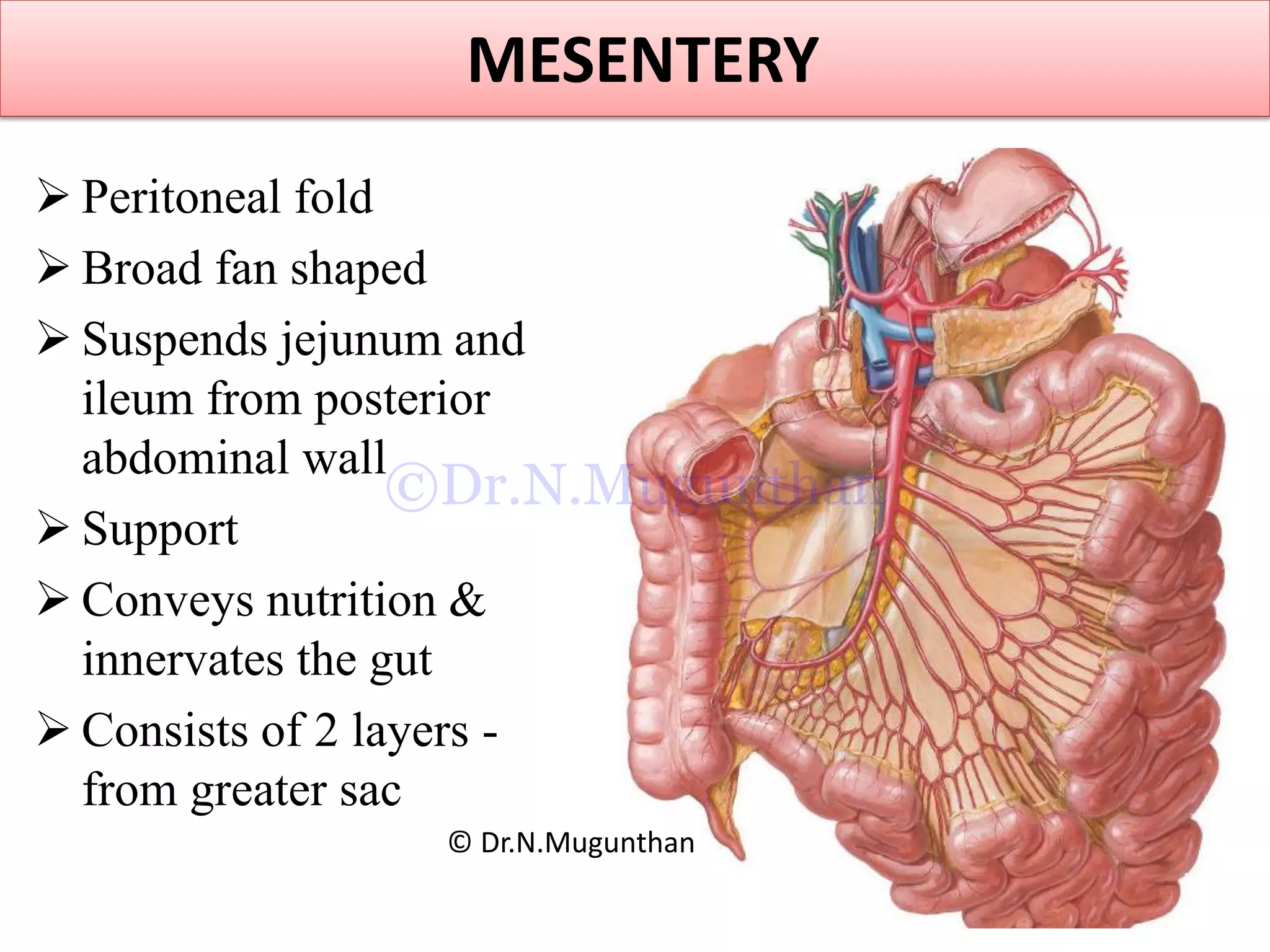
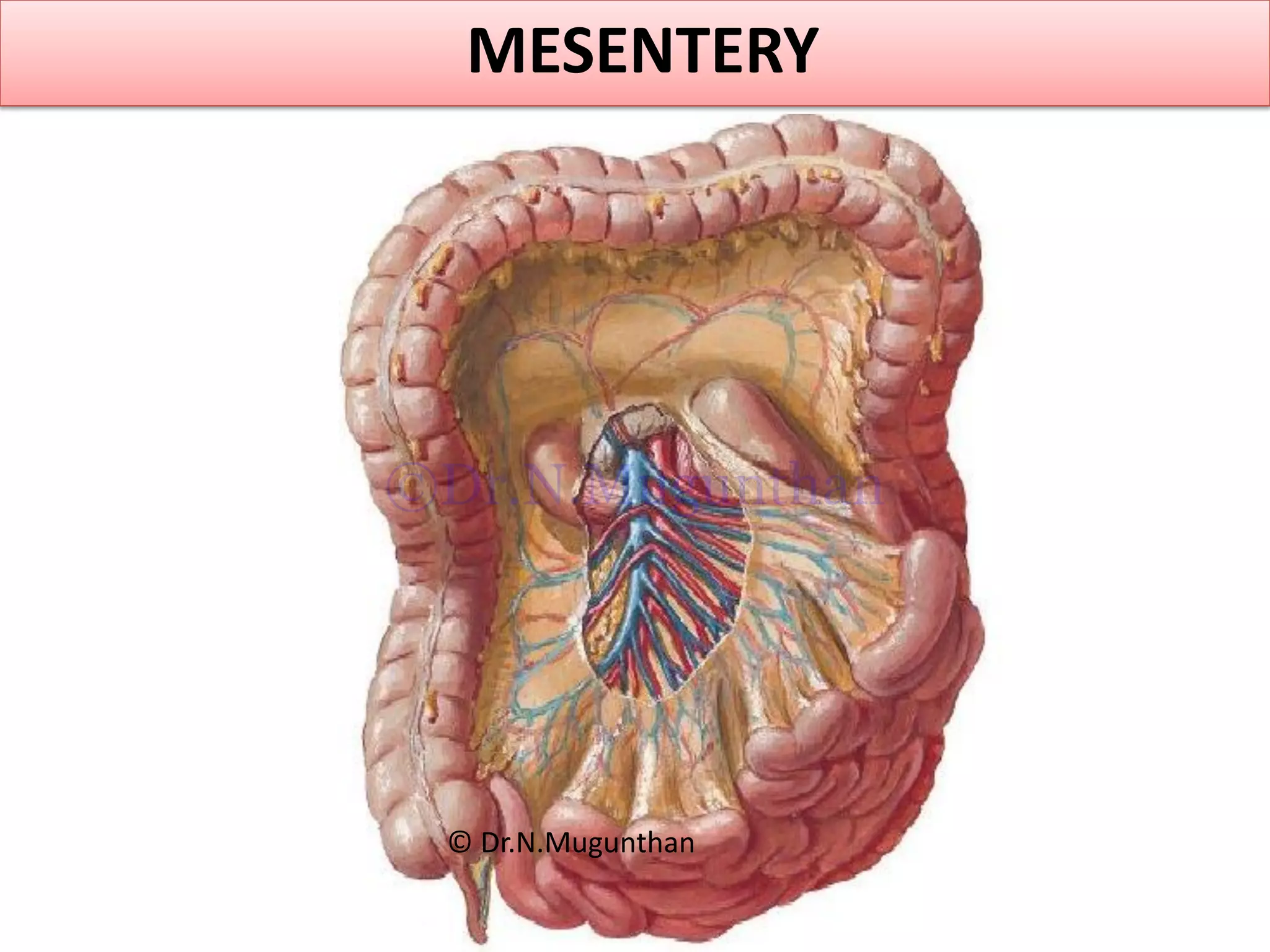
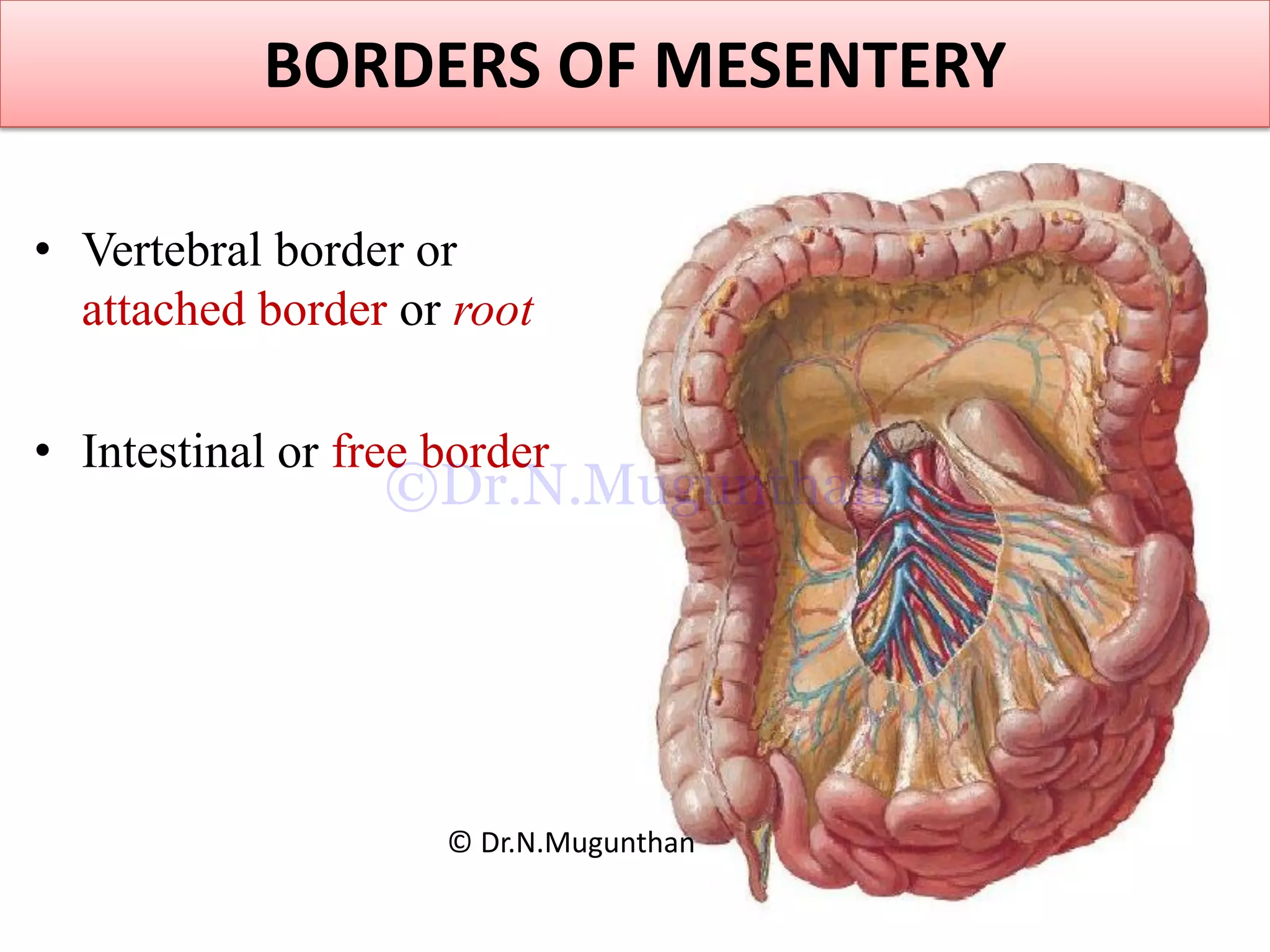
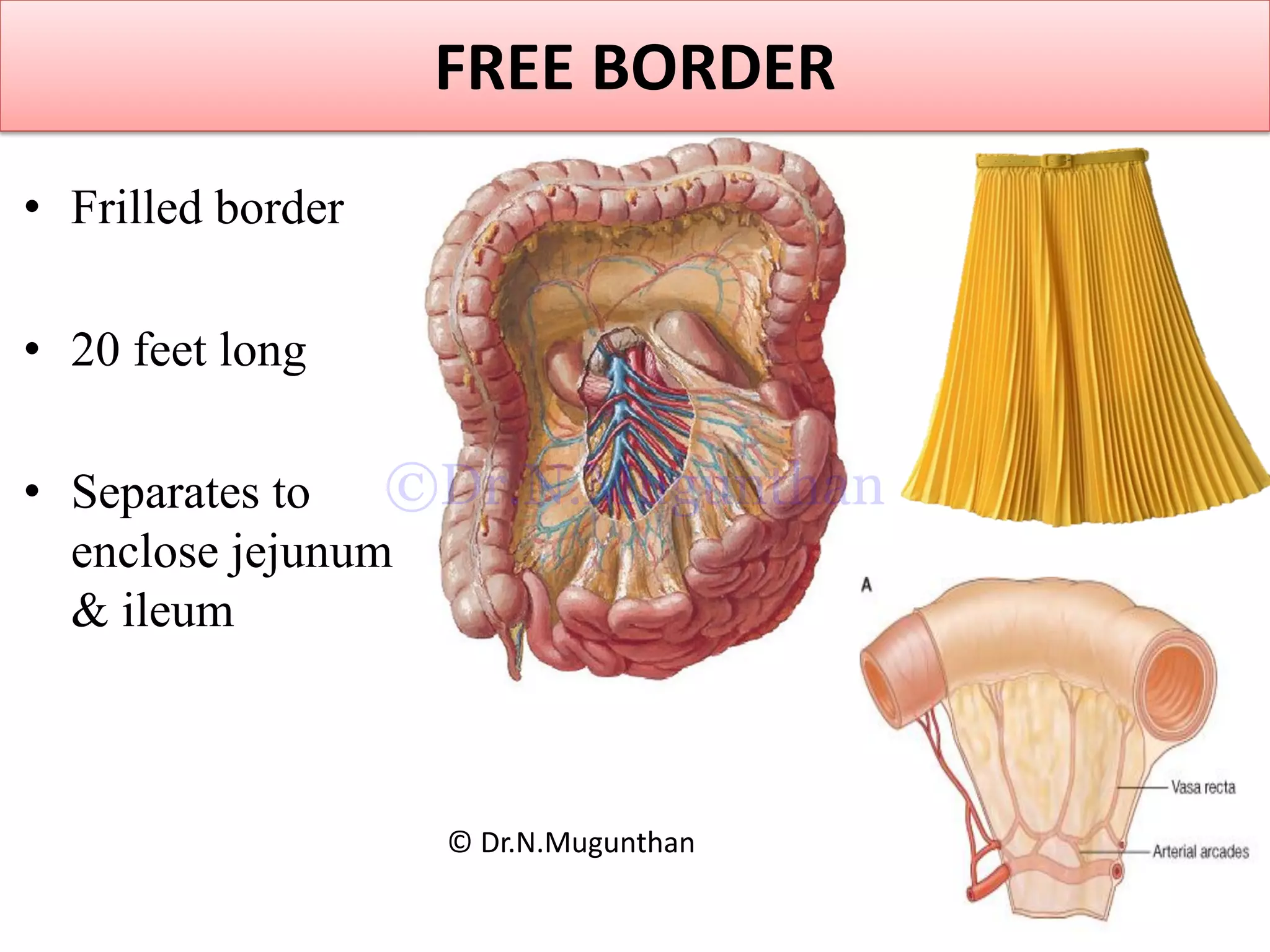
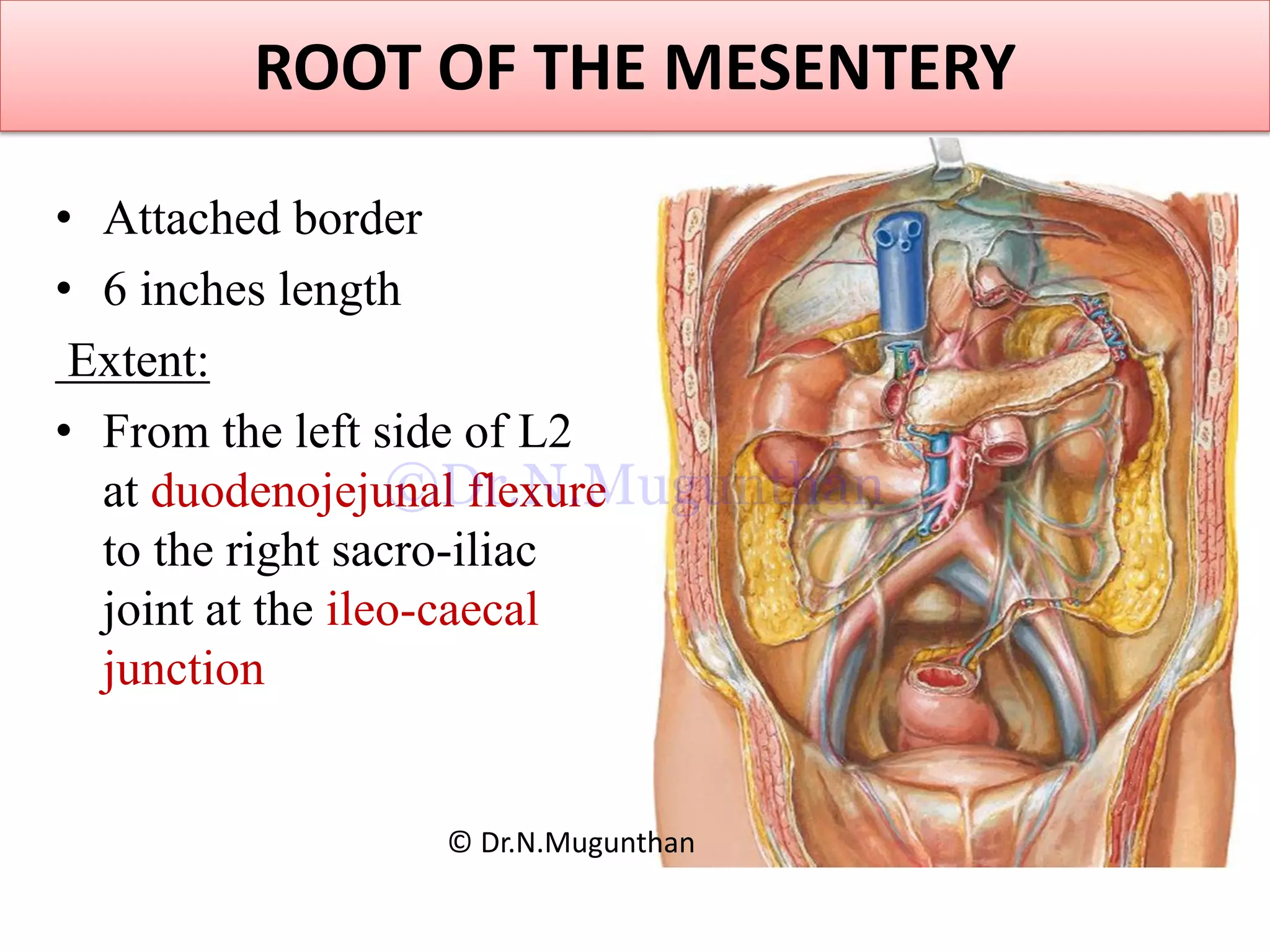
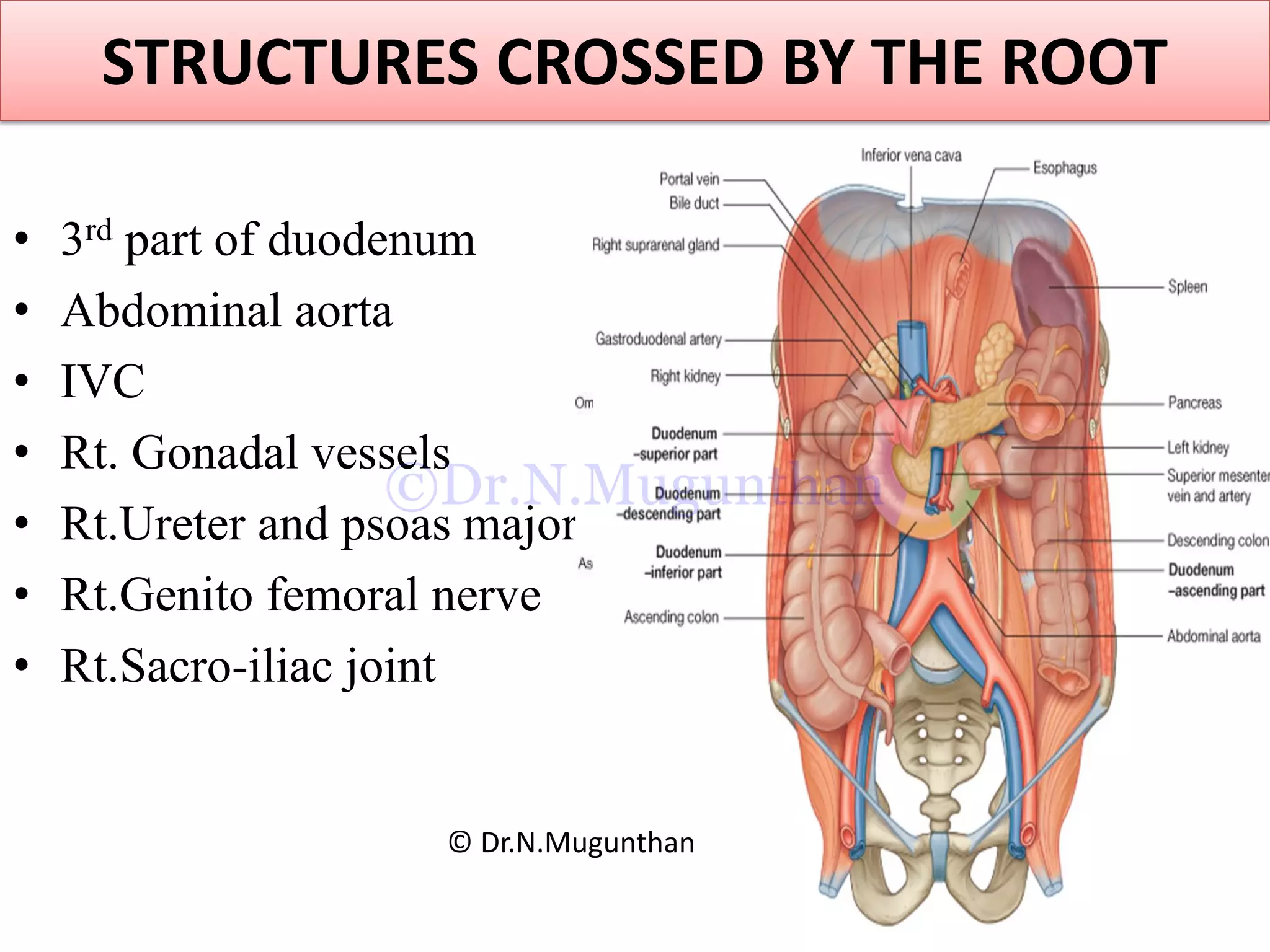
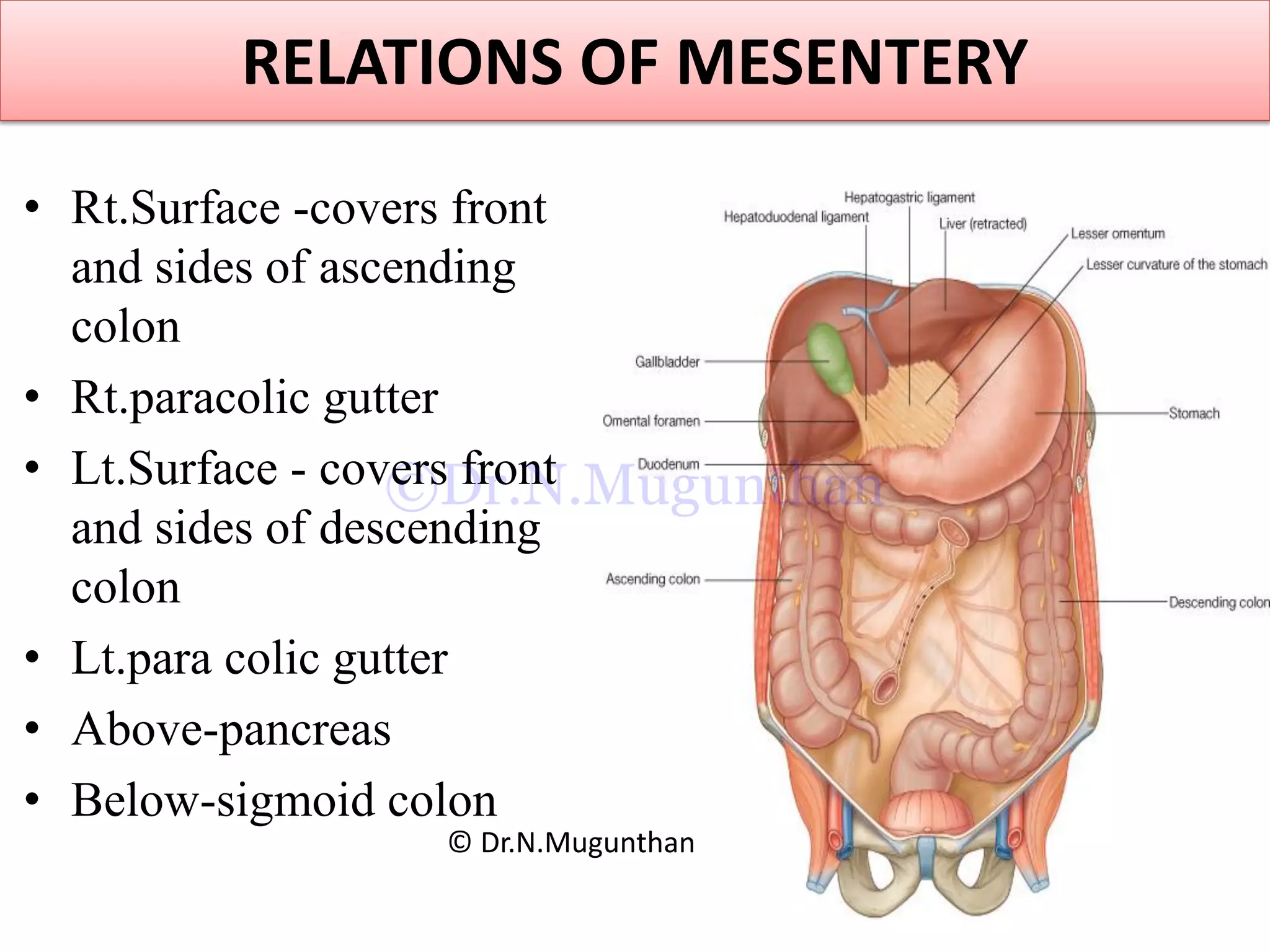
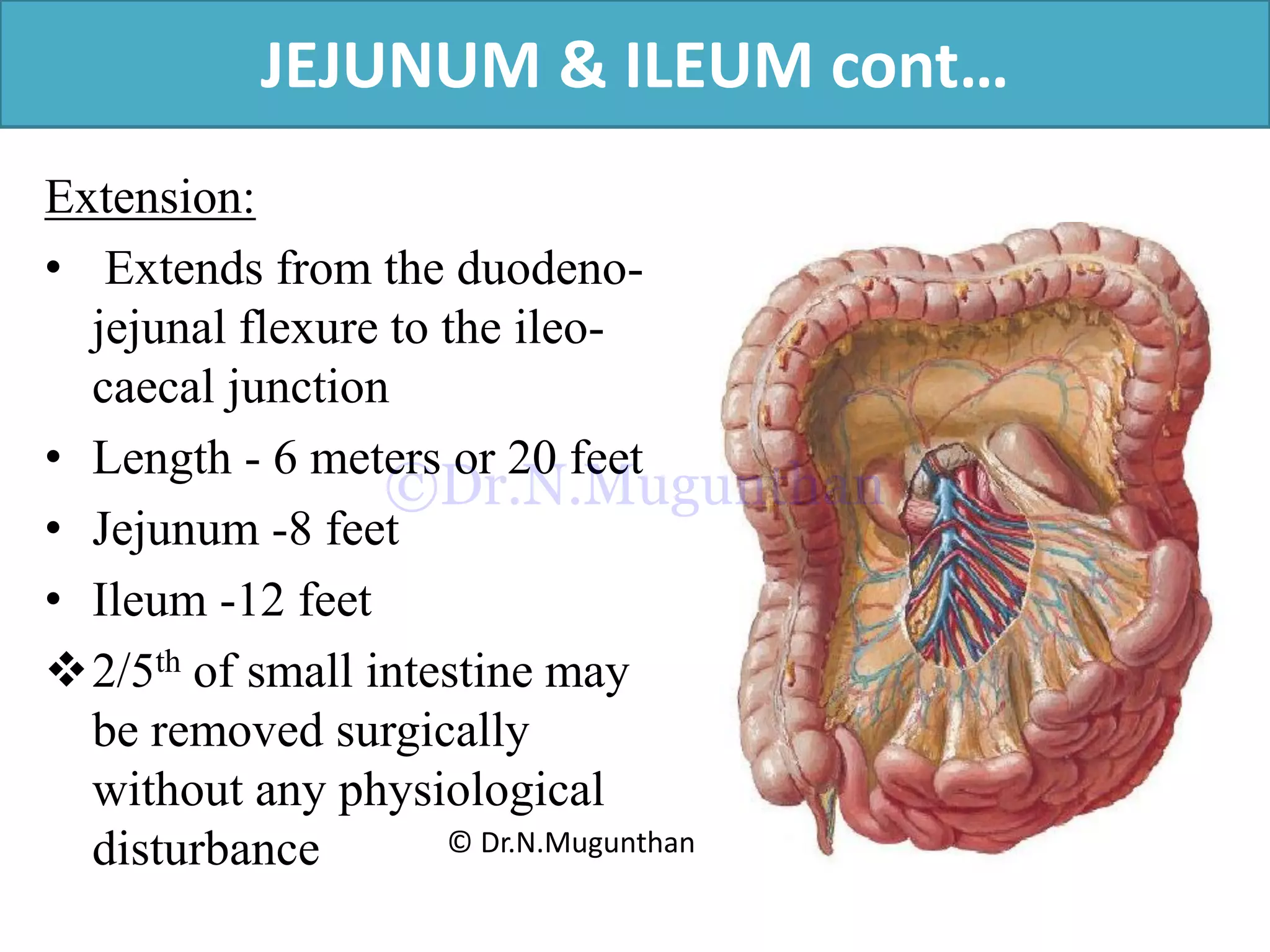
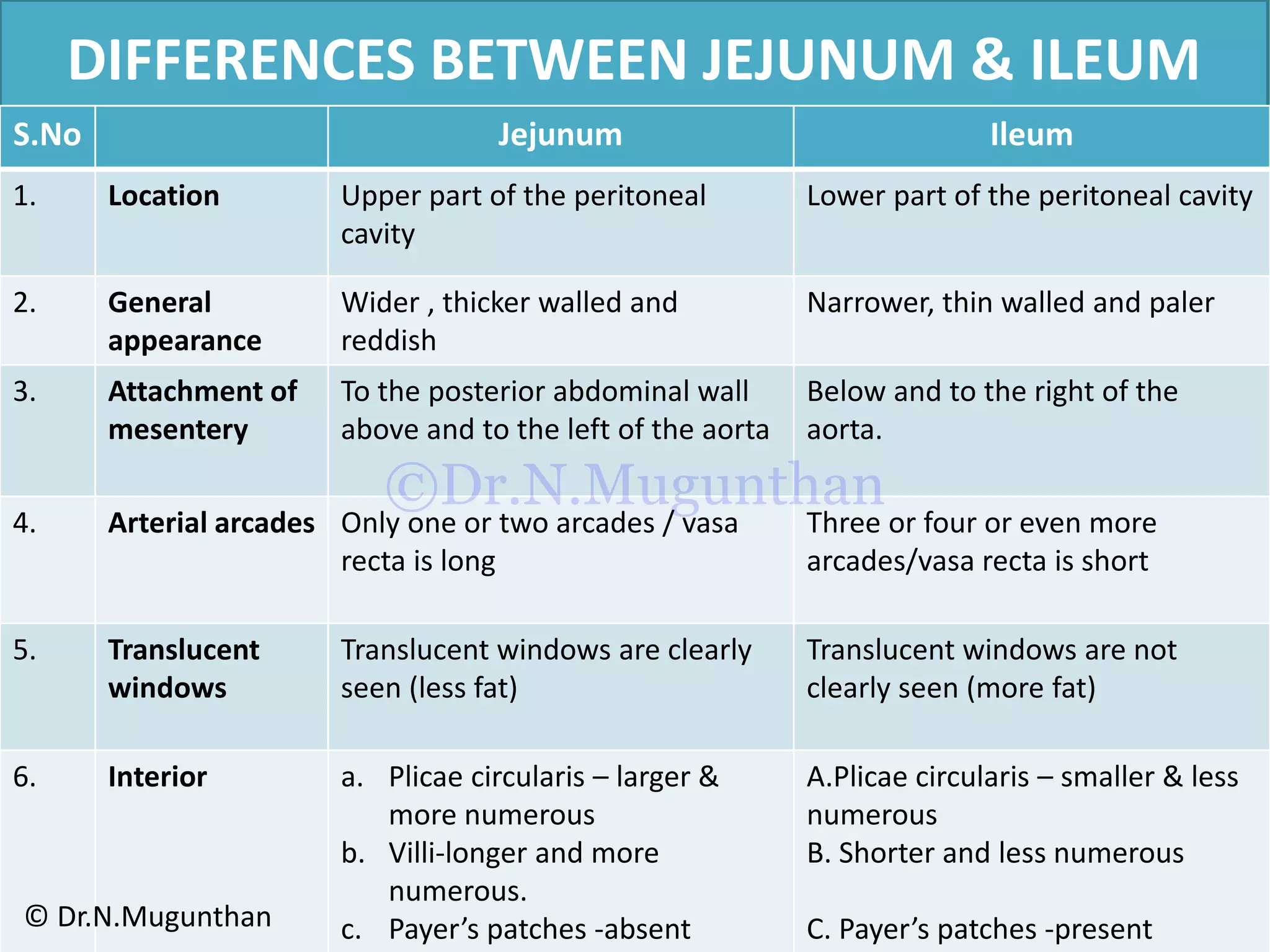
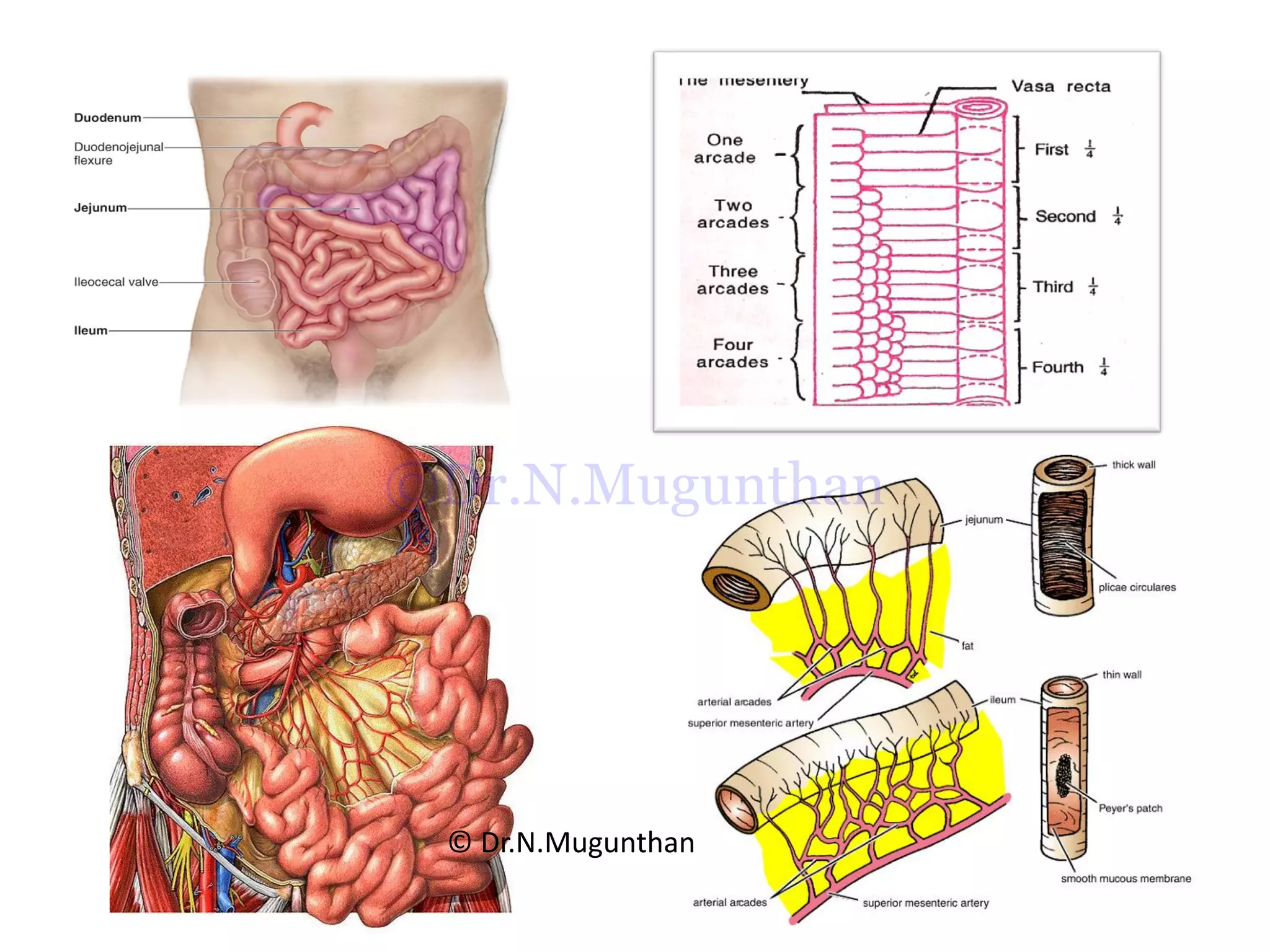
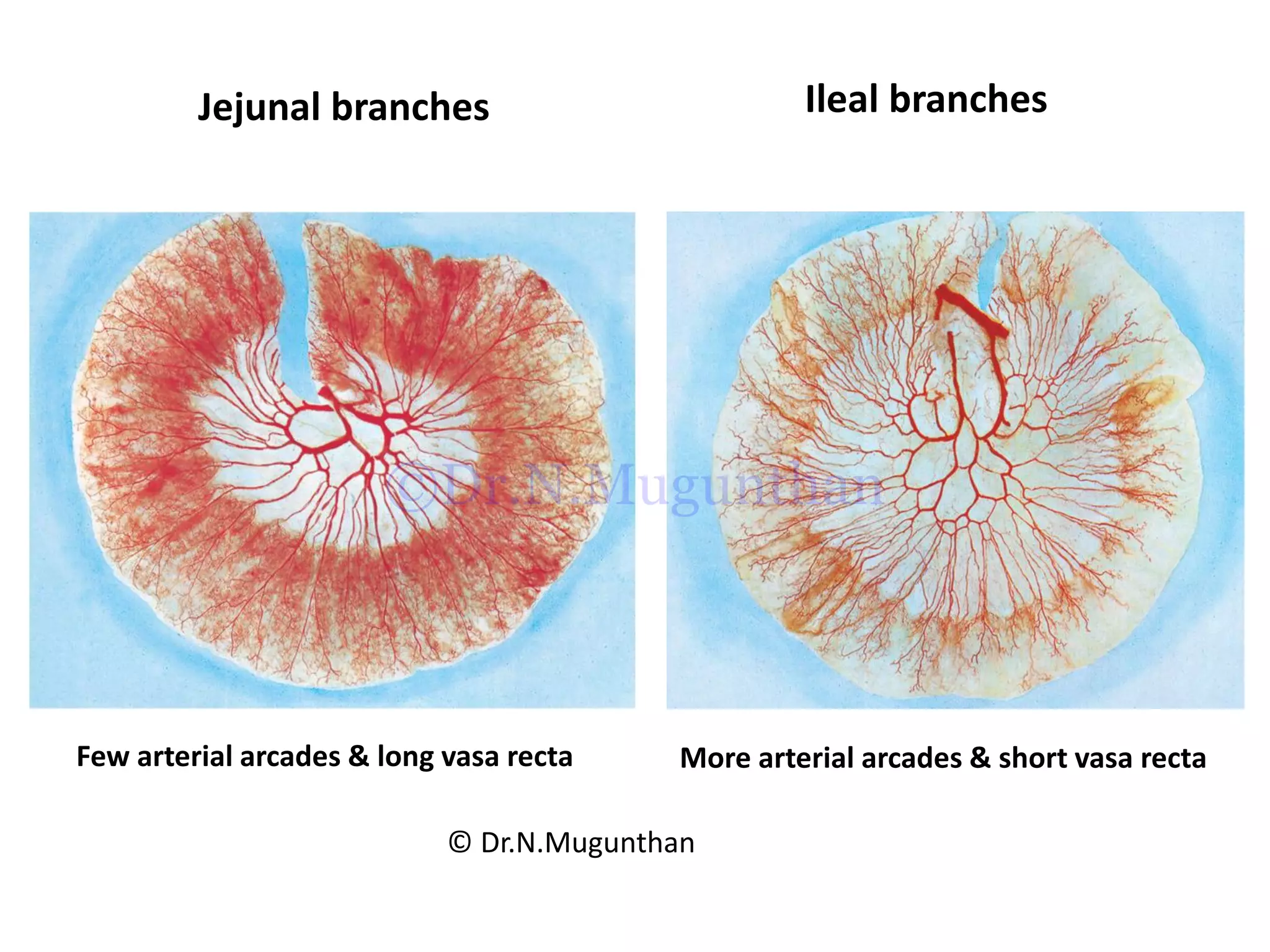
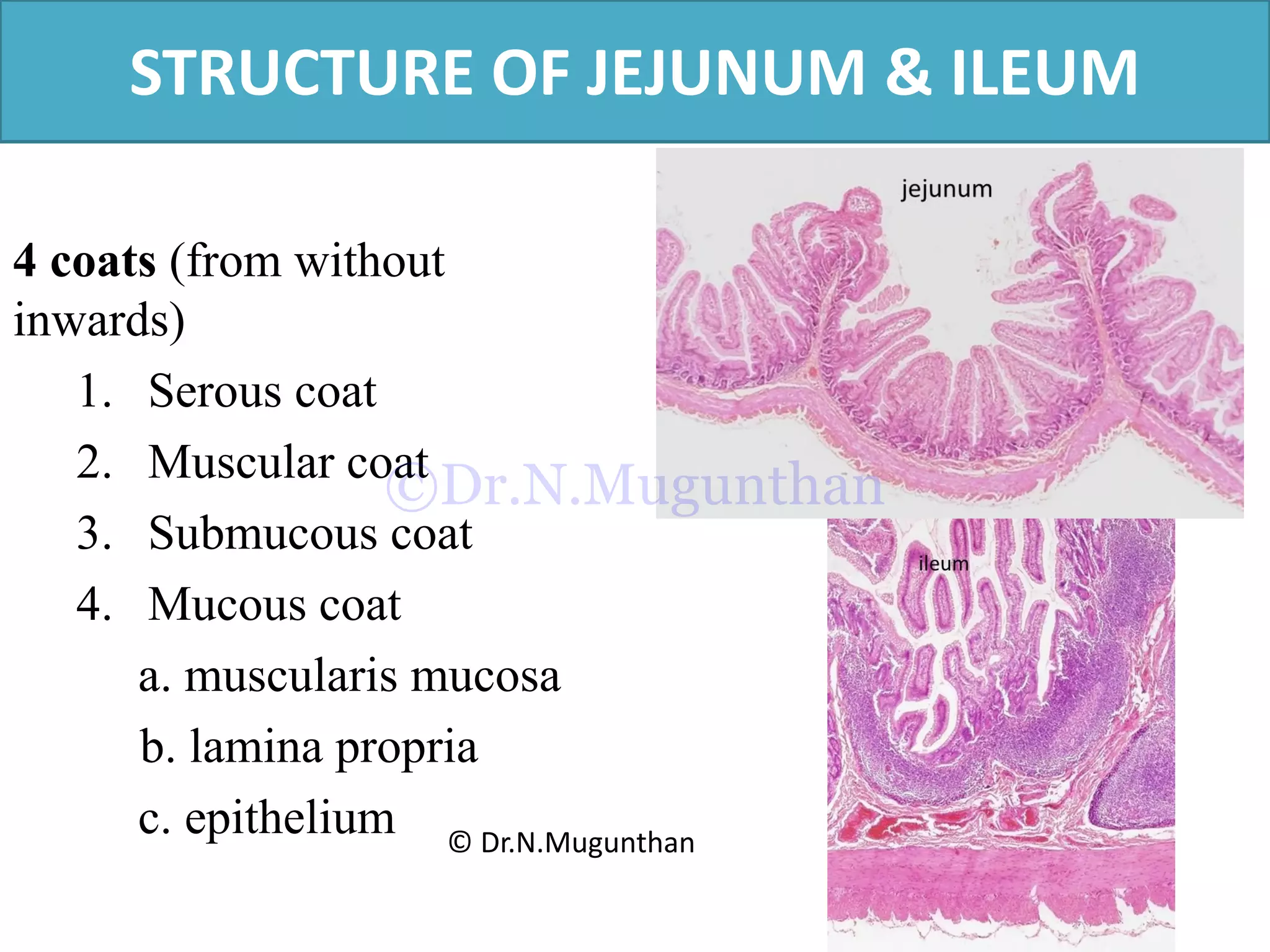
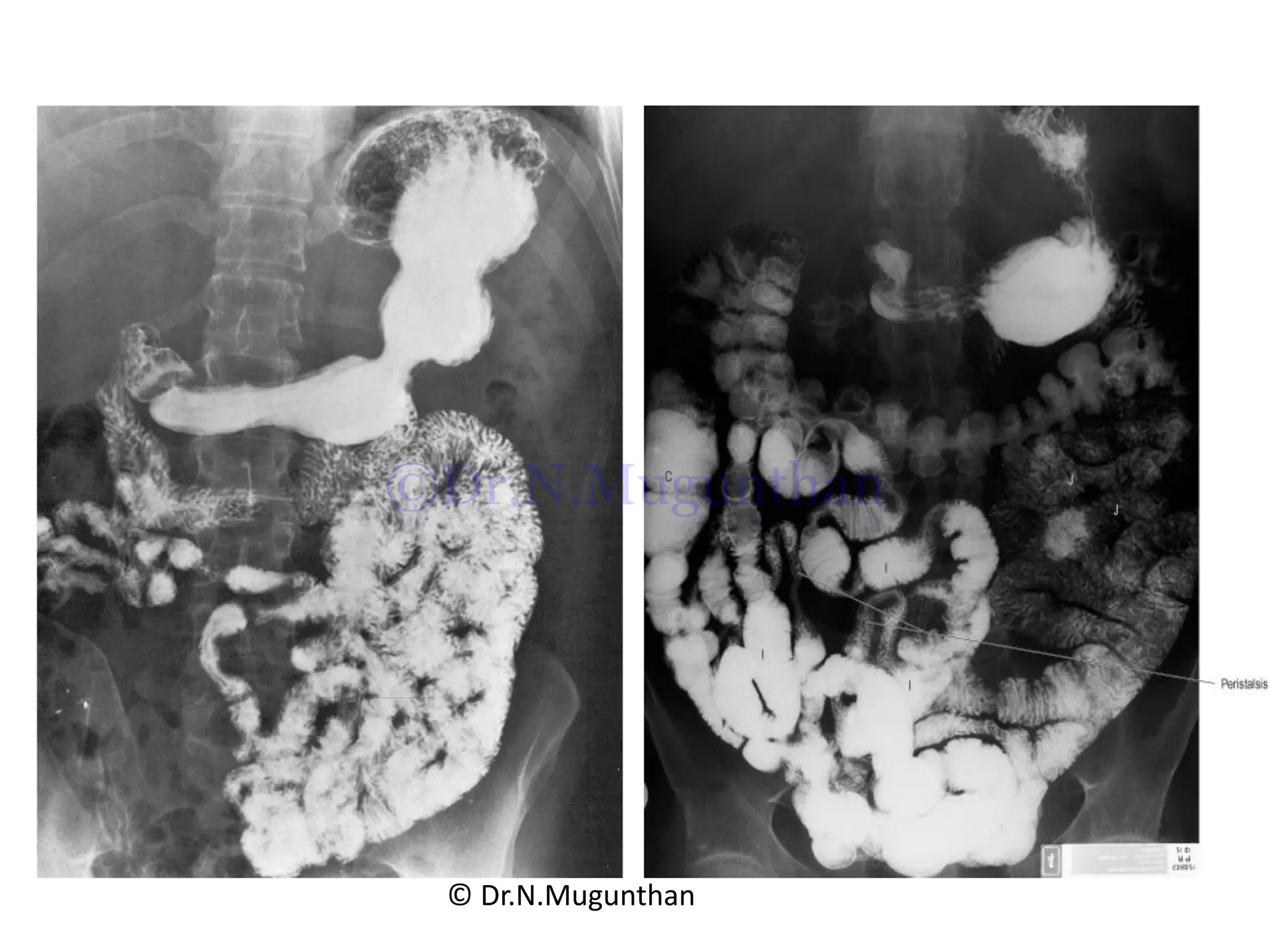
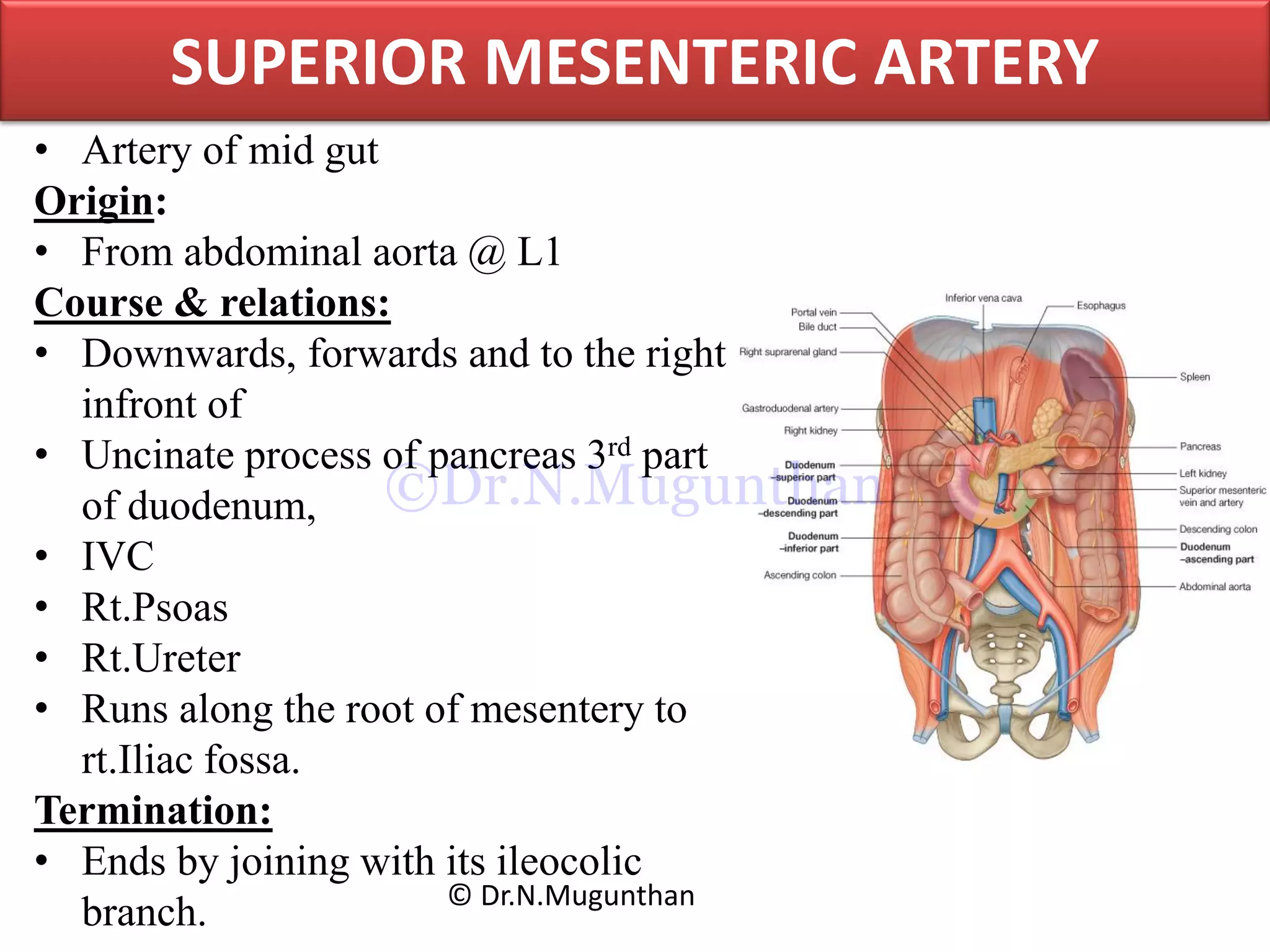
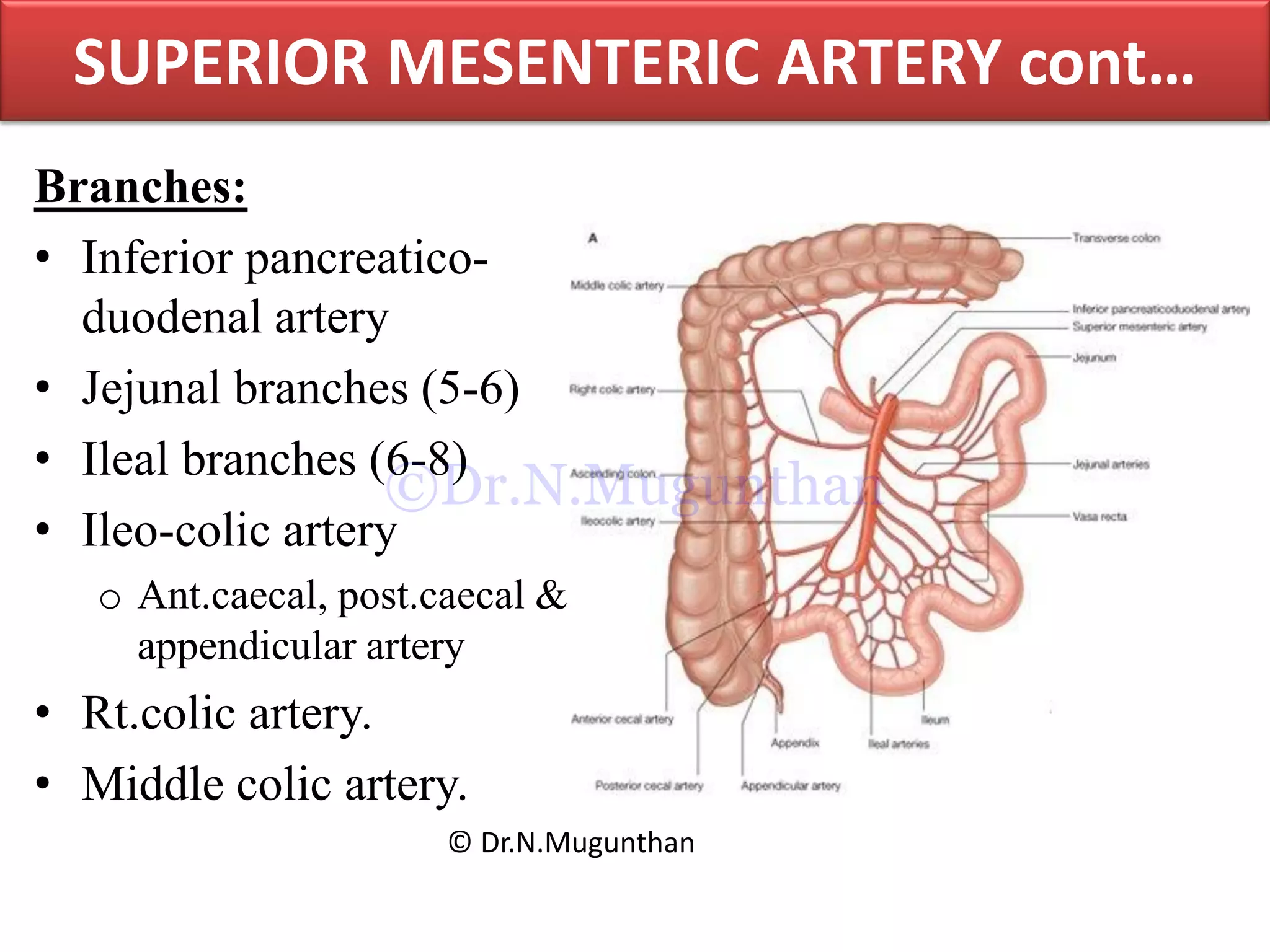
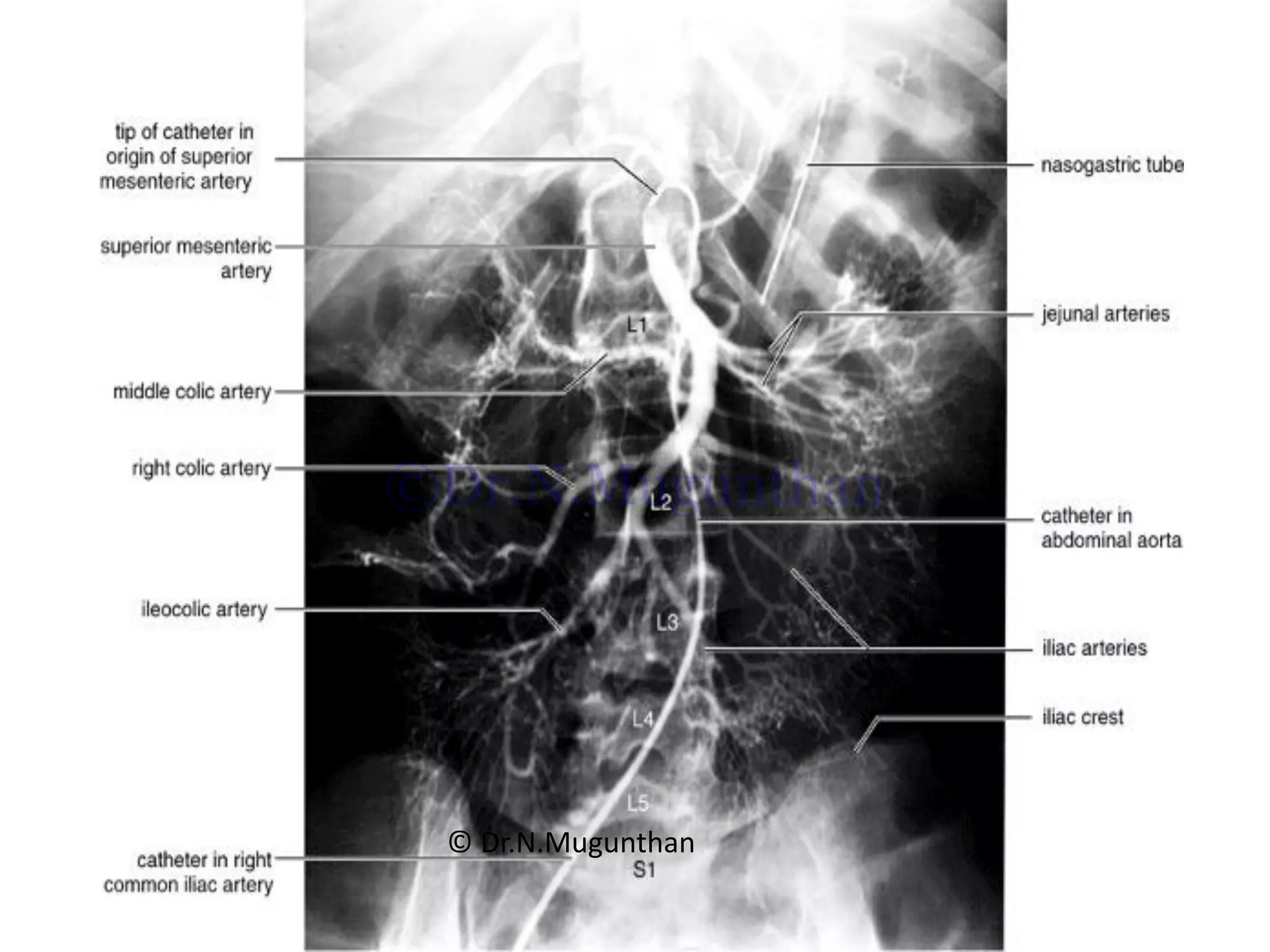
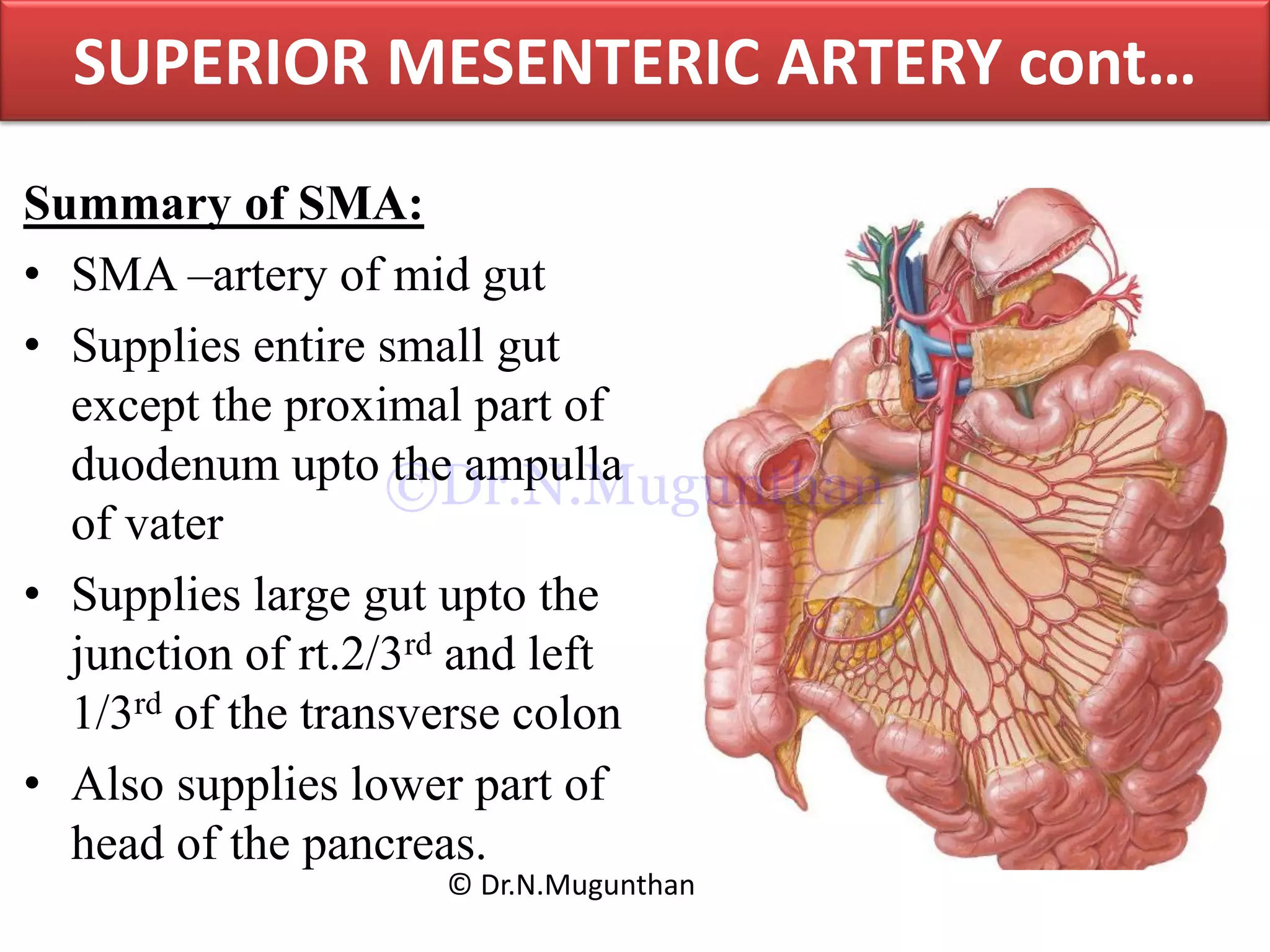
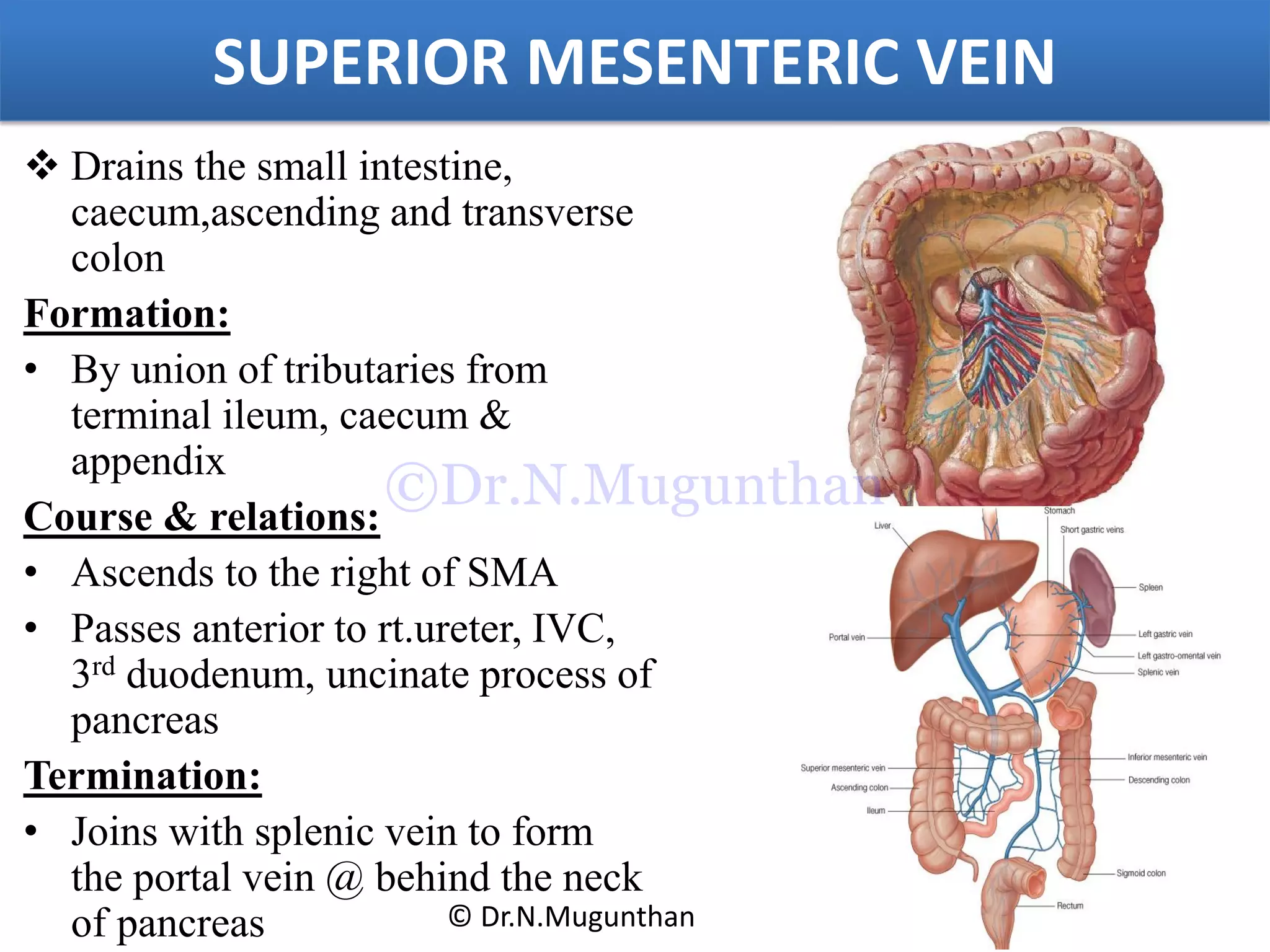
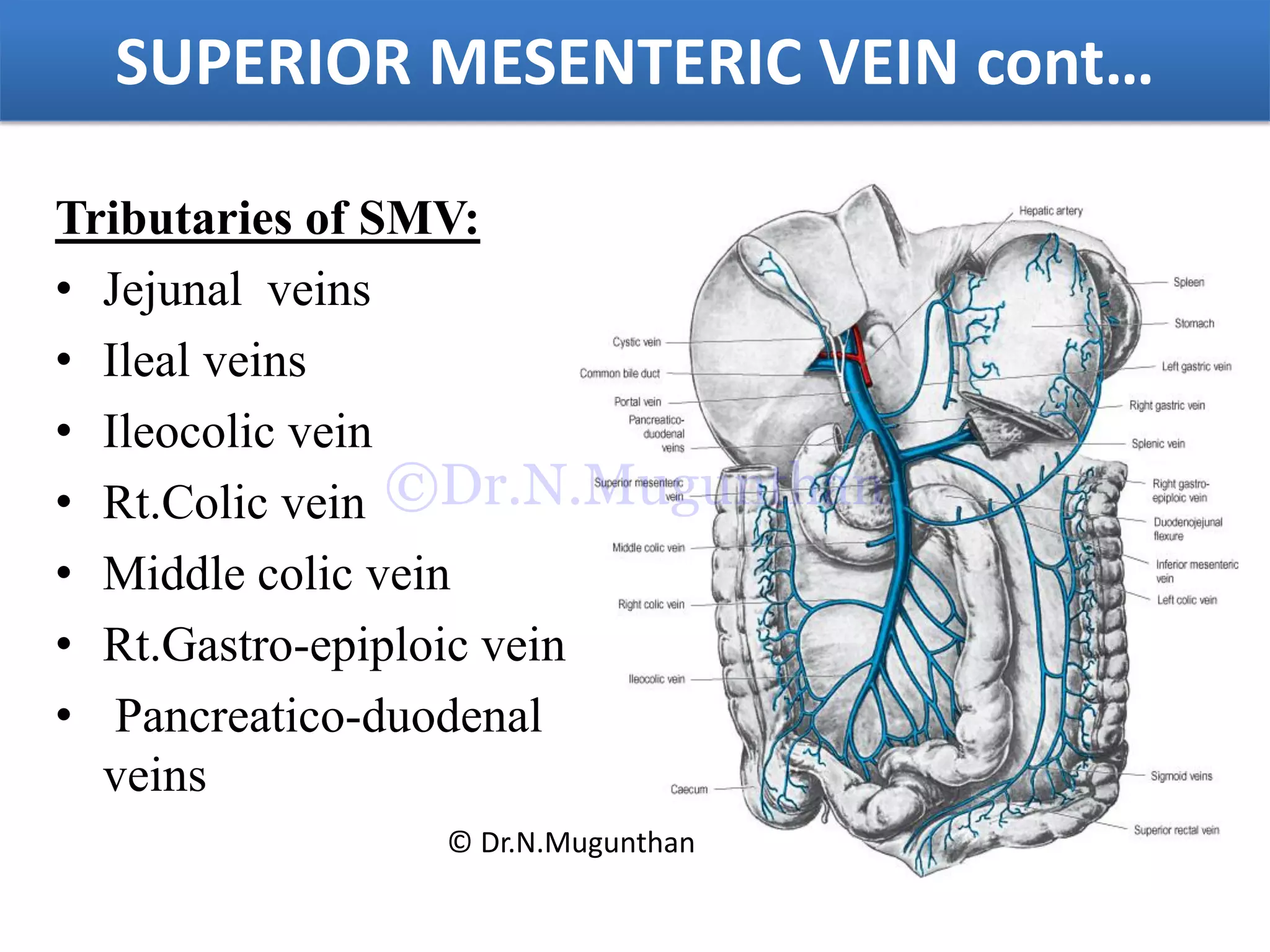
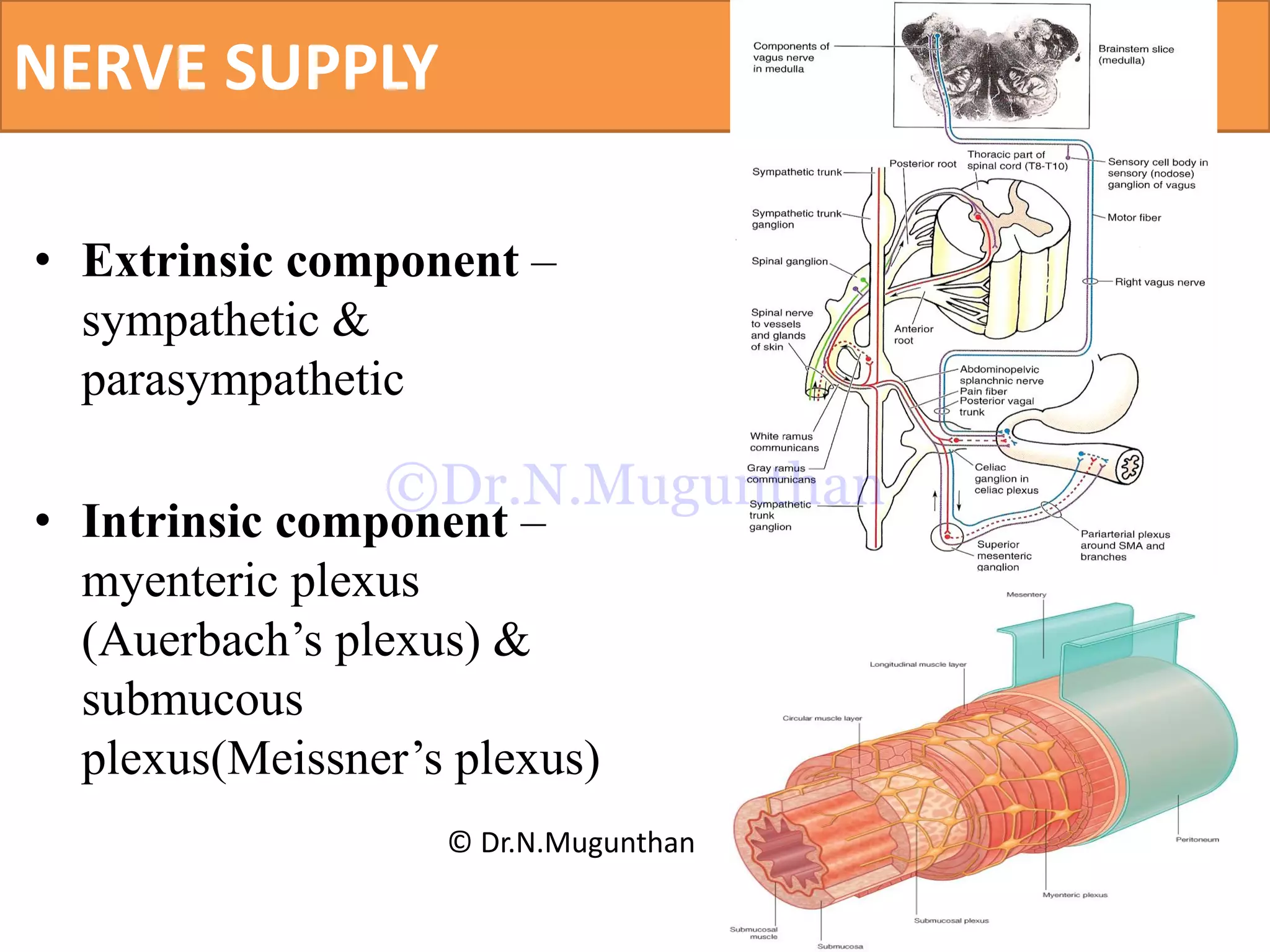
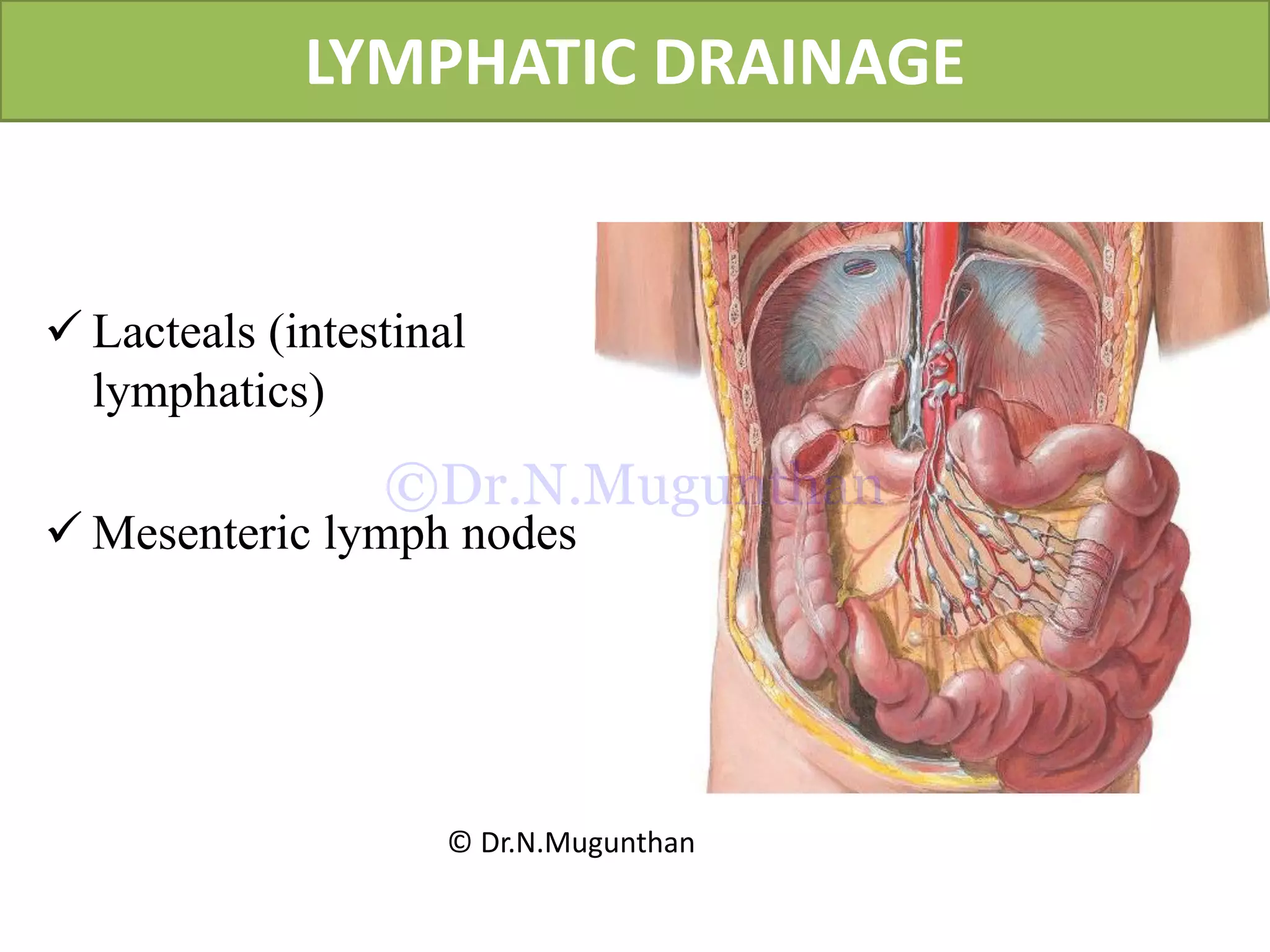
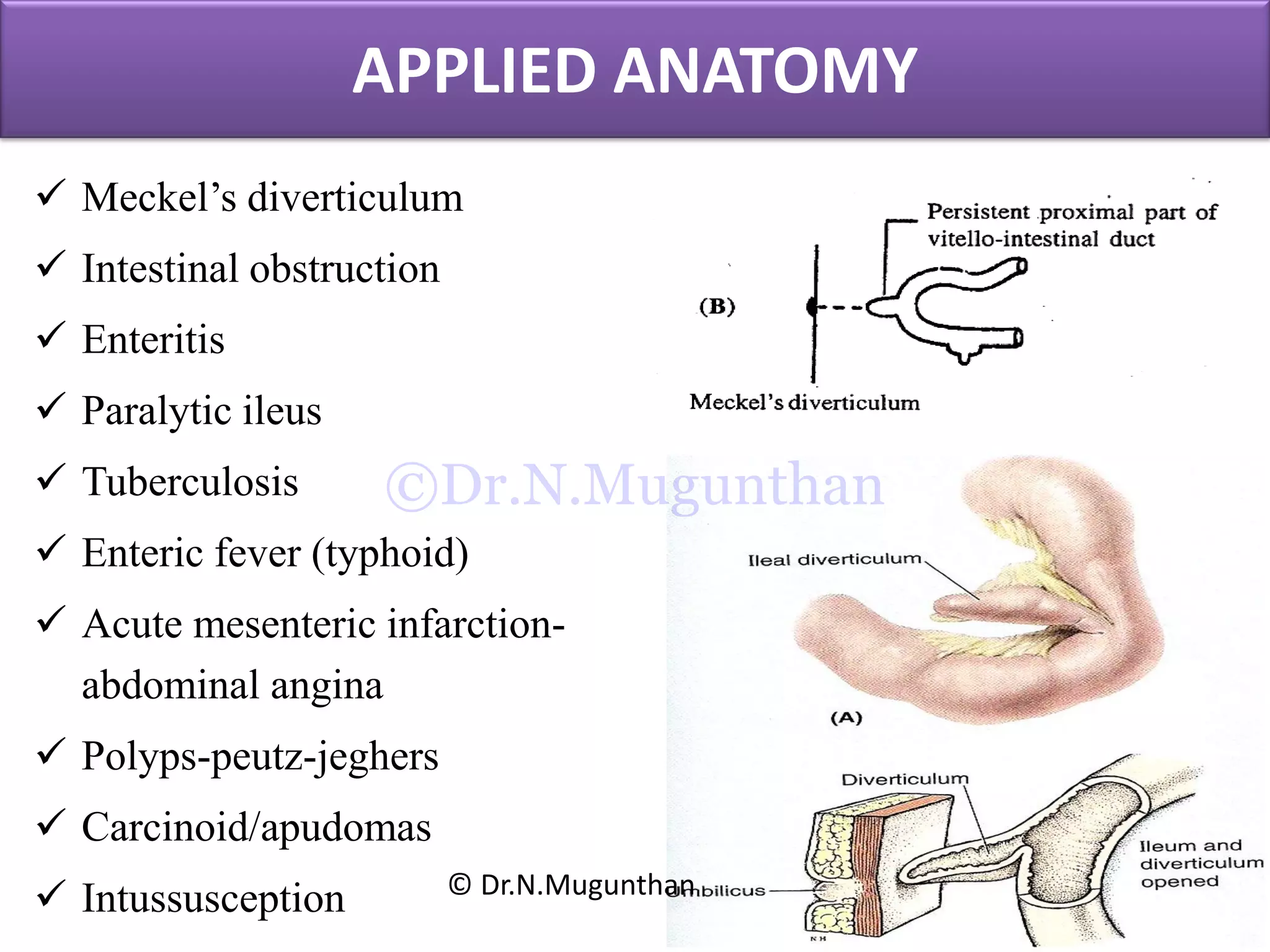
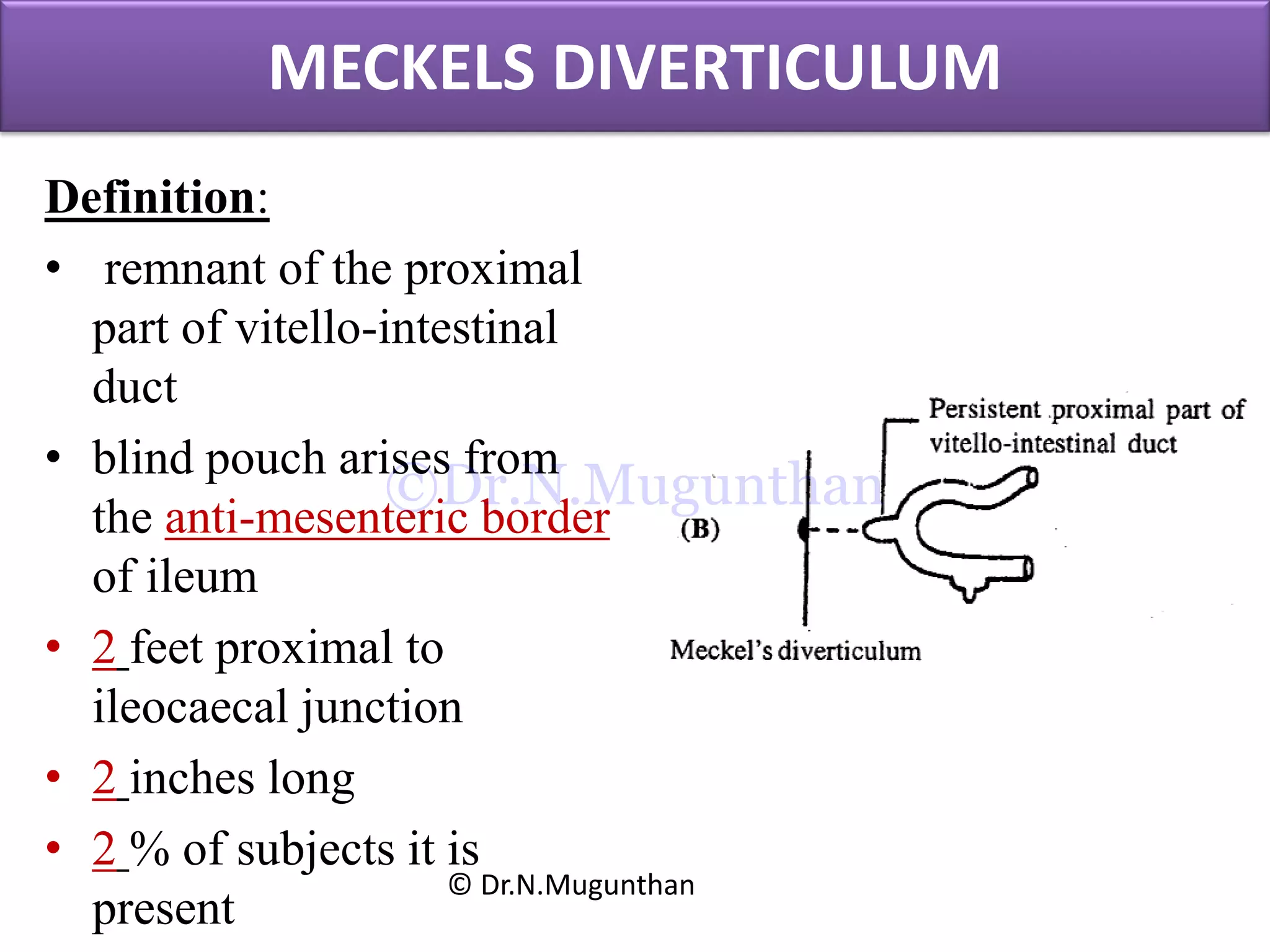
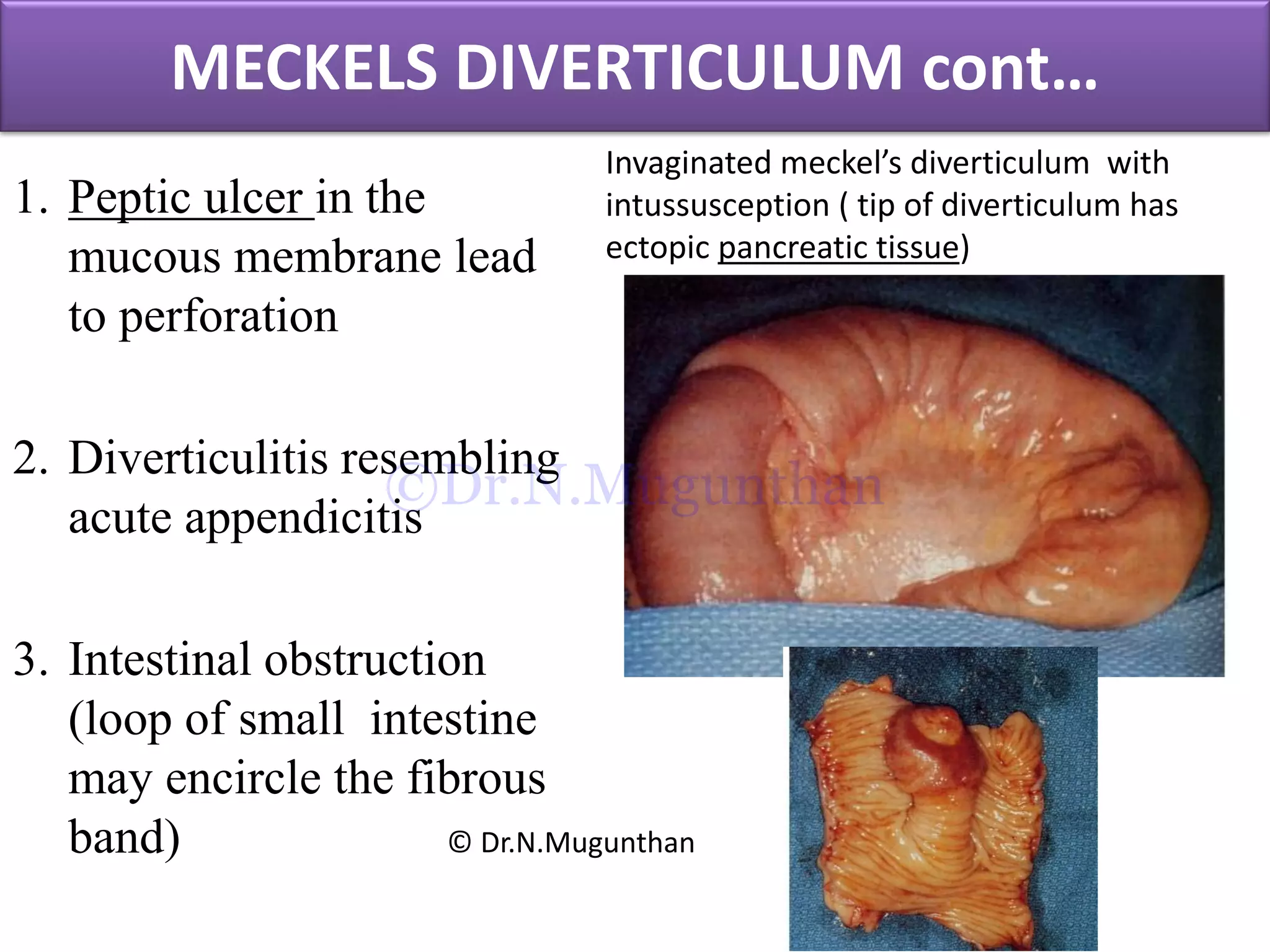
This document discusses the anatomy of the mesentery and related structures. It describes the mesentery as the peritoneal fold that suspends the jejunum and ileum from the posterior abdominal wall. It provides blood supply and innervation to the intestines. The root of the mesentery extends from L2 to the right sacroiliac joint and crosses several structures. The superior mesenteric artery supplies the midgut and branches to form the jejunal and ileal arteries. Meckel's diverticulum is described as a remnant of the vitelline duct that can cause complications like perforation or intestinal obstruction.