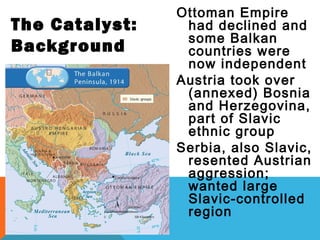
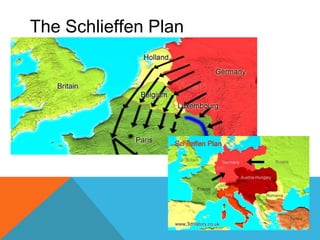
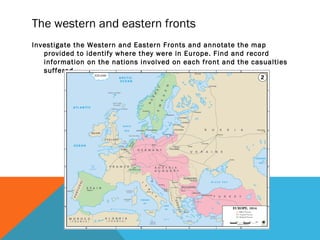
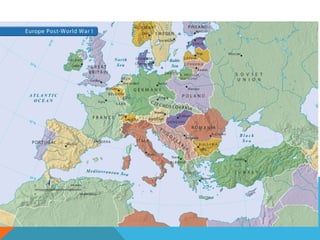
World War I was caused by militarism, alliances, imperialism, and nationalism in Europe leading up to 1914. The immediate trigger was the assassination of Archduke Ferdinand by Serbian nationalists. This caused Austria-Hungary to declare war on Serbia and drew in allies on both sides through a series of interlinking alliances. The war became global and total war as more countries joined and all domestic resources were devoted to the war effort. Fighting lasted from 1914-1918 and was especially deadly and prolonged on the Western and Eastern Fronts. The U.S. entry into the war in 1917 helped ensure an Allied victory. After huge losses, the war finally ended with the defeat of Germany and the Treaty of