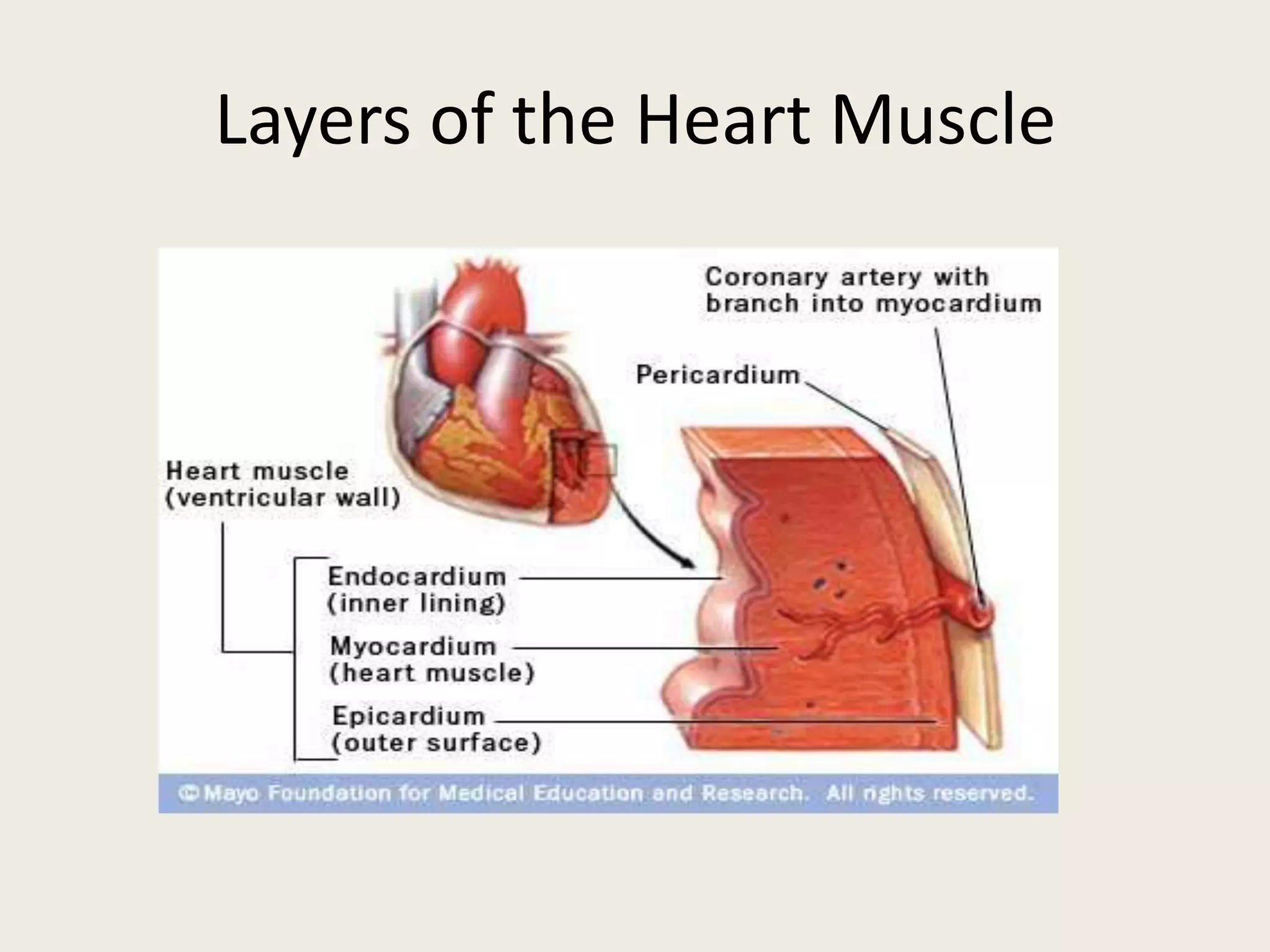
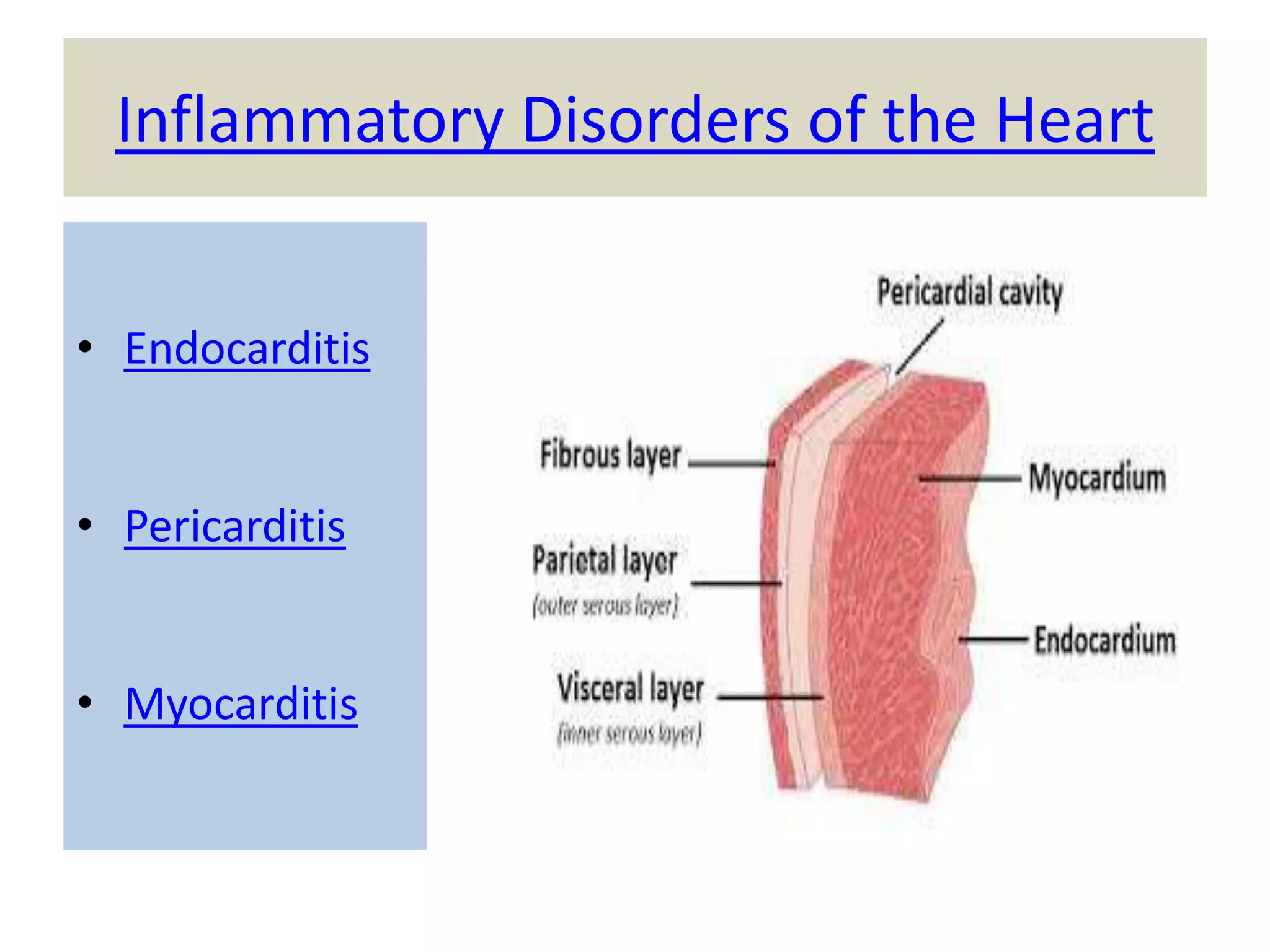
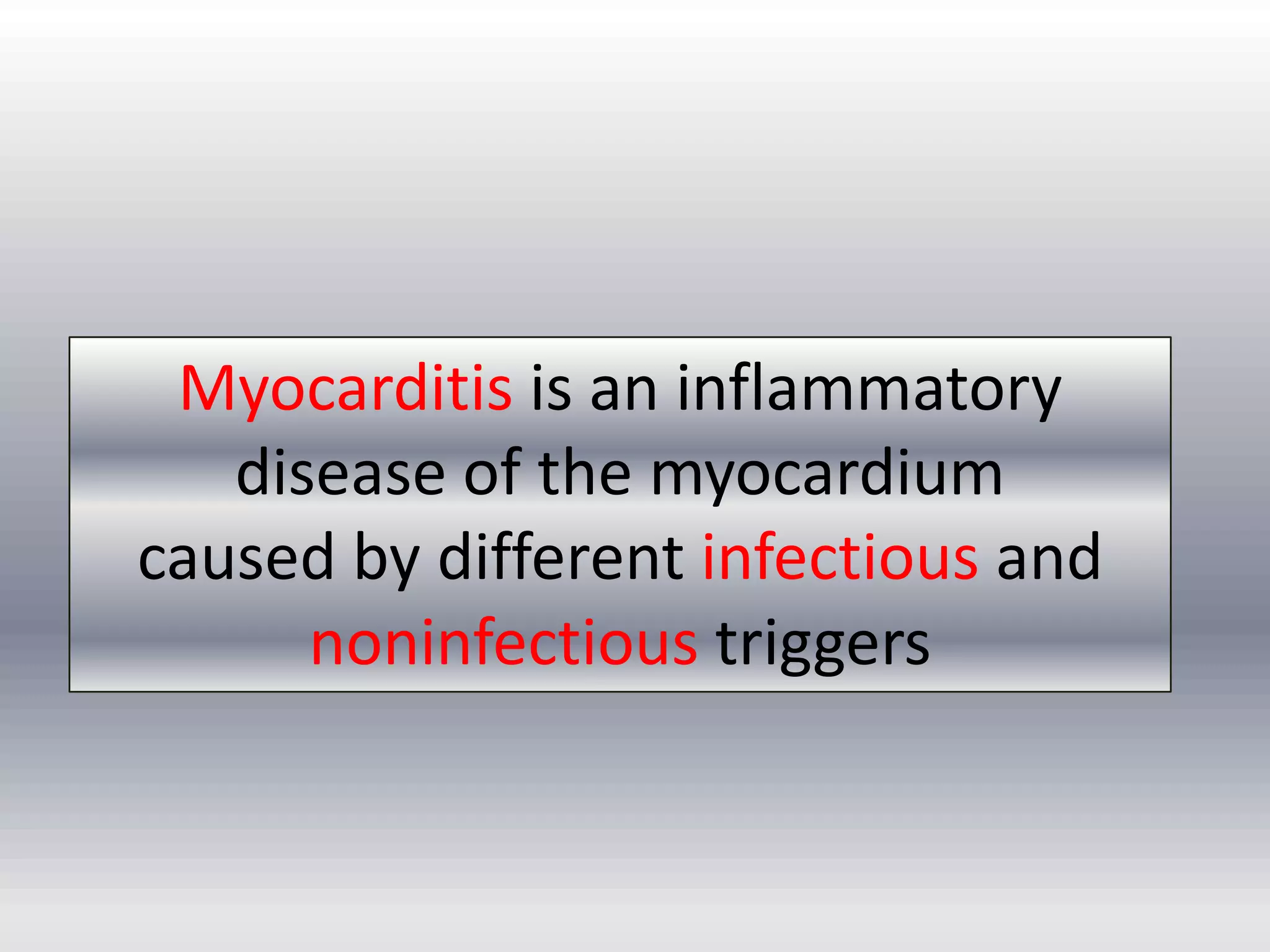
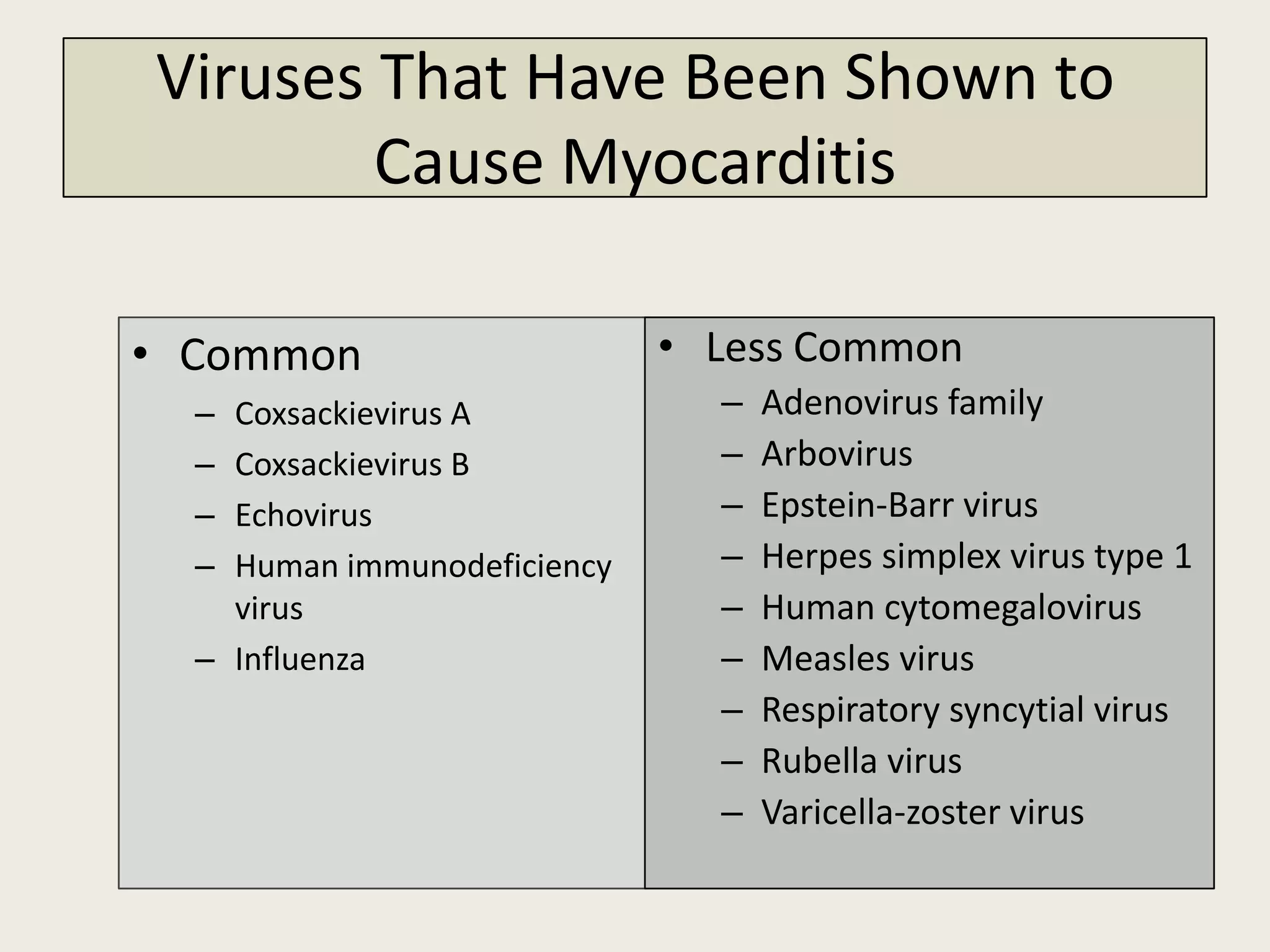
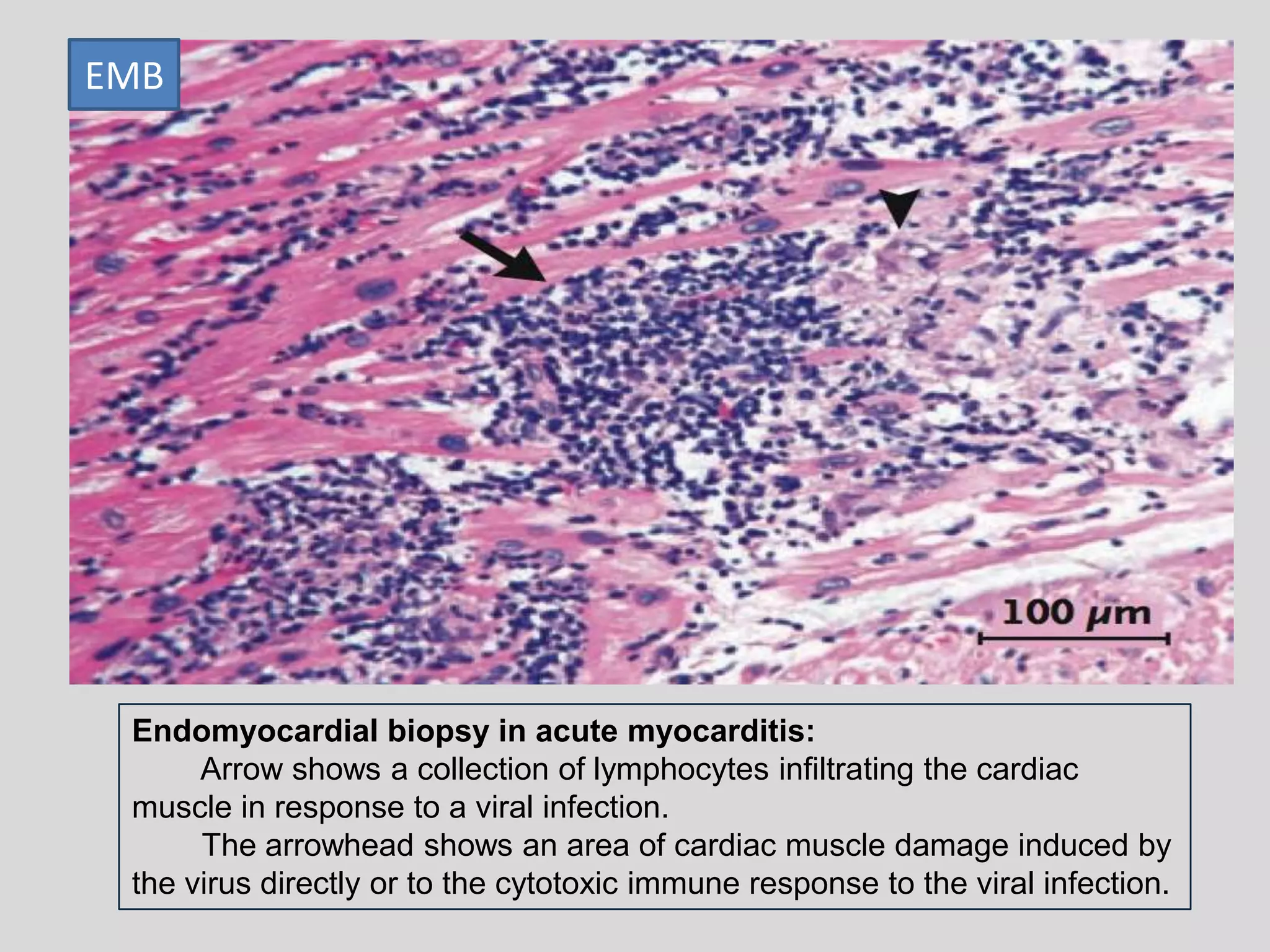
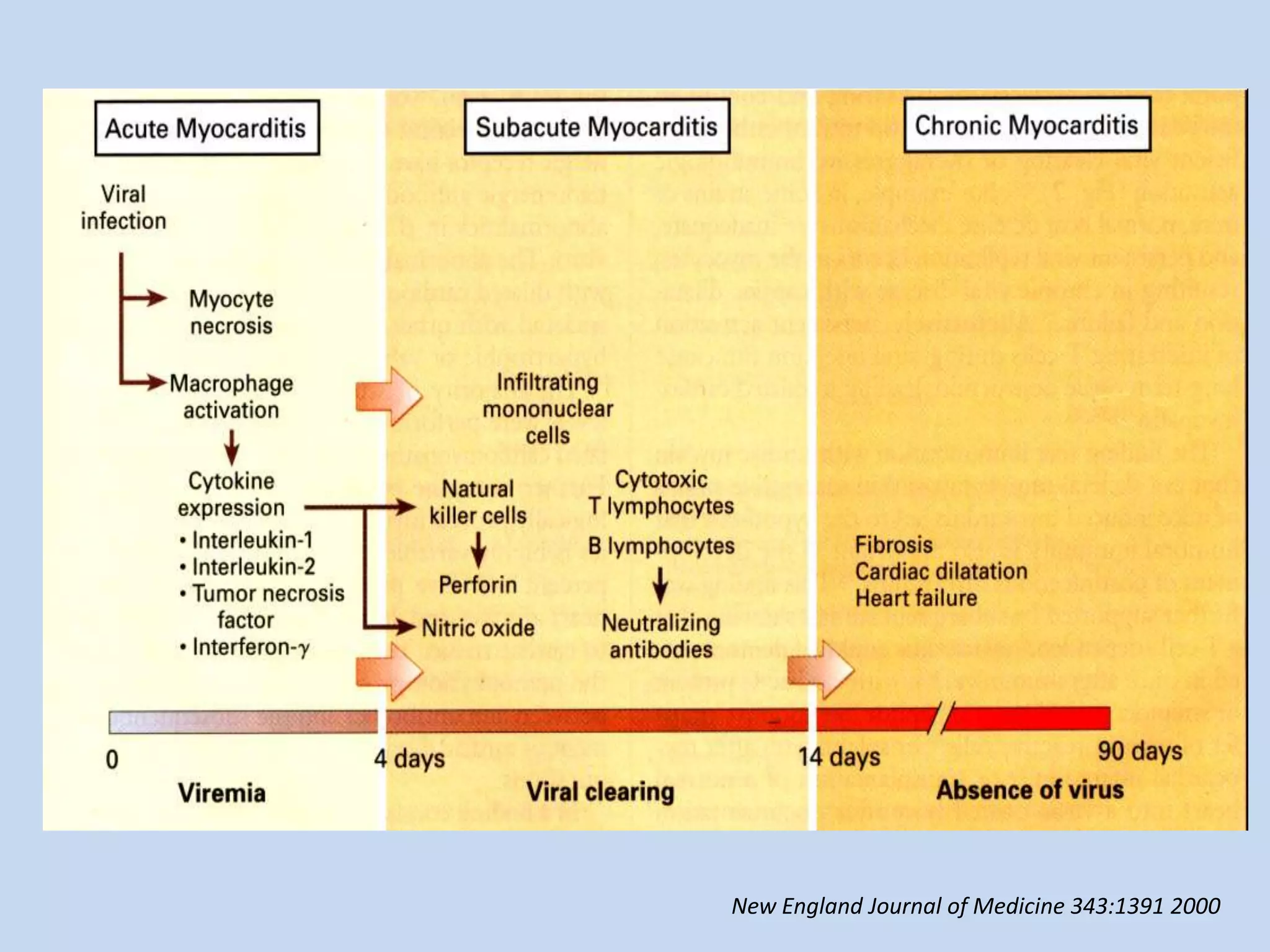
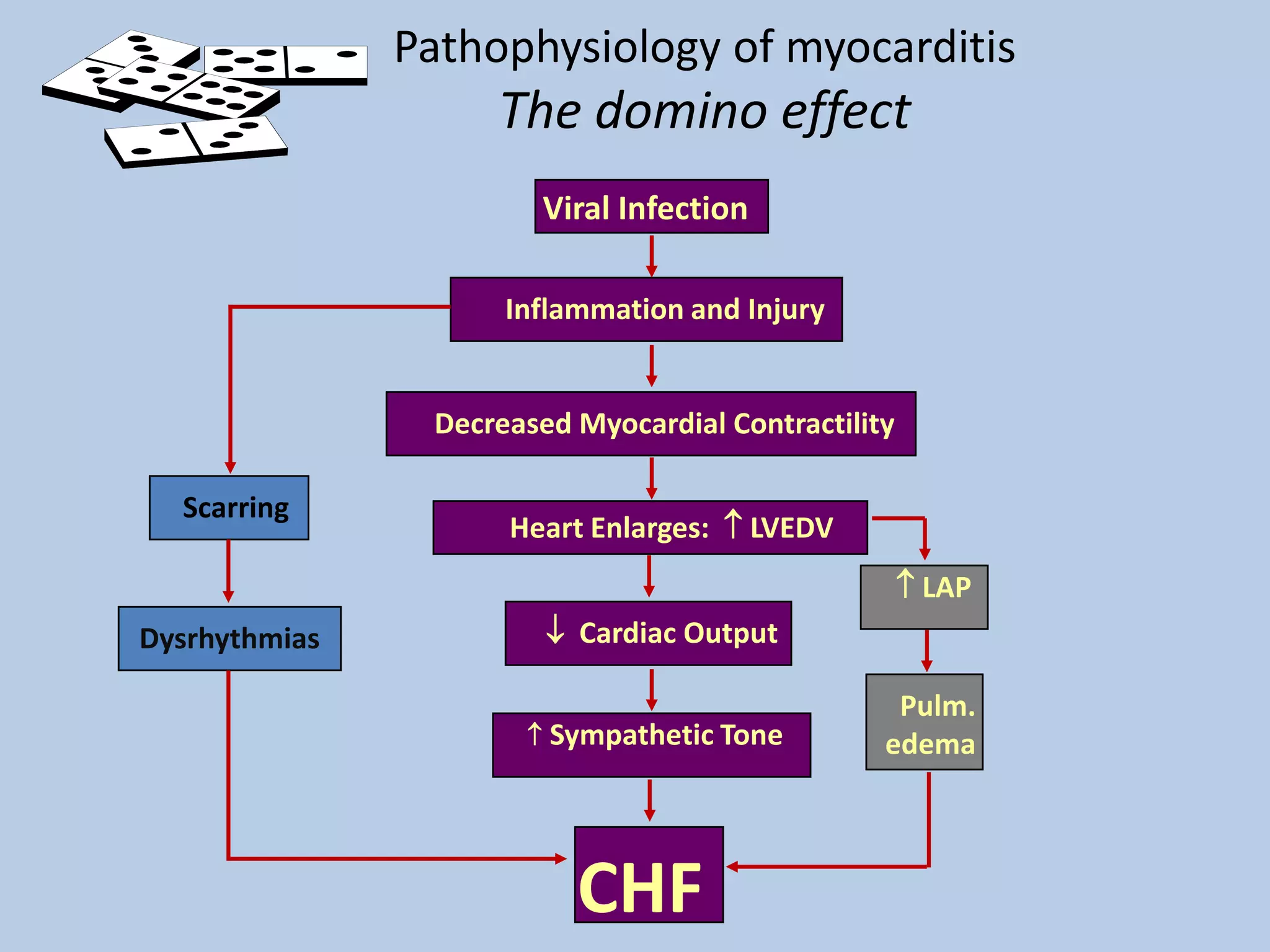
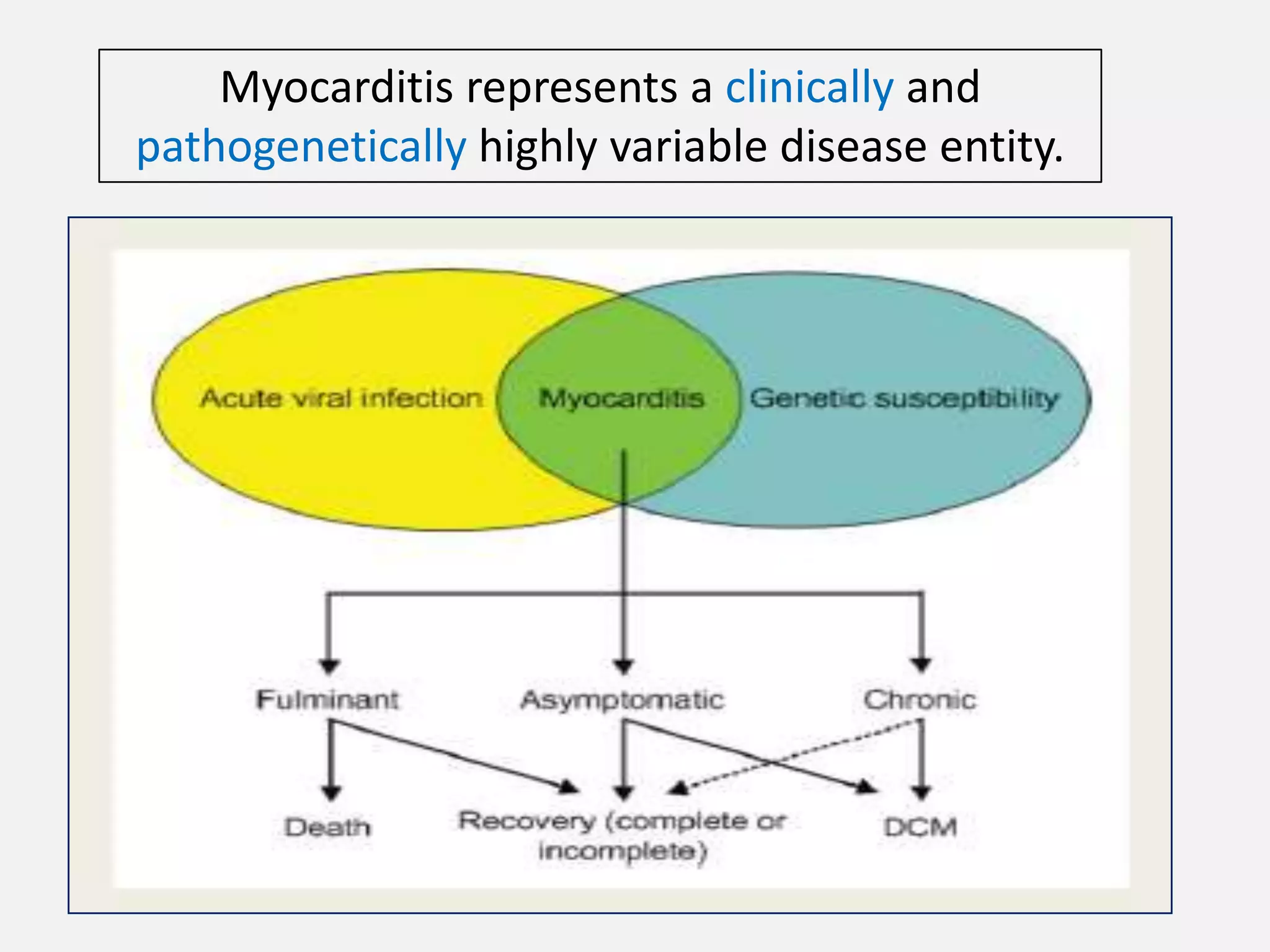
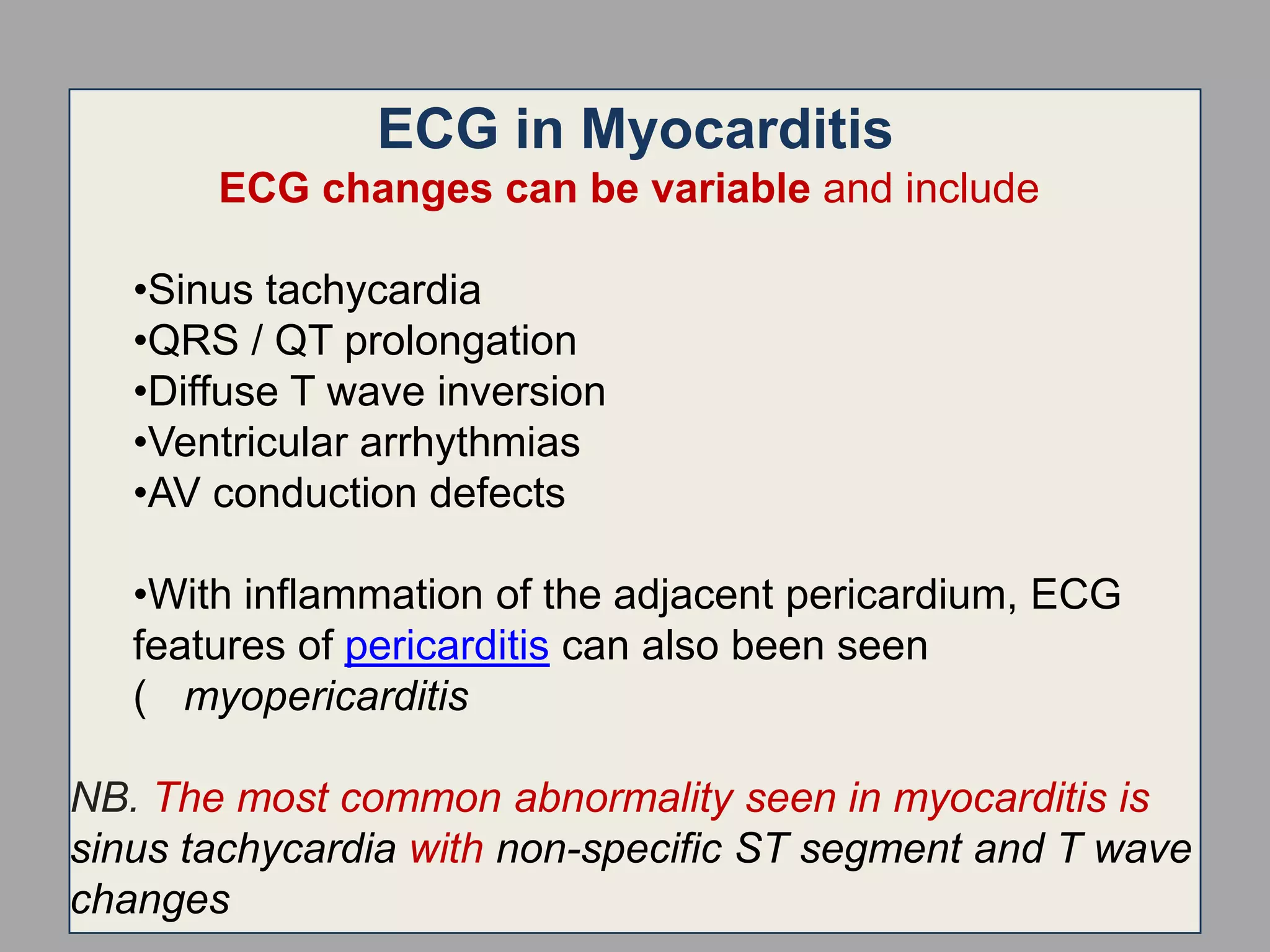
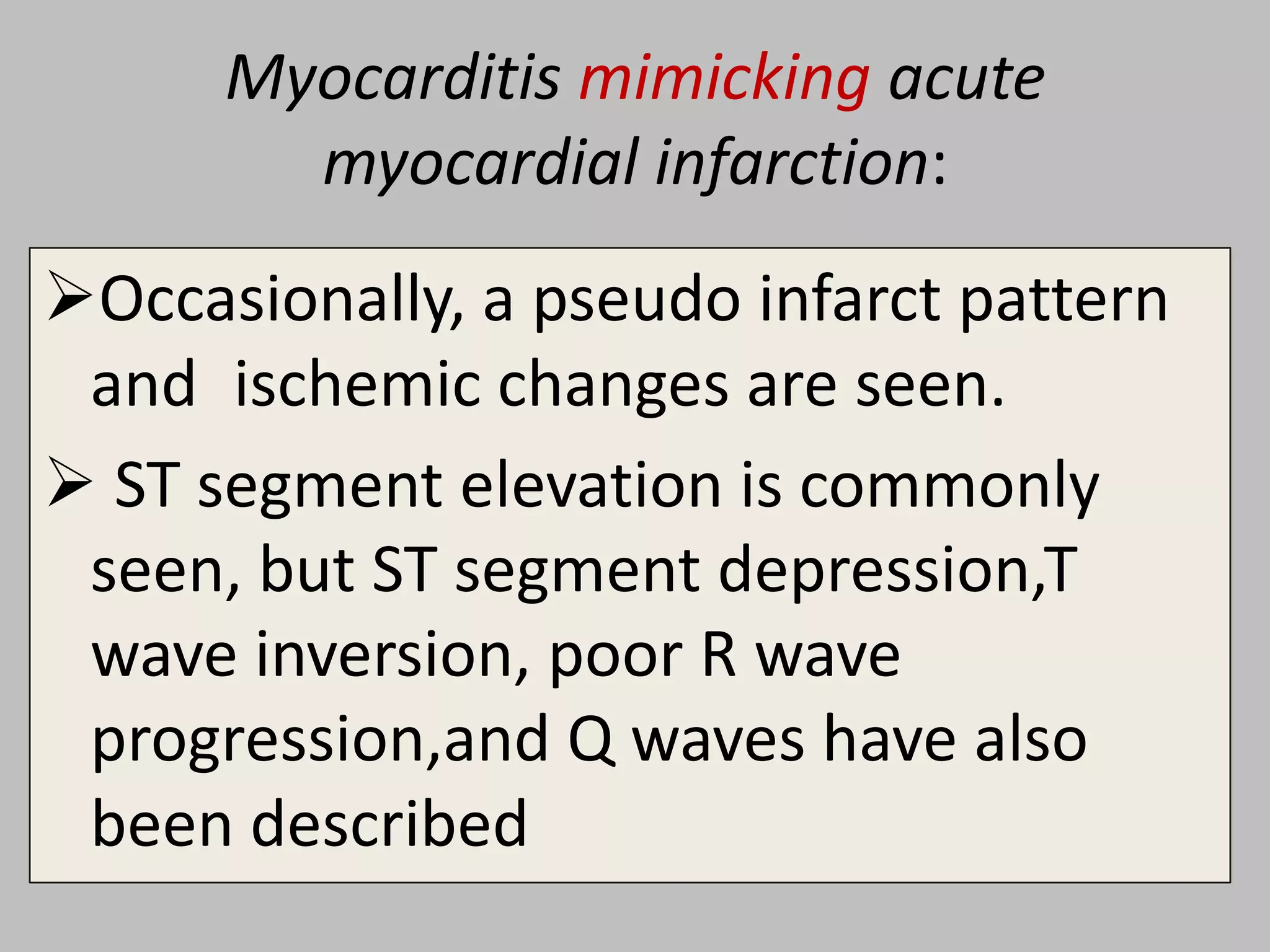
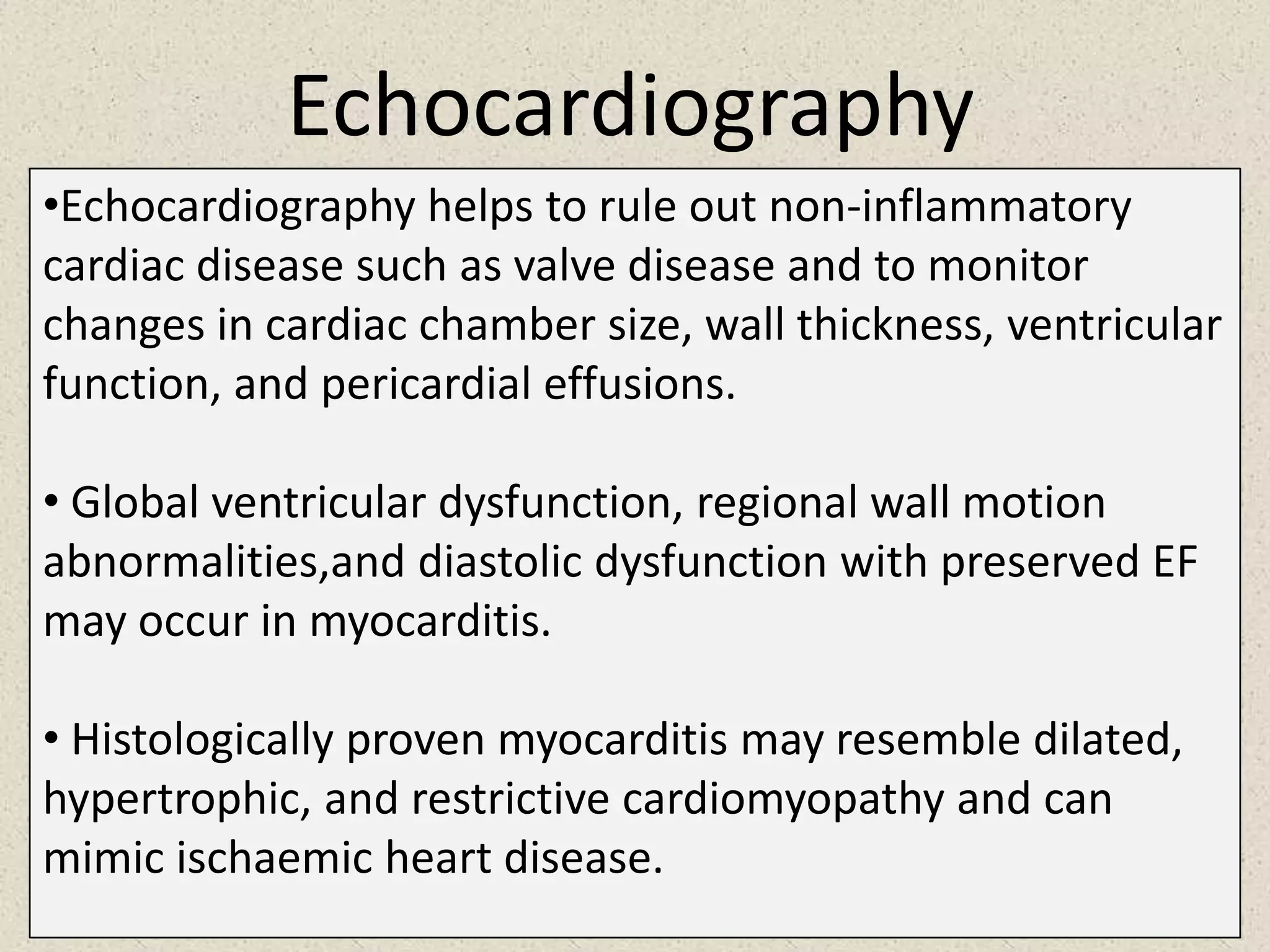
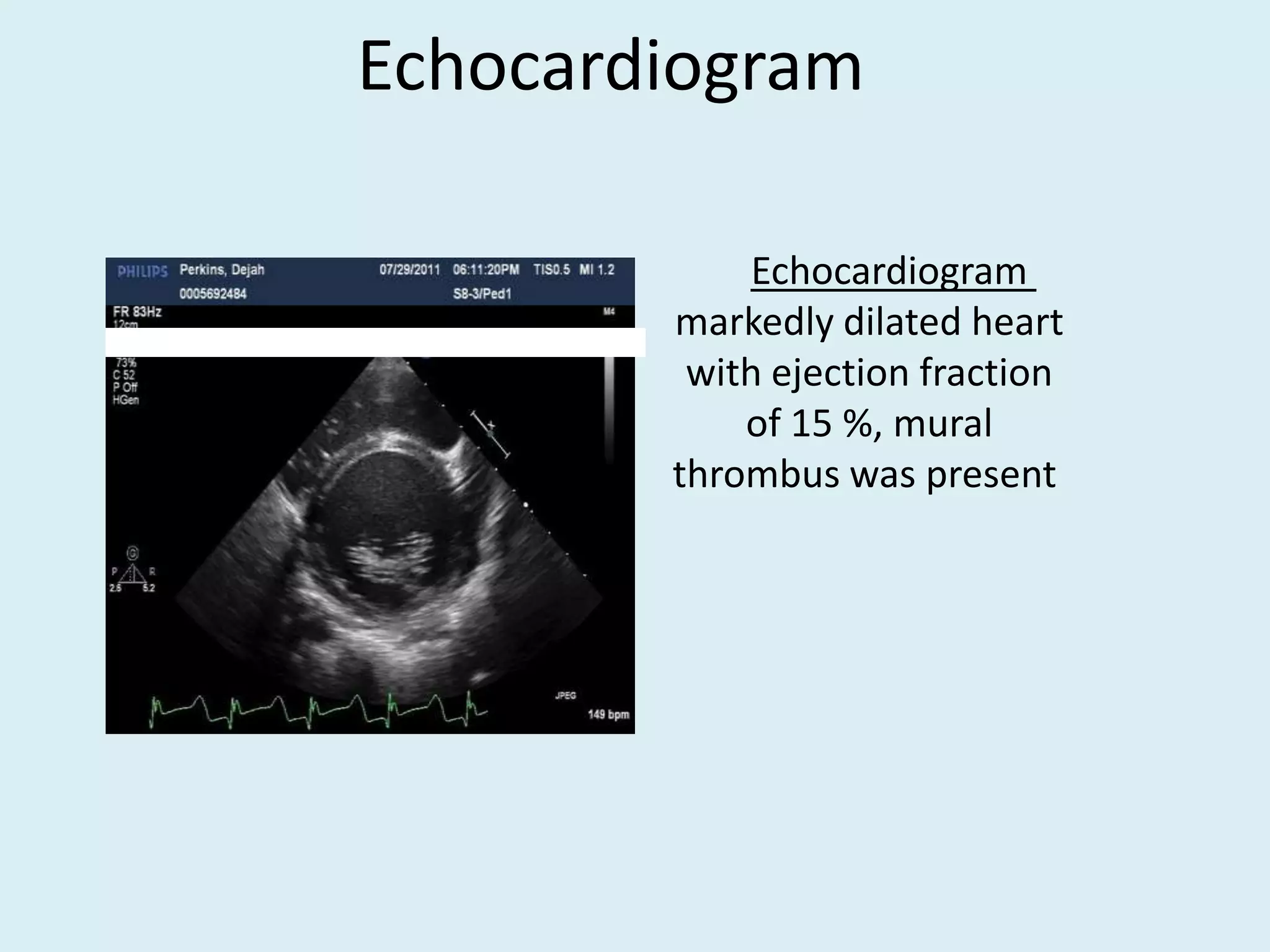
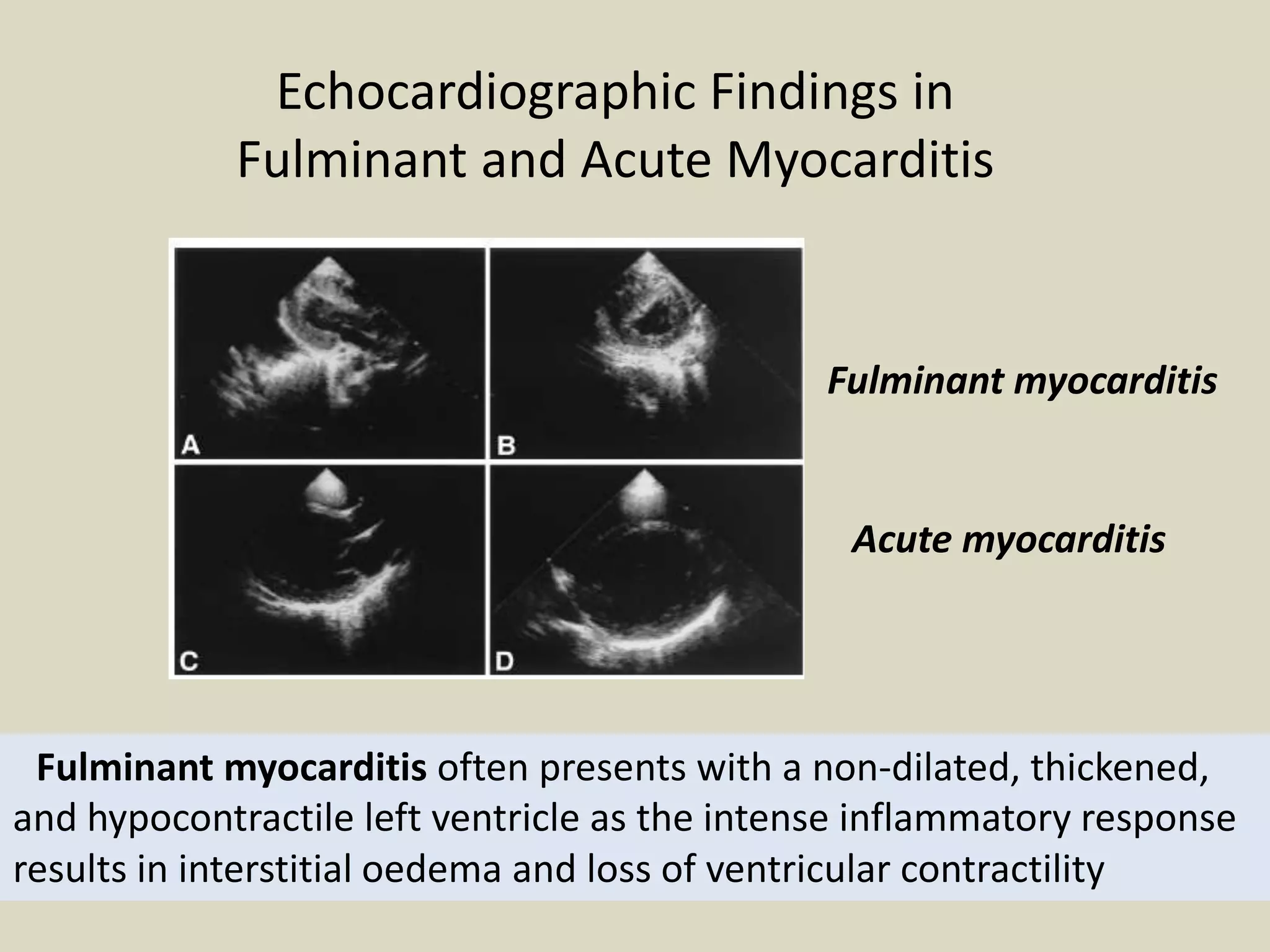
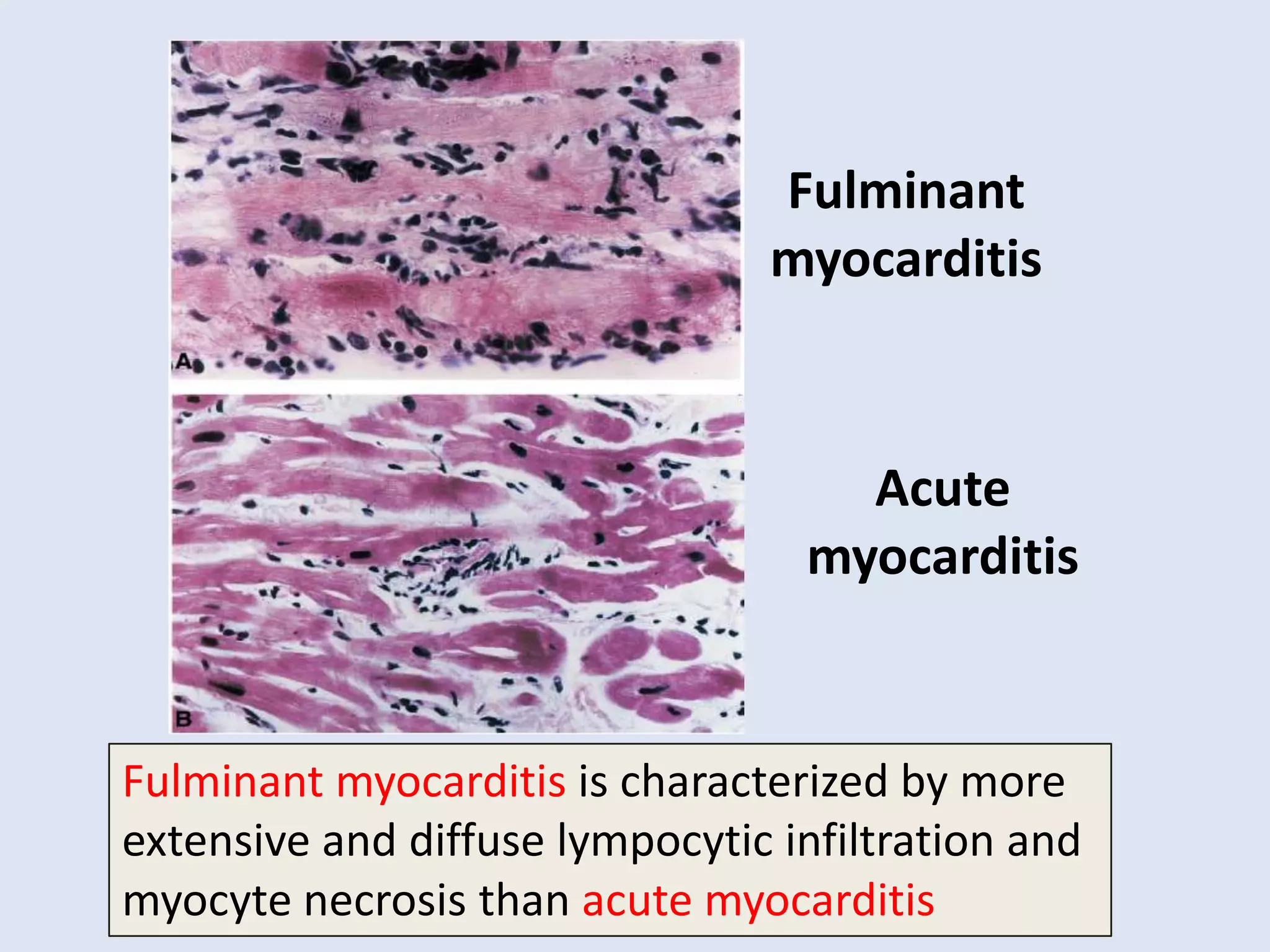
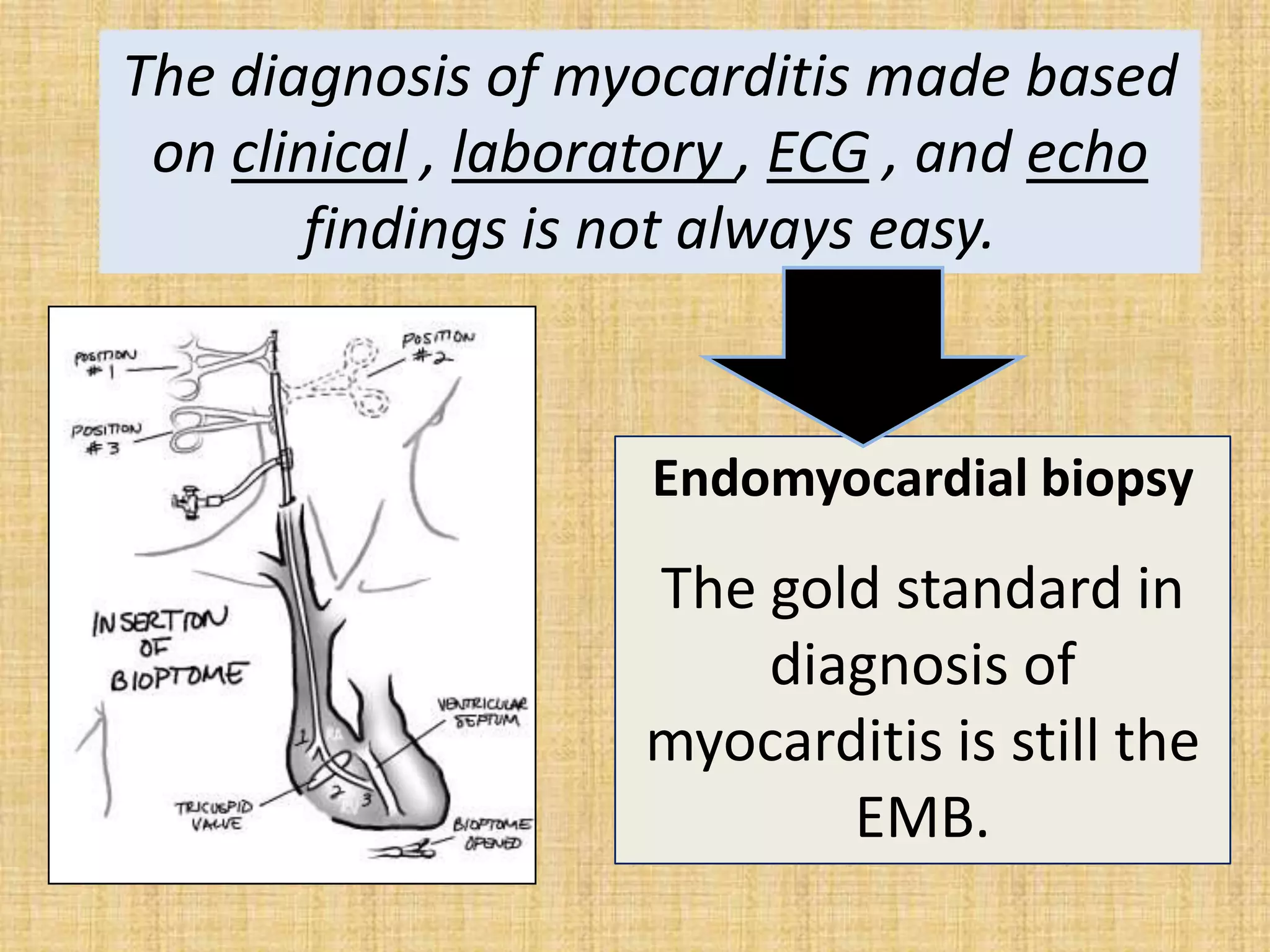
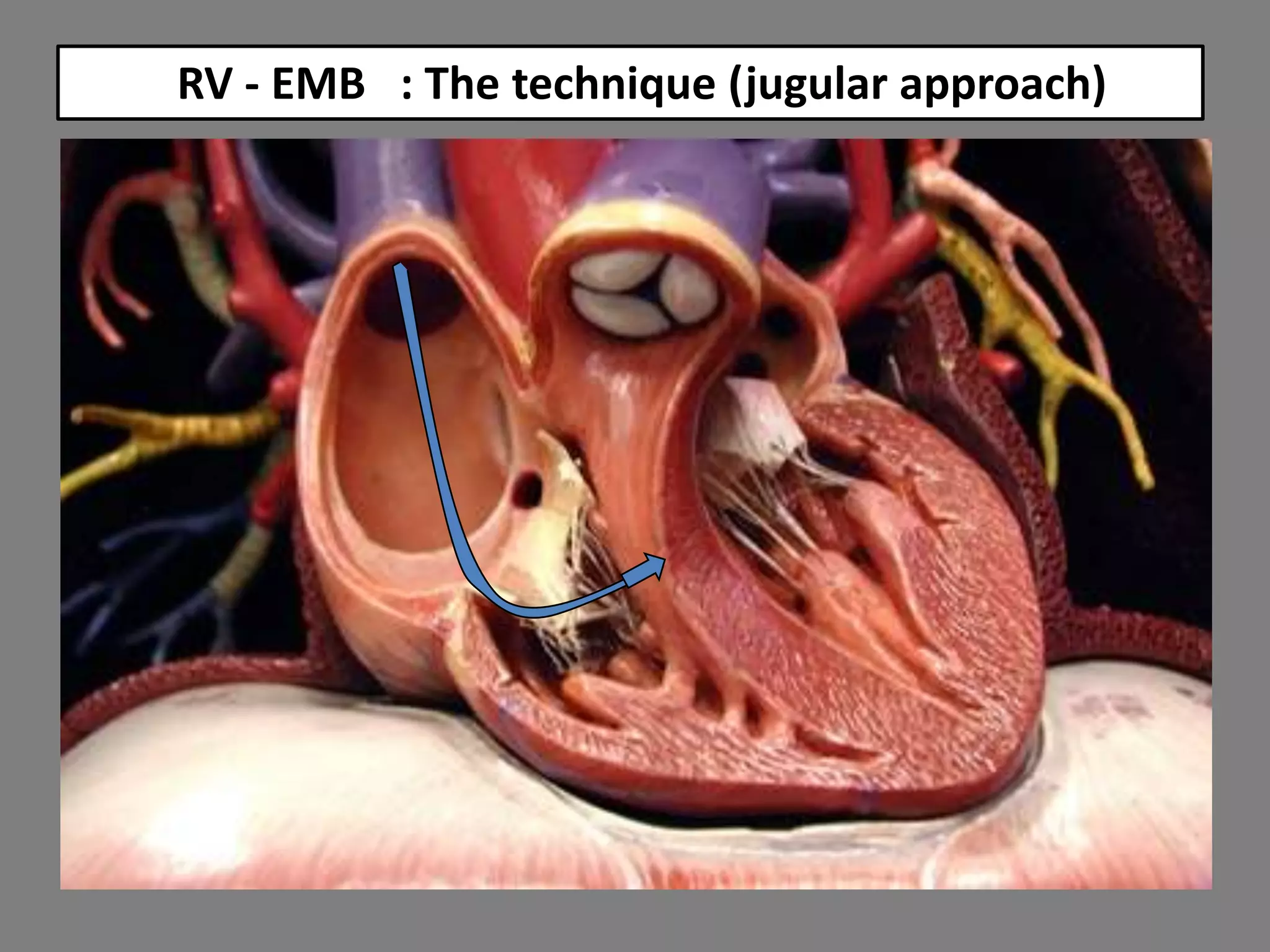
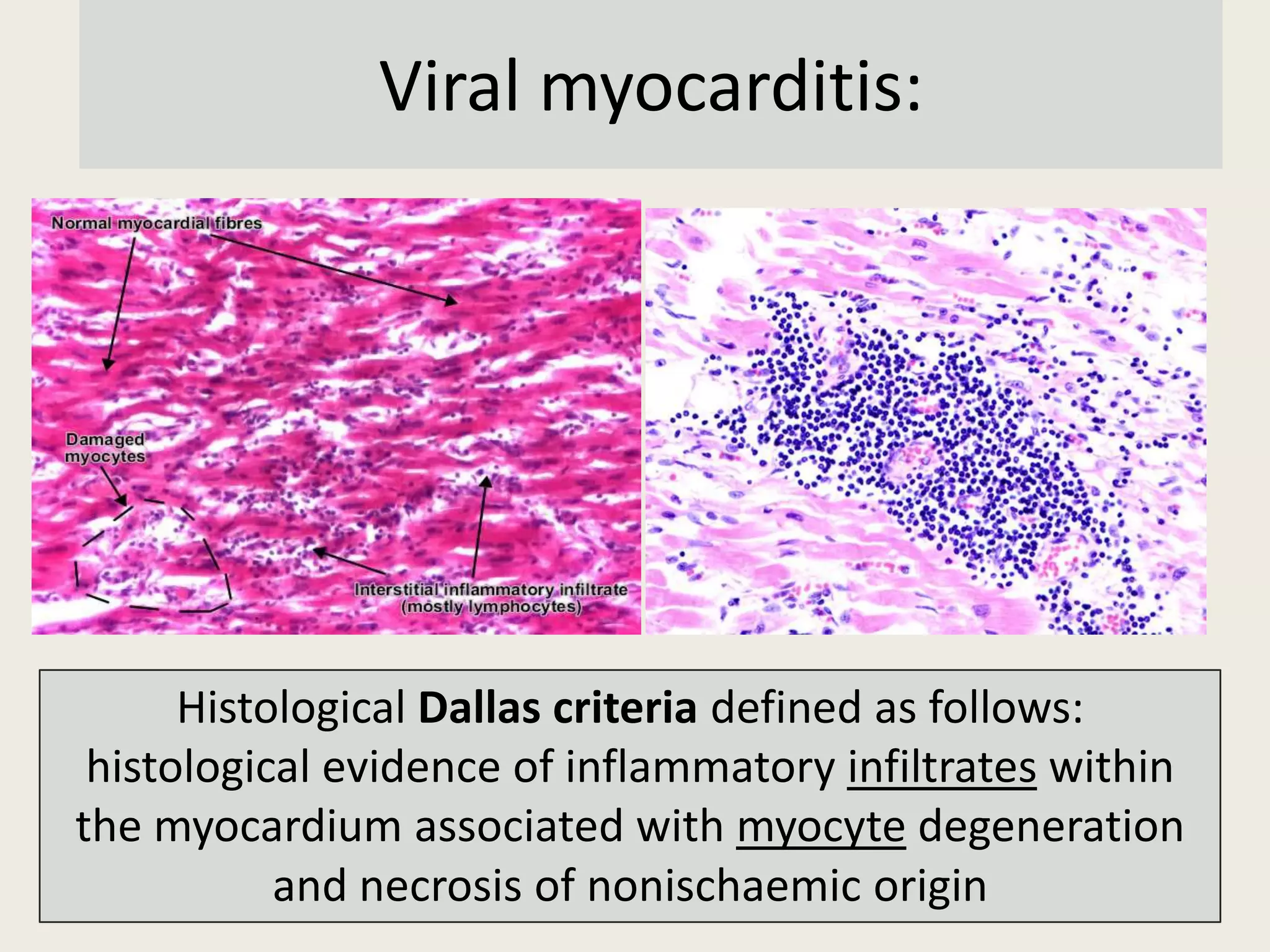
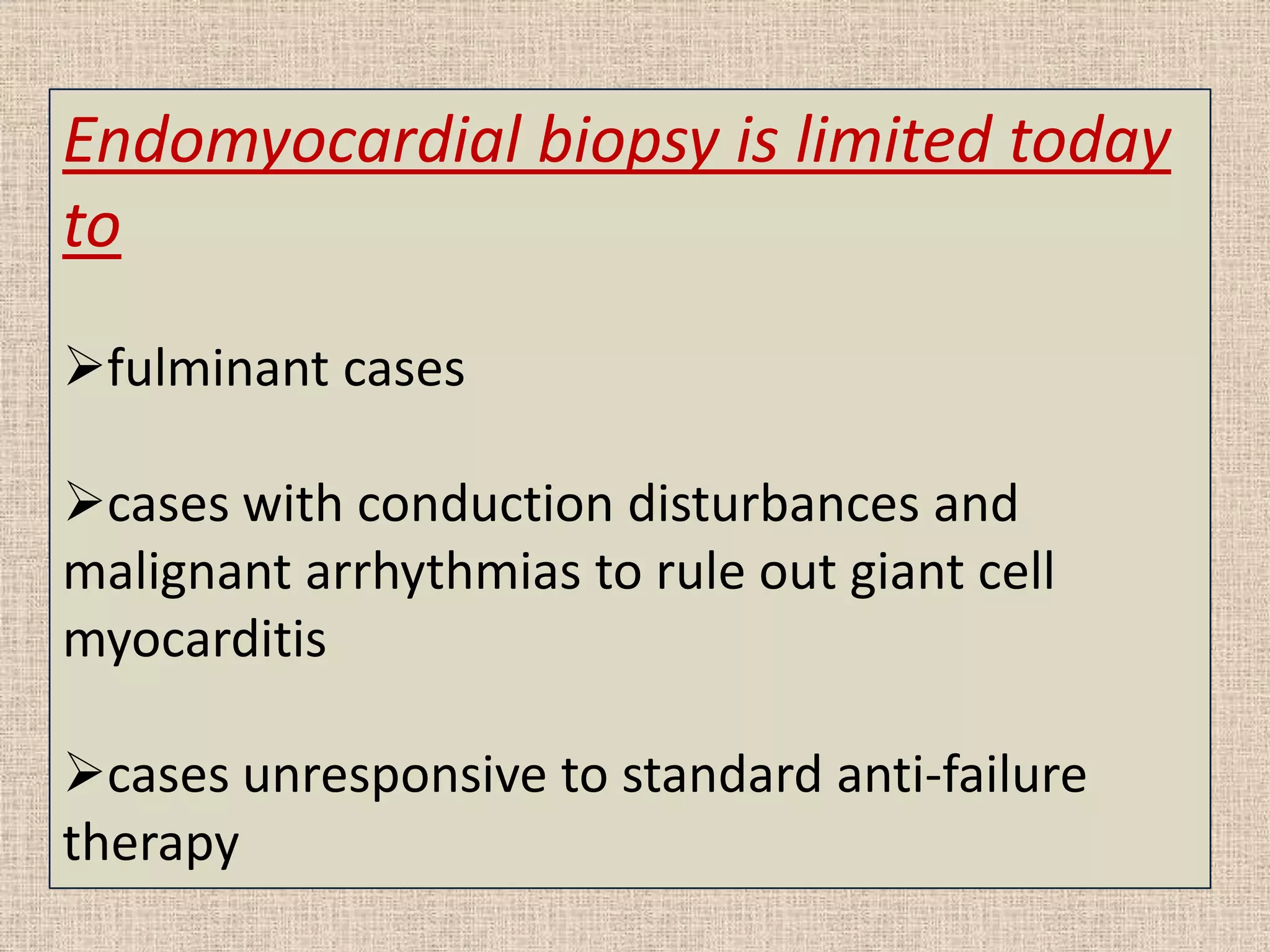
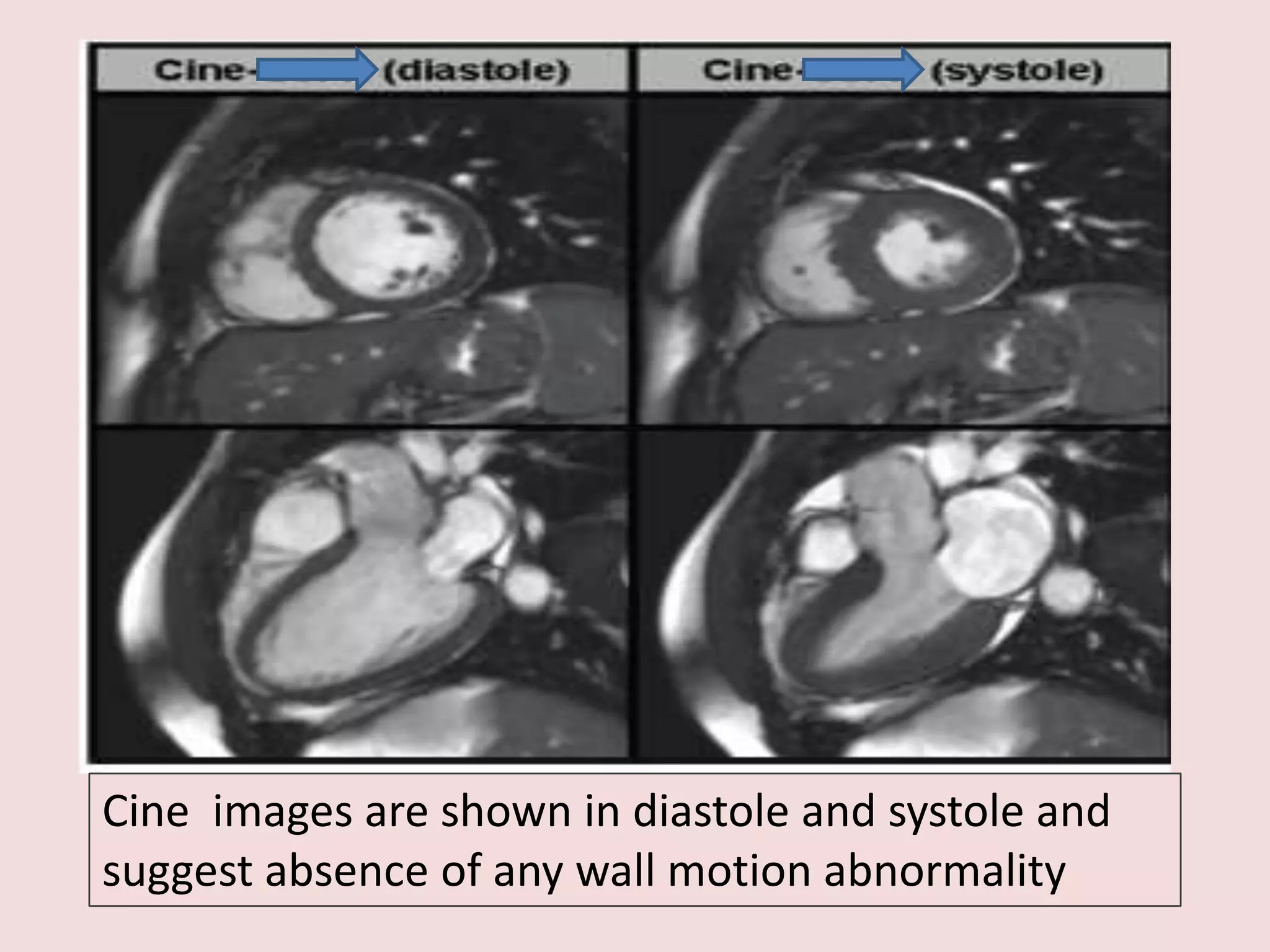
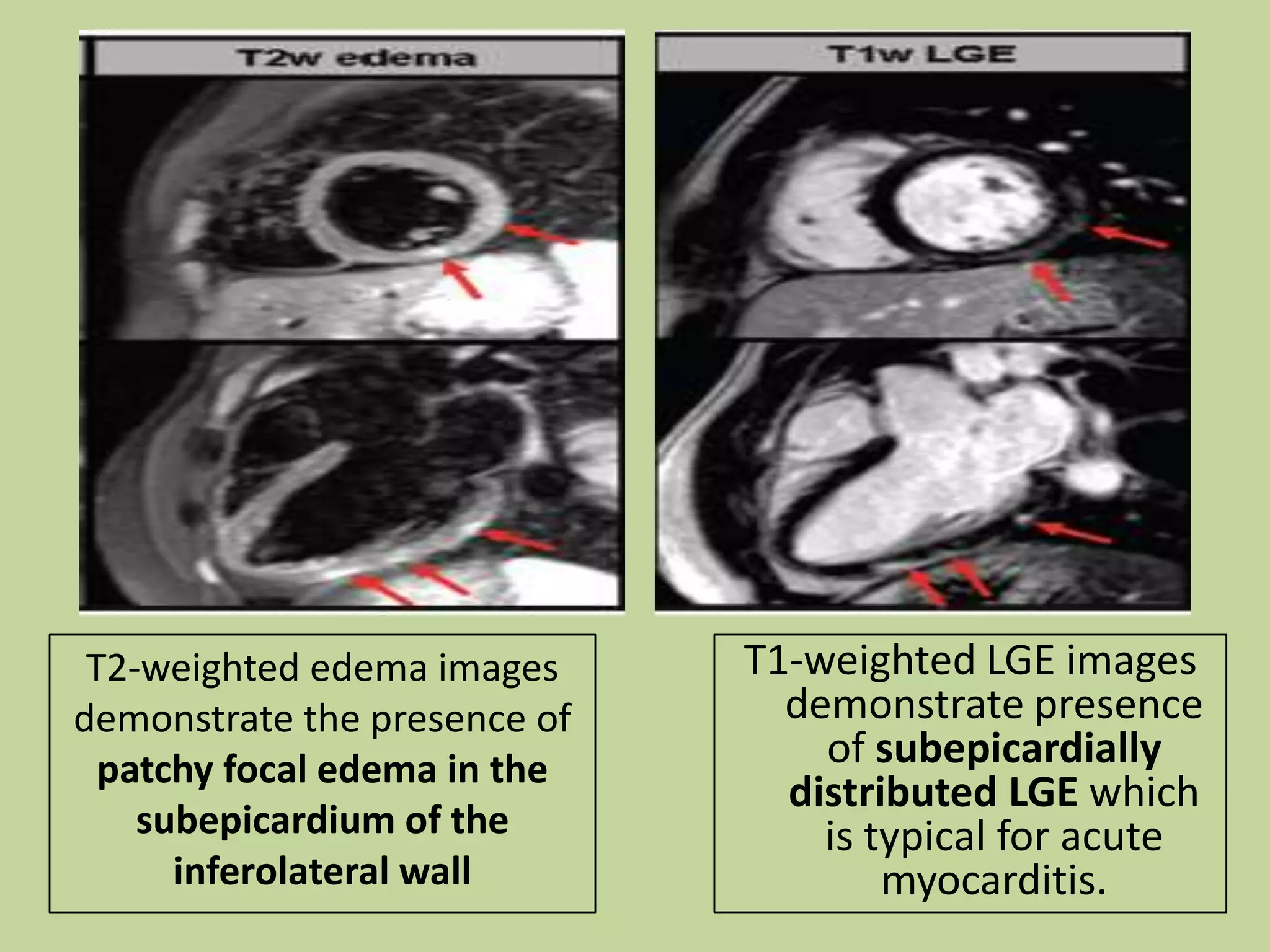
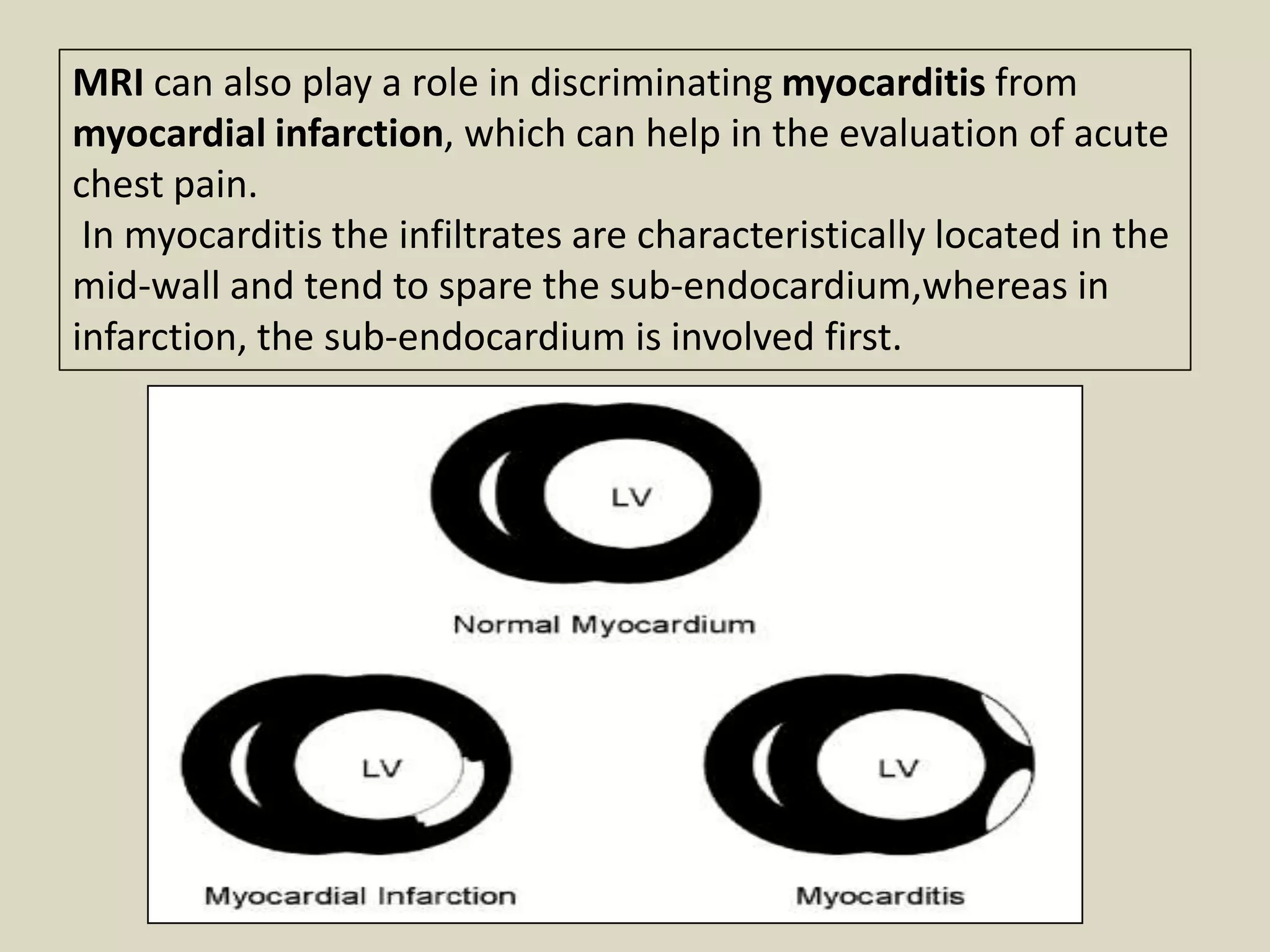
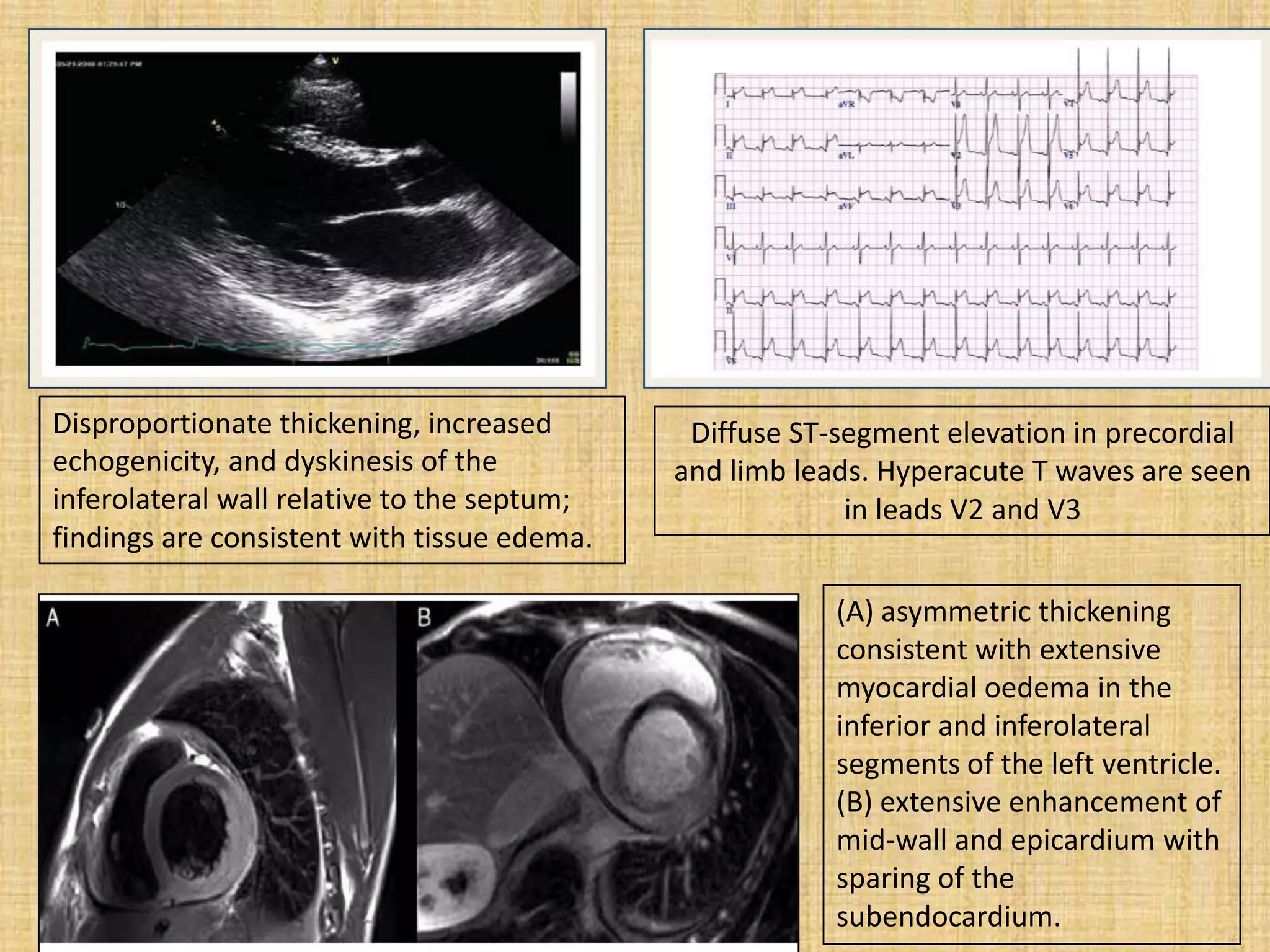
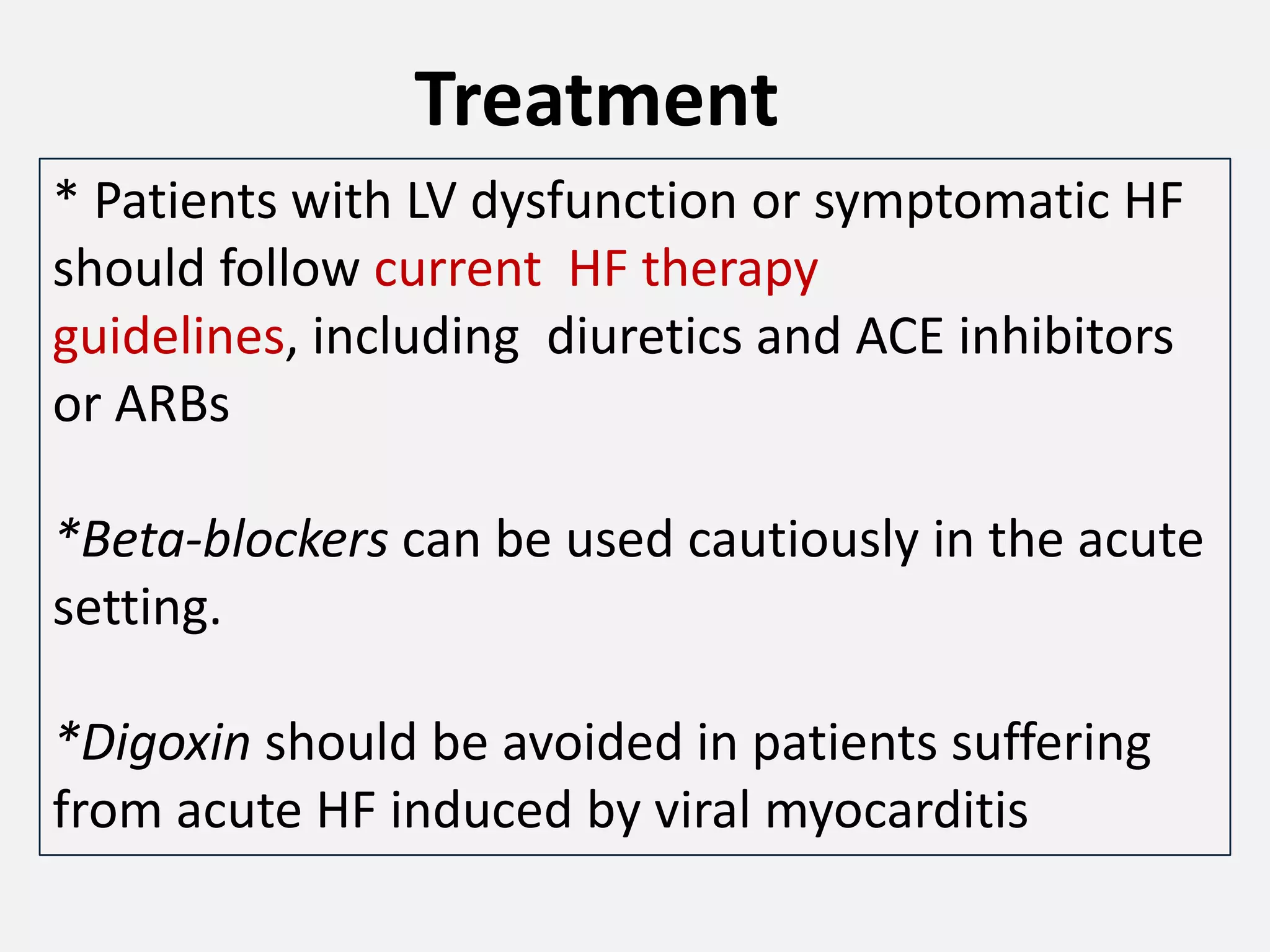
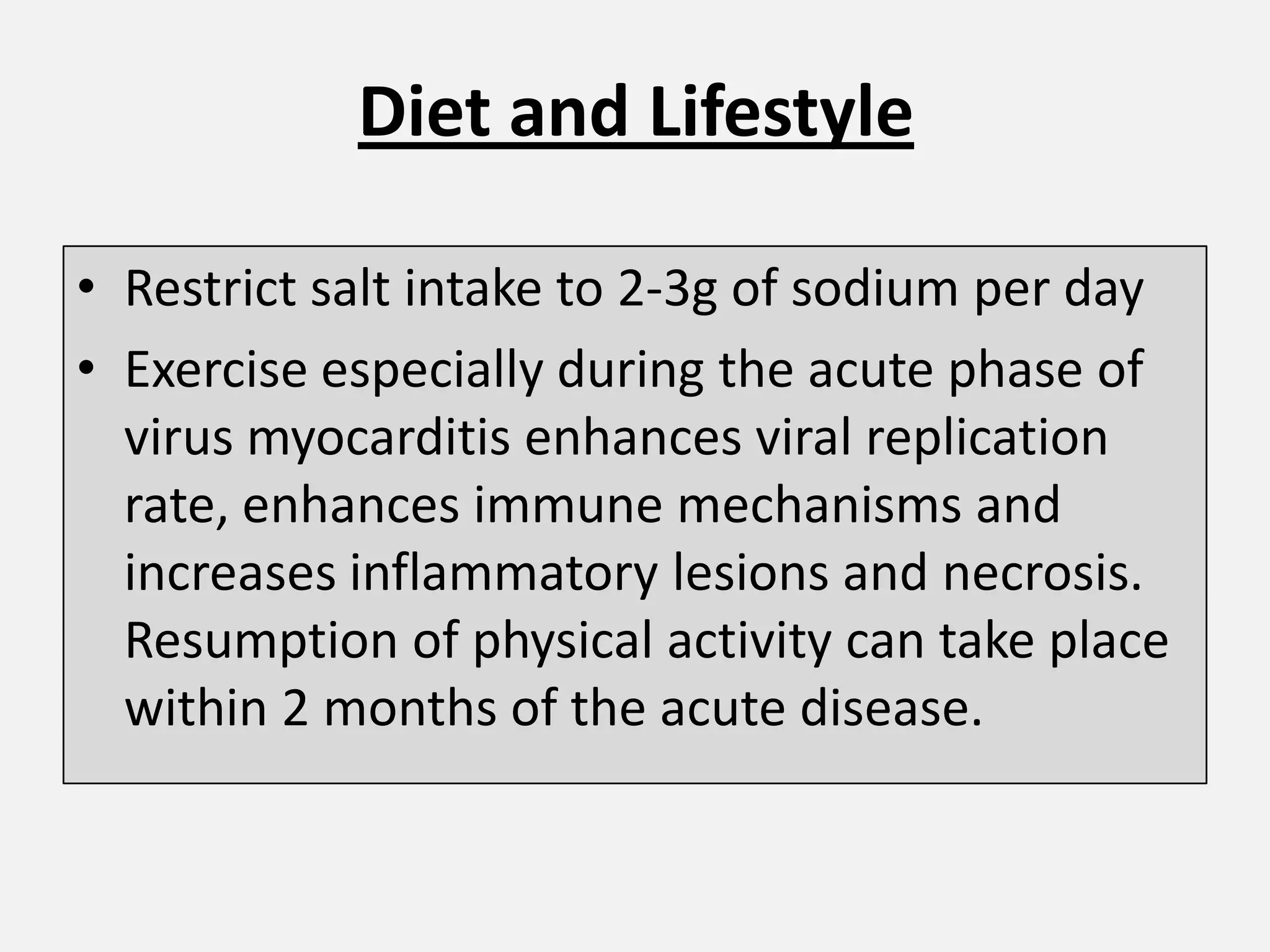
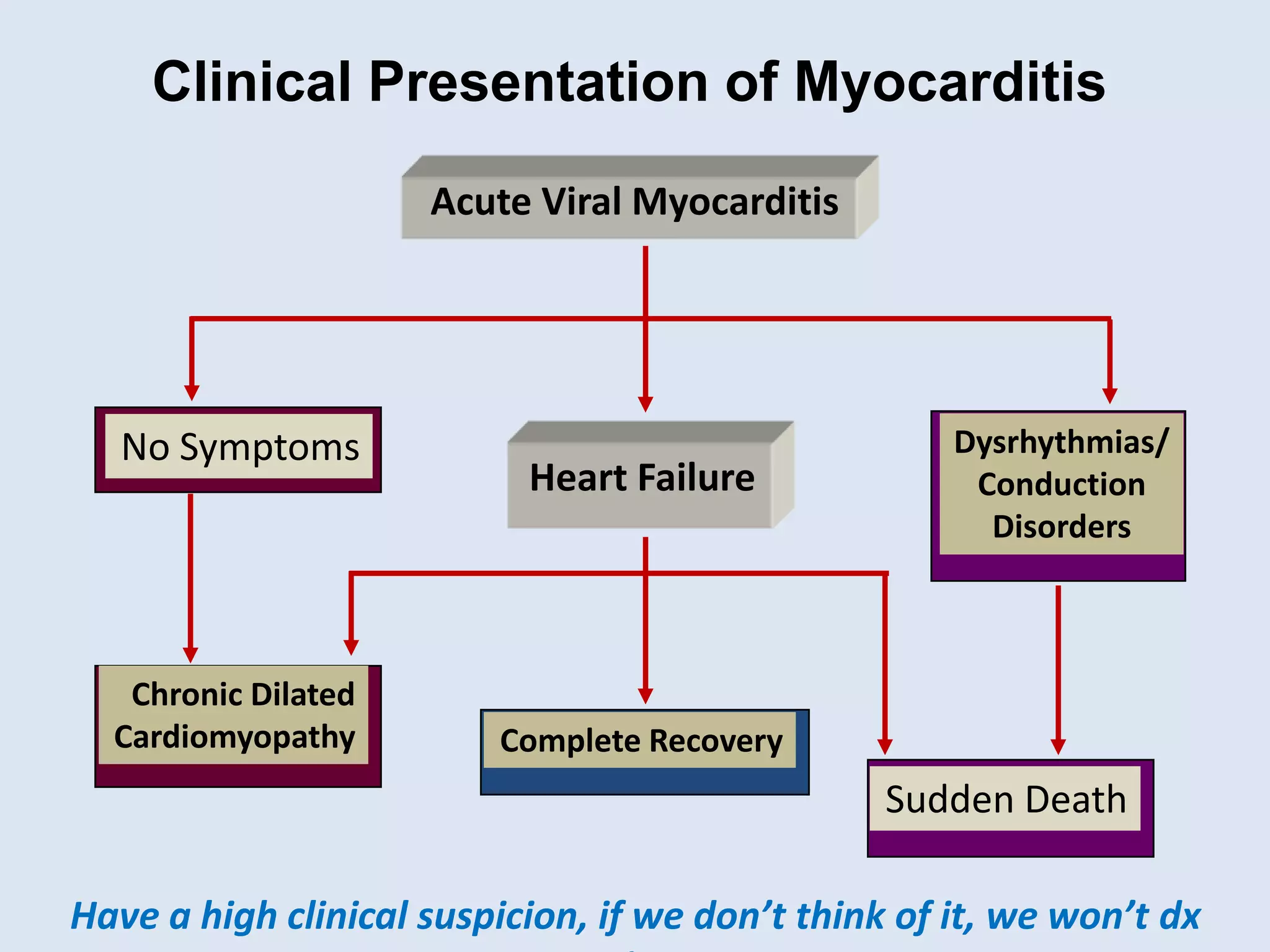
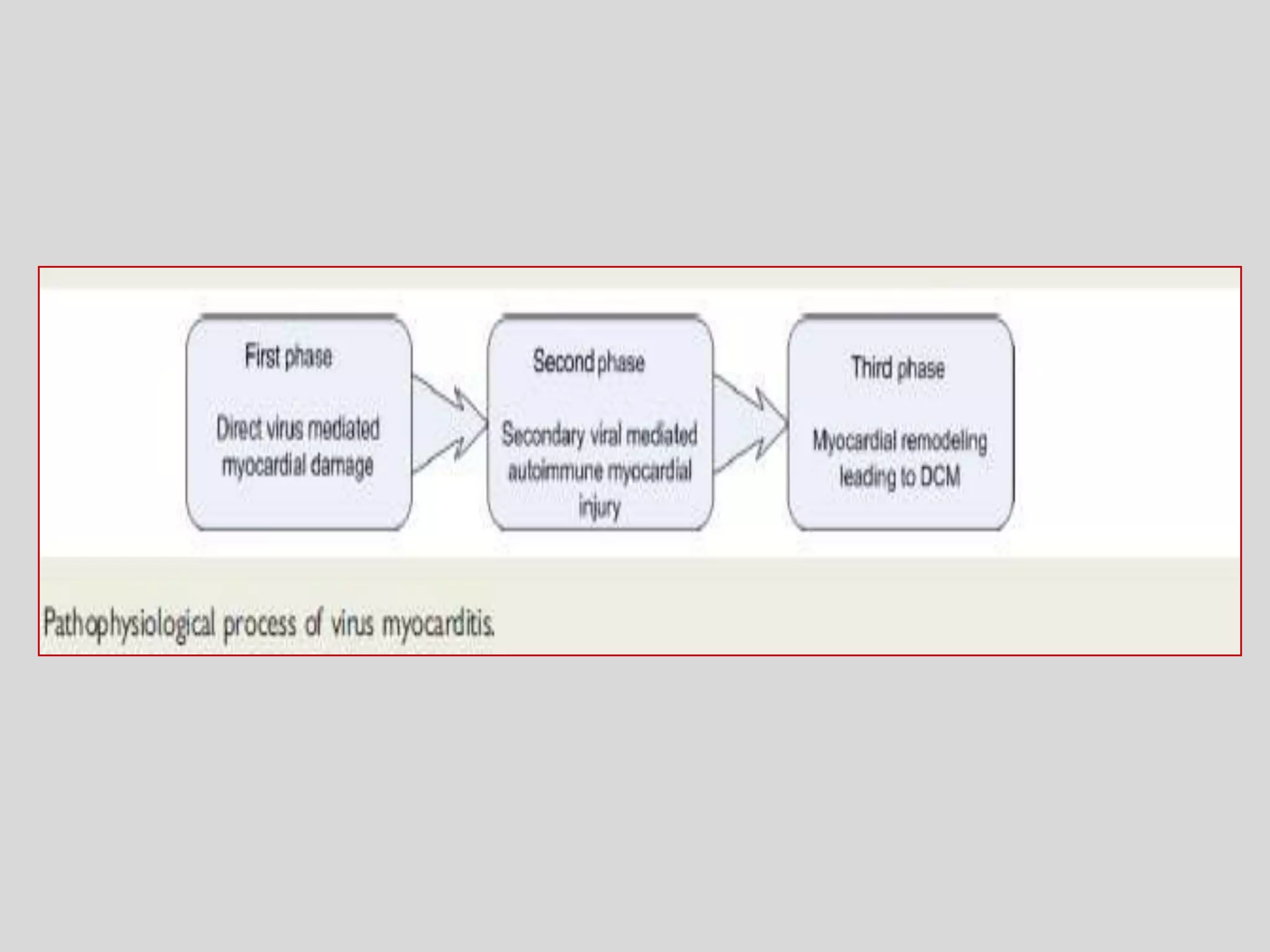
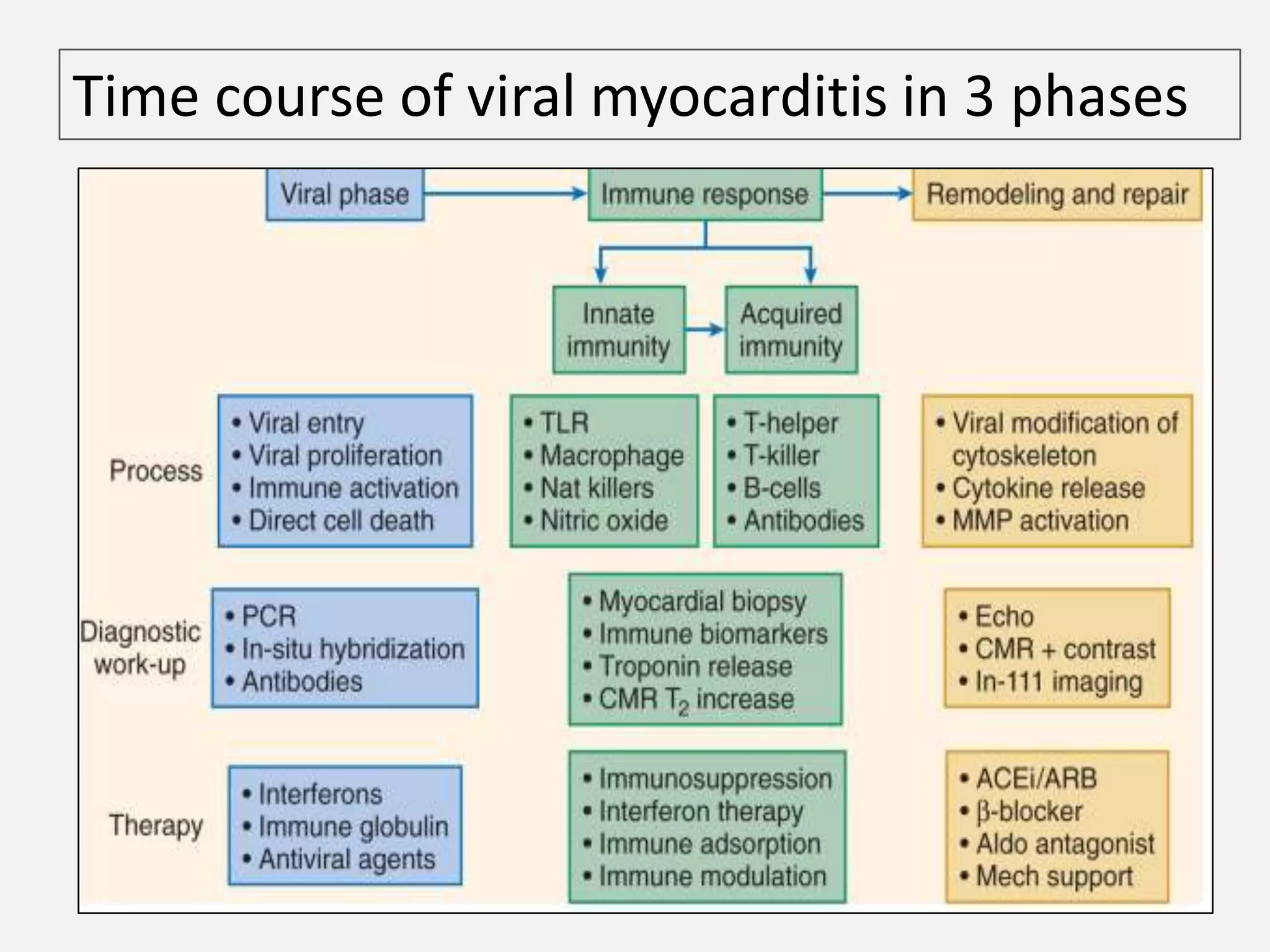
Myocarditis is an inflammatory disease of the heart muscle that can be caused by infectious or non-infectious triggers. It has a variable clinical presentation ranging from mild symptoms to life-threatening cardiogenic shock. Diagnosis is challenging but can involve elevated cardiac biomarkers, ECG abnormalities, echocardiogram findings of ventricular dysfunction, and cardiovascular MRI or endomyocardial biopsy showing inflammatory infiltrates. Treatment focuses on managing heart failure symptoms and arrhythmias with medications like diuretics, ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, and avoiding digoxin in acute heart failure. The prognosis varies from complete recovery to chronic dilated cardiomyopathy or sudden death.