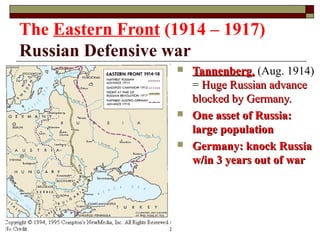
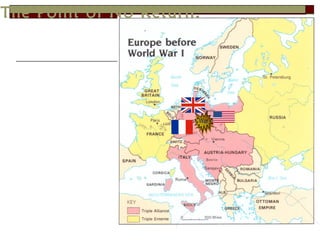
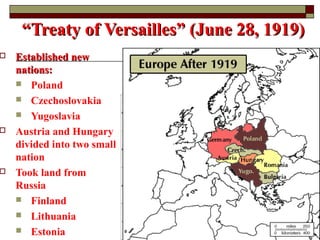
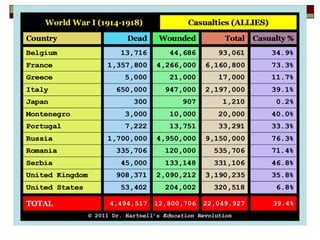
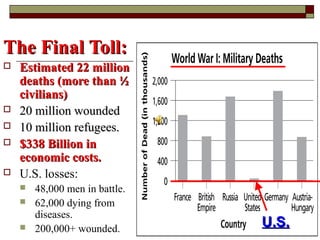
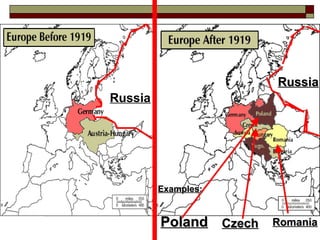
The document provides information about World War 1, including the key countries involved on both sides of the war and some of the major events and battles that took place. It discusses the Central Powers of Germany and Austria-Hungary versus the Allied Powers like France, Britain, Russia and later the US. Some of the major battles covered include the Marne, where the Allies stopped the German advance on Paris, and the Somme, which resulted in heavy British casualties. The document also discusses the entry of the US into the war, the end of Germany's war efforts, and the eventual Treaty of Versailles that formalized Germany's surrender but has been criticized for punishing Germany harshly.