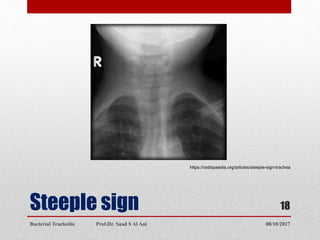
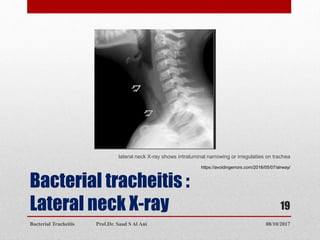
Bacterial tracheitis is an infectious inflammation of the trachea that presents with croup-like symptoms such as barking cough, stridor, and fever. It is caused by common bacterial pathogens invading the trachea through injury or preceding viral infection. Patients typically range from 3 weeks to 16 years old. Clinical examination may reveal inspiratory stridor, cough, respiratory distress, and toxic appearance. Diagnosis is made through visualization of purulent secretions in the trachea via laryngoscopy. Treatment involves antibiotics, maintaining the airway, and possible intubation. Complete recovery is expected once the acute phase passes.