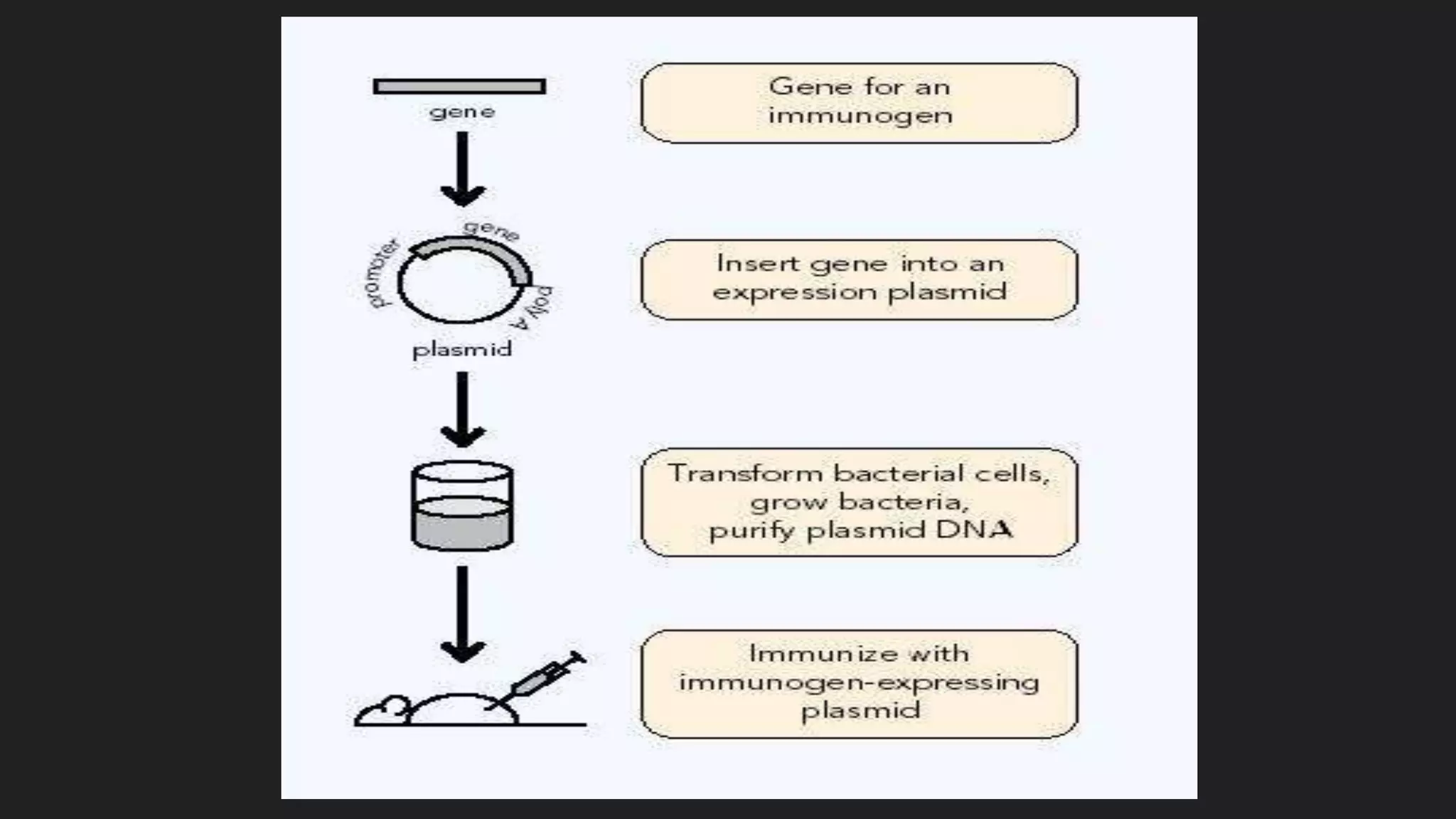
This document provides an introduction to vaccines, including their principles, types, and examples. The main types discussed are inactivated/killed vaccines, live attenuated vaccines, toxoids, subunit vaccines, DNA vaccines, and recombinant live vaccines. Inactivated vaccines use killed disease-causing microbes, and stimulate a weak immune response but require boosters. Live attenuated vaccines use weakened live organisms to stimulate excellent lifelong immunity but rarely carry risk of disease if attenuation fails. Toxoids are made from inactivated toxins and cannot cause disease but may require adjuvants or boosters. DNA vaccines work by directly introducing genetic material that codes for antigens. They allow for rapid, low-cost production and generate therapeutic potential for chronic infections.