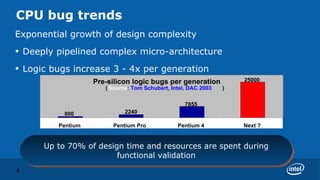
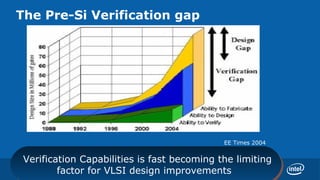
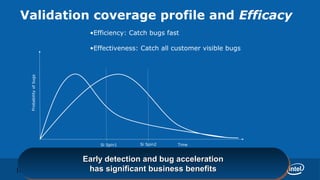
Praveen Vishakantaiah, President of Intel India, discussed the challenges of validating next generation CPUs. Validation is increasingly complex due to factors like rising design complexity from multi-core processors and chipset integration, as well as shorter time to market windows. Validation efforts are also not scaling incrementally with post-silicon development. Addressing these challenges requires experienced architects and validators working closely together, instrumentation of design models to enable validation, reuse of validation tools, and scaling of emulation and formal verification techniques. Validation is critical to meeting customer satisfaction and business goals around schedule and costs.