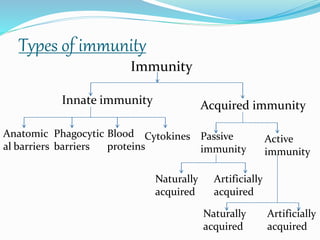
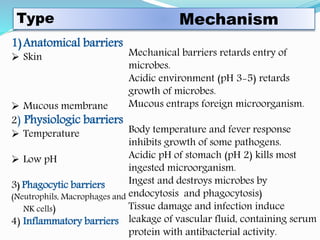
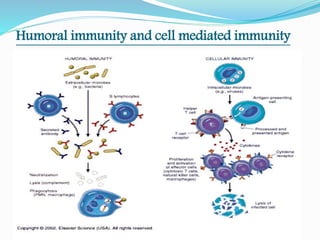
The document provides an overview of immunity, detailing its types, which include innate and acquired immunity. Innate immunity features rapid, pre-existing defenses such as anatomical and phagocytic barriers, while acquired immunity develops post-exposure and can be categorized into active and passive forms. Key characteristics of acquired immunity include antigen specificity, diversity, memory, and self/non-self recognition.