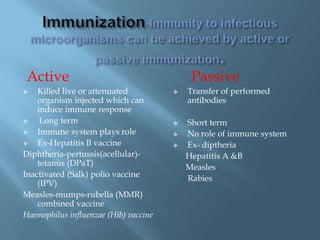
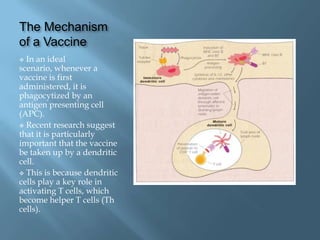
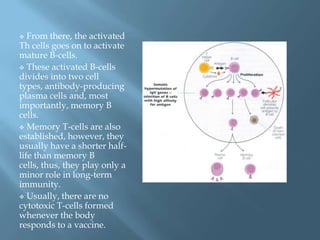
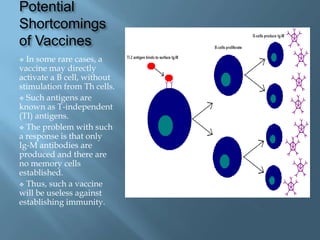
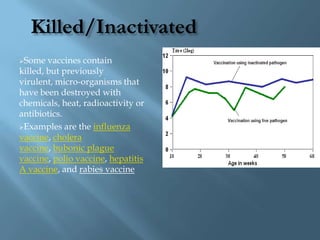
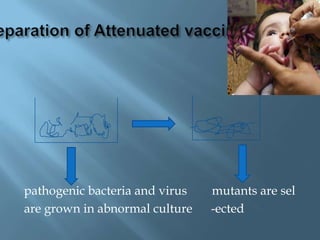
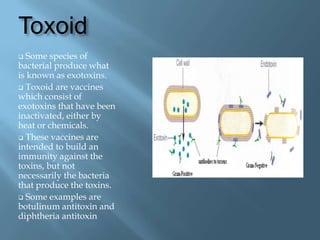
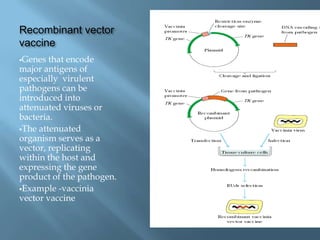
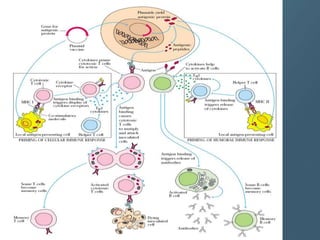
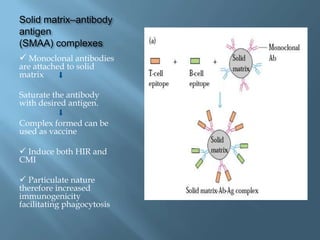
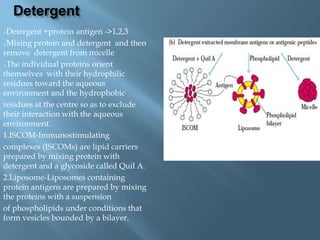
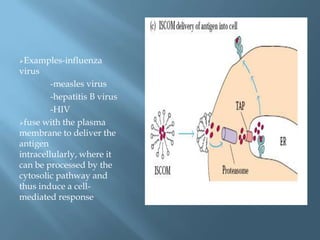
Vaccines work by activating the immune system through active immunization with live attenuated or killed pathogens. They provide long term immunity through memory B and T cells. Common types include killed/inactivated, attenuated, toxoid, recombinant, and DNA vaccines. Vaccines are manufactured through in vivo, in vitro, or chemical synthesis methods. Potential risks include vaccine strain infection, superantigen effects, and allergic reactions.