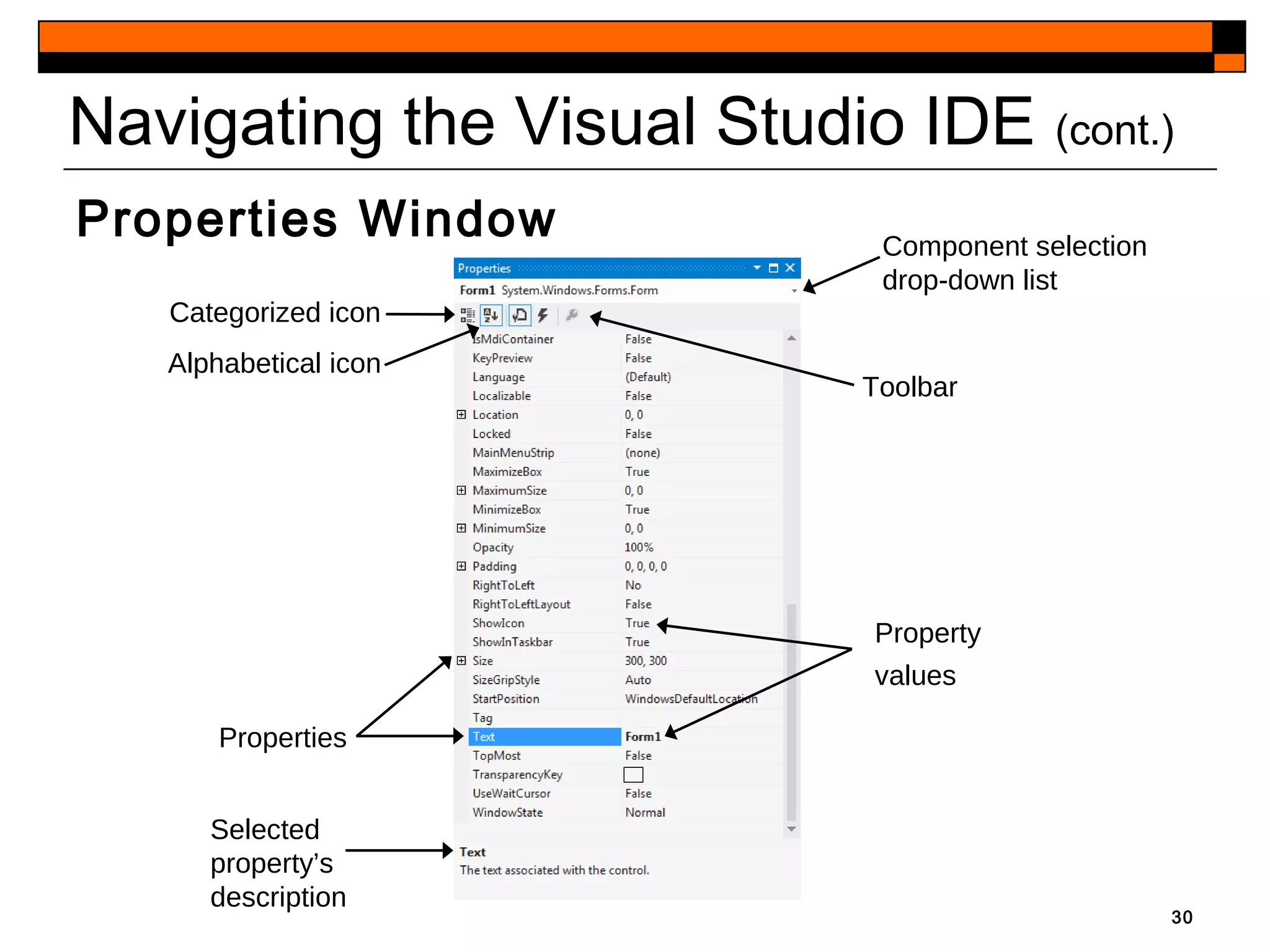
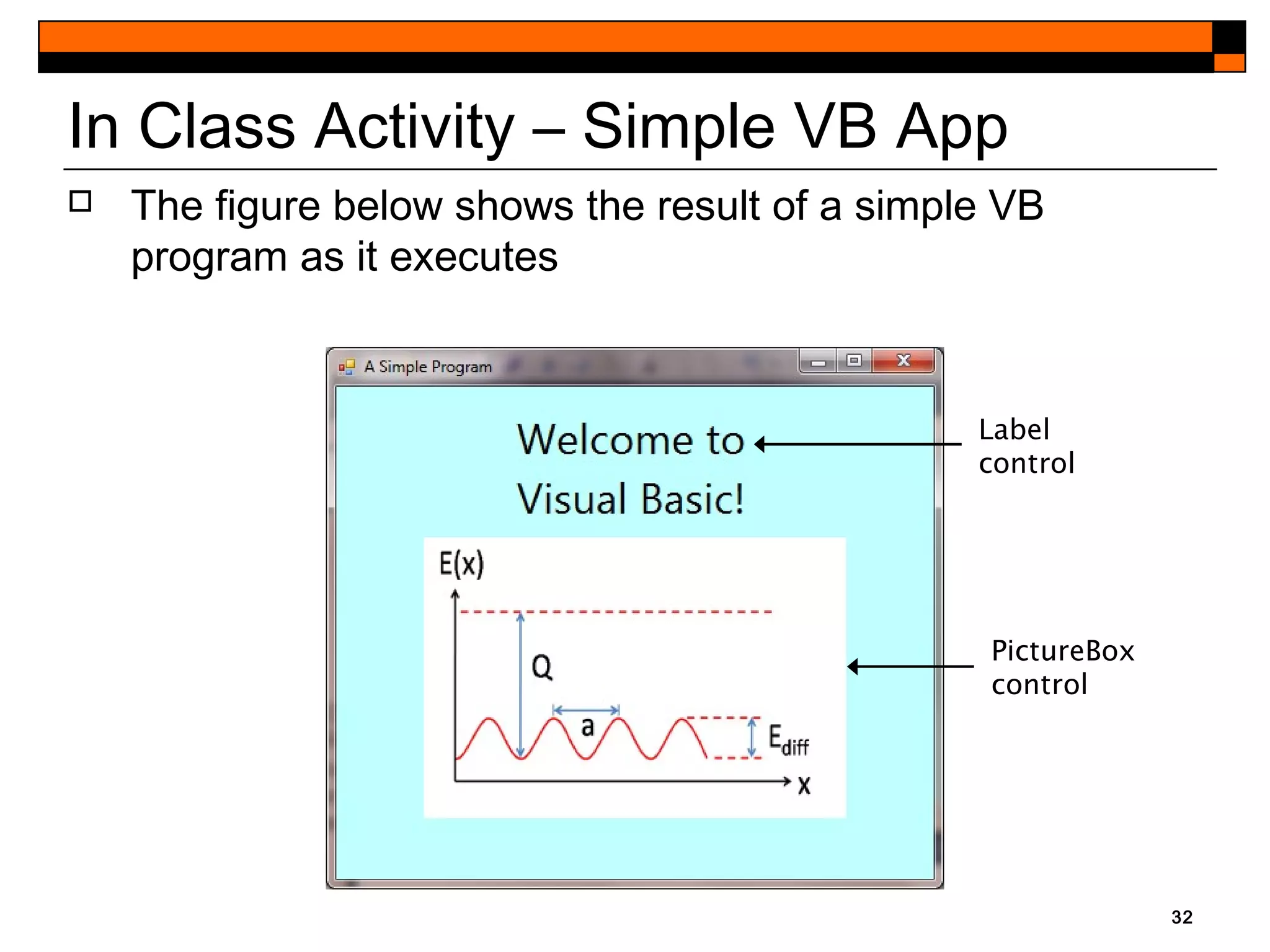
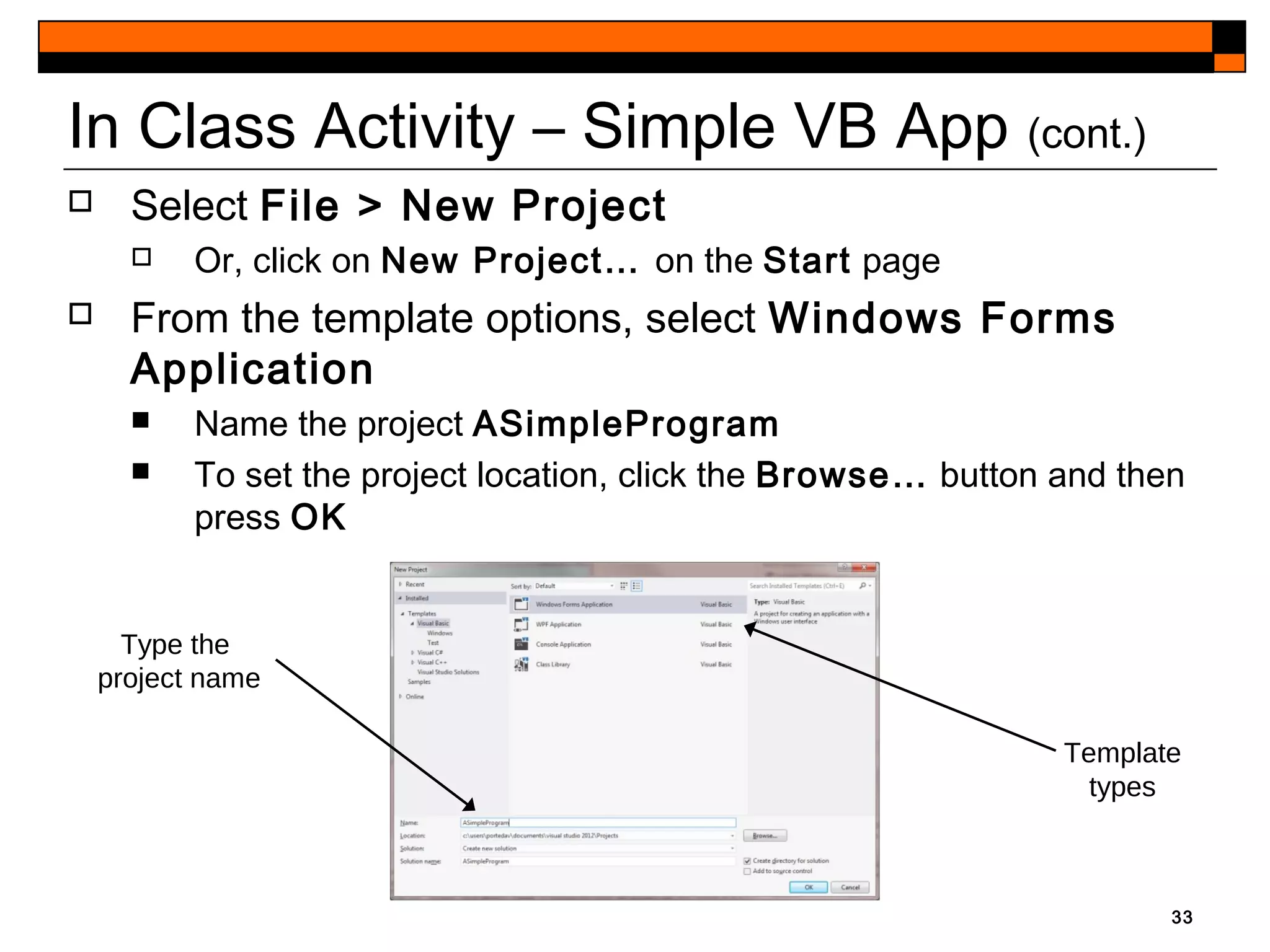
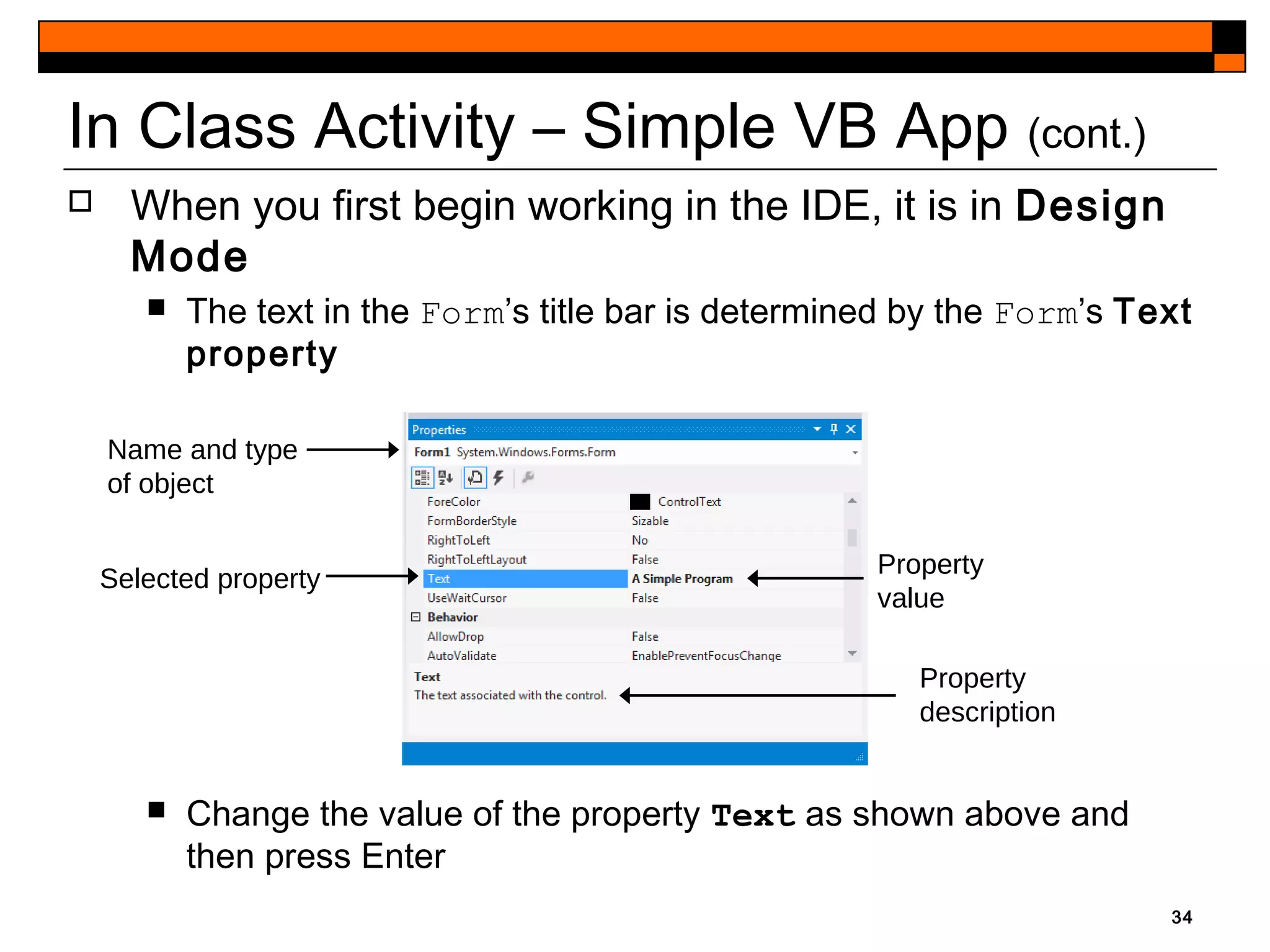
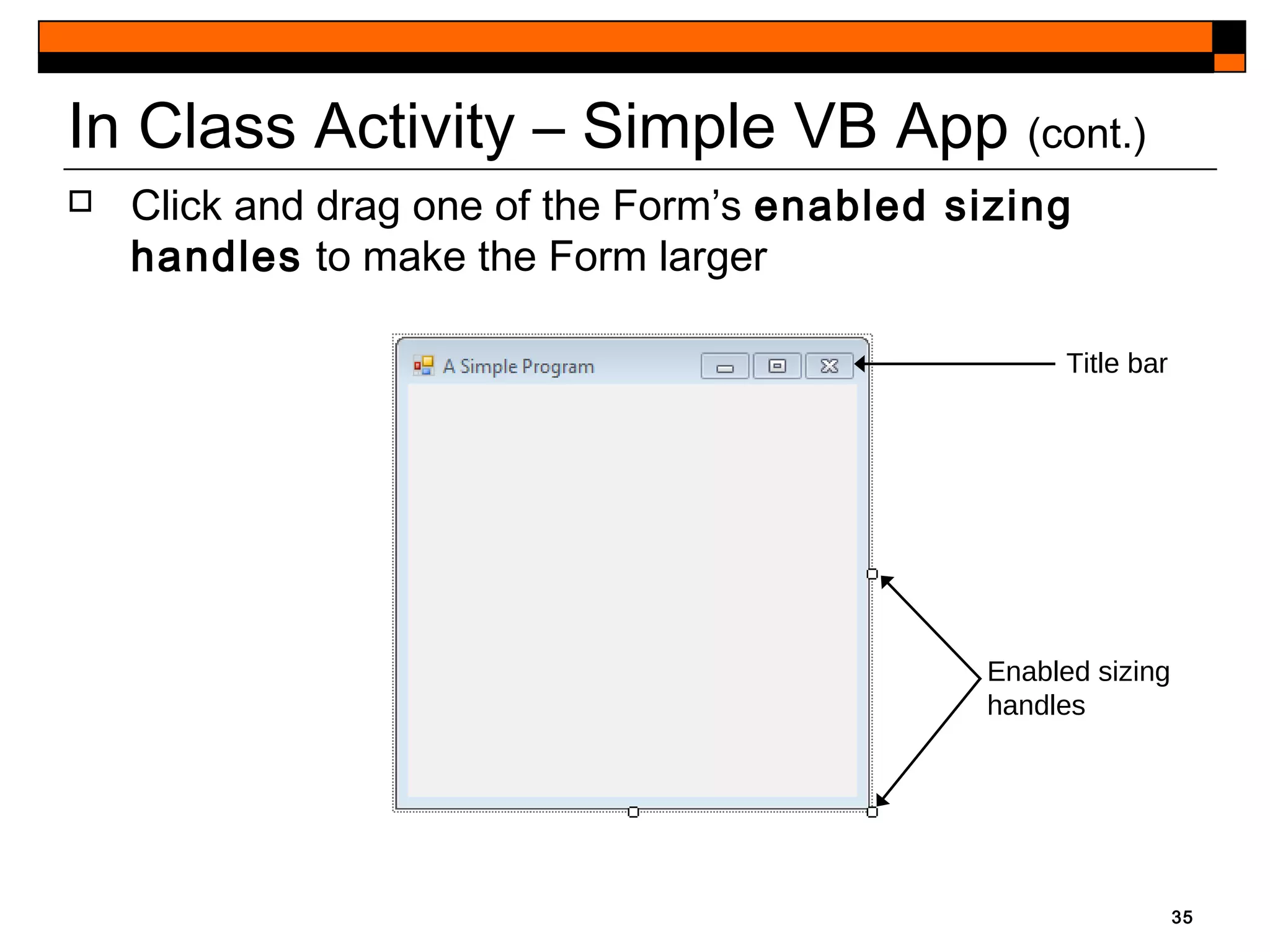
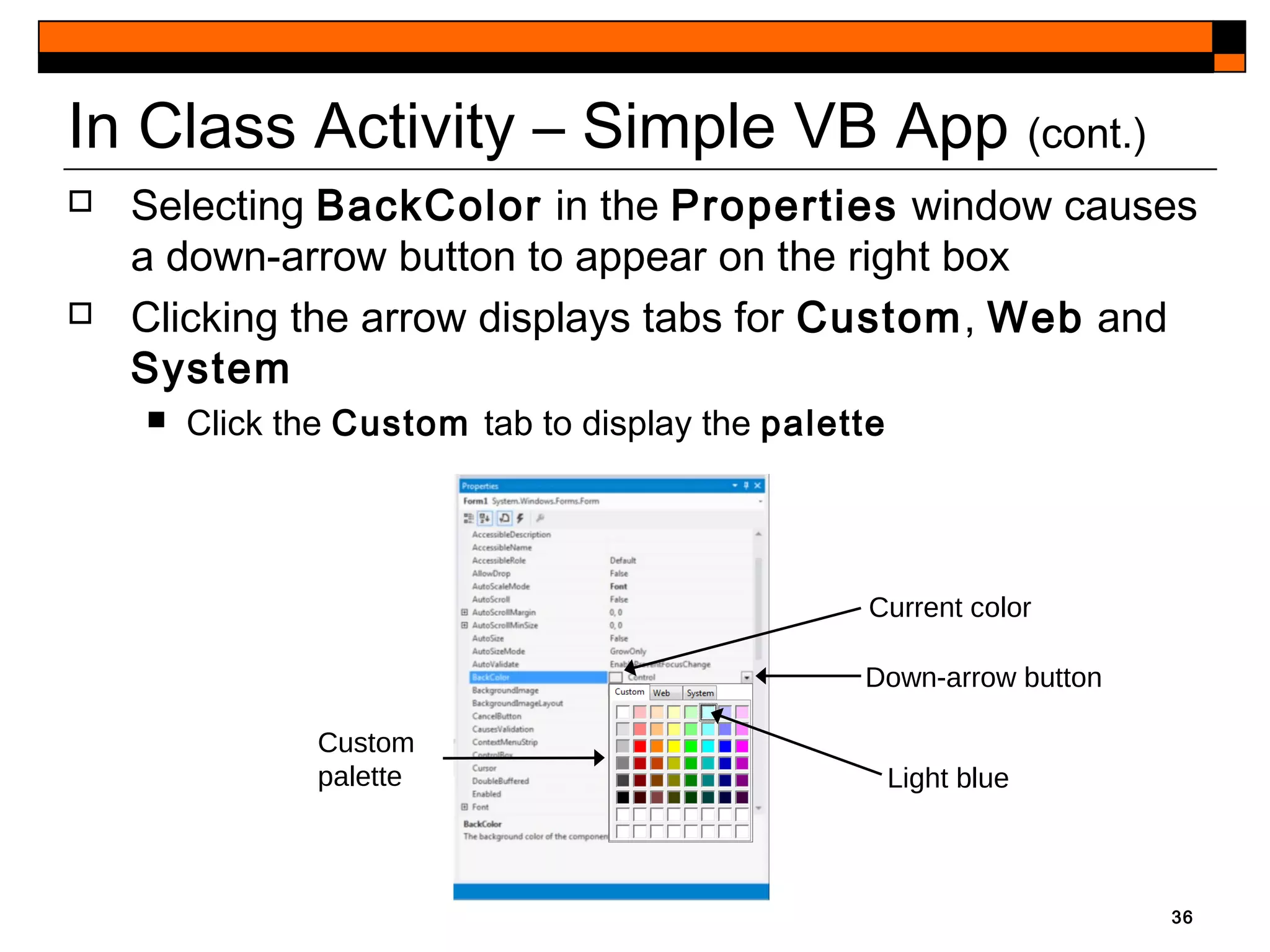
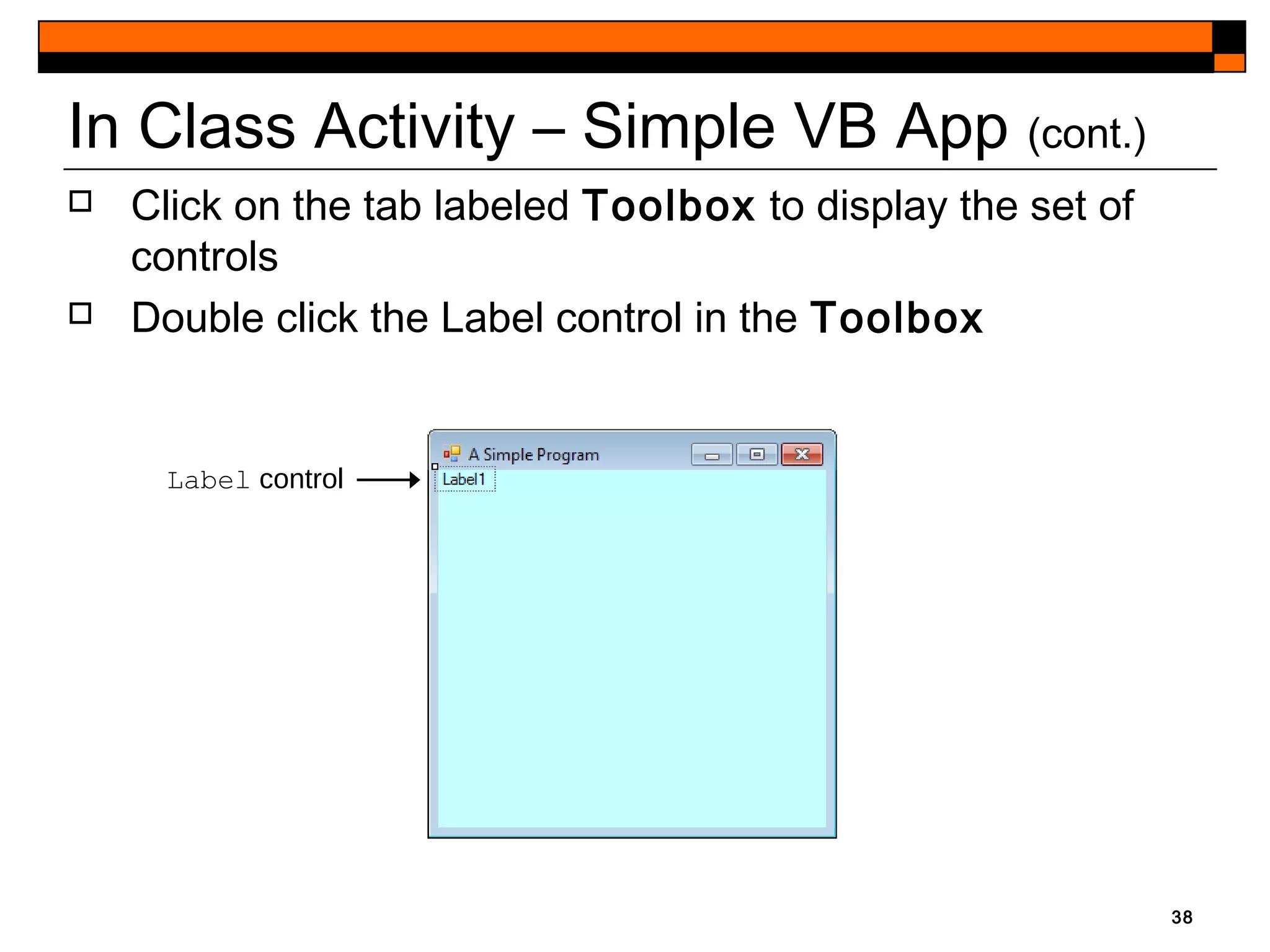
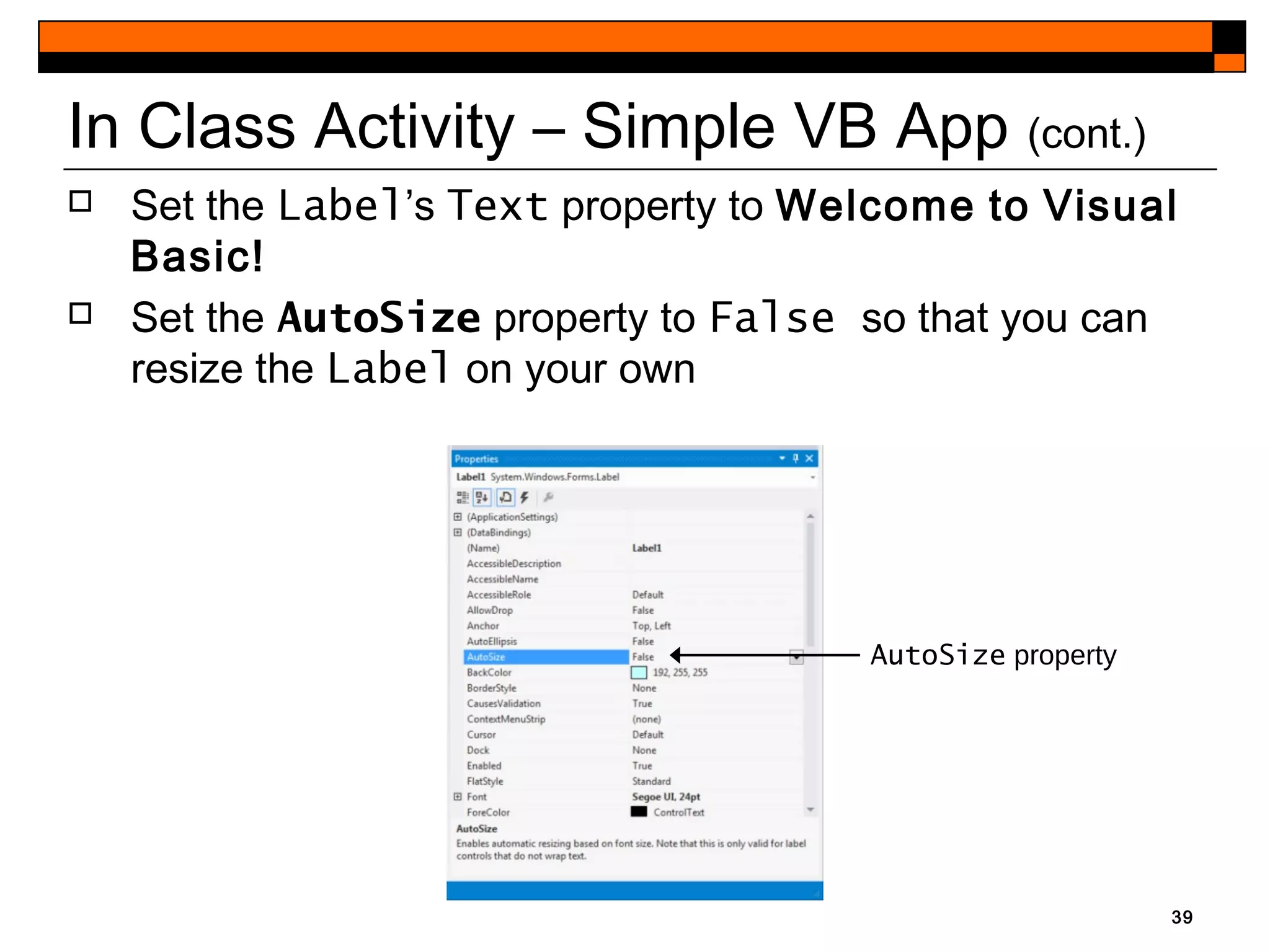
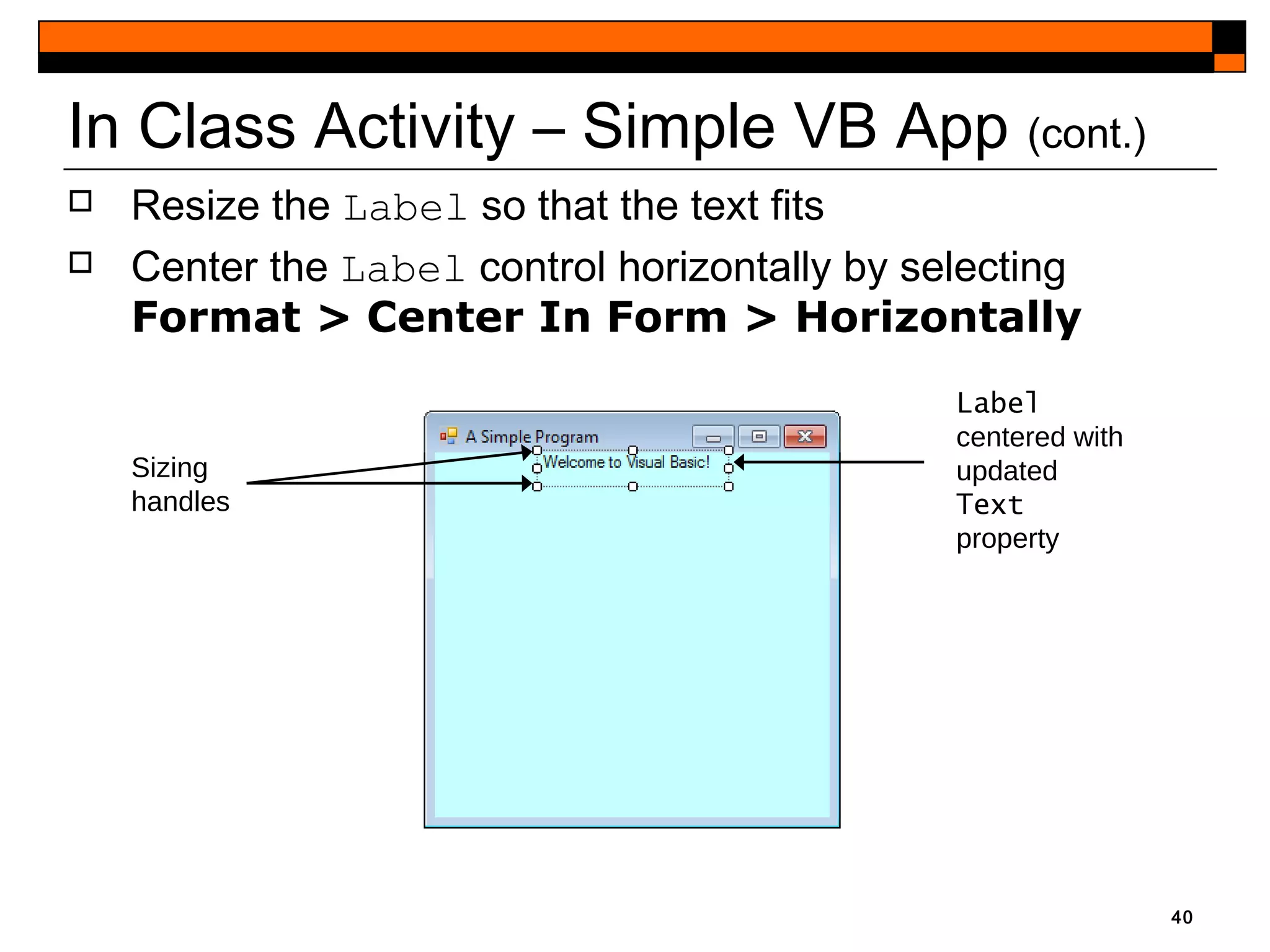
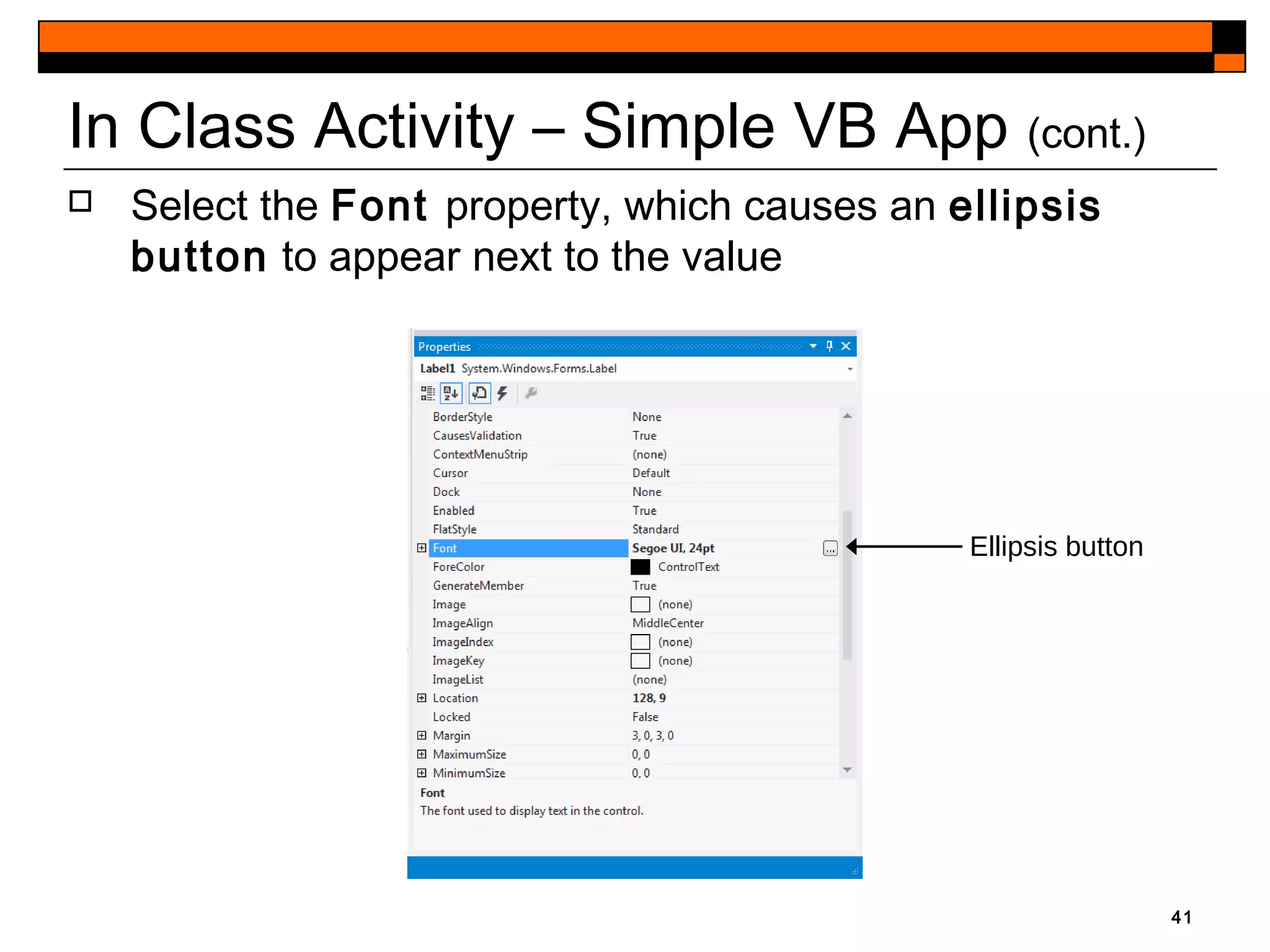
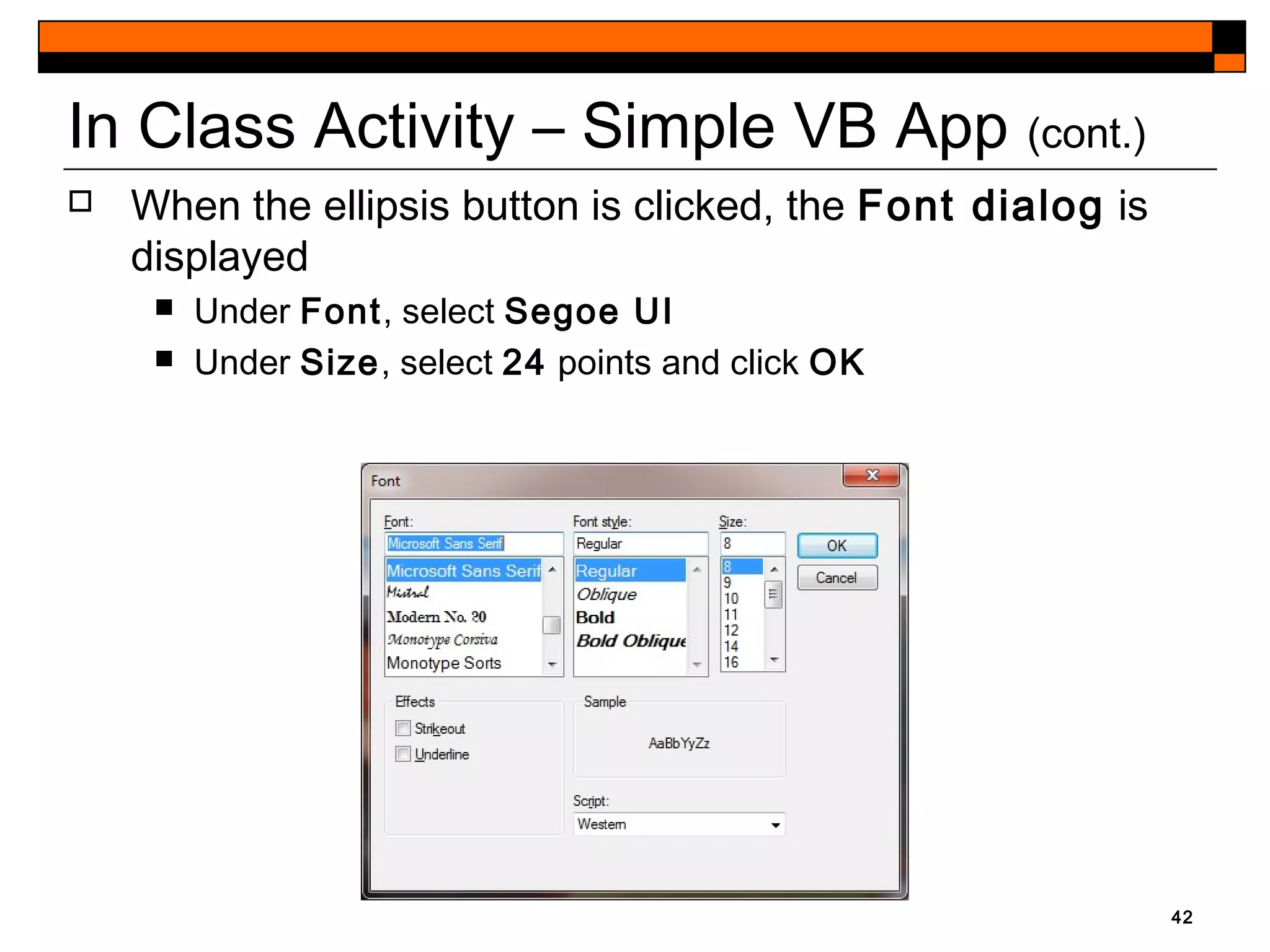
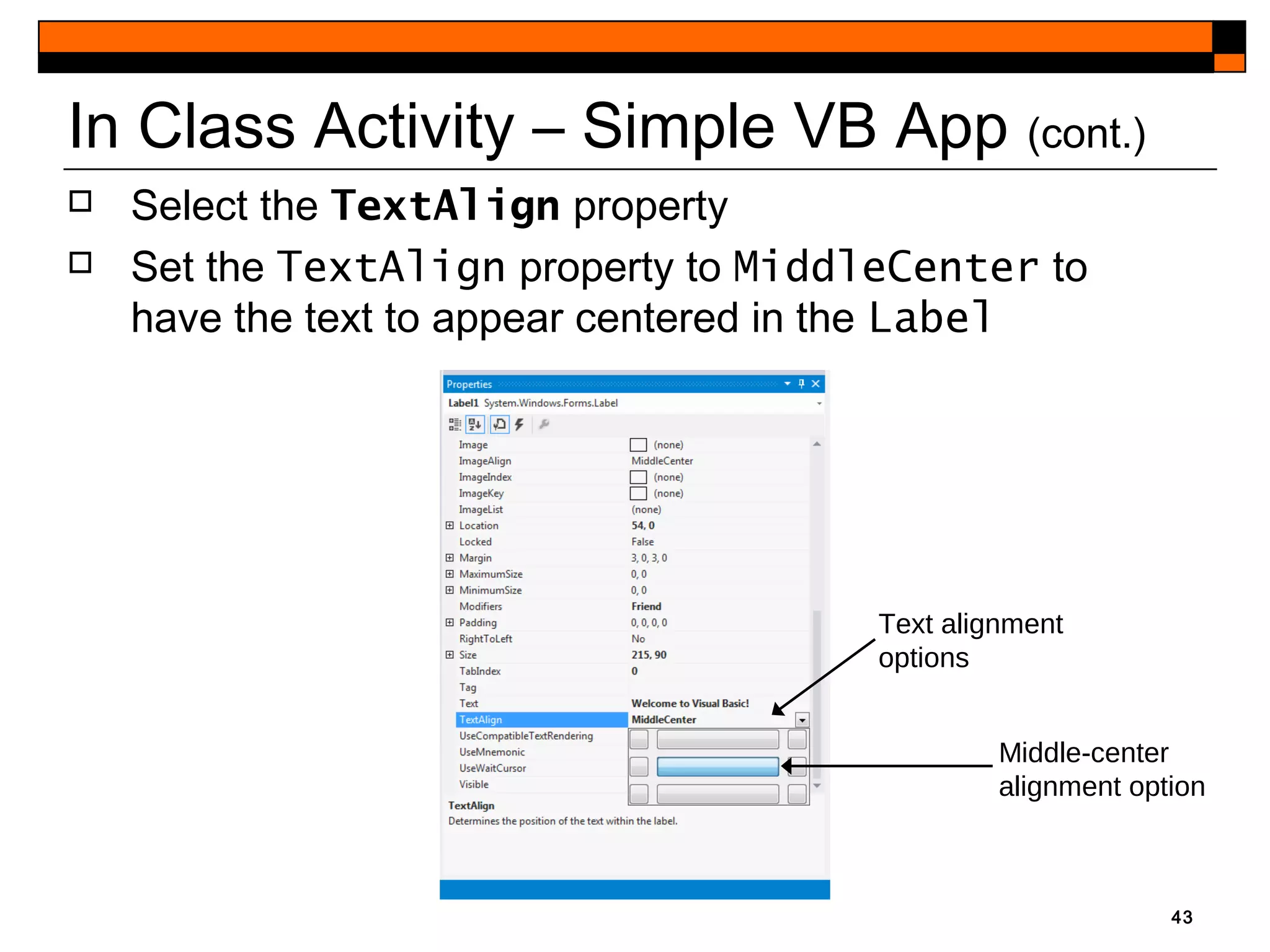
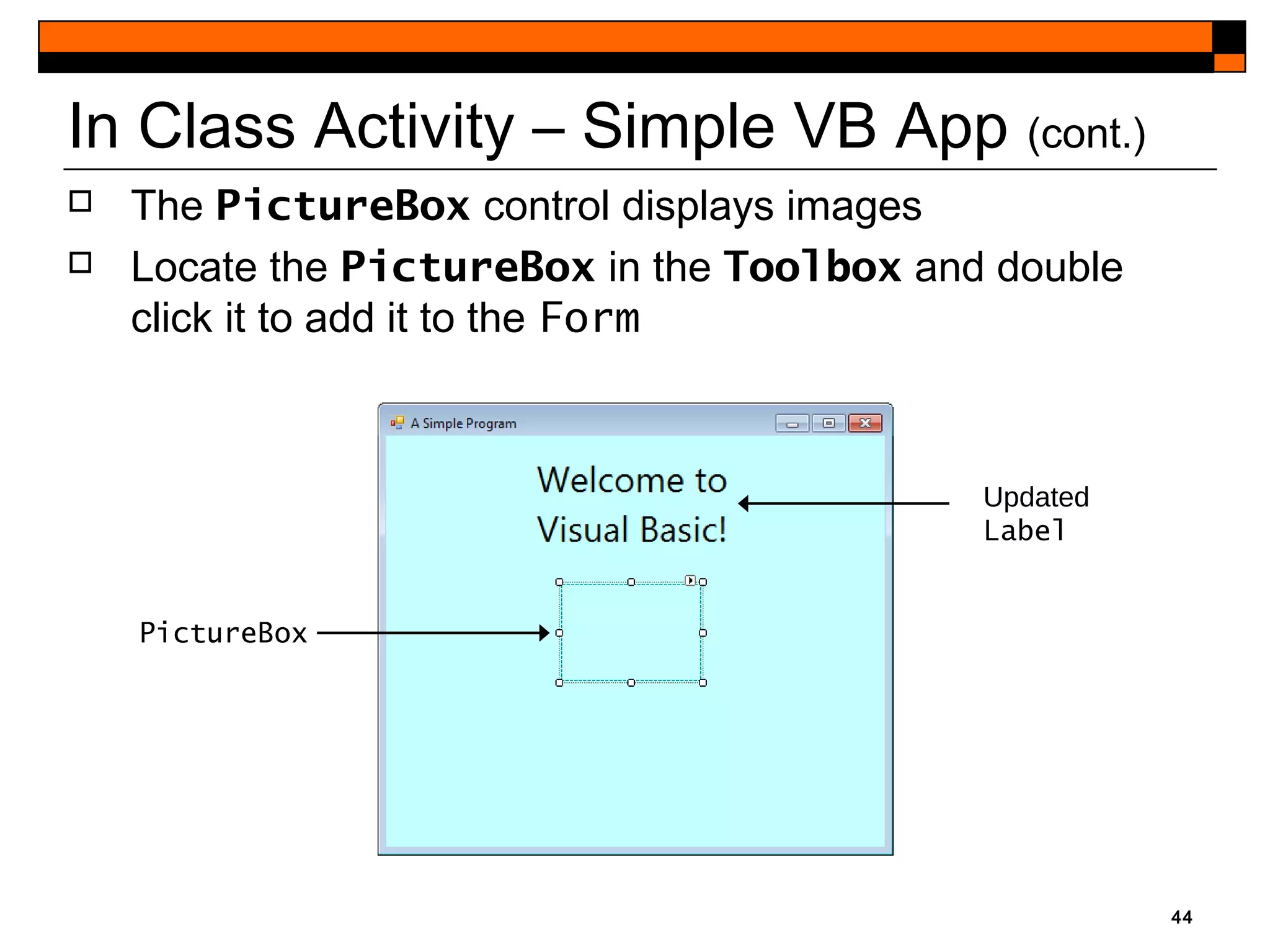
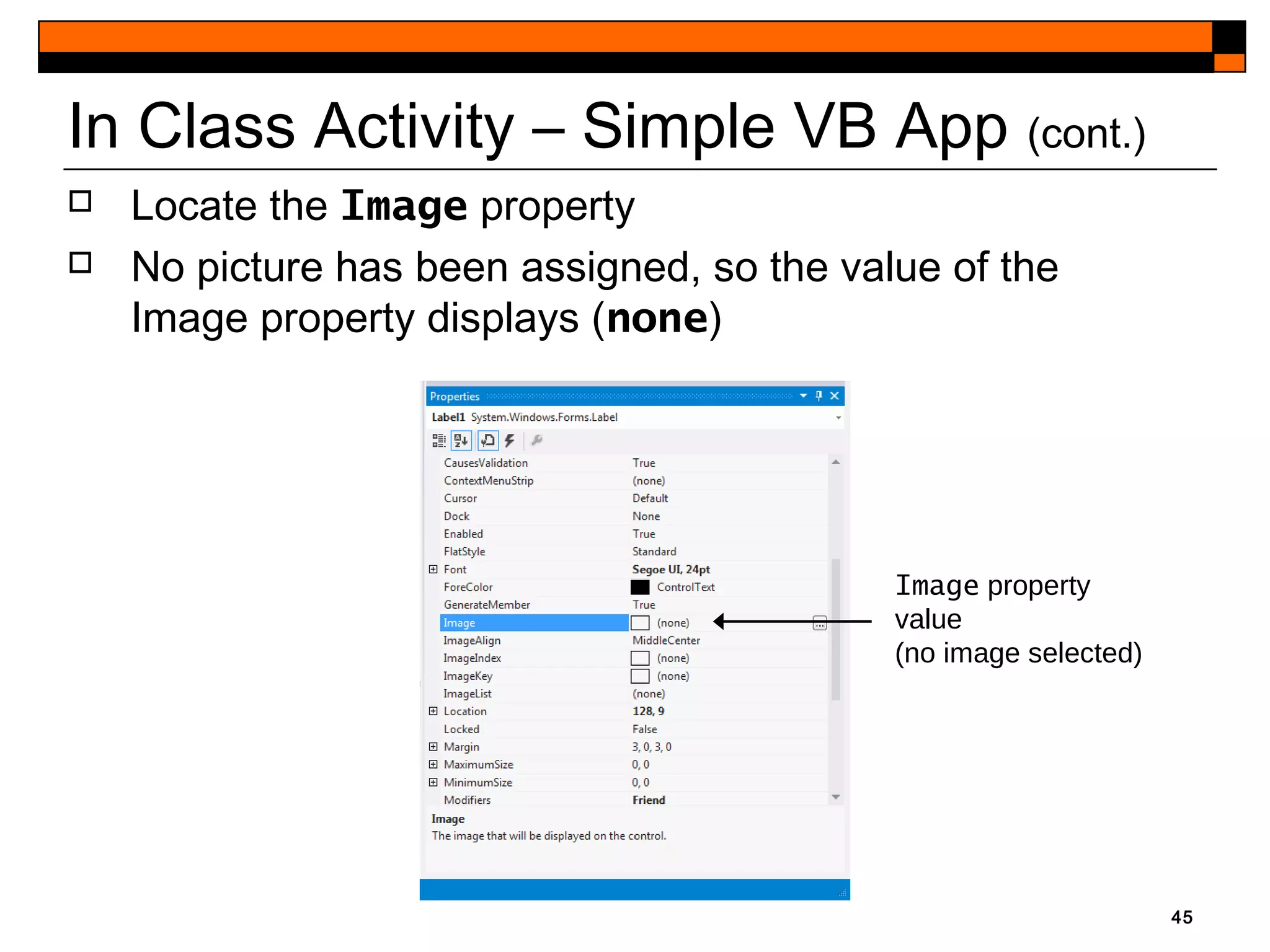
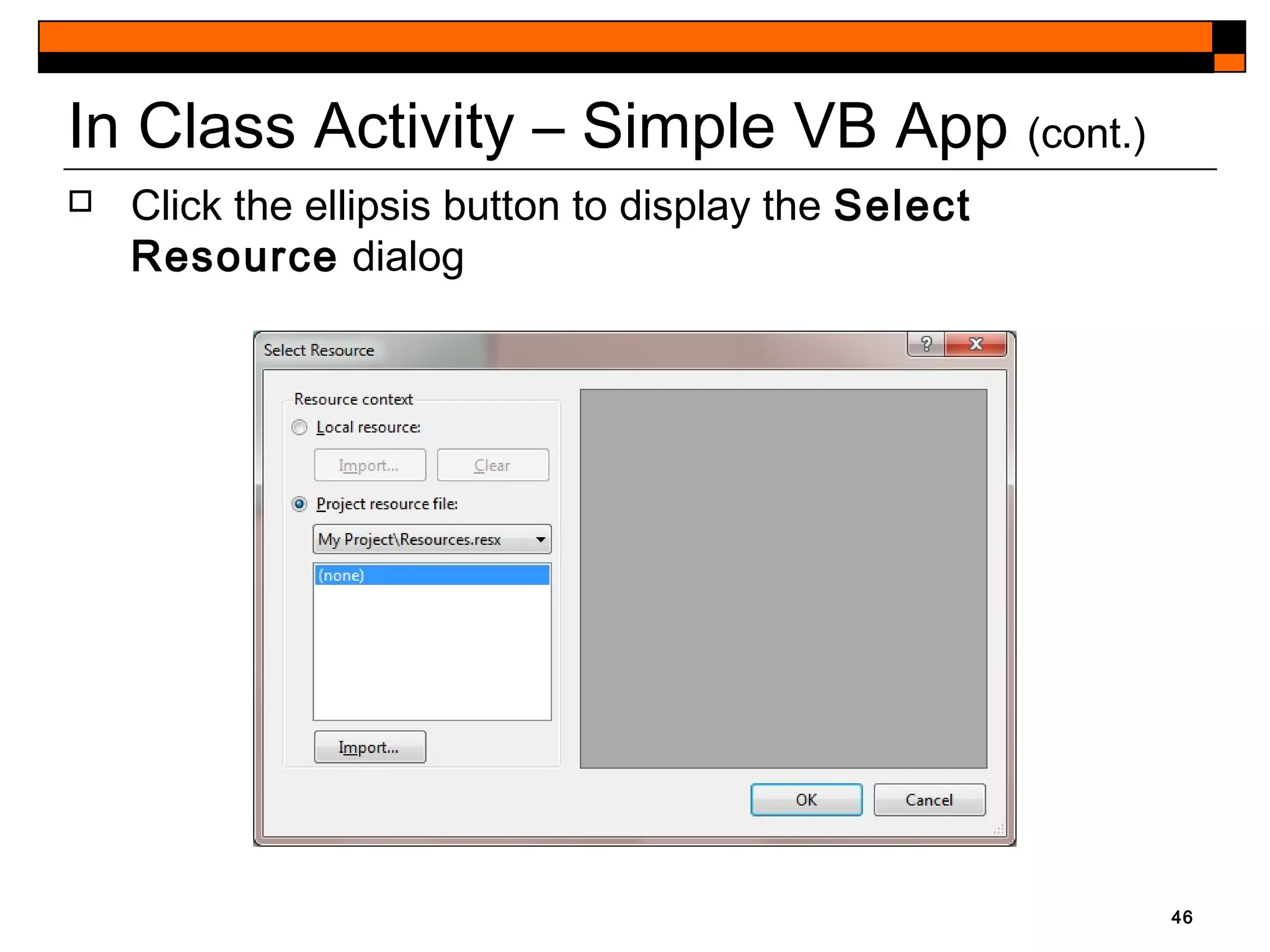
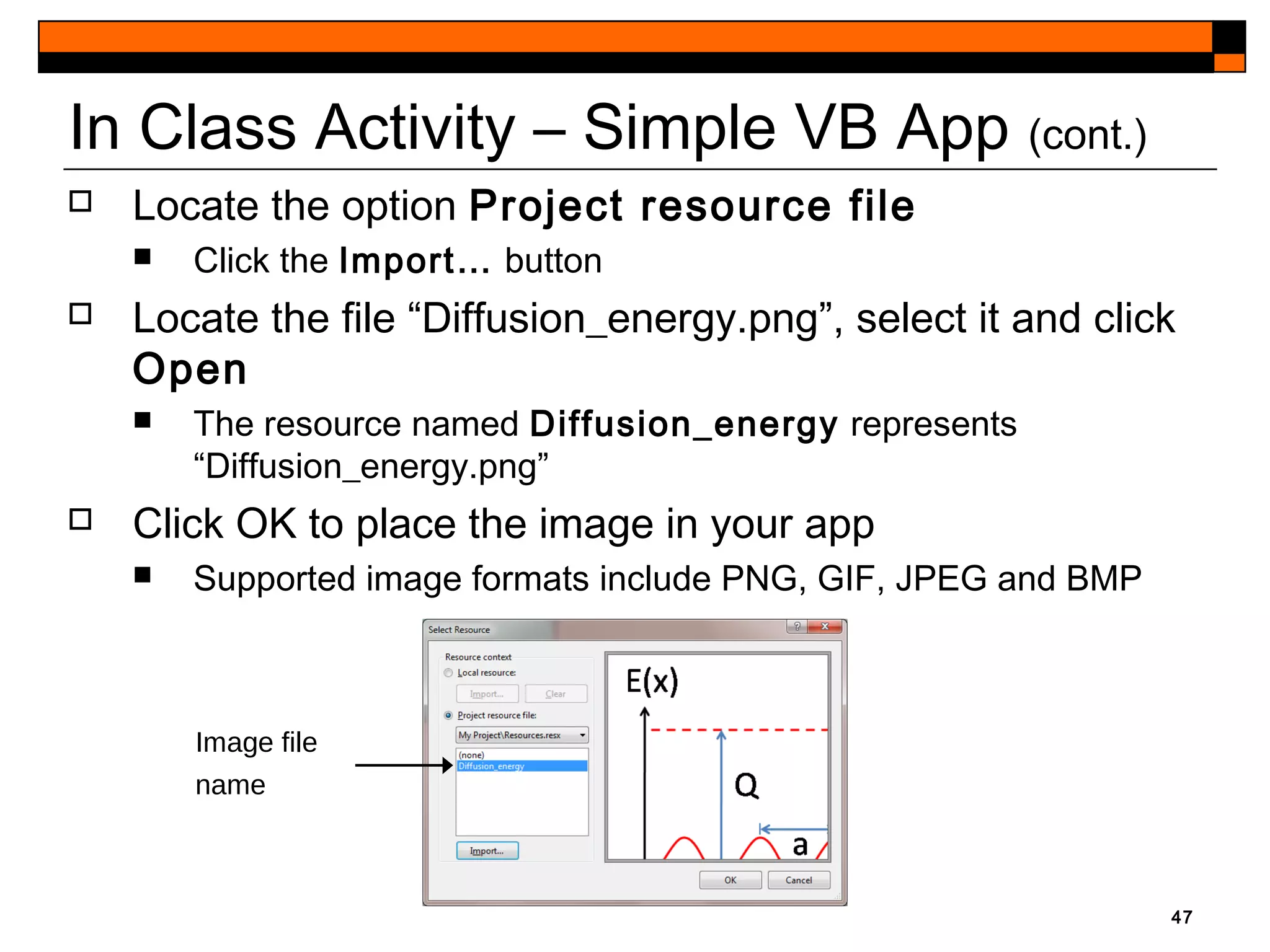
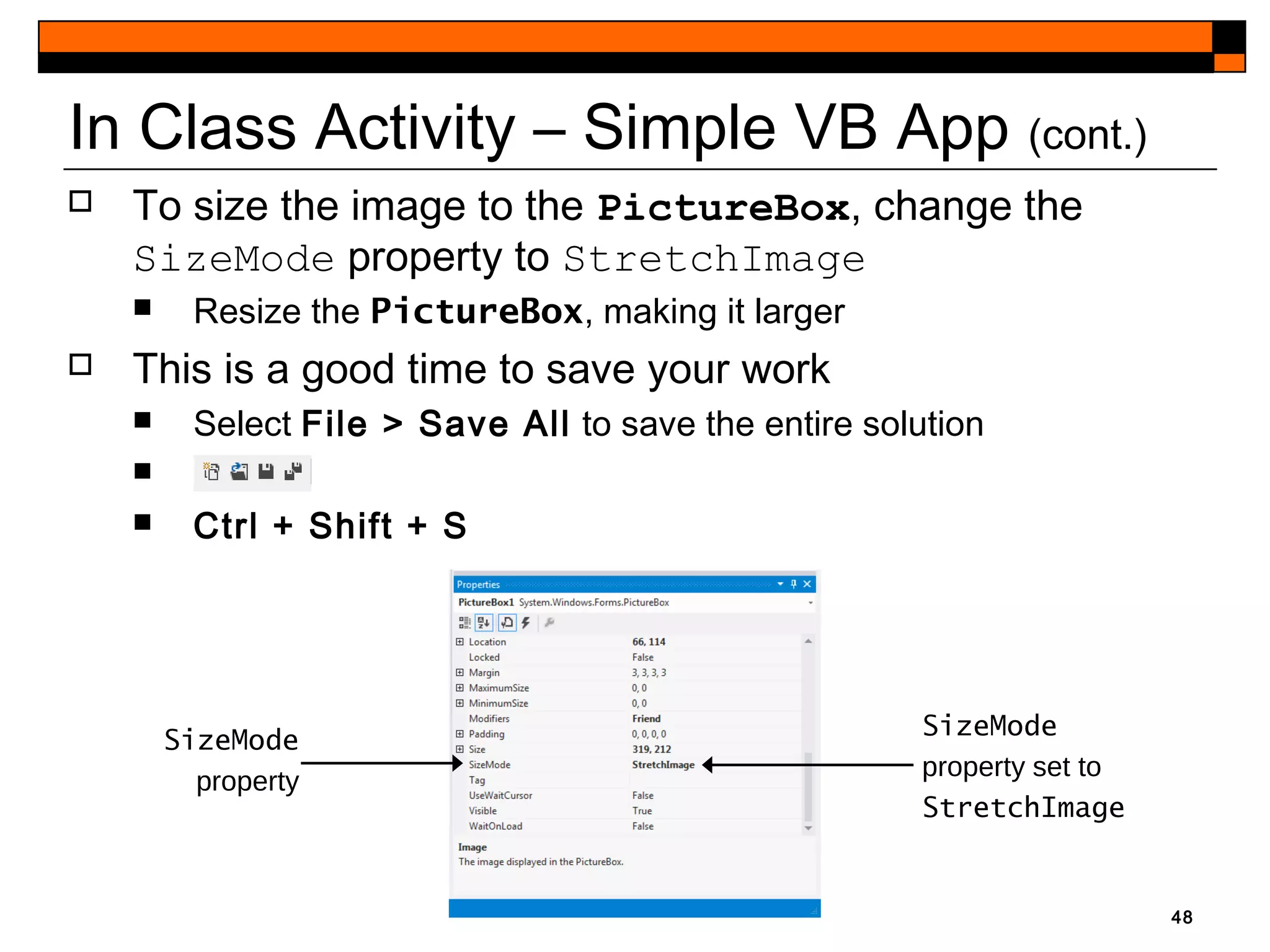
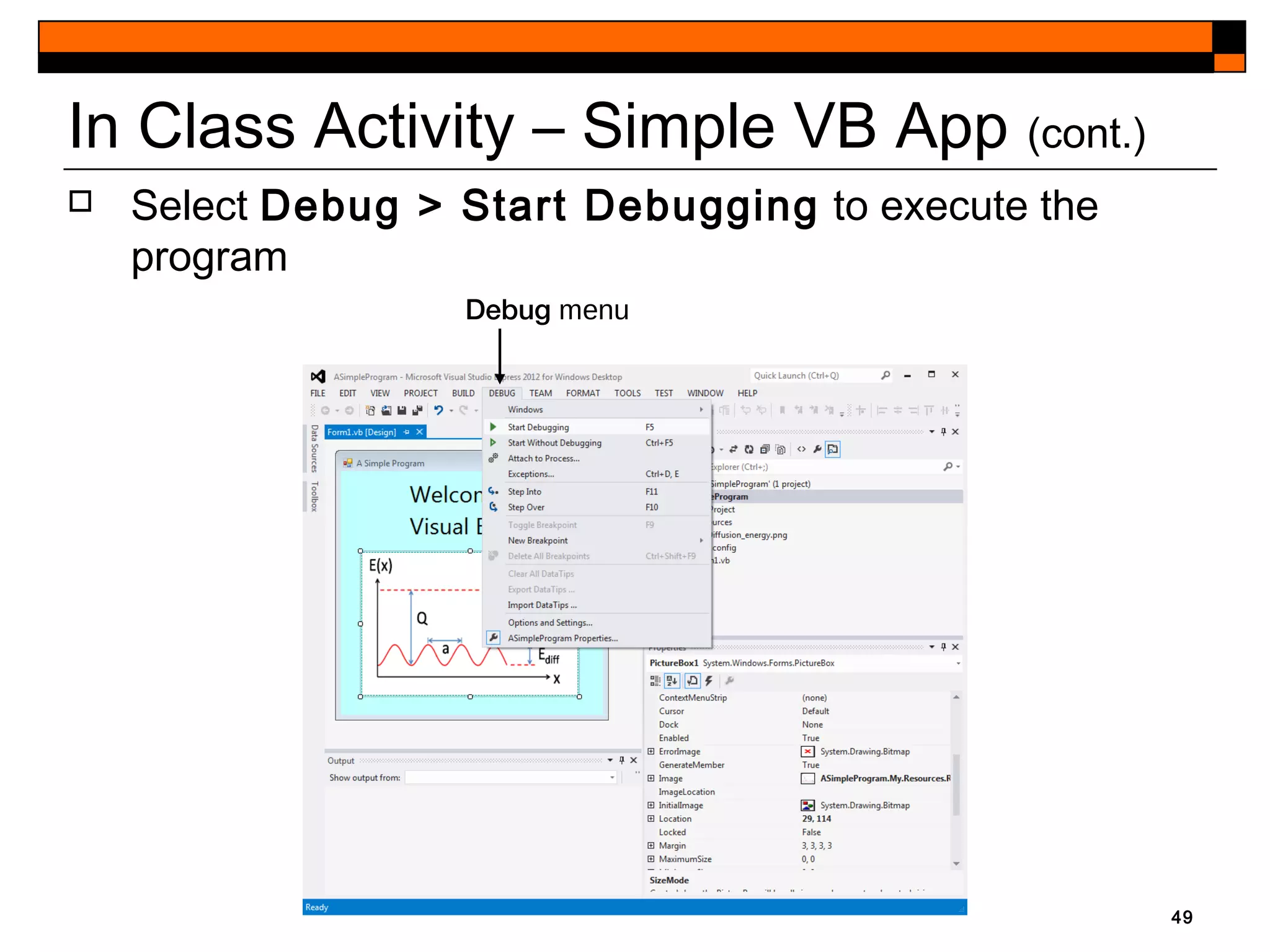
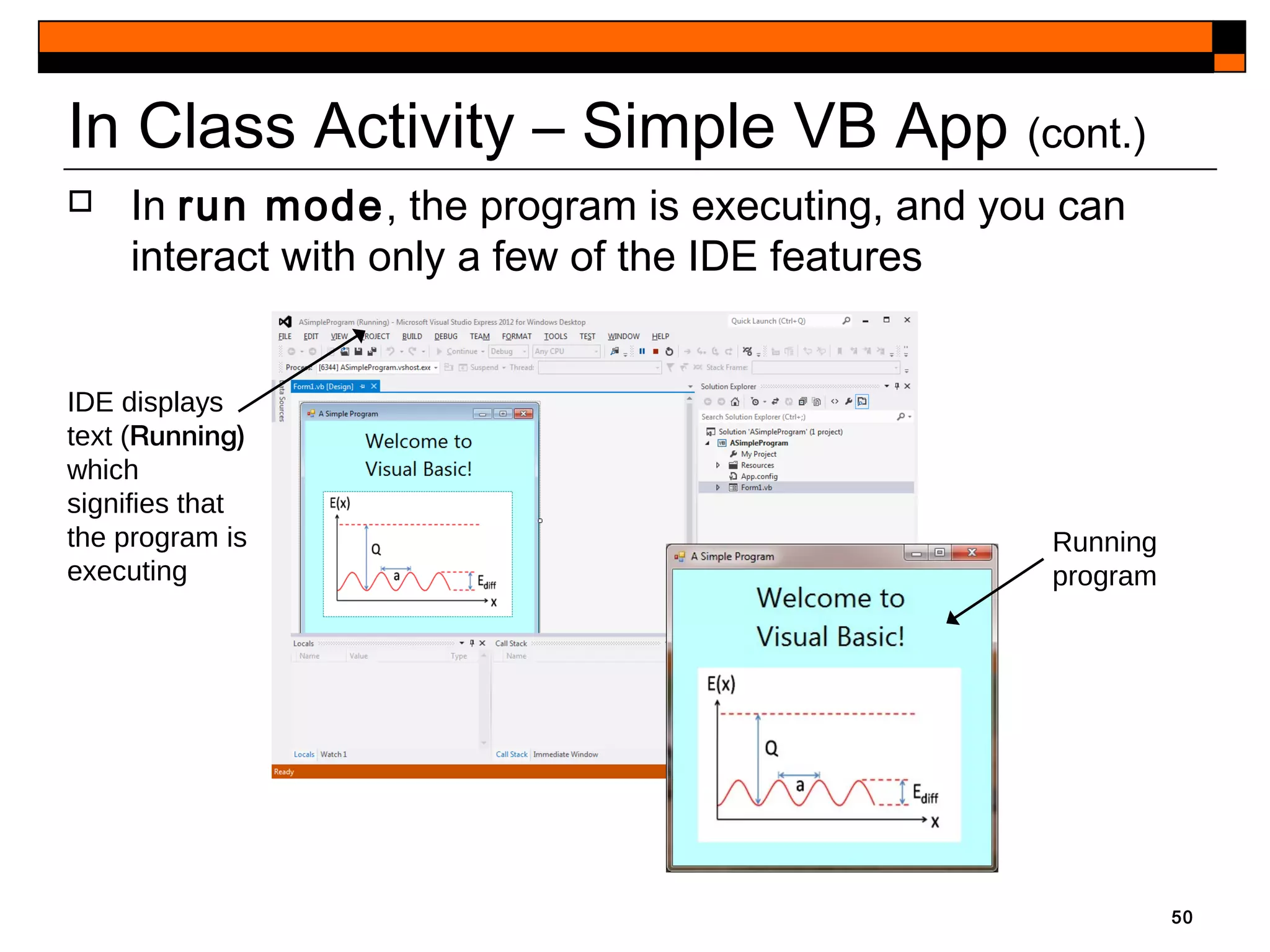
This document provides an introduction to Visual Studio 2012 for Windows desktop integrated development environment (IDE), focusing on creating, running, and debugging applications using Visual Basic. It covers the basics of the IDE, including managing projects, utilizing help features, and the components of the interface, such as the toolbox and properties window. The module includes instructions for developing a simple Visual Basic app through visual app development, emphasizing drag-and-drop functionality and property modification.