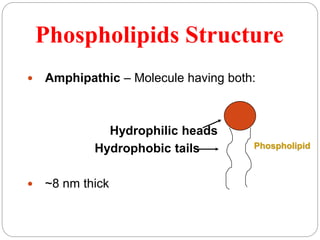
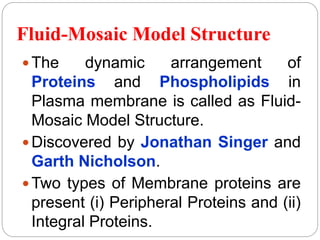
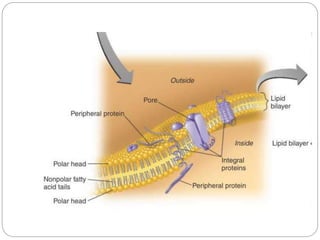
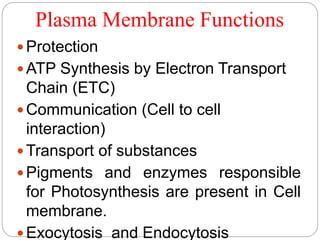
The plasma membrane is a 5-10 nm thick bilayer that acts as the boundary of the cell. It is made of phospholipids, proteins, carbohydrates, and cholesterol. The fluid mosaic model describes the plasma membrane as a fluid bilayer with integral and peripheral proteins embedded within. Integral proteins span the membrane while peripheral proteins are attached to either surface. Glycoproteins and glycolipids on the outer surface contain carbohydrates that protect and lubricate the cell. The plasma membrane performs critical functions like protection, ATP synthesis, communication, transport, and endocytosis/exocytosis.