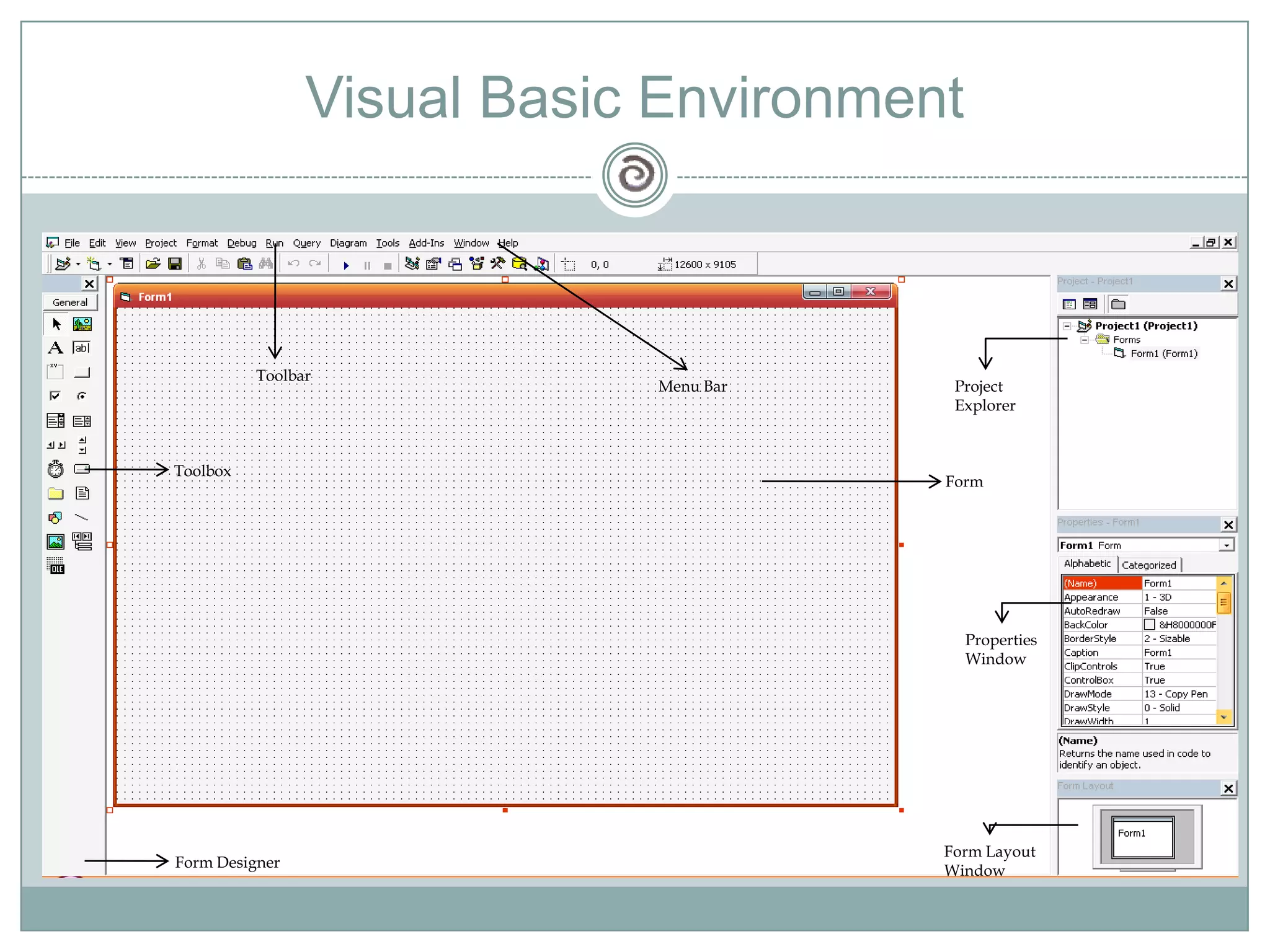
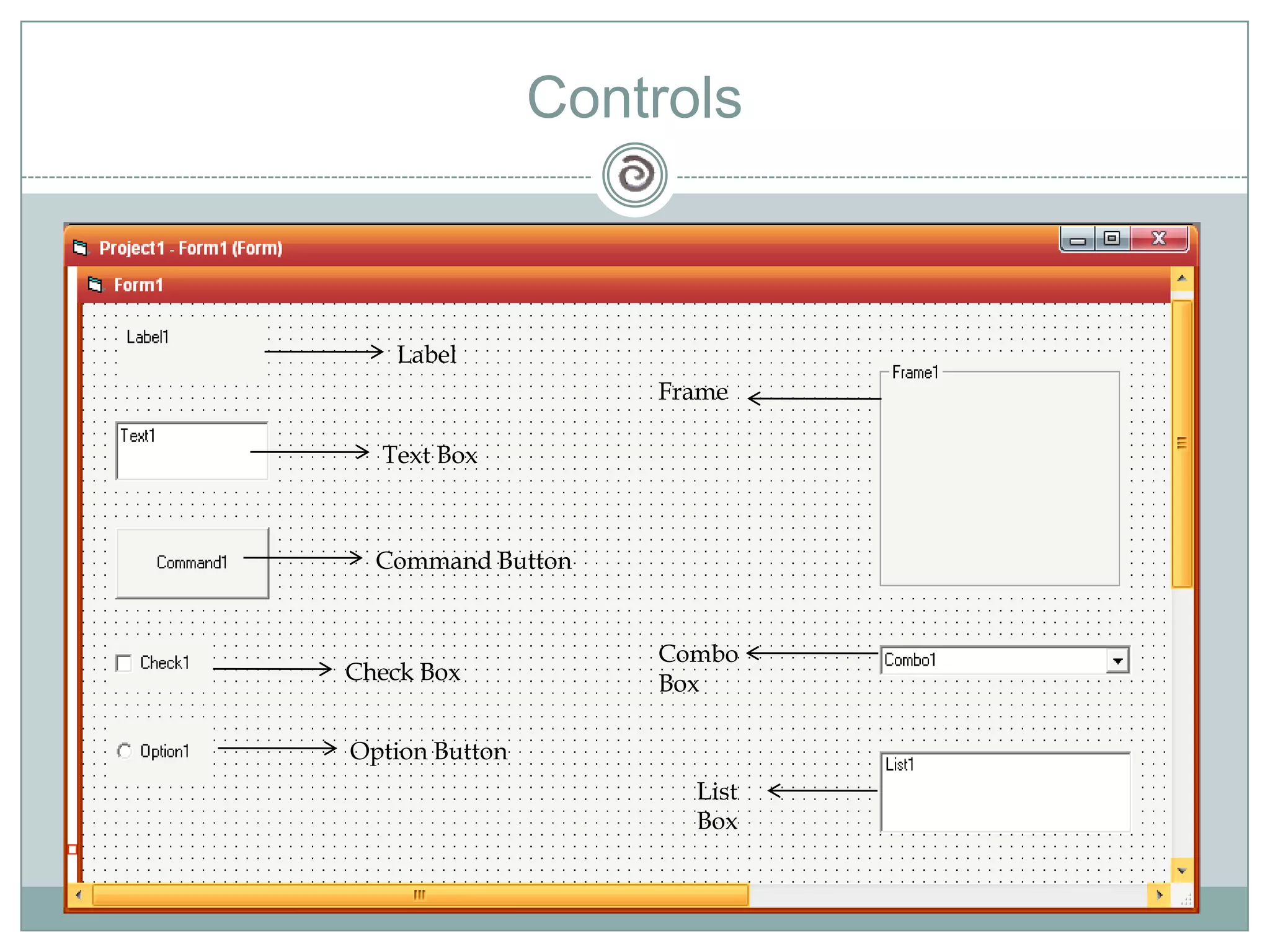
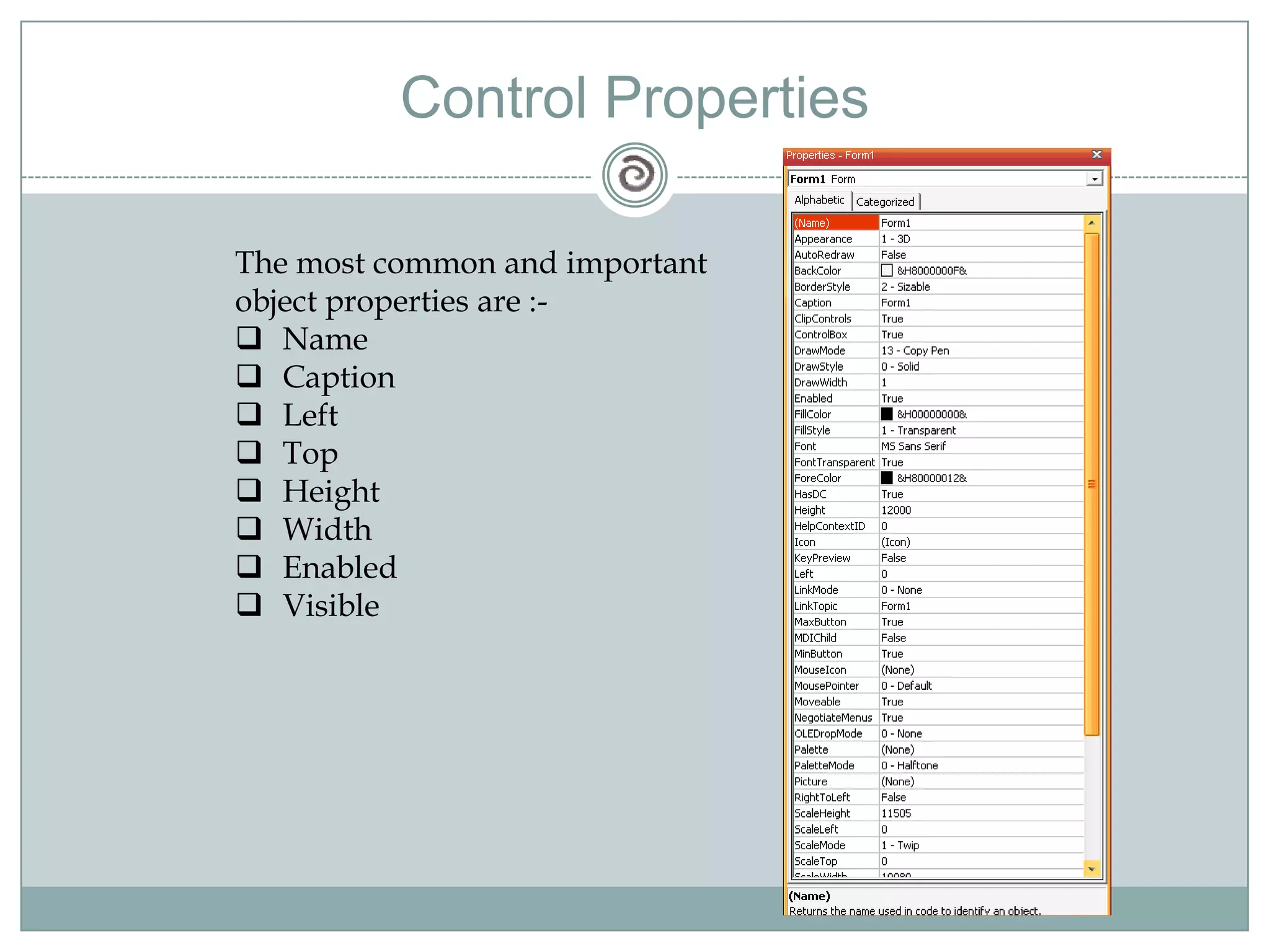
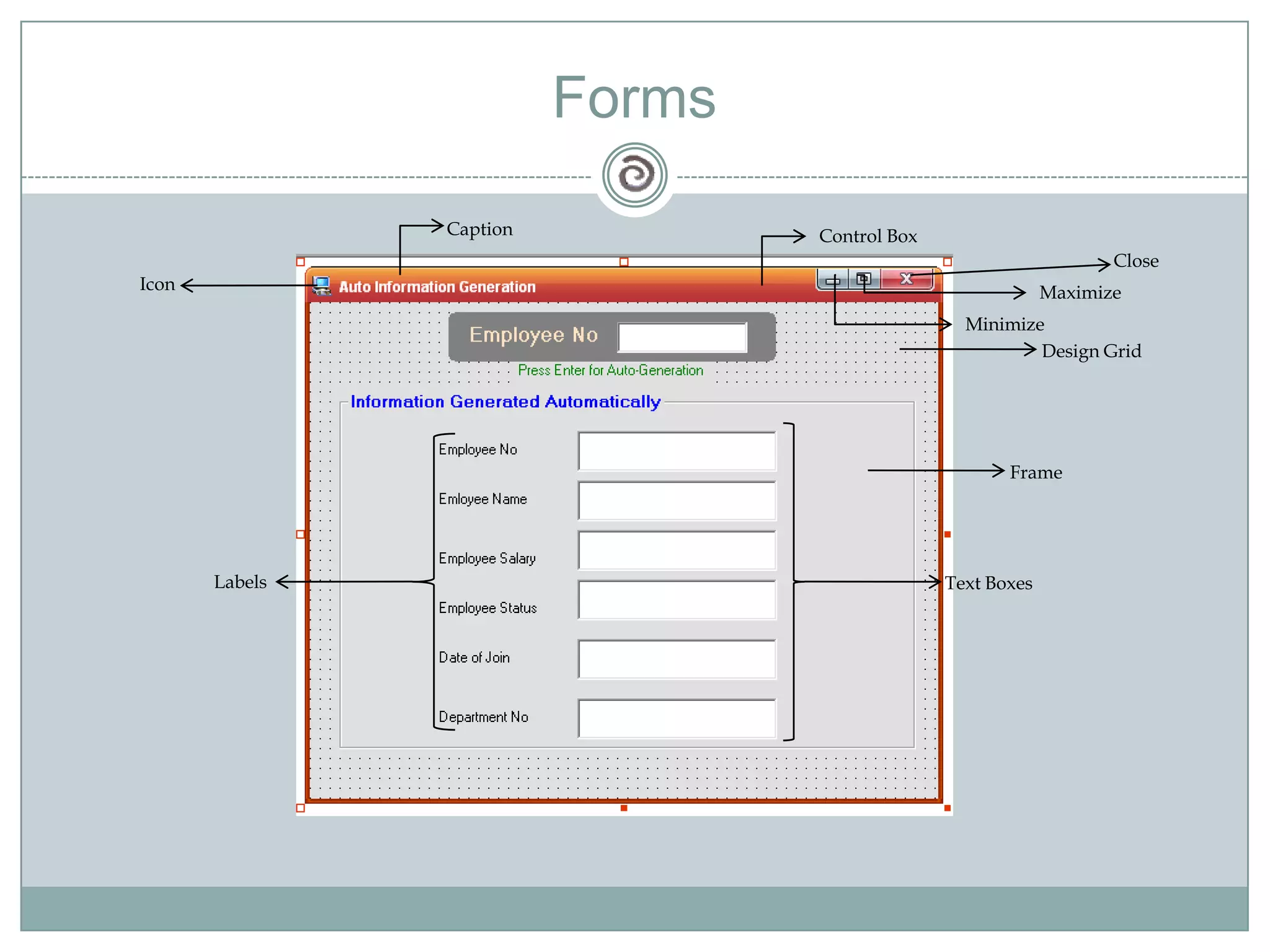
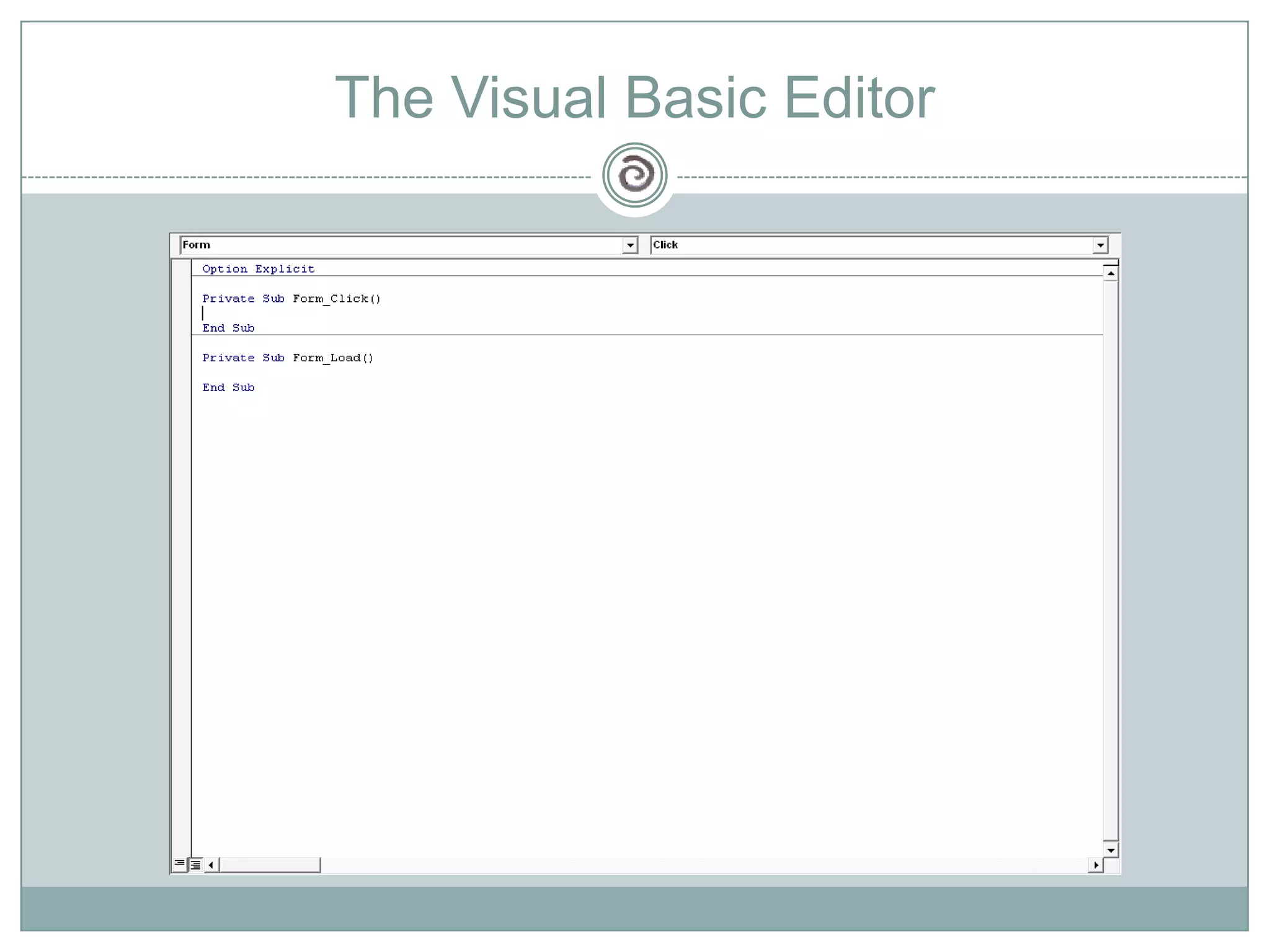
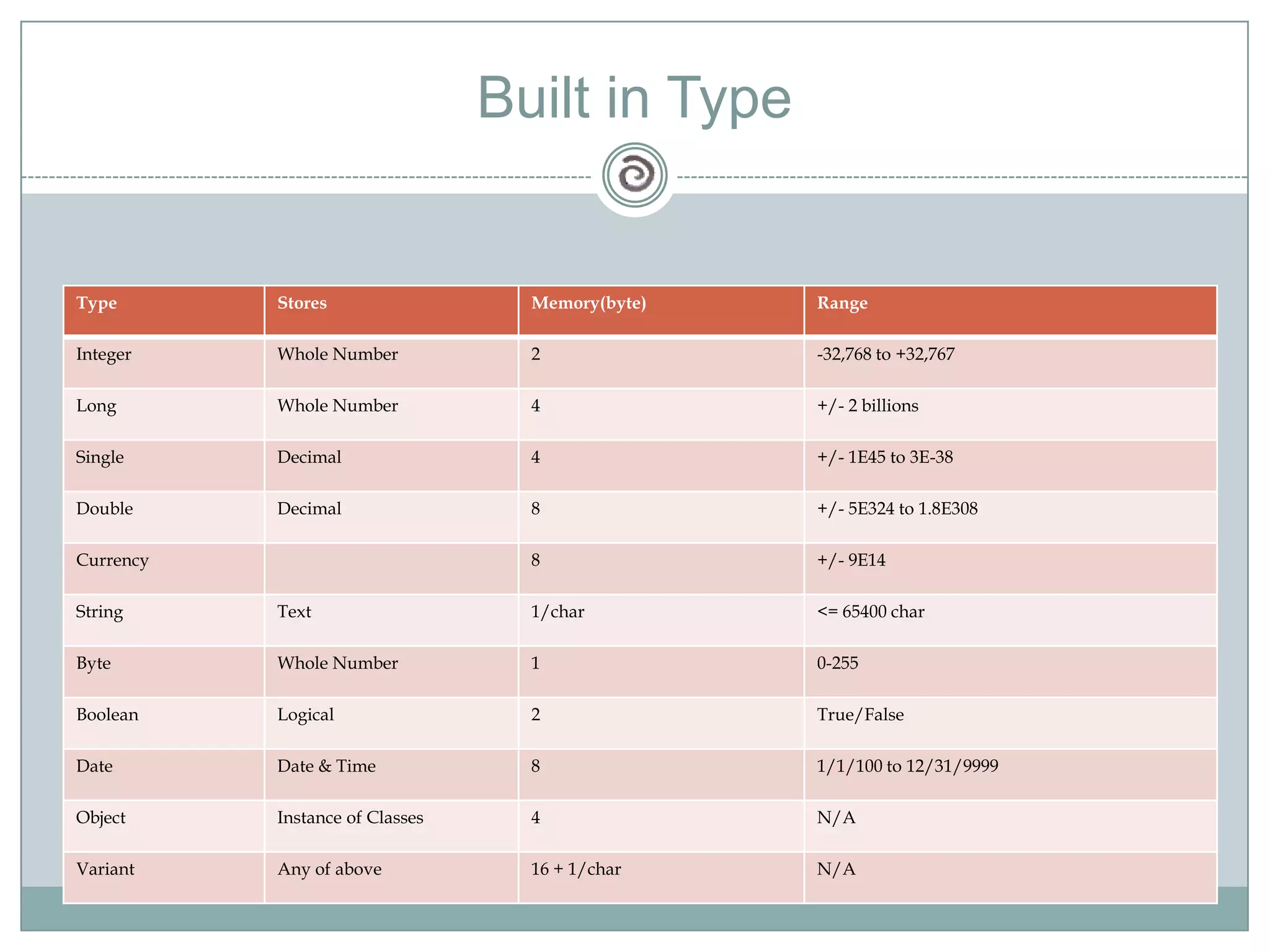
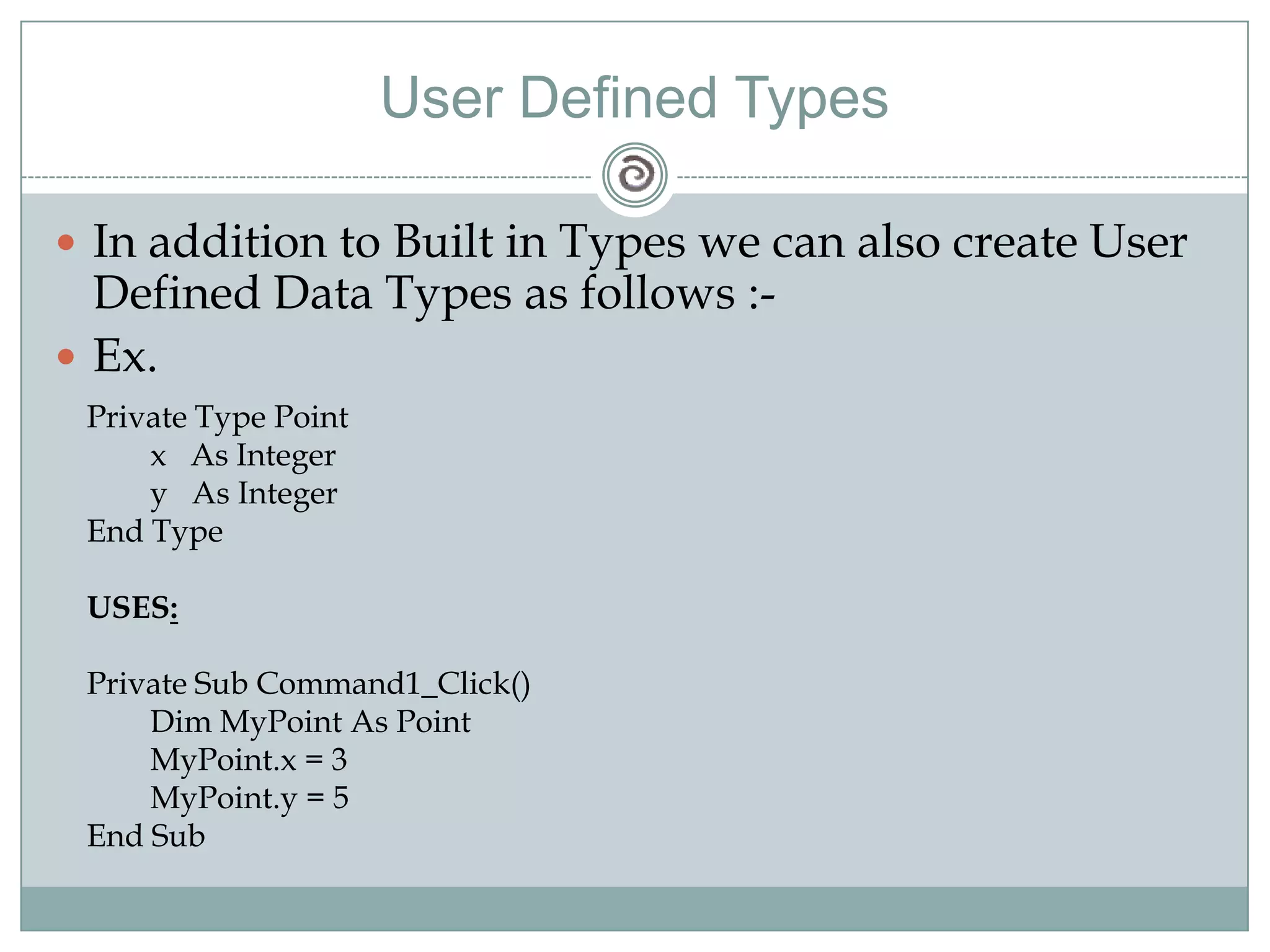
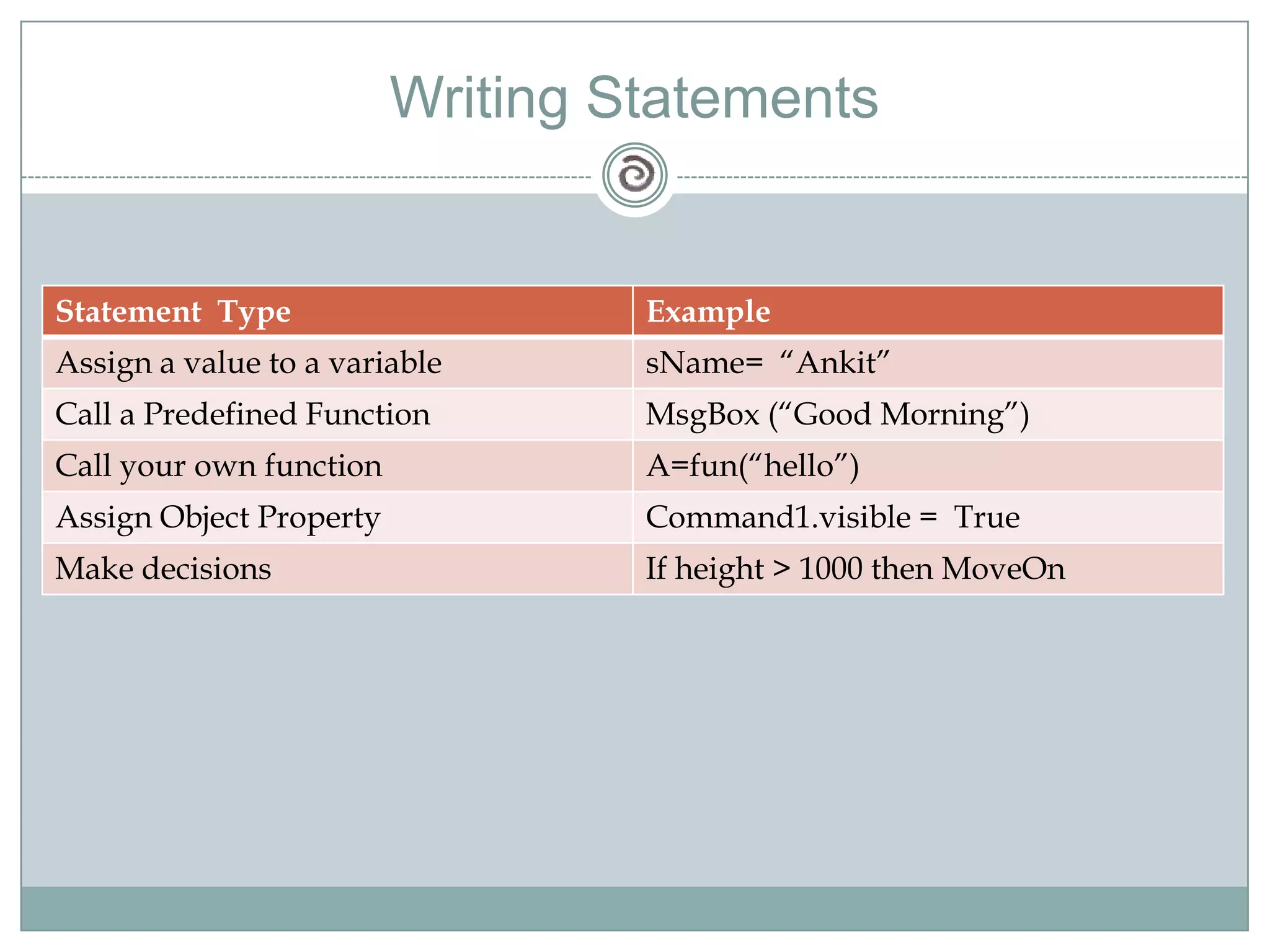
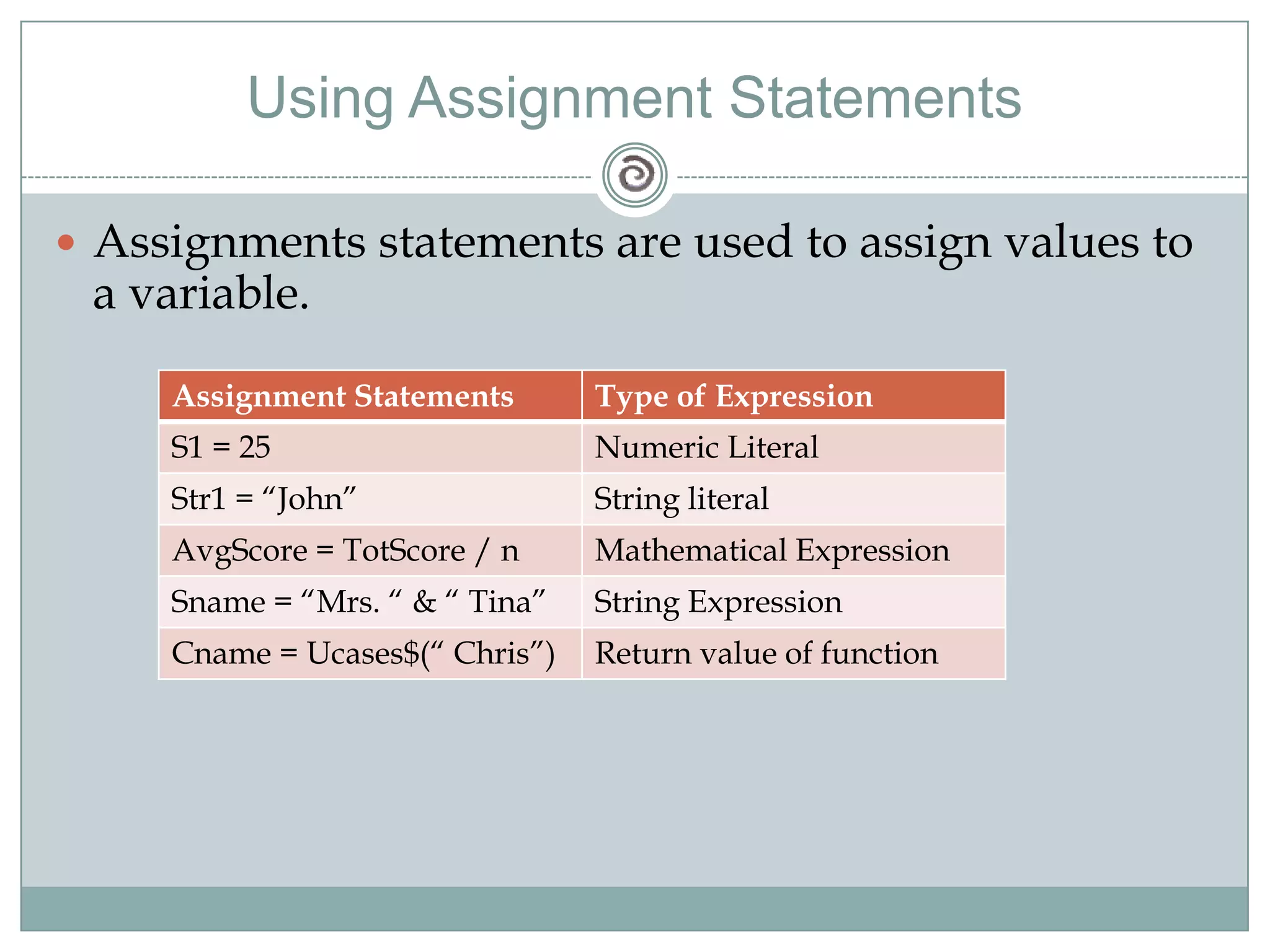
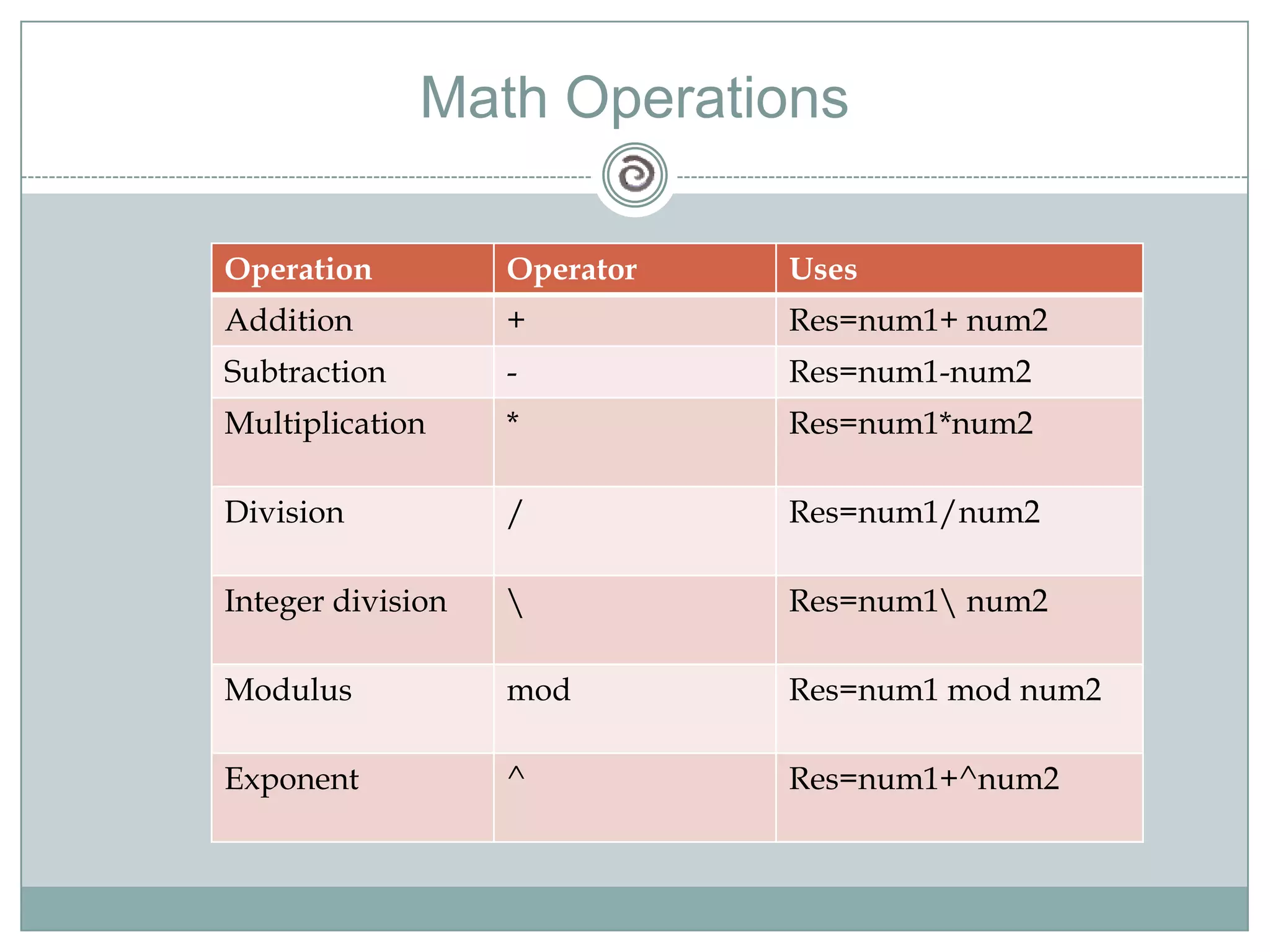
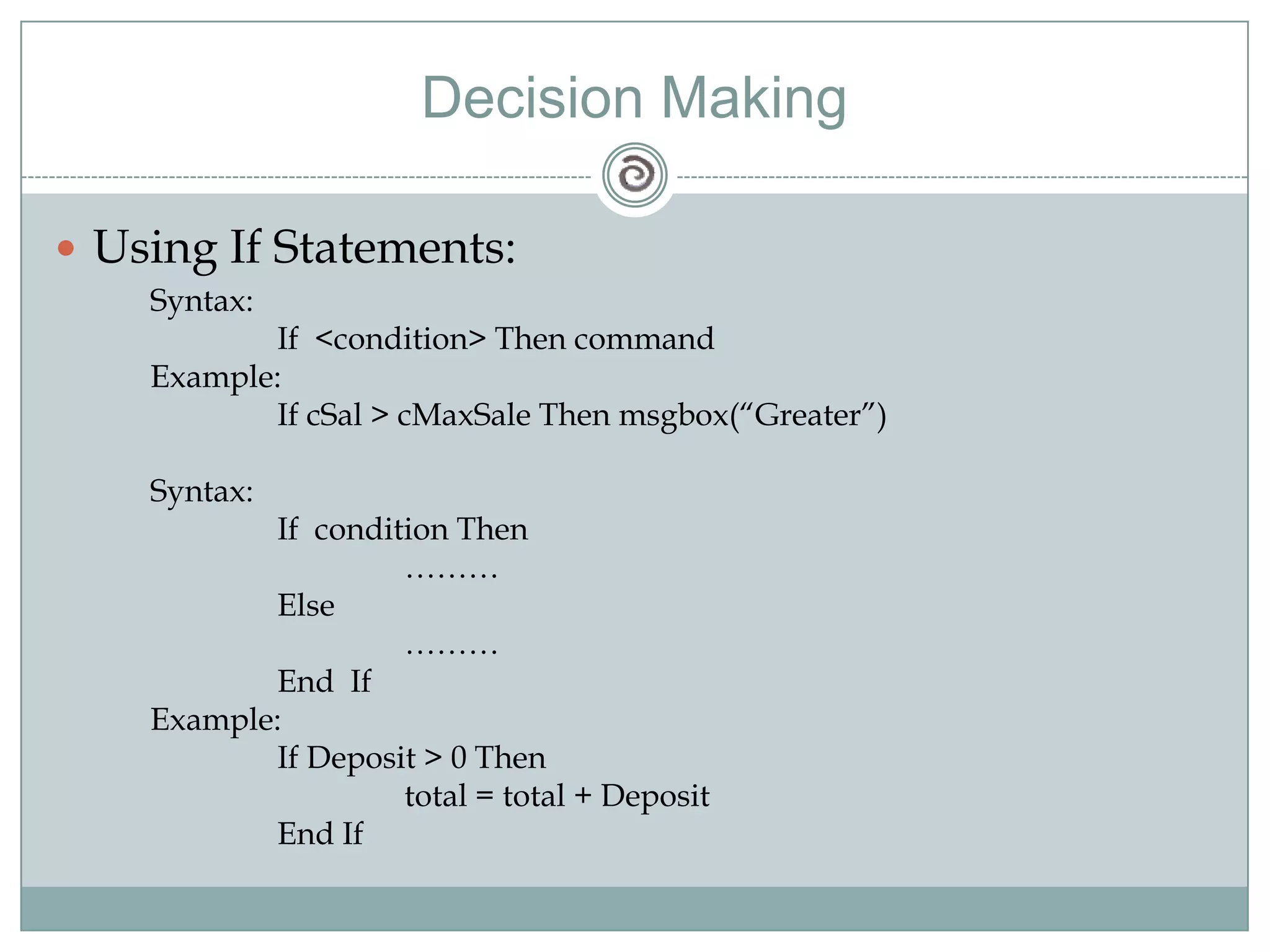
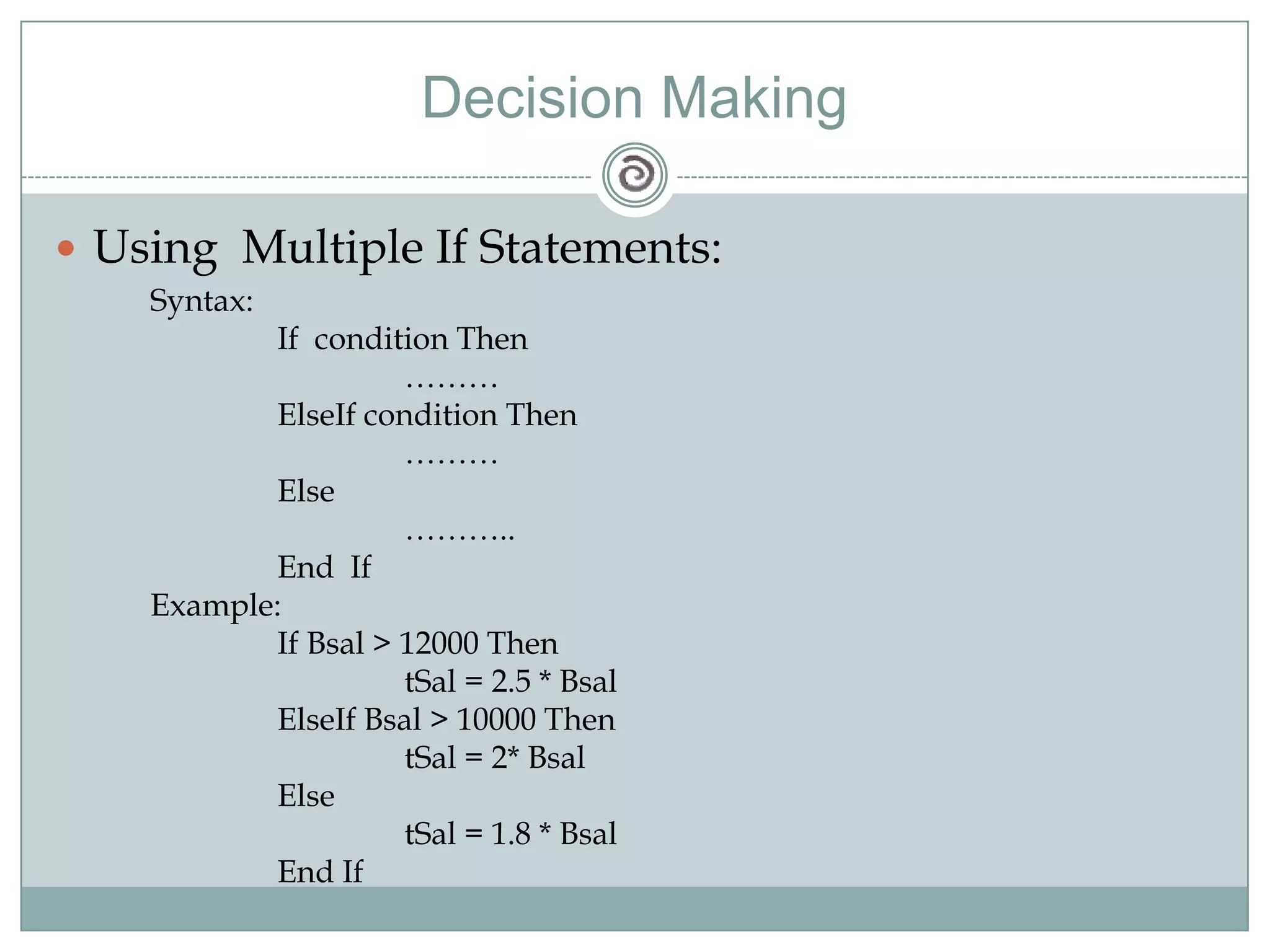
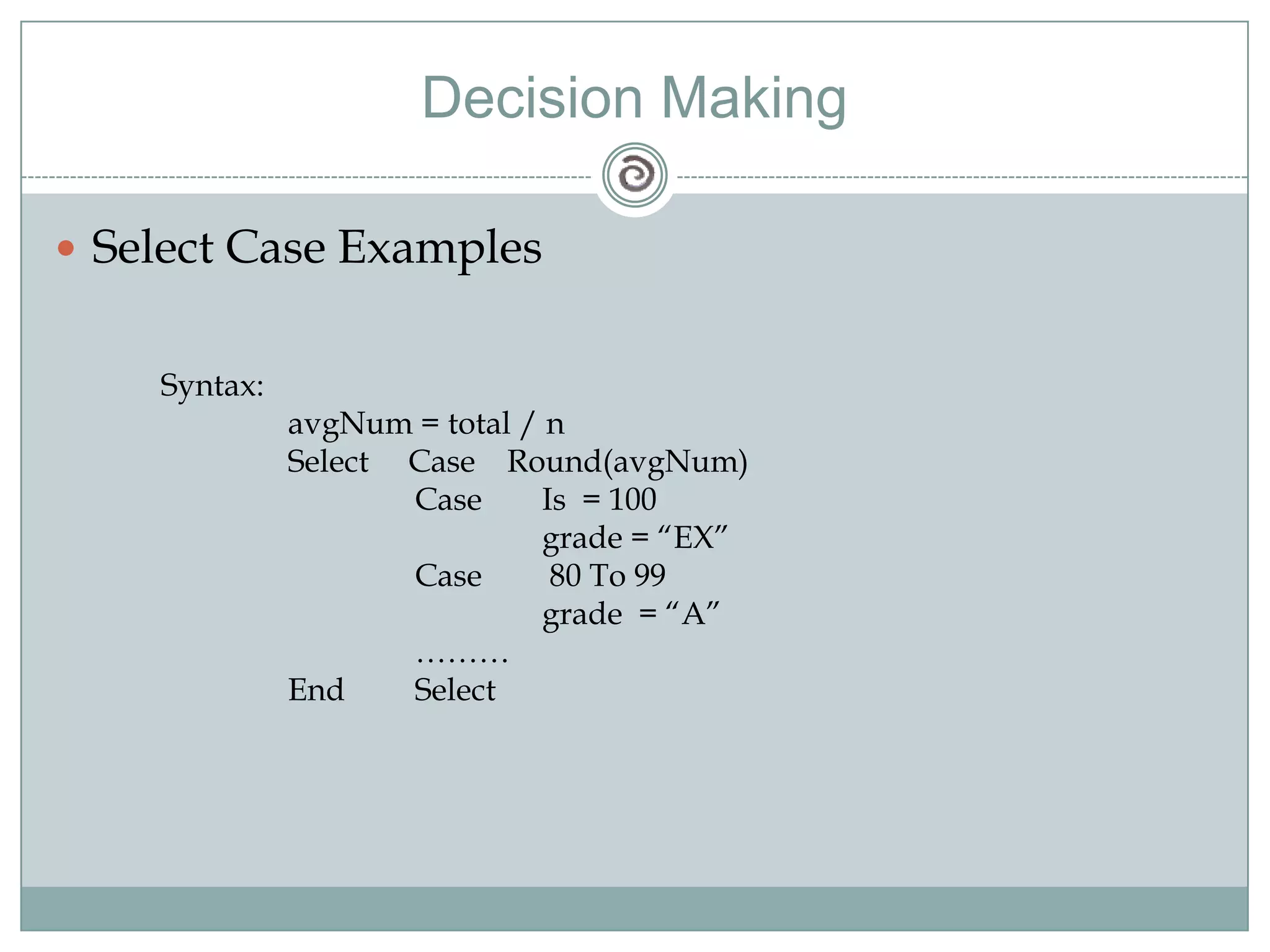
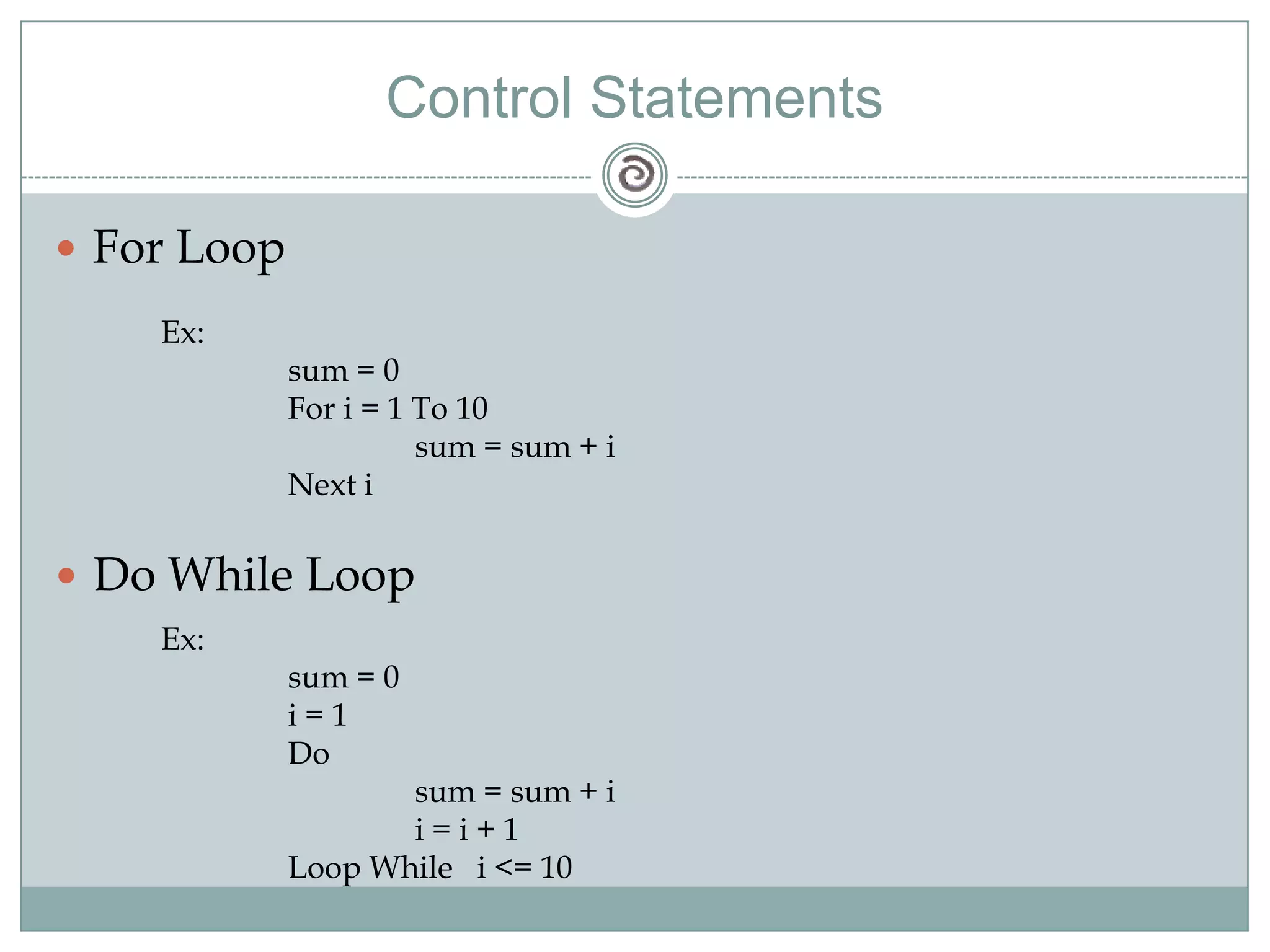
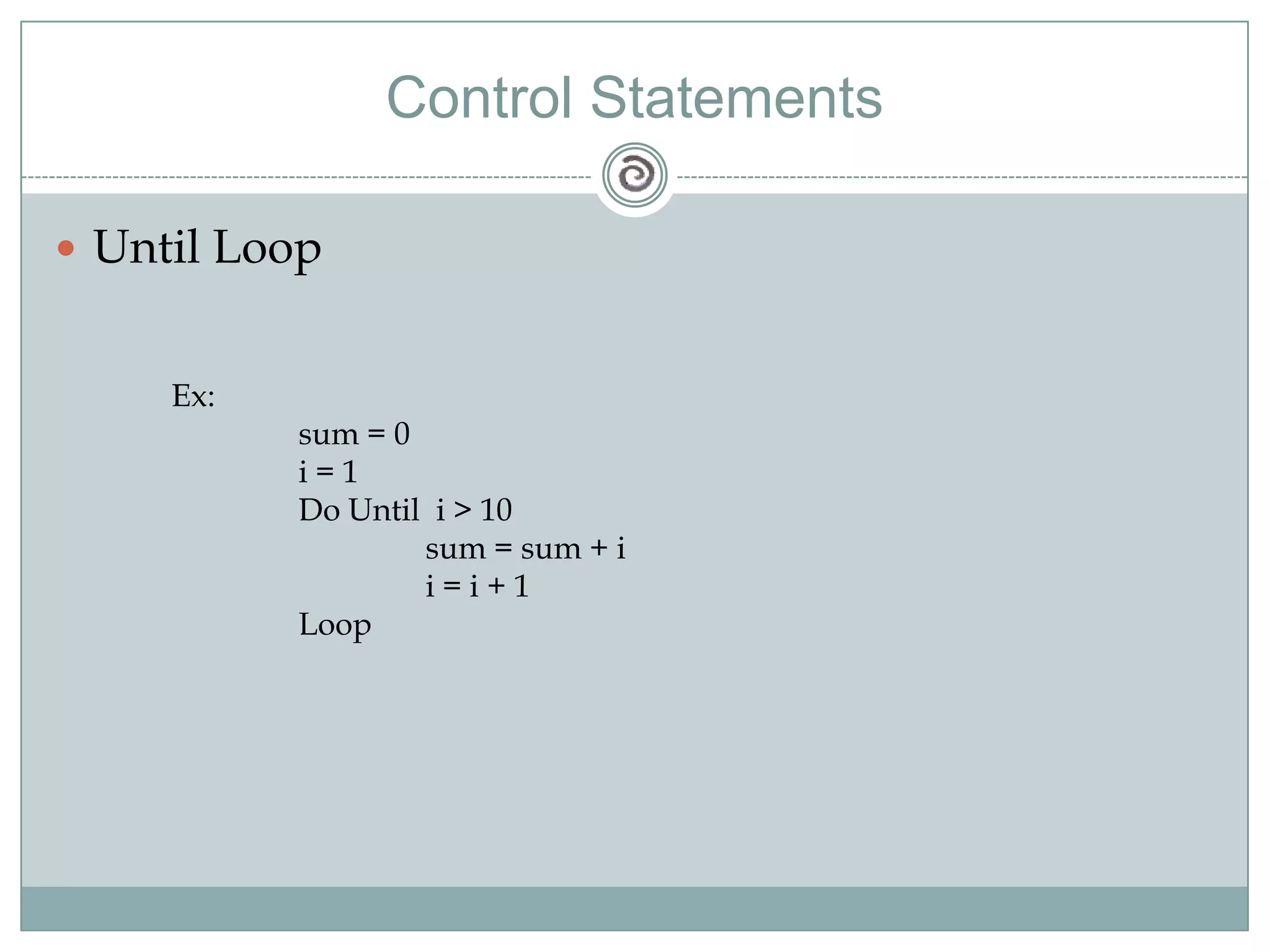
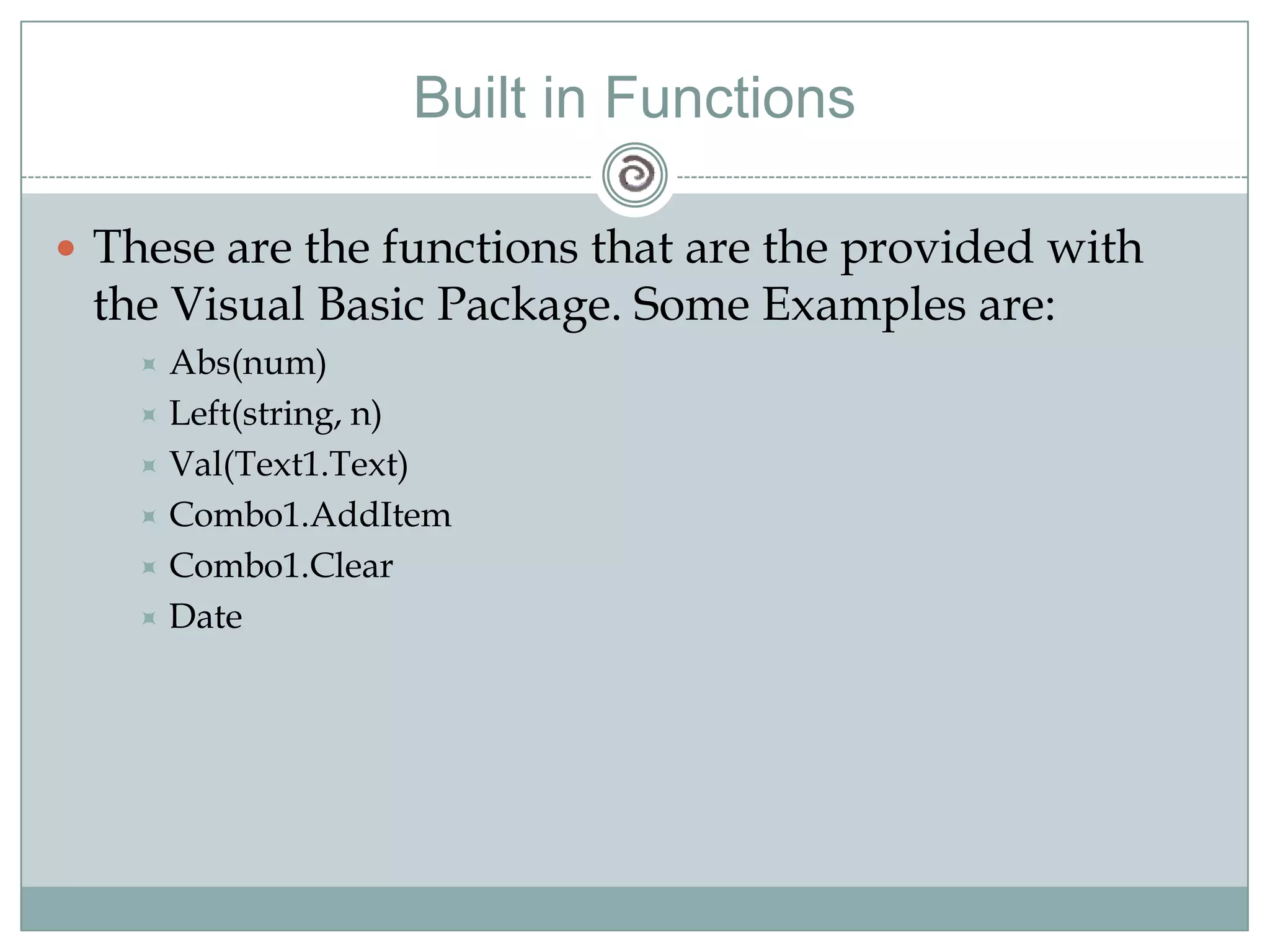
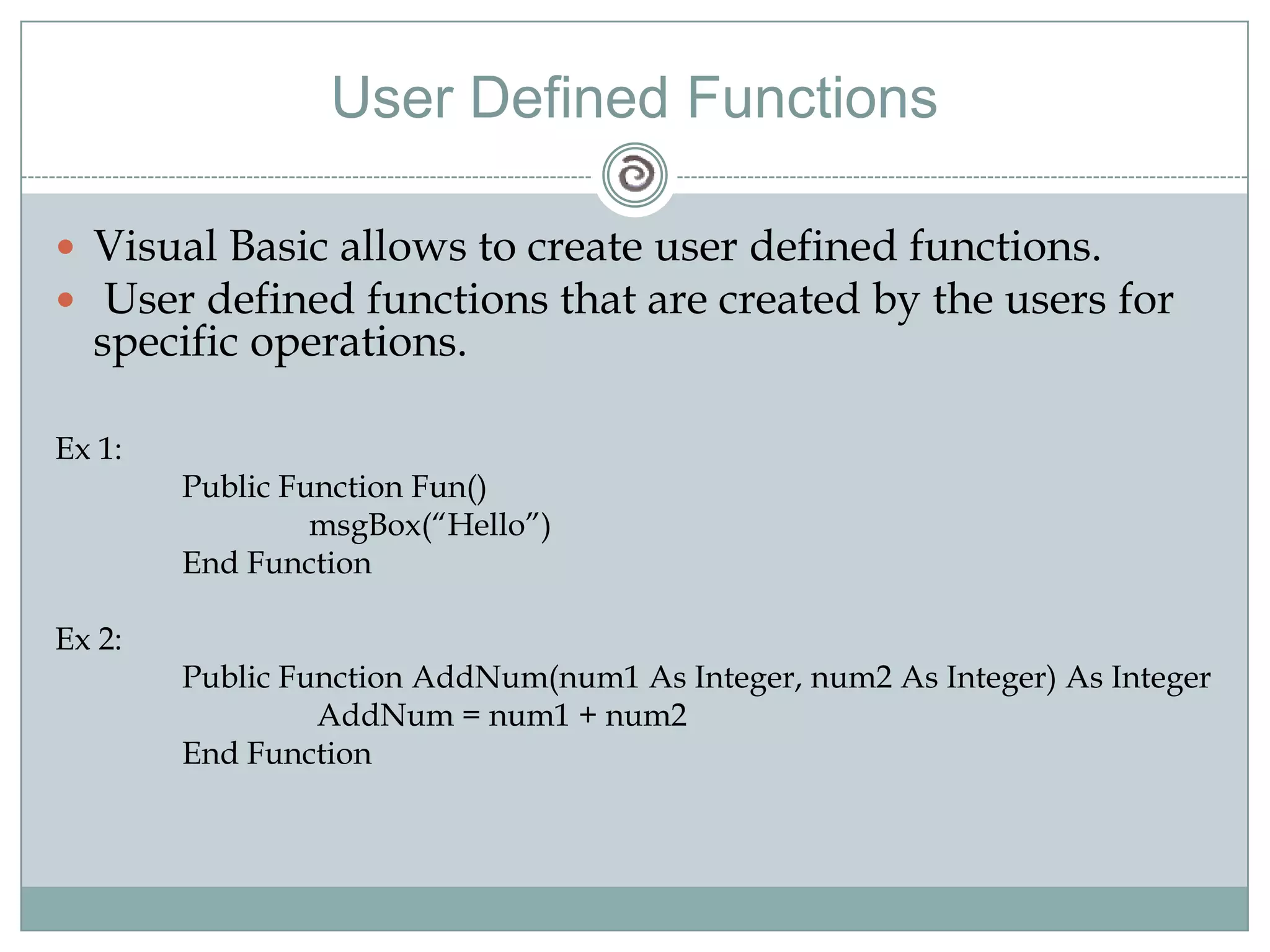
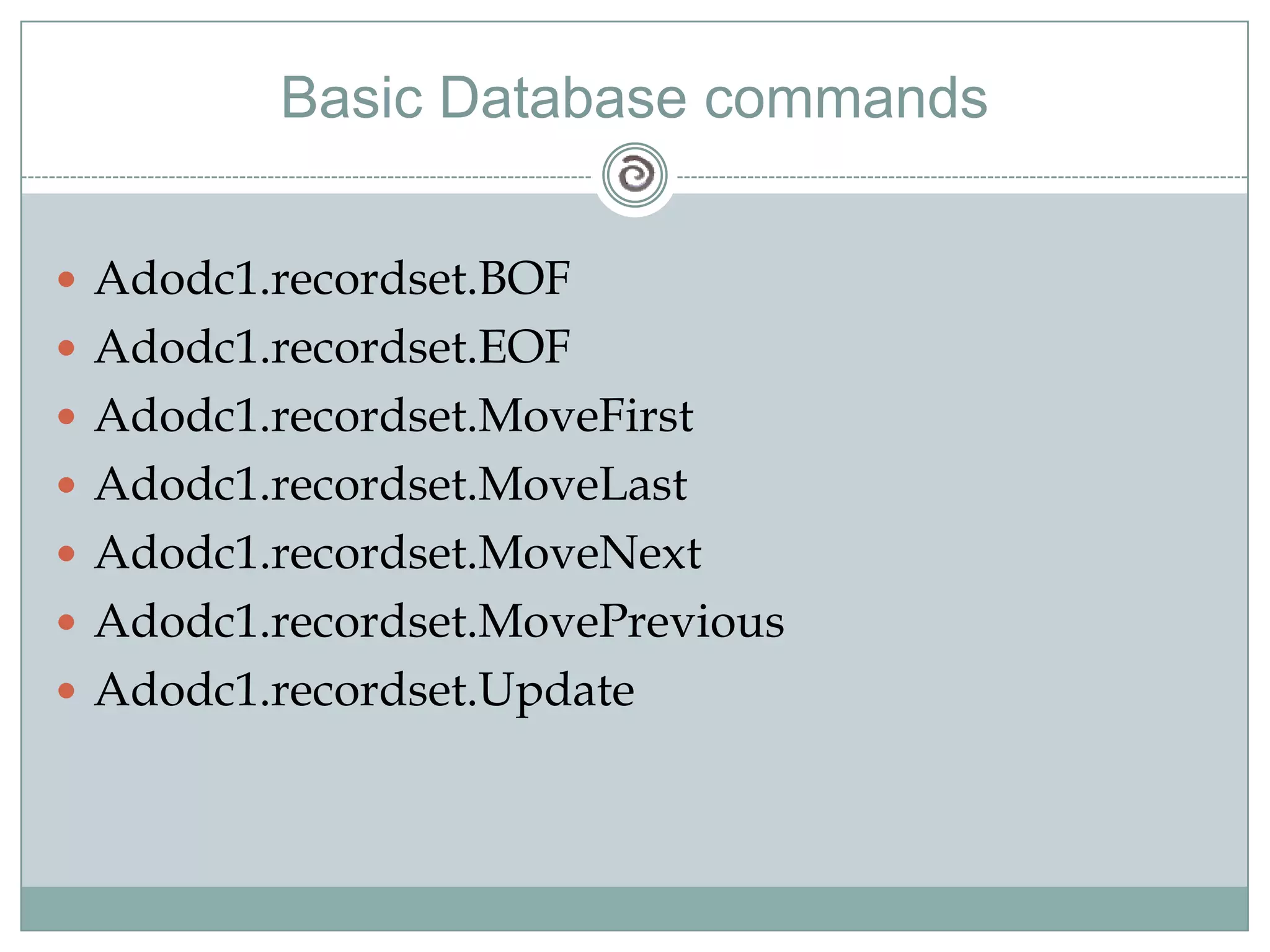
Visual Basic 6 allows users to design graphical user interfaces and develop Windows applications. It uses an event-driven programming model where code executes in response to events like user input. The language provides features for creating windows, accessing databases, and using ActiveX technologies. Visual Basic compiles and interprets code as it is written to catch errors early in development. Key concepts include windows, events, and messages which allow applications to respond to user input and system events.