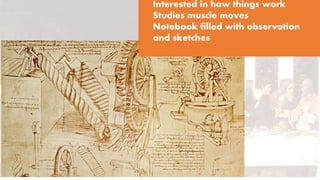
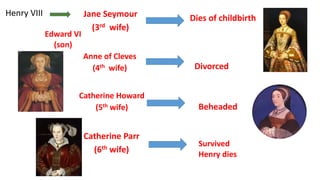
This document provides an overview of key people and events during the Renaissance period in Europe. It discusses early Italian Renaissance figures like Michelangelo, Leonardo da Vinci, and Raphael. It then covers the Protestant Reformation sparked by Martin Luther and his 95 Theses. Key figures in the English Reformation like King Henry VIII and his wives are outlined. The effects of the English Reformation on later monarchs like Edward VI, Mary I, and Elizabeth I are summarized.