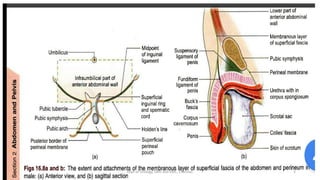
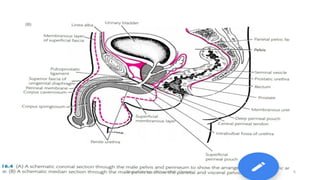
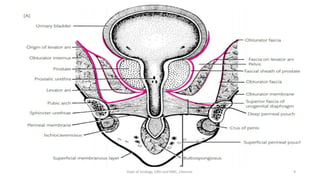
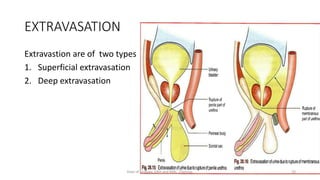
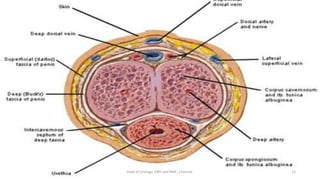
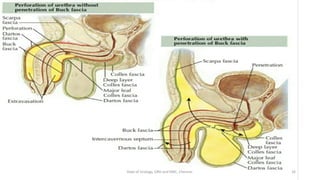
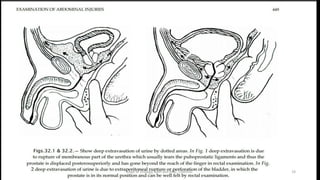
This document discusses urinary extravasation, which is when urine leaks out of the urinary tract into other body cavities. It defines two types - superficial and deep extravasation. Superficial extravasation occurs above the perineal membrane and is usually caused by injuries to the penile urethra during instrumentation. Deep extravasation occurs below the perineal membrane due to injuries of the membranous urethra or extraperitoneal bladder from pelvic trauma. Management involves pain relief, antibiotics, suprapubic catheterization, and sometimes surgical exploration and drainage of collections.