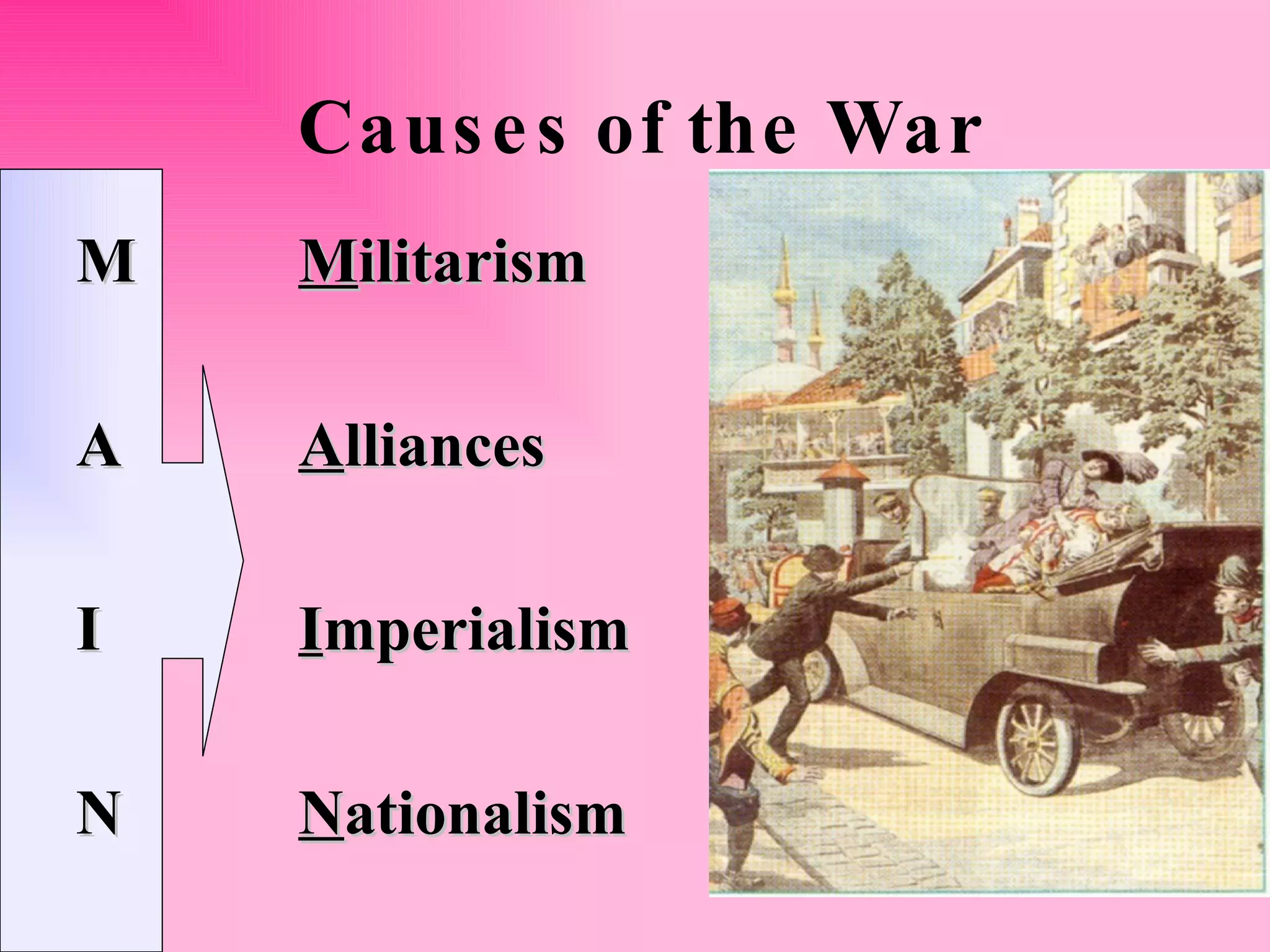
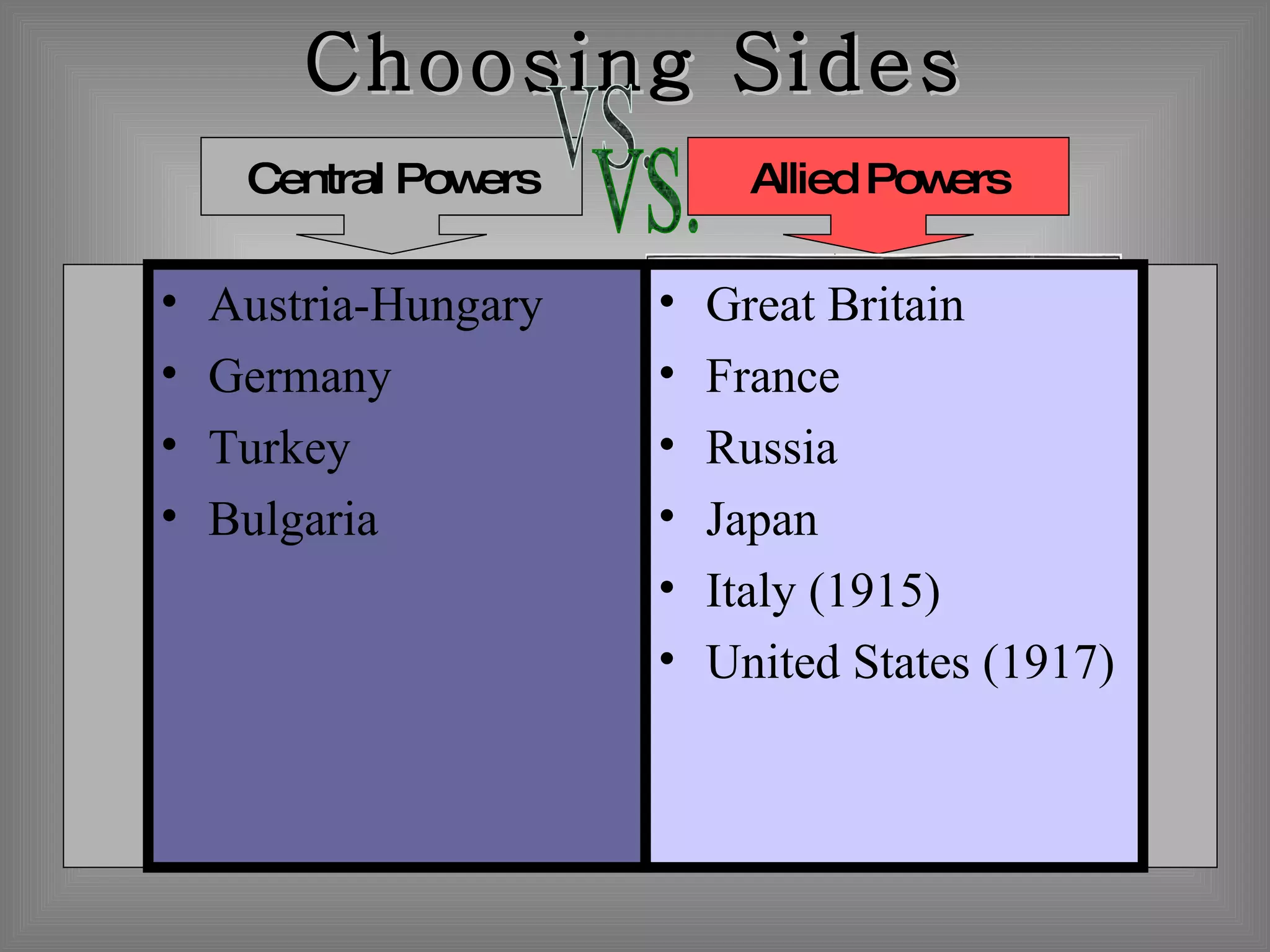
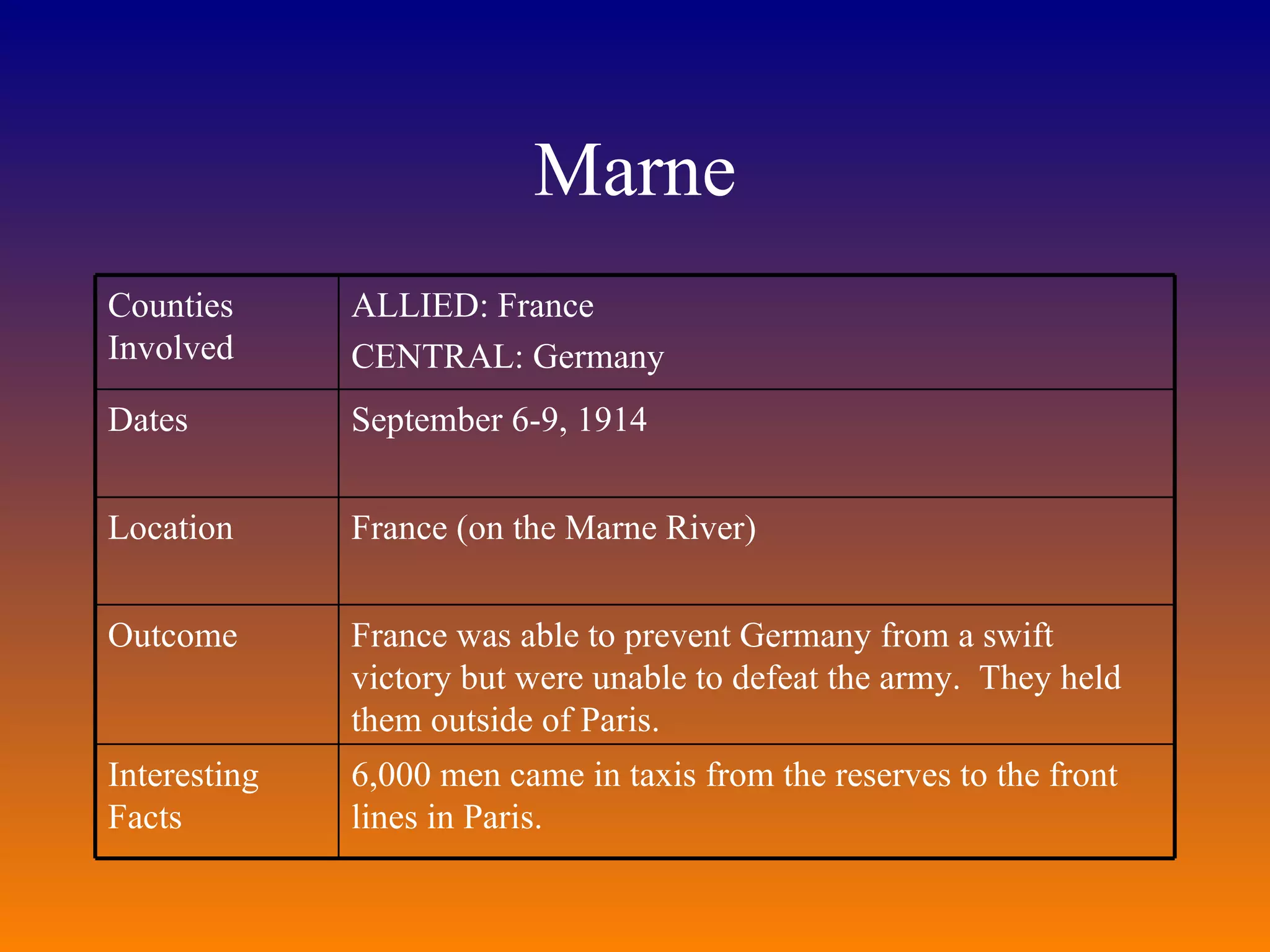
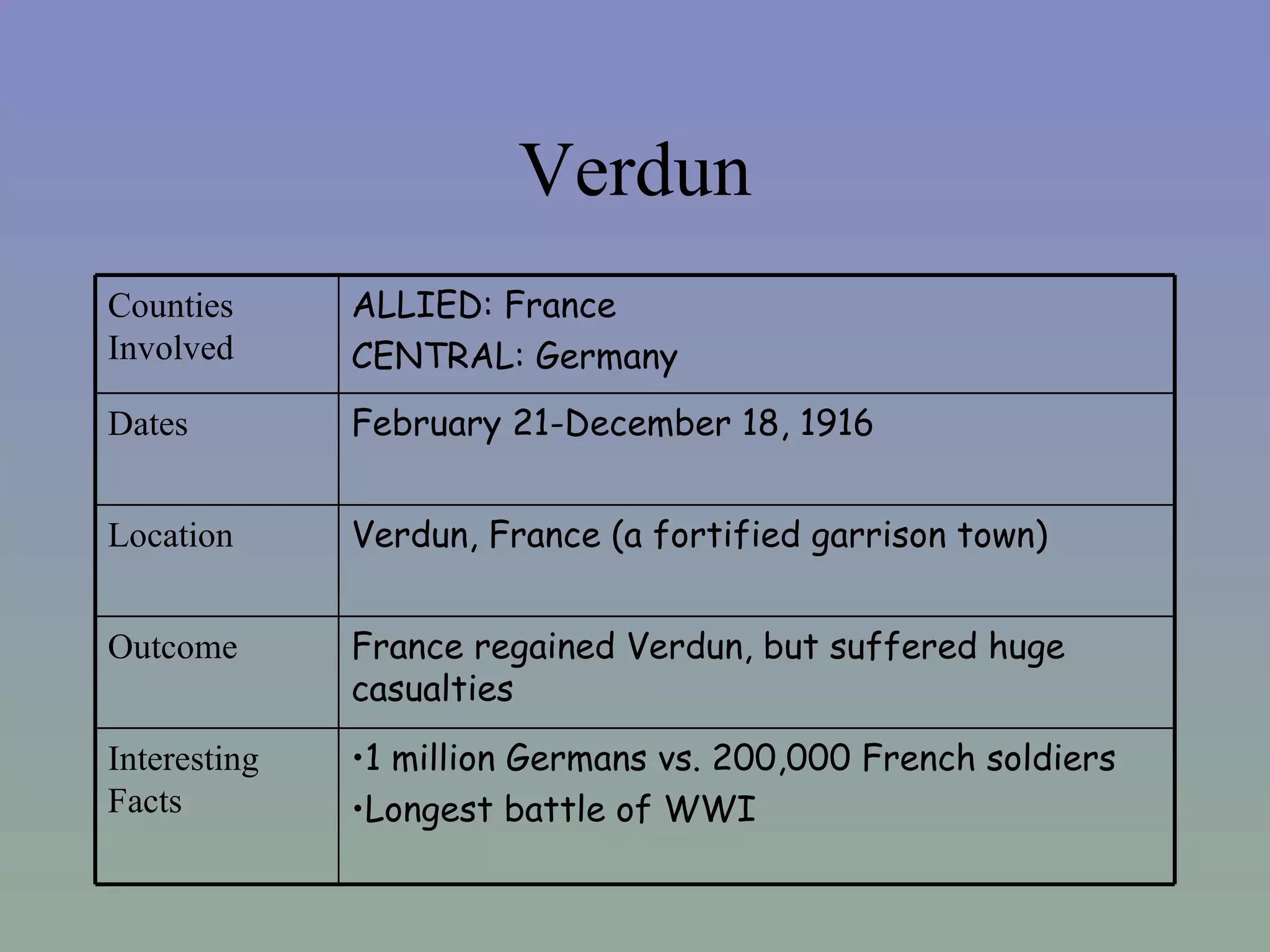
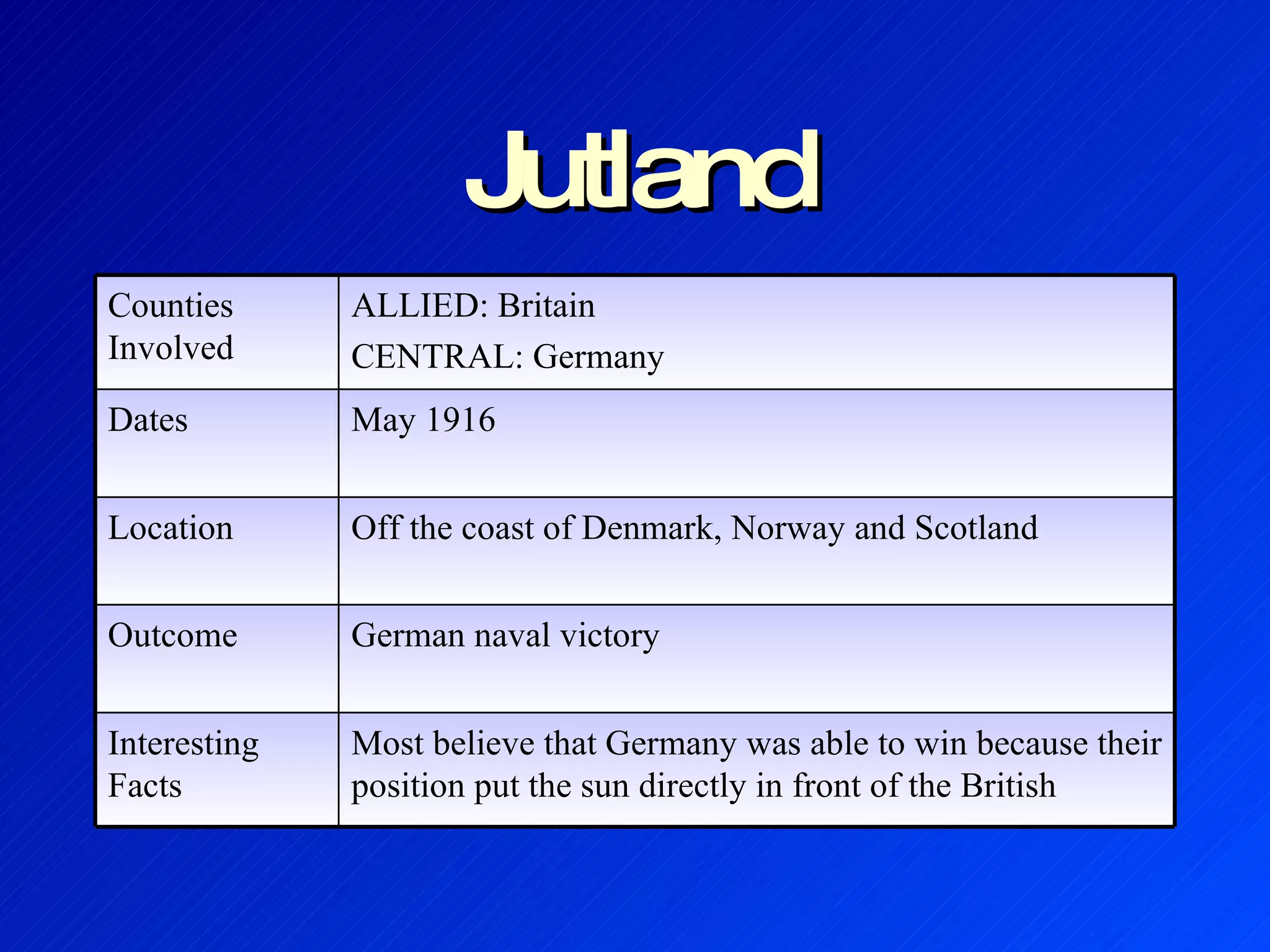
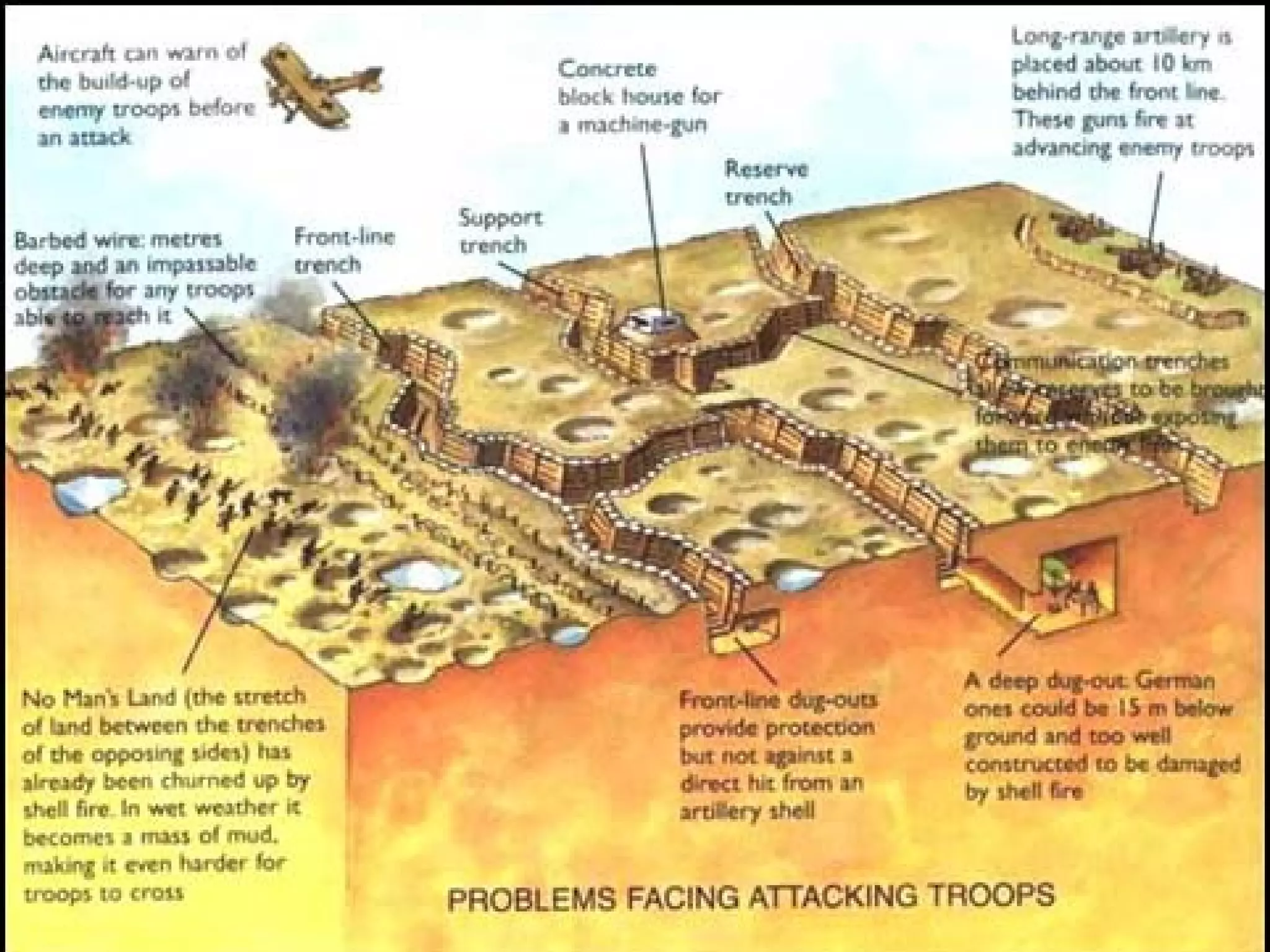
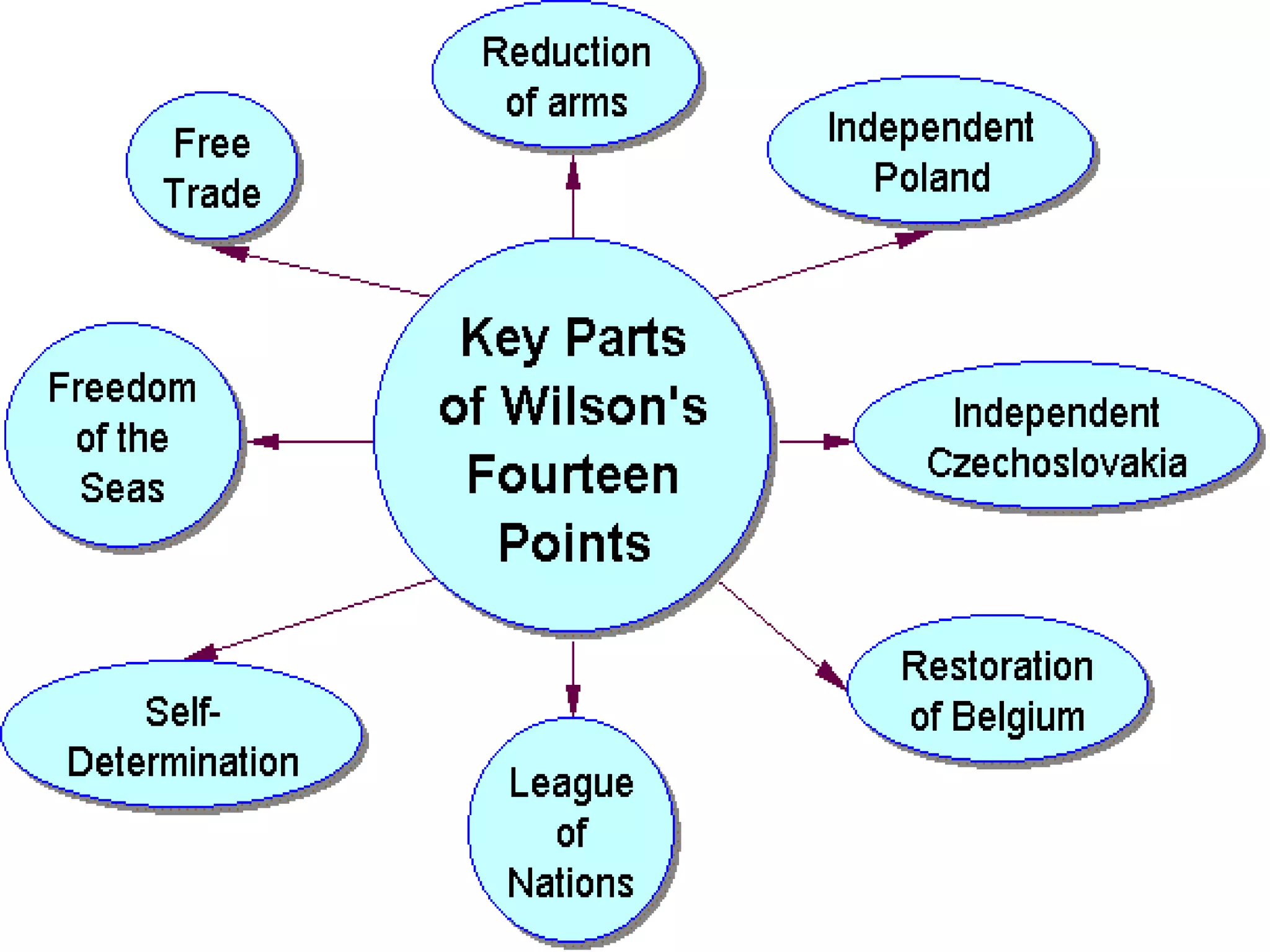
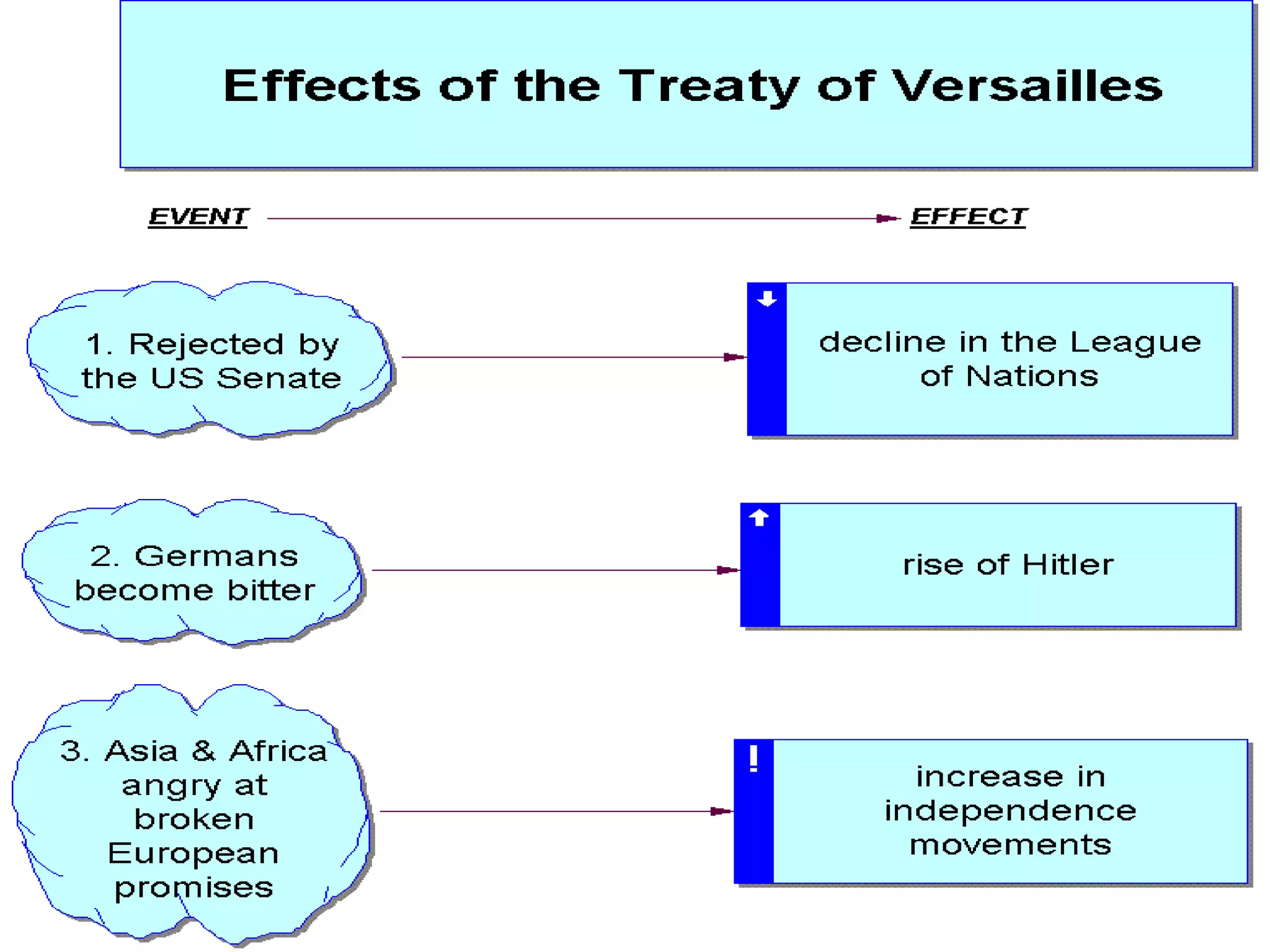
The document provides background information on the causes and key events of World War I involving the United States. It discusses the U.S. remaining neutral at first while supplying both sides, with greater support and trade going to the Allies. Two main events, the sinking of the Lusitania and the Zimmerman Telegram, shifted American opinion towards supporting the Allies. The U.S. entered the war in 1917 and sent troops to help achieve an Allied victory by 1918.