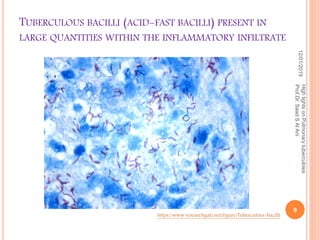
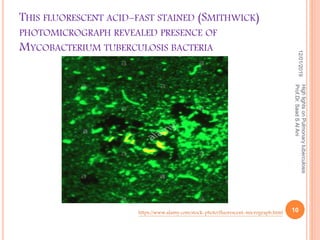
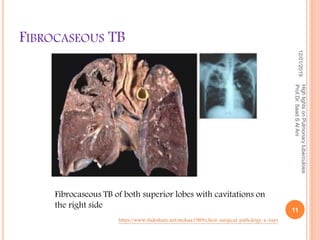
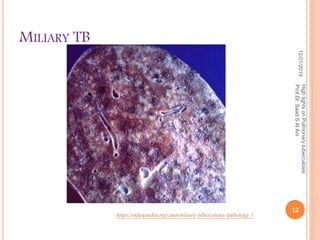
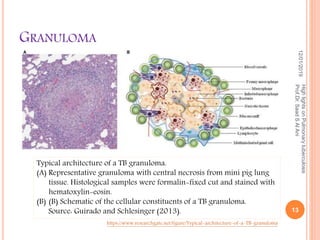
Prof. Dr. Saad S. Al Ani discusses the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis (TB), emphasizing the importance of considering TB in differential diagnoses when symptoms are present. He outlines the typical progression of the disease, various predisposing factors, and the initial treatment regimen involving four first-line drugs. The presentation also highlights barriers to treatment adherence and strategies for improving patient compliance, including directly observed therapy.