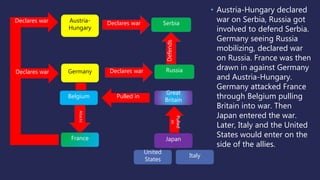
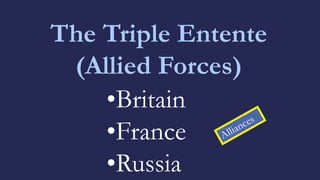
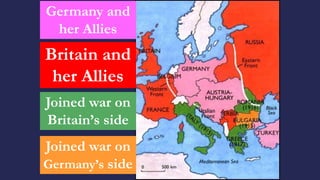
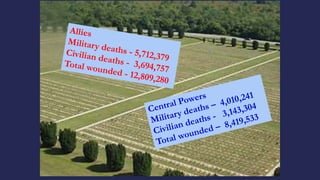
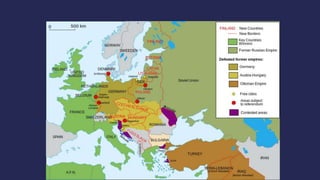
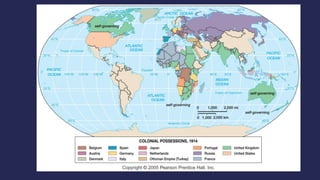
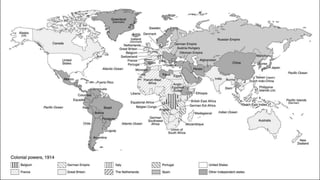
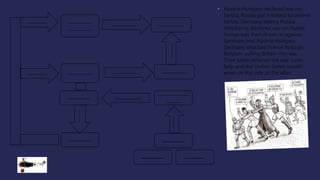
The document discusses America before World War I. It describes the 1912 presidential election and Wilson's victory. At home, progressive reforms addressed the economy and child labor. Abroad, tensions rose over Mexico's revolution and Pancho Villa's attacks. When Europe entered World War I due to alliances and the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand, America remained neutral though tensions grew from attacks on U.S. ships until America joined the Allies in 1917 after the Zimmerman Telegram.