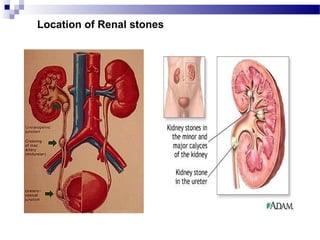
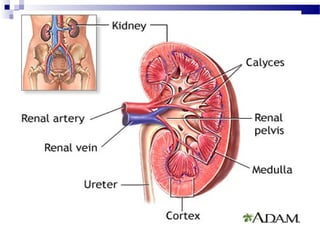
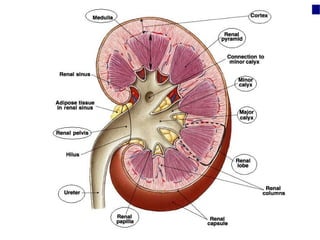
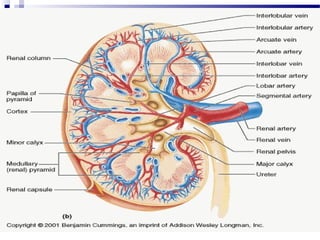
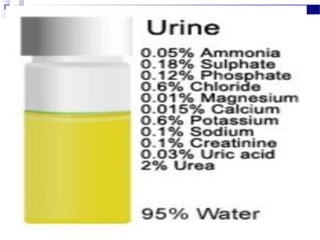
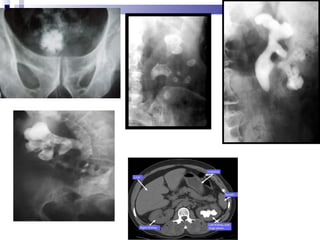
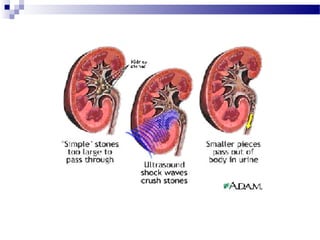
Renal calculi, also known as kidney stones, form when minerals in urine crystallize and deposit on the inner surfaces of the kidneys. The most common types are calcium-containing stones, uric acid stones, struvite-carbonate stones, and cystine stones. Risk factors include dehydration, genetics, diet high in purines or oxalates, and urinary tract infections. Symptoms include flank pain, nausea, and blood in the urine. Diagnosis involves urine analysis, blood tests, imaging like ultrasounds or CT scans. Treatment focuses on pain relief, preventing recurrence through increased fluid intake and dietary changes, and removing stones through extracorporeal shockwave lithotripsy, surgery