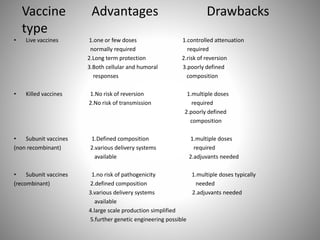
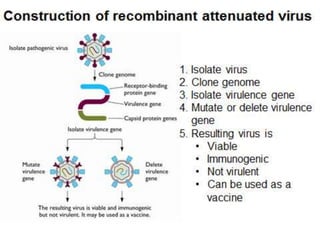
Recombinant vaccines use genetic engineering techniques to produce antigens that induce protective immunity. They offer advantages over conventional vaccines like improved safety and defined composition. Recombinant vaccines work by inserting genes for antigens into vectors like viruses. This allows the vector to produce the antigen and elicit an immune response. They can target specific cells and induce immunity through multiple routes of administration. While live recombinant vaccines carry a risk of reversion, they elicit strong immune responses from just one or a few doses. Future areas of development include improved delivery methods and use of immunomodulators and plant expression systems.