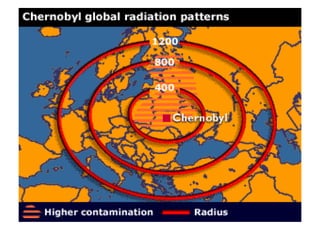
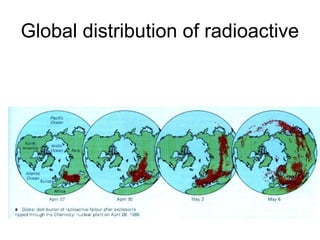
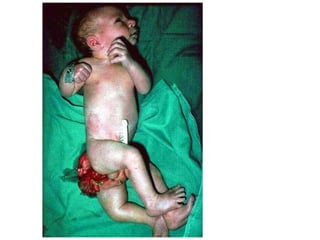
Gerald Ford became President after Nixon resigned due to the Watergate scandal. Ford pardoned Nixon to help the country move past Watergate. He also signed laws increasing campaign finance regulations and government ethics oversight. Jimmy Carter focused on the energy crisis and reducing US dependence on foreign oil through conservation and the National Energy Act. Carter advanced human rights both domestically by appointing more minorities and women, and internationally by cutting aid to rights-abusing countries. He helped broker the Camp David Accords between Israel and Egypt. The 1970s also saw environmental concerns rise with events like the publication of Silent Spring and the creation of the EPA. The Three Mile Island incident highlighted issues with nuclear energy safety.