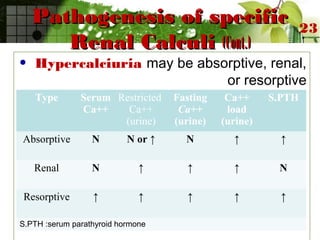
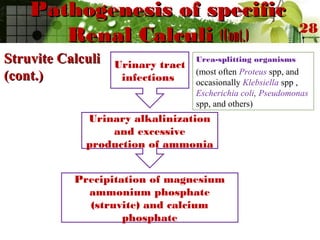
This document discusses urinary lithiasis (kidney stones) in children. It covers the causes, types, and treatment of stones. The most common types are calcium oxalate and calcium phosphate stones, caused by hypercalciuria in 30-60% of cases. Other causes include cystinuria, struvite stones related to urinary tract infections, and uric acid stones. Treatment depends on the stone location and composition but may involve removal procedures like lithotripsy or addressing the underlying metabolic condition through diet, medication, or surgery. The goal is to dissolve or pass existing stones and prevent new stone formation.