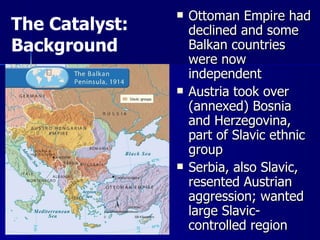
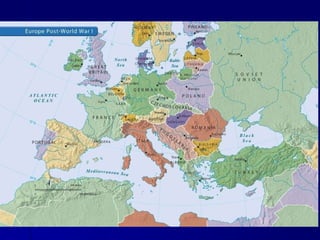
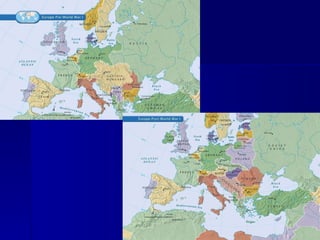
World War I, known as the 'Great War', was fueled by militarism, alliances, imperialism, and nationalism, with the assassination of Archduke Ferdinand serving as the catalyst for the conflict. The war saw major powers divided into the Central Powers and Allied Powers, with trench warfare and global participation marking the fighting on multiple fronts. The war concluded with the Treaty of Versailles, which imposed heavy penalties on Germany, reshaped national borders, and led to significant political changes worldwide.