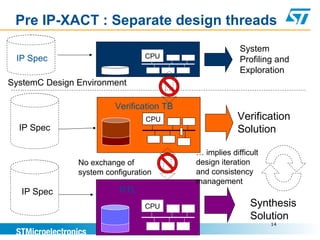
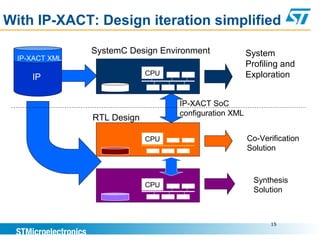
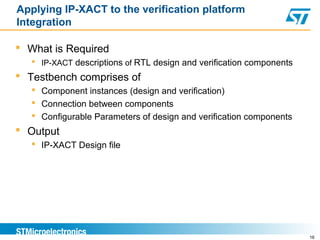
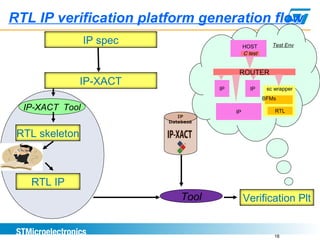
This document discusses using the IP-XACT standard to address challenges in verification automation. IP-XACT allows generating verification platforms, register tests, and other elements from a single IP description. It standardizes IP information exchange and reduces duplication. Using IP-XACT, a verification flow is proposed where the testbench, models, and register tests are automatically generated from an IP-XACT file, improving consistency and reducing turnaround times. IP-XACT is now an IEEE standard developed by the SPIRIT consortium to describe IPs in a vendor-neutral way and enable maximum automation.












![19
Registers : Typical scenario
Cost per register type
Specifications ( 0.5 page )
Datasheets
Register tests
RTL register decoder / netlist
TLM models / netlist
Register tests ( 30 lines per registers* [1..n] )
Register C header, eSW (20 lines per registers *[1..n])
Memory map representation ( ?? )
There are hundreds of register in a typical IP
Who will ensure coherency ?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/verificationautomationusingipxact-jindalandsingla-130422131843-phpapp02/85/Verification-Automation-Using-IPXACT-19-320.jpg)











