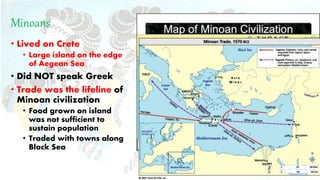
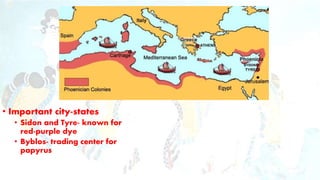
The Minoans lived on the island of Crete from around 2000-1400 BC. As a seafaring people, they relied heavily on trade since local agriculture could not sustain their population. They exported fine pottery and spread their unique architecture, art, and religious practices throughout the Mediterranean, acting as a "stepping stone" for cultural exchange. Minoan society was possibly matriarchal, as evidenced by frescoes depicting women in positions of power and authority equal to men. Their capital of Knossos was ruled by King Minos and was notable for lacking fortifications. The Minoan civilization ultimately declined after a major volcanic eruption destroyed their navy and trade networks, leaving them vulnerable to invasion by the