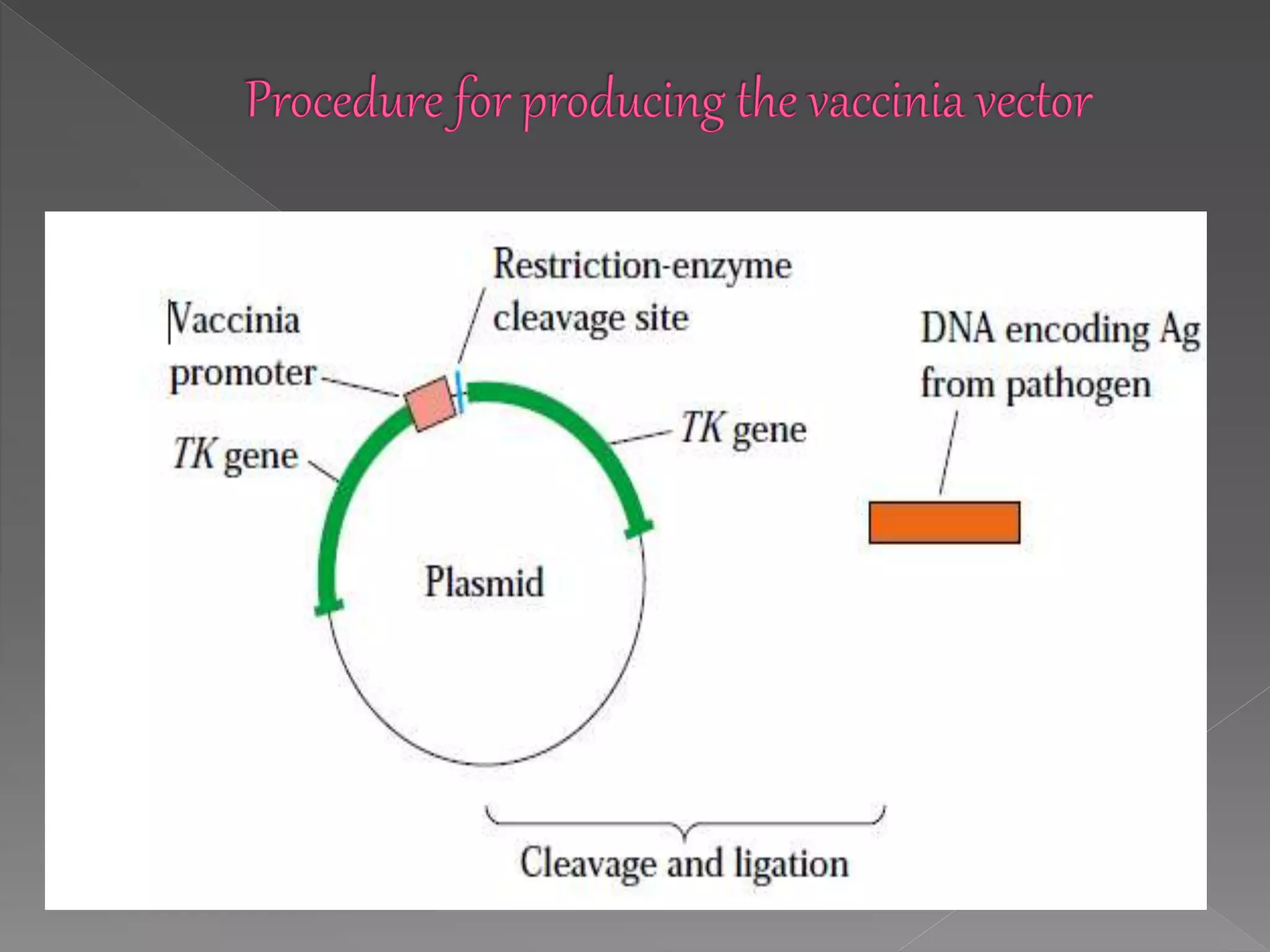
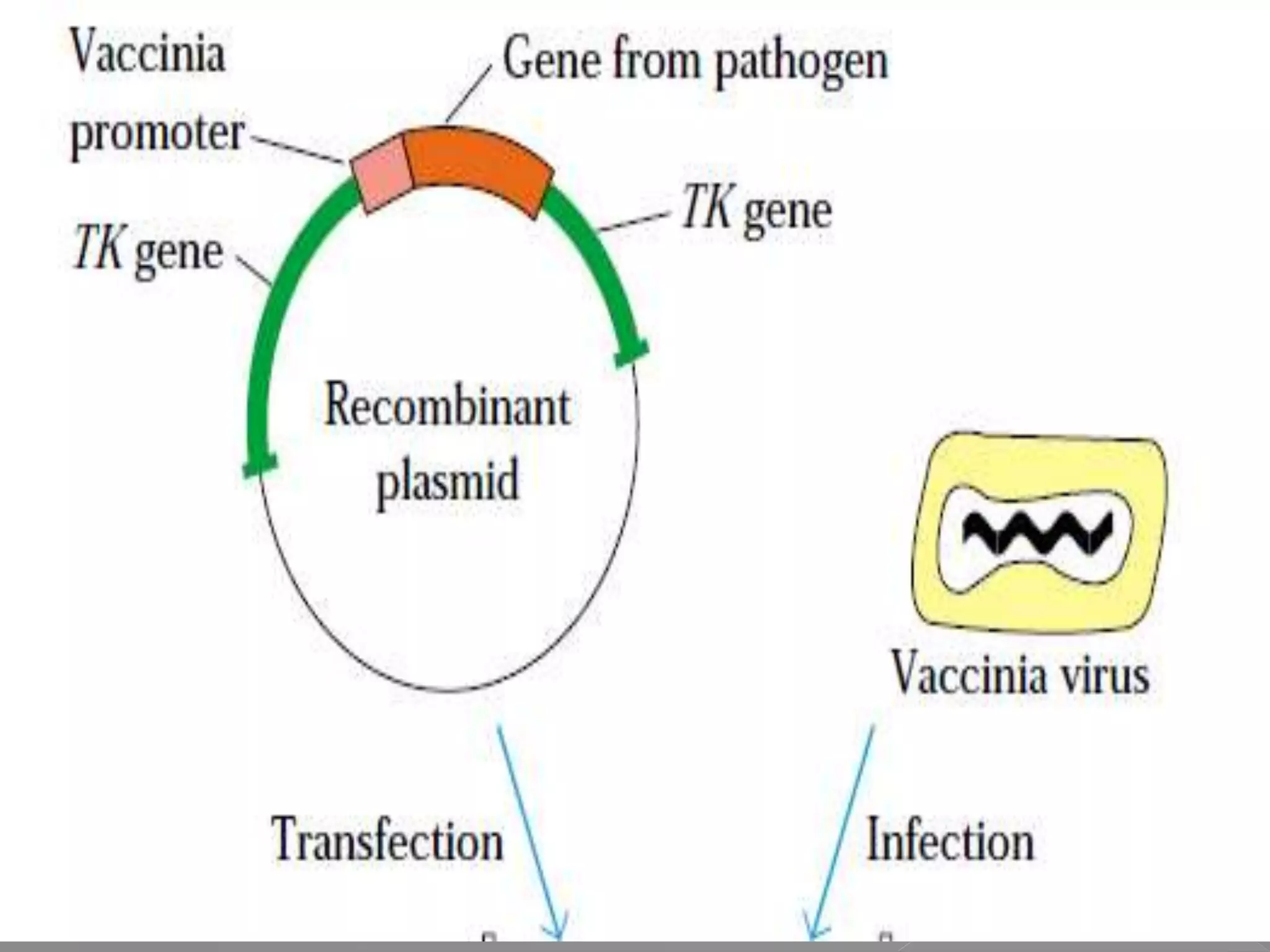
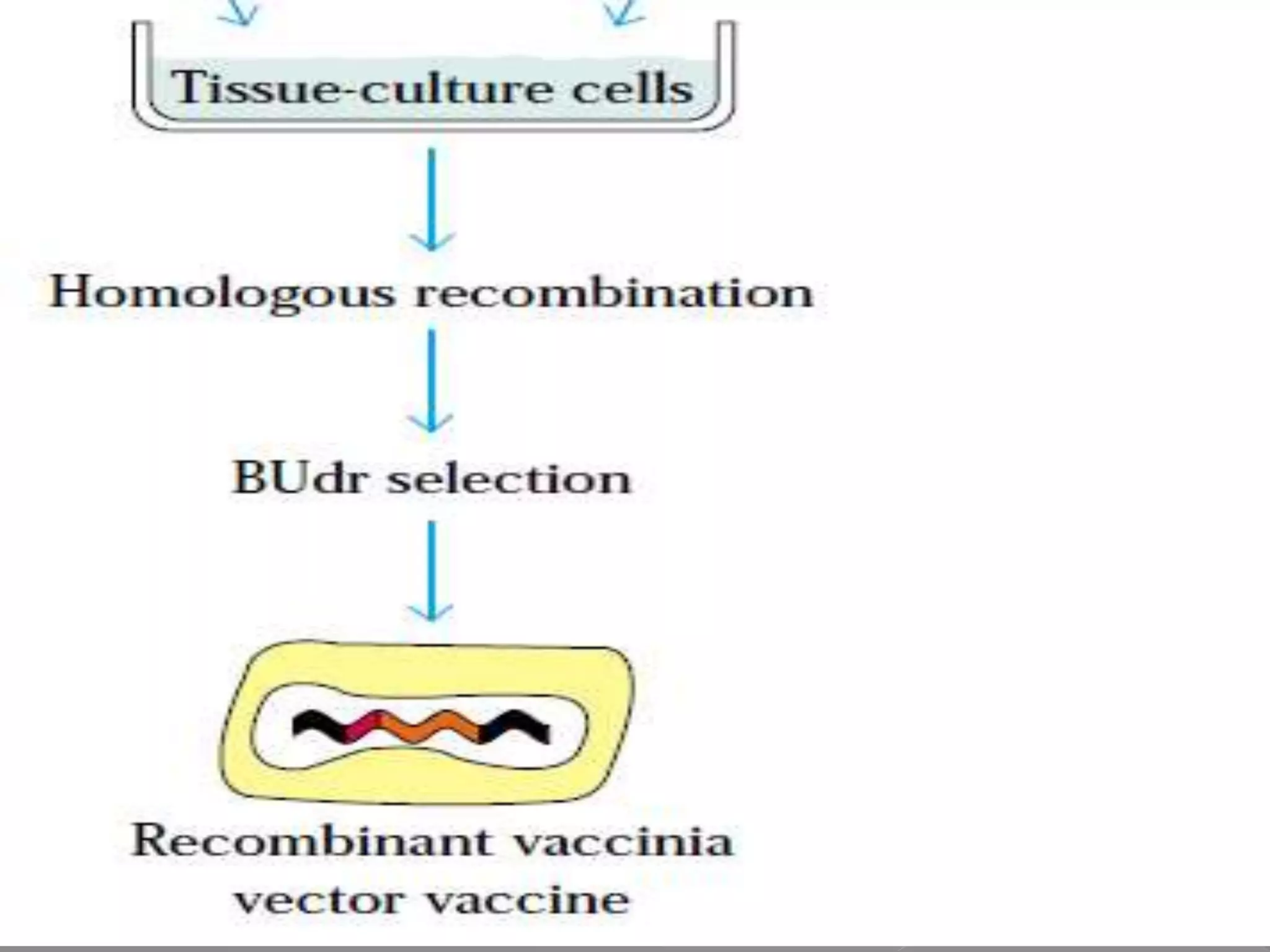
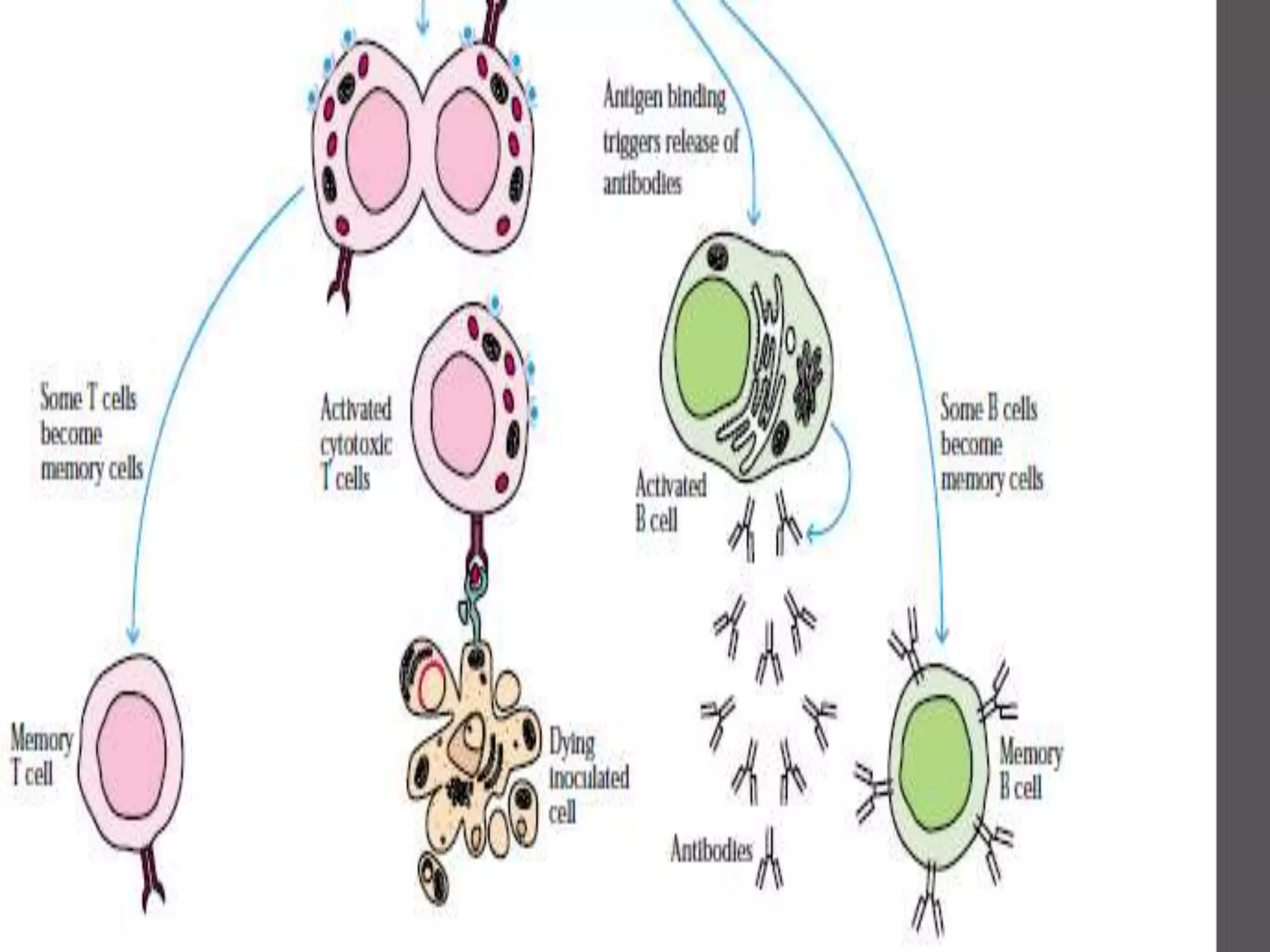
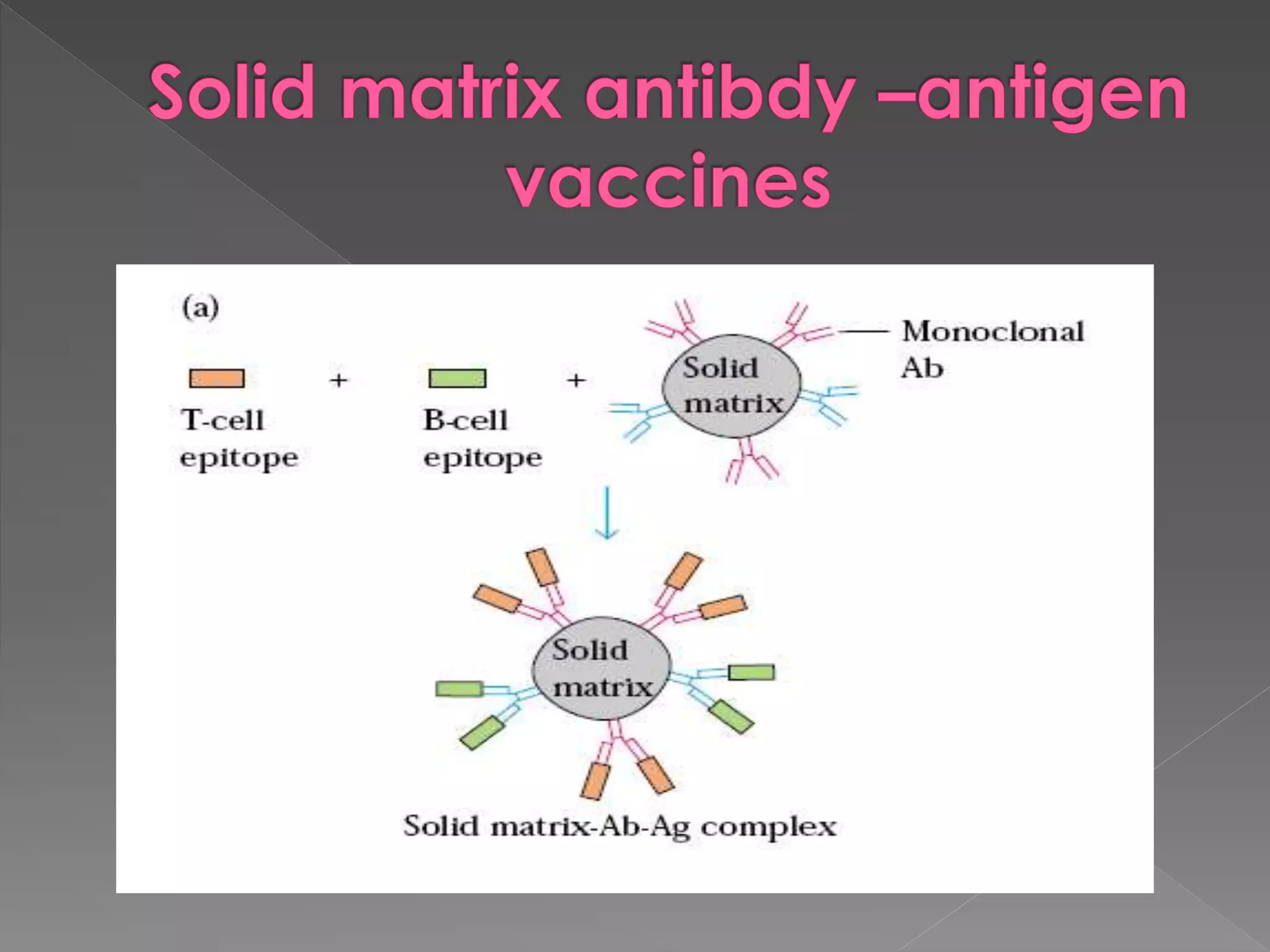
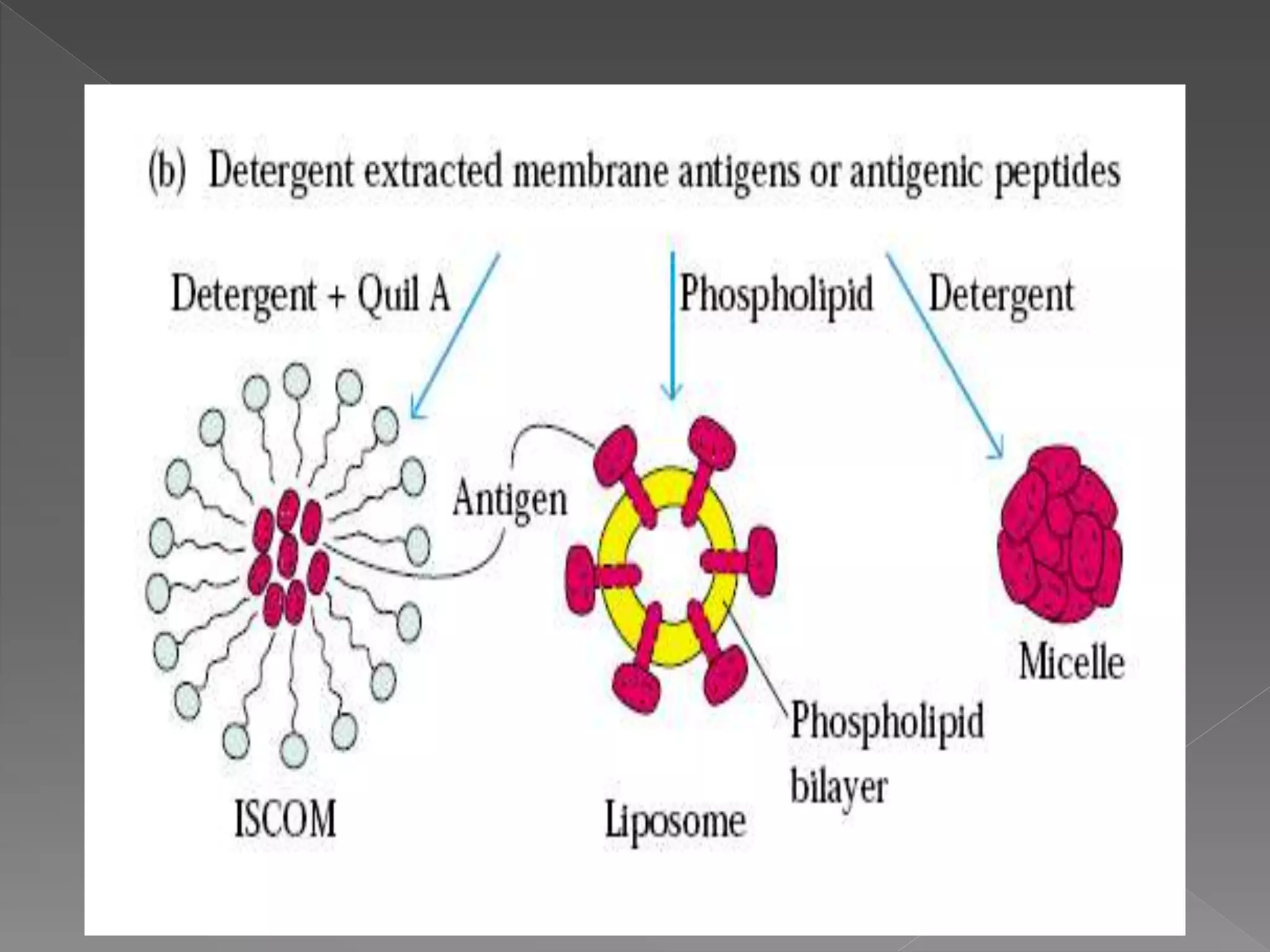
The document discusses different types of vaccines, including live attenuated vaccines, inactivated vaccines, subunit vaccines, recombinant vaccines, DNA vaccines, and conjugate vaccines. Live attenuated vaccines use weakened live pathogens to induce immunity, while inactivated vaccines use killed pathogens. Subunit vaccines contain purified antigens from pathogens. Recombinant vaccines produce antigens using genetic engineering, while DNA vaccines use DNA encoding antigens. Conjugate vaccines chemically link bacterial coat proteins to carrier proteins to generate stronger immune responses.