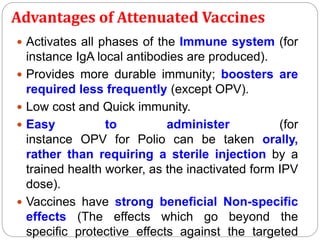
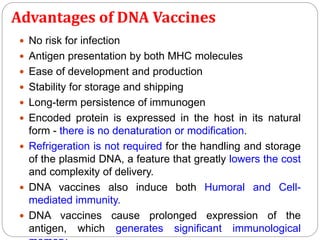
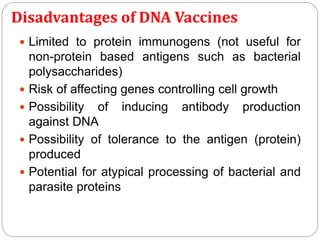
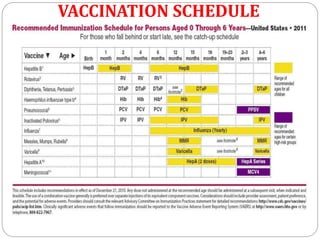
Vaccines work by exposing the immune system to weakened or killed forms of pathogens to stimulate antibody production against them. There are several types of vaccines including live attenuated vaccines using weakened live pathogens, inactivated vaccines using killed pathogens, subunit vaccines using pathogen proteins, DNA vaccines using genetic material, synthetic peptide vaccines, and toxoid vaccines using inactivated bacterial toxins. Vaccines provide active immunity and are the most effective method of preventing infectious diseases.